MCAT General Chemistry Chapter 3: Bonding and Chemical Interactions Diagram | Quizlet
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
octet rule
An attraction between two atoms resulting from a sharing of outer-shell electrons or the presence of opposite charges on the atoms. The bonded atoms gain complete outer electron shells.
8 e- in outer shell
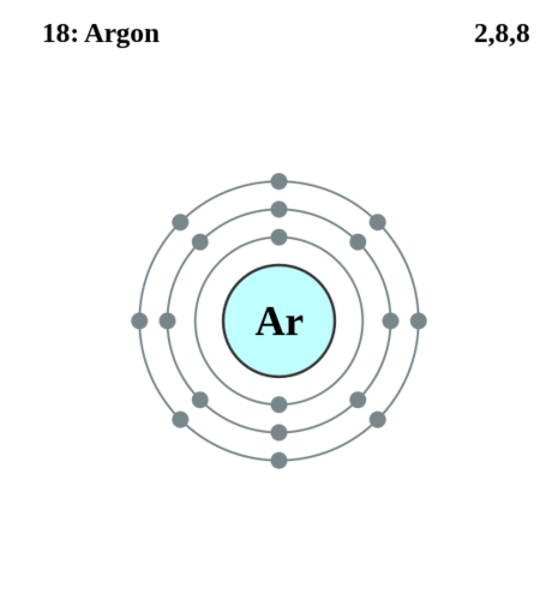
electron configuration of argon
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
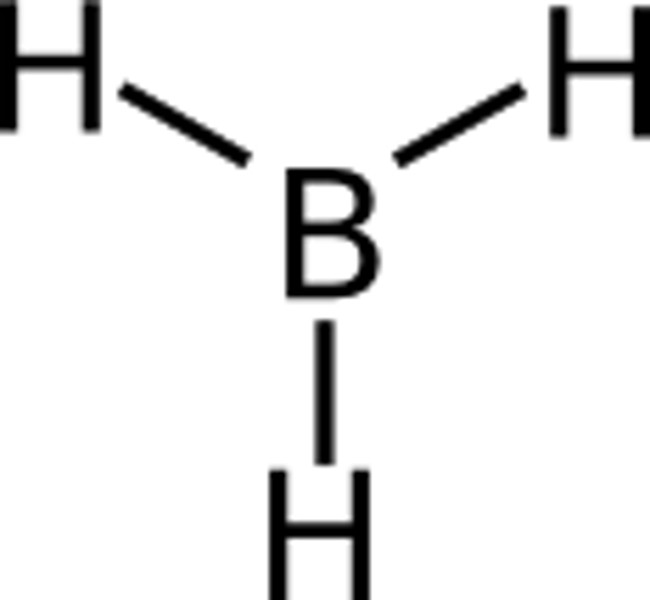
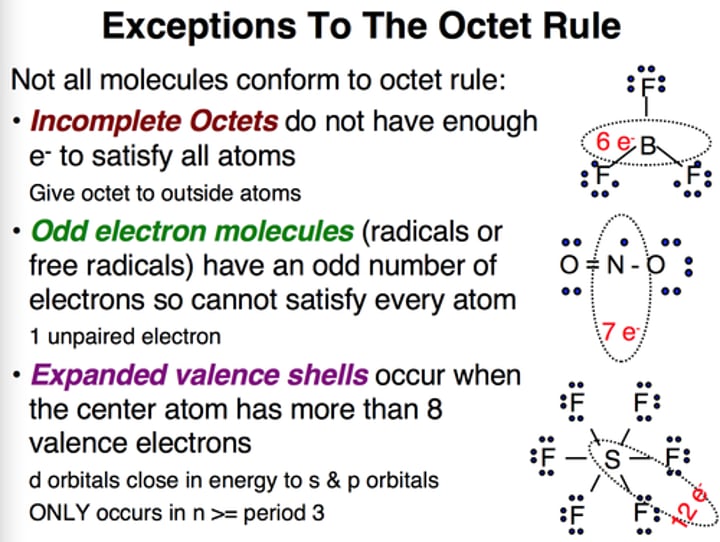
Elements with incomplete octet and are stable
These elements are stable with fewer than eight electrons in their valence shell and include hydrogen (2), helium (2), lithium (2), beryllium (4), and boron (6)
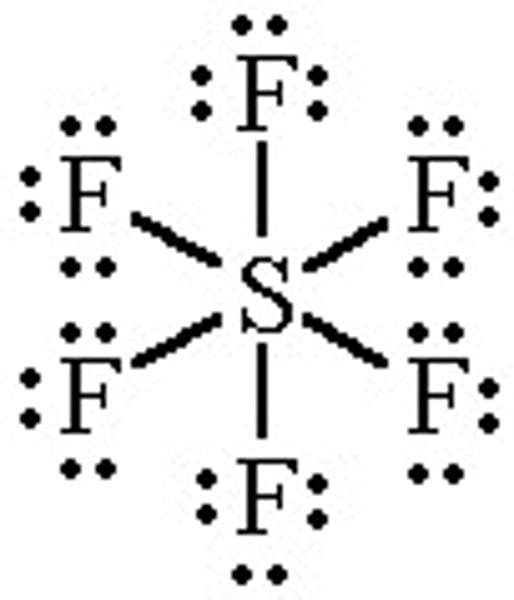
Expanded Octet examples are after which row on the periodic table
An exception to the octet rule that permits atoms in the third row or lower on the periodic table to have more than eight electrons in a Lewis structure.
Ex; *phosphorus (10), sulfur (12),
chlorine (14*), etc.
odd number of electrons examples are
any molecule with odd number of valence electrons cannot distribute those electrons to give eight to each atom
free radicals
Ex: Nitric oxide (NO) has eleven valence electrons
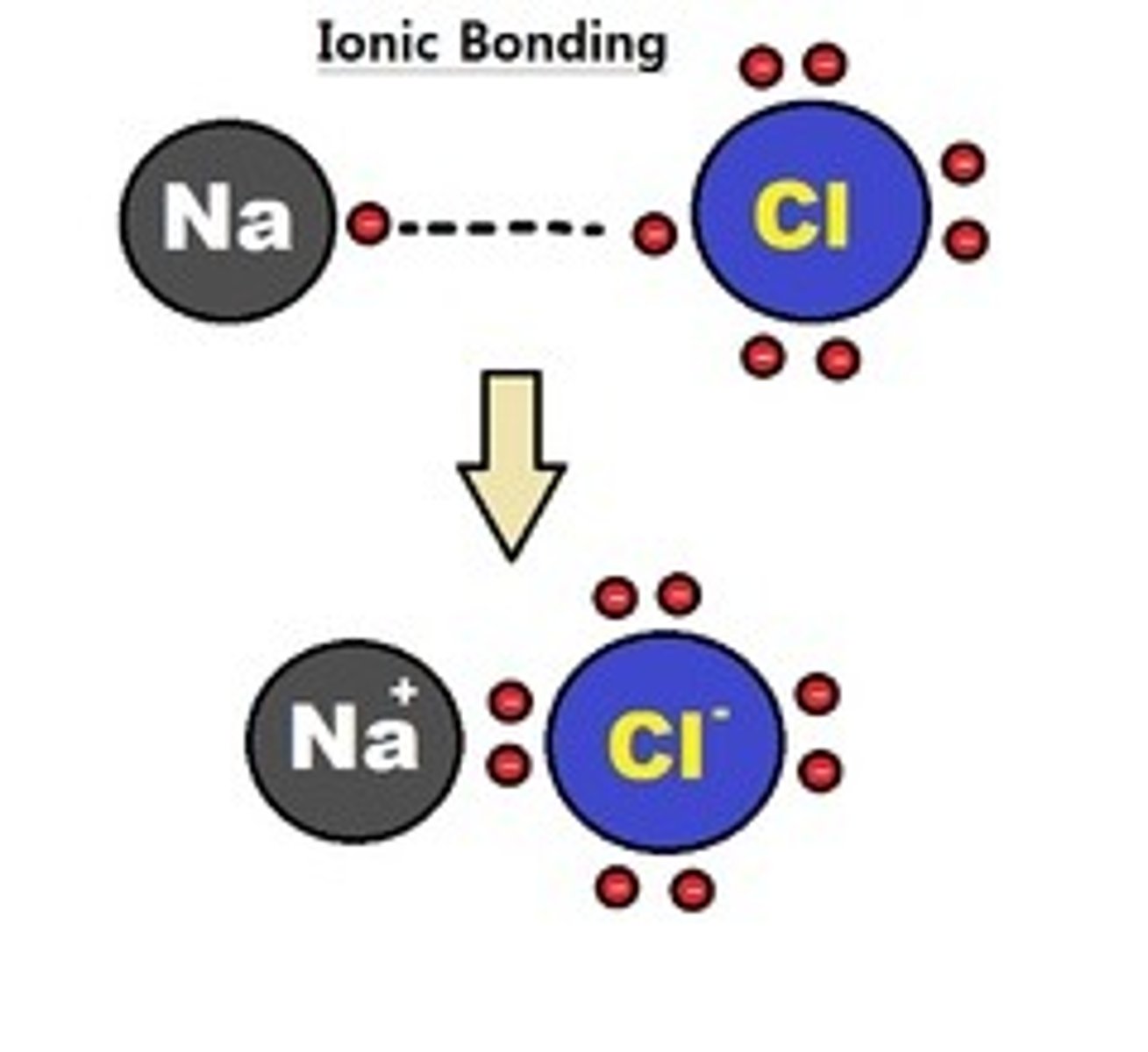
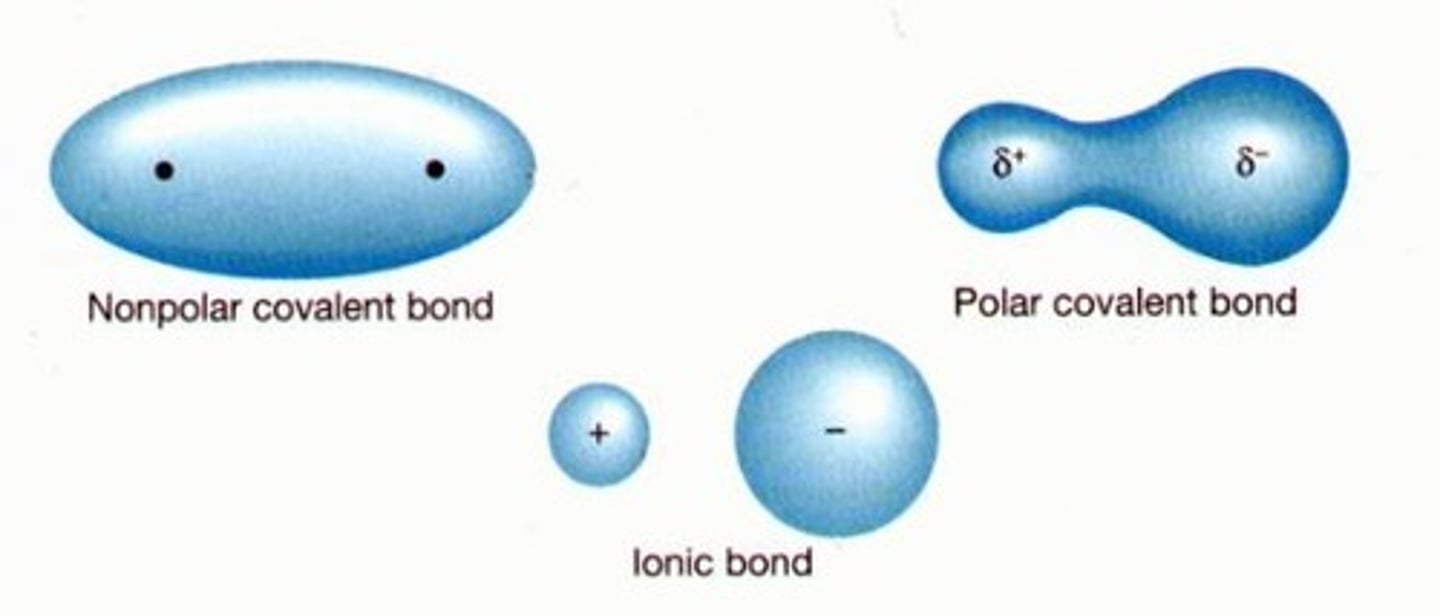
ionic bonding
one or more electrons from an atom with low ionization energy, generally a metal, are transferred to an atom with a high electron affinity, typically a nonmetal.
change in EN > 1.7.
Ex: NaCl
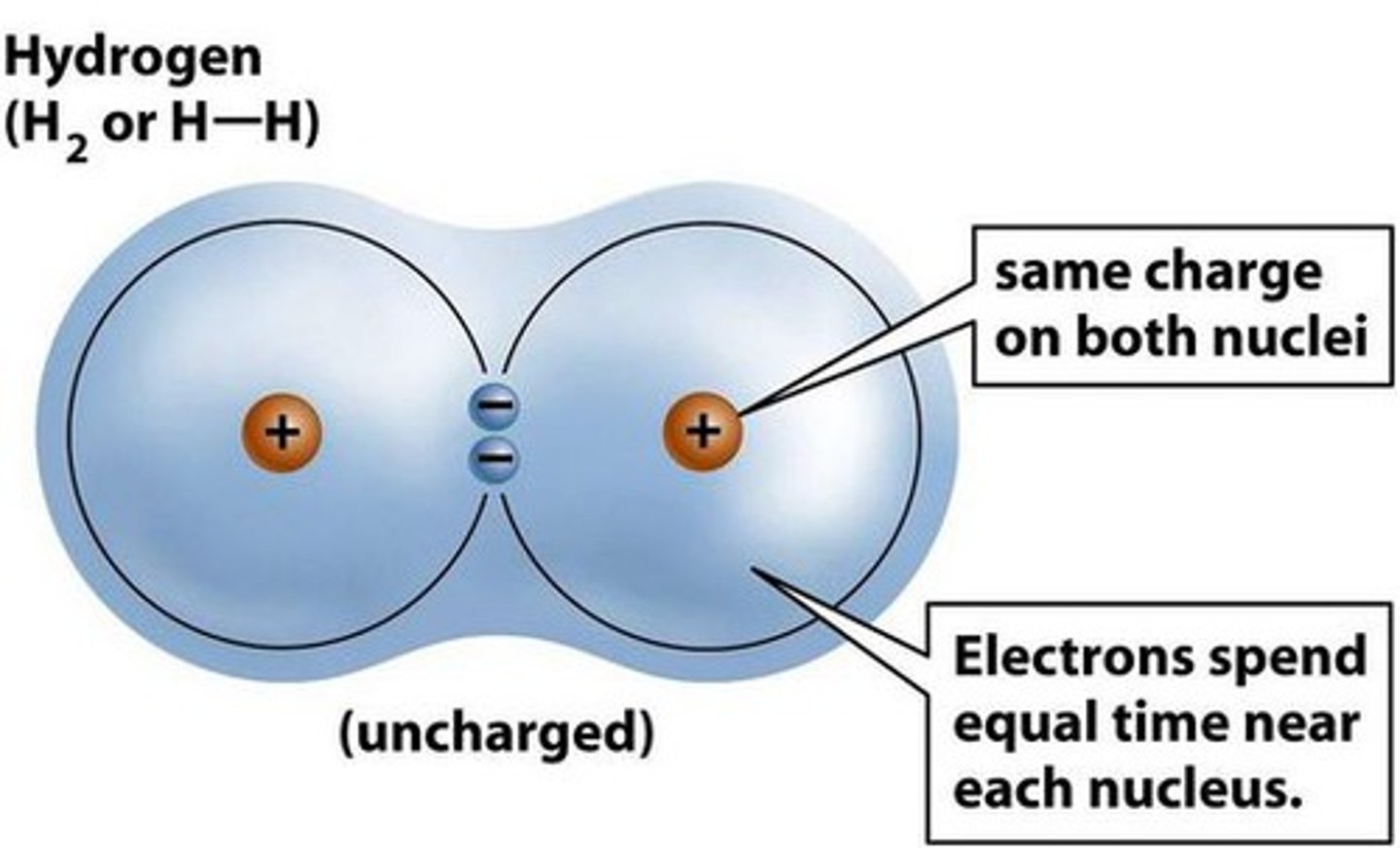
covalent bonding
results from the sharing of electron pairs between two atoms with similar EN
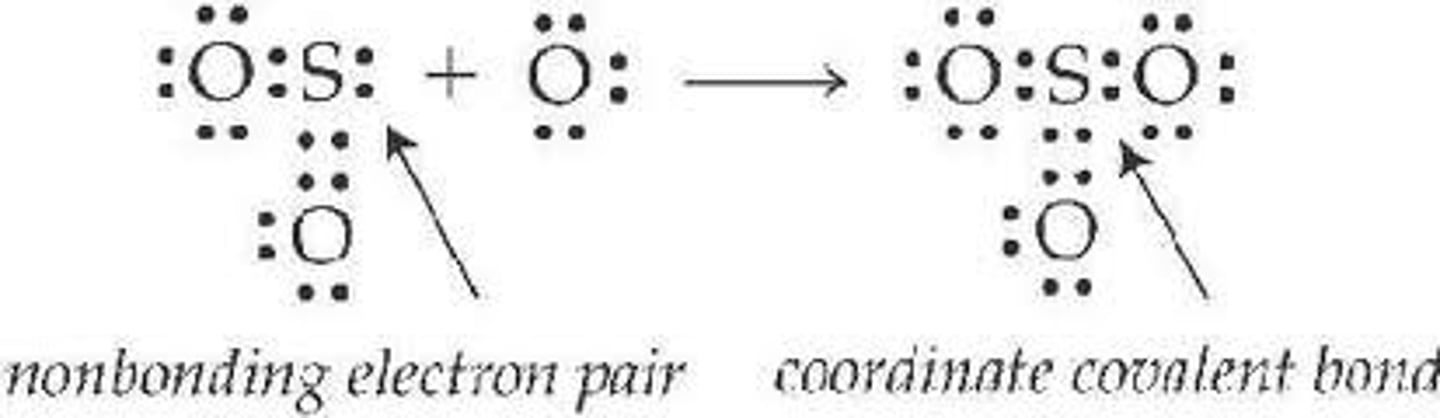
coordinate covalent
a covalent bond in which one atom contributes both bonding electrons ( usual in lewis acid/base examples)
cation
positively charged ion (loses electrons)
anion
A negatively charged ion, gains electronS
crystalline lattice
Large, organized arrays of ions.
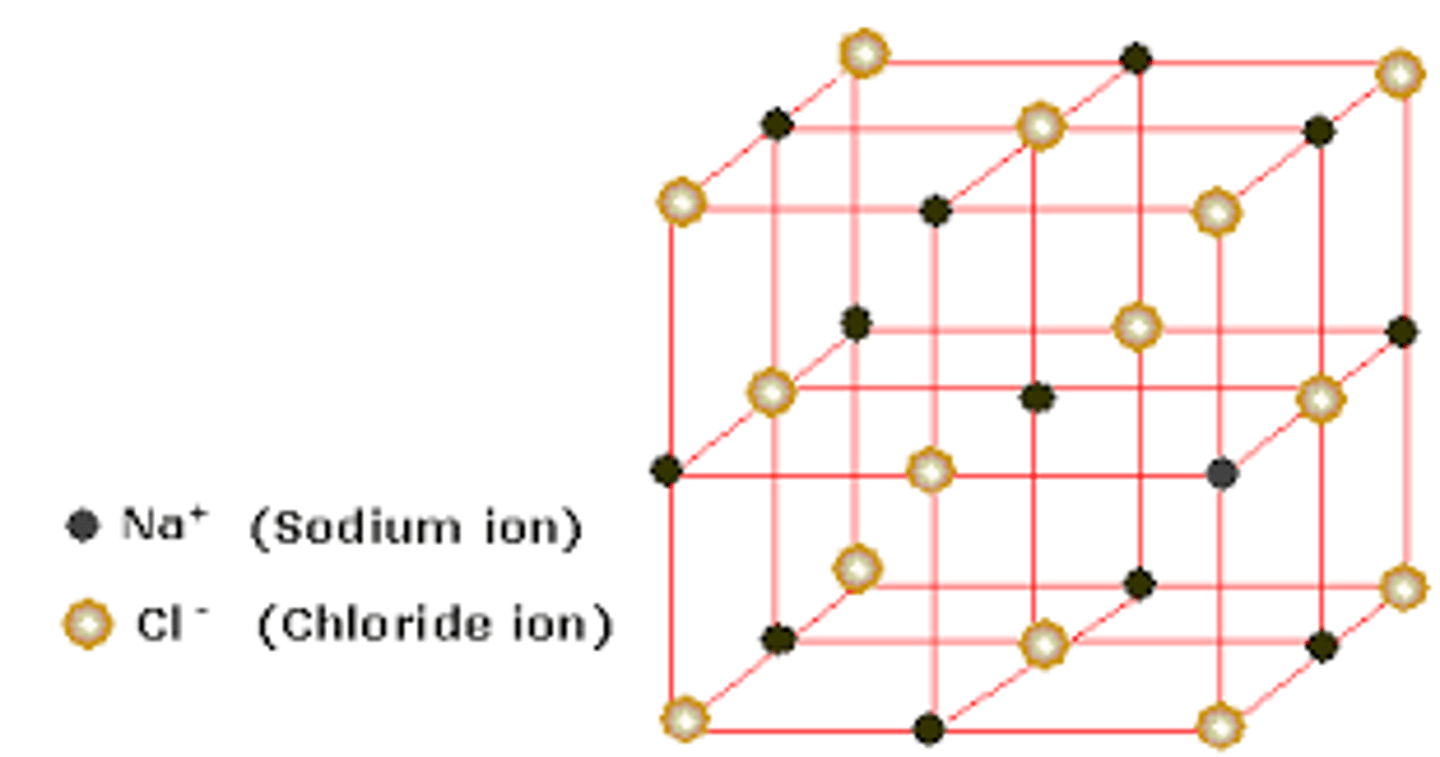
characteristics of ionic compounds
1. high melting point
2. high boiling point
3. solubility of ions in water
4. good conductors of heat and electricity
5. crystal lattice arrangement to minimize repulsive forces
6. large electronegativity differences between ions
many more
bond order
the number of bonds between atoms: 1 for a single bond, 2 for a double bond, and 3 for a triple bond
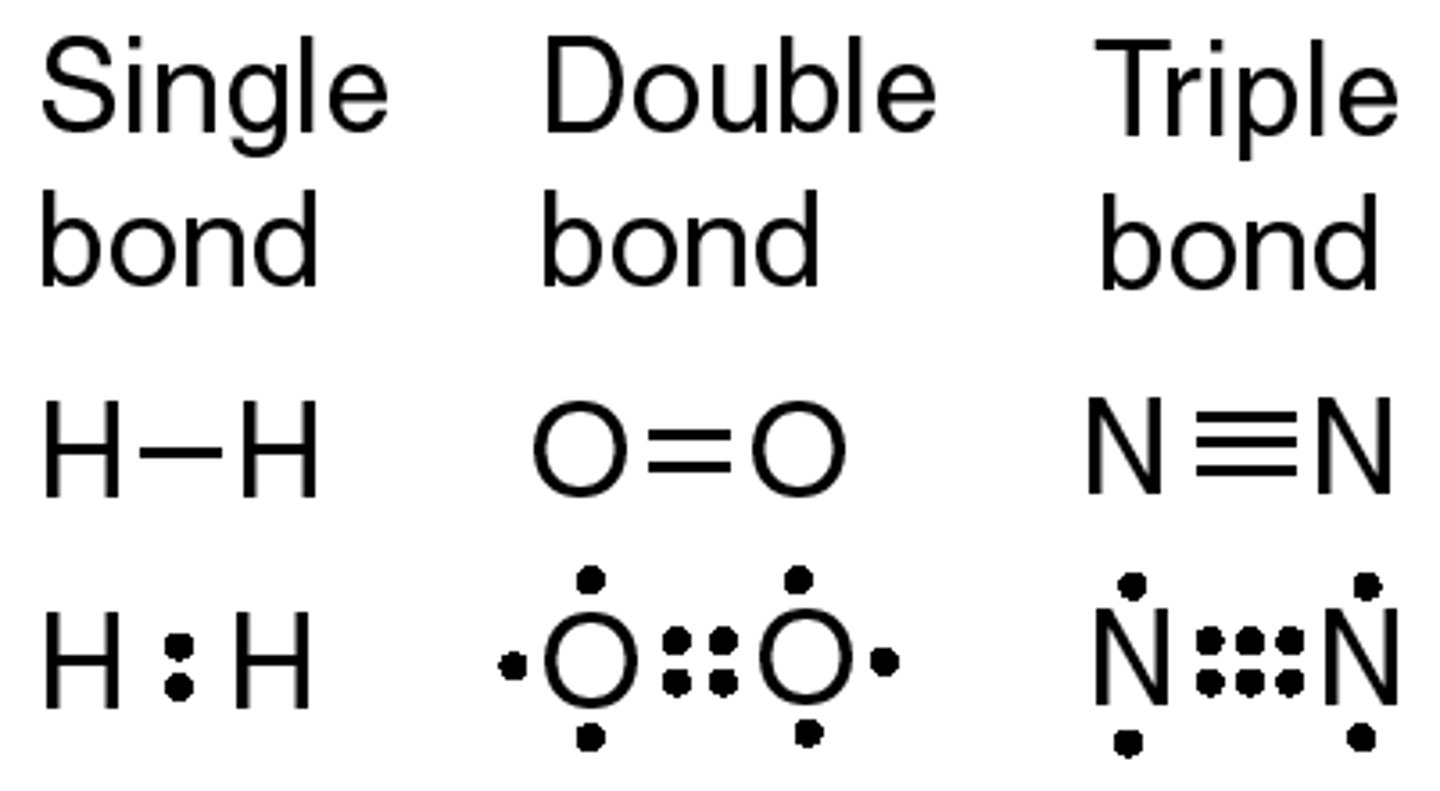
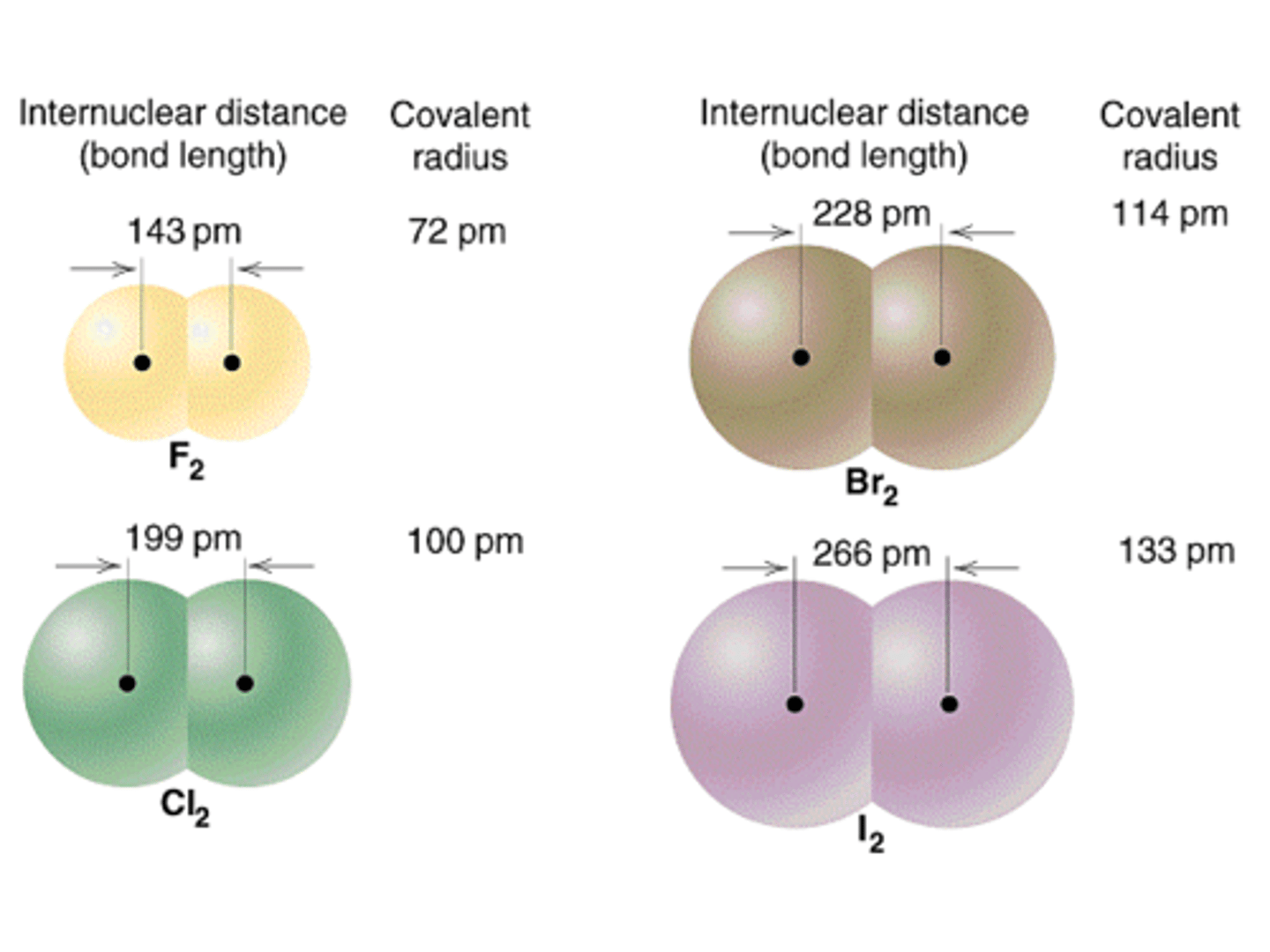
bond length
the distance between two bonded atoms at their minimum potential energy, that is, the average distance between two bonded atoms
bond energy
the energy required to break a chemical bond and form neutral isolated atoms
As bond order increases
bond strength__
bond energy _
bond length_
As bond order increases
bond strength inc
bond energy inc
bond length dec
polarity -change in EN is b/w _ & _.
the property of having poles or being polar
DEN is between 0.5 and 1.7
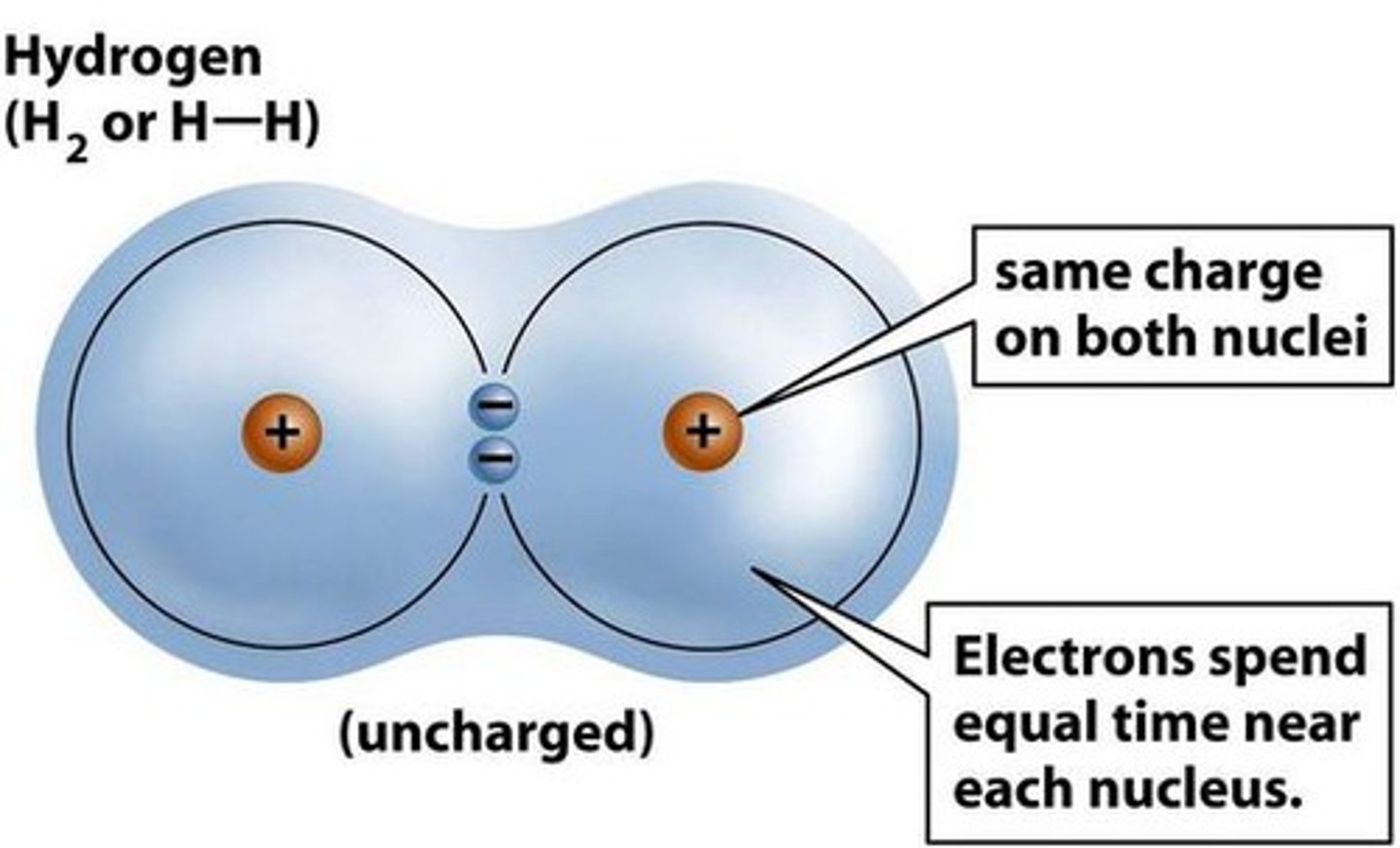
nonpolar covalent bond change in EN is _
A type of covalent bond in which electrons are shared equally between two atoms of similar electronegativity.
change in EN is
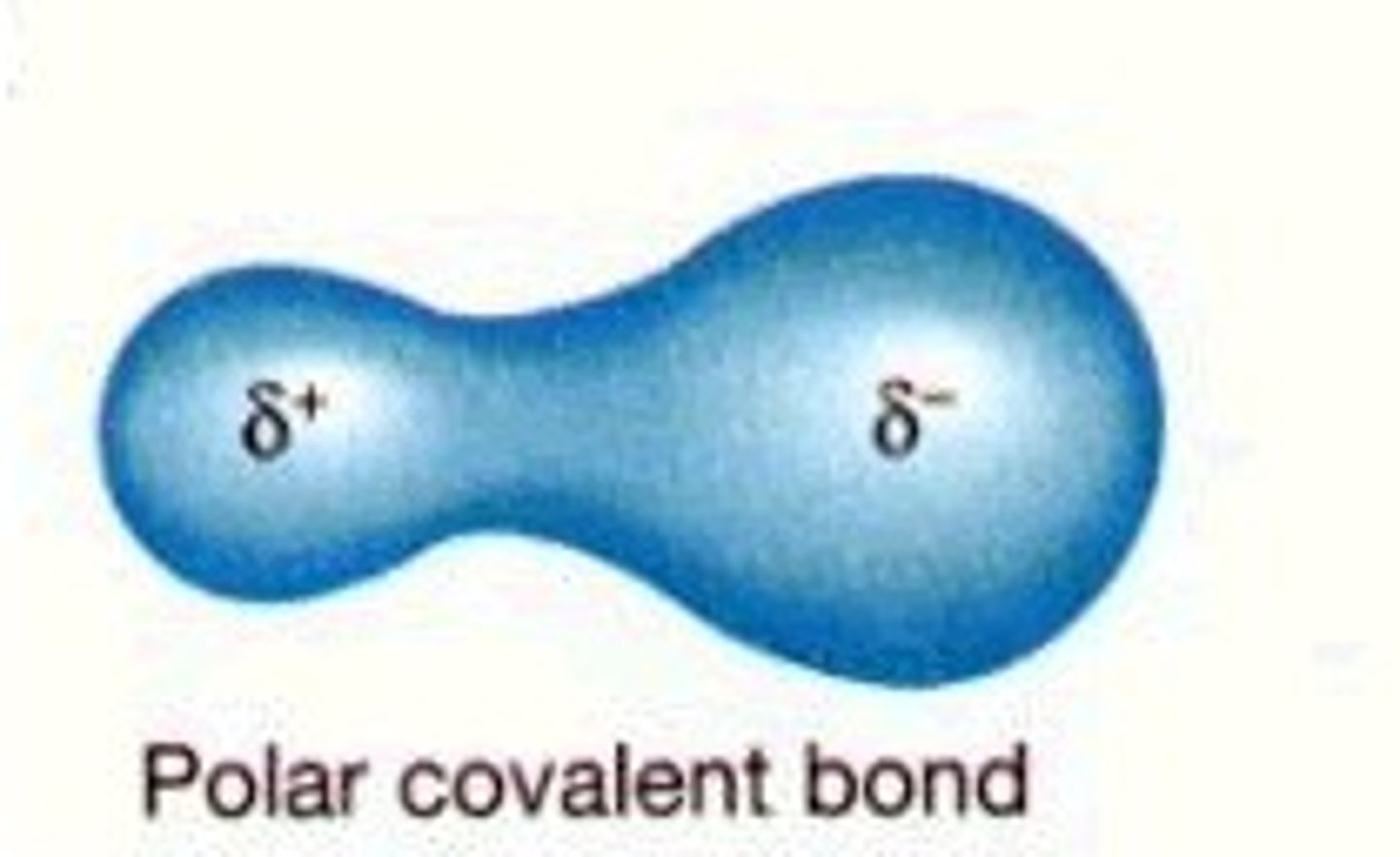
polar covalent bond
A covalent bond between atoms that differ in electronegativity. The shared electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom, making it slightly negative and the other atom slightly positive.
DEN is between 0.5 and 1.7
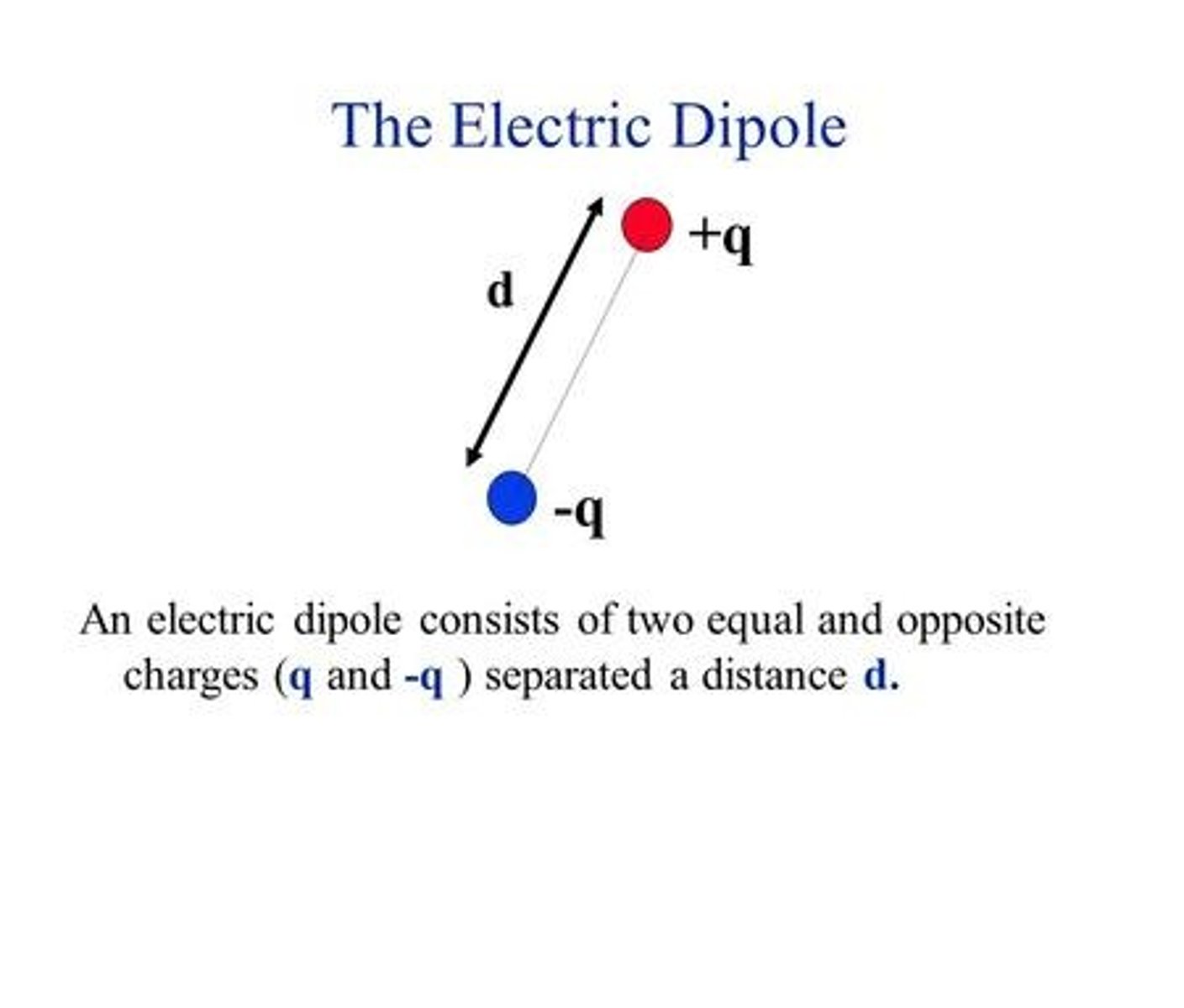
dipole moment
a property of a molecule whose charge distribution can be represented by a center of positive charge and a center of negative charge
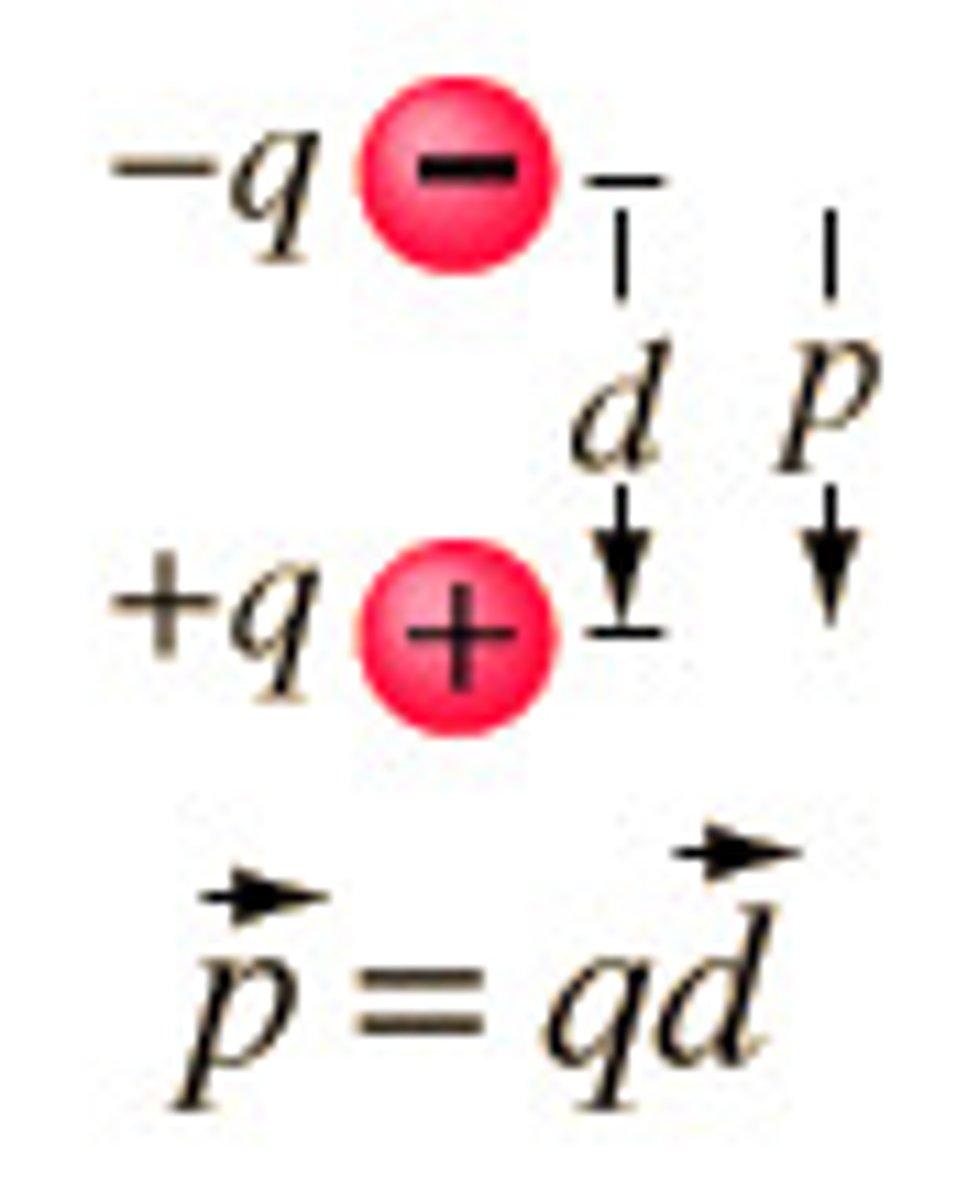
p=qd
dipole moment equation
p=dipole moment
q=magnitude of charge
d=displacement vector separating the partial charges
debye units
coulomb - meters
units of the dipole moment
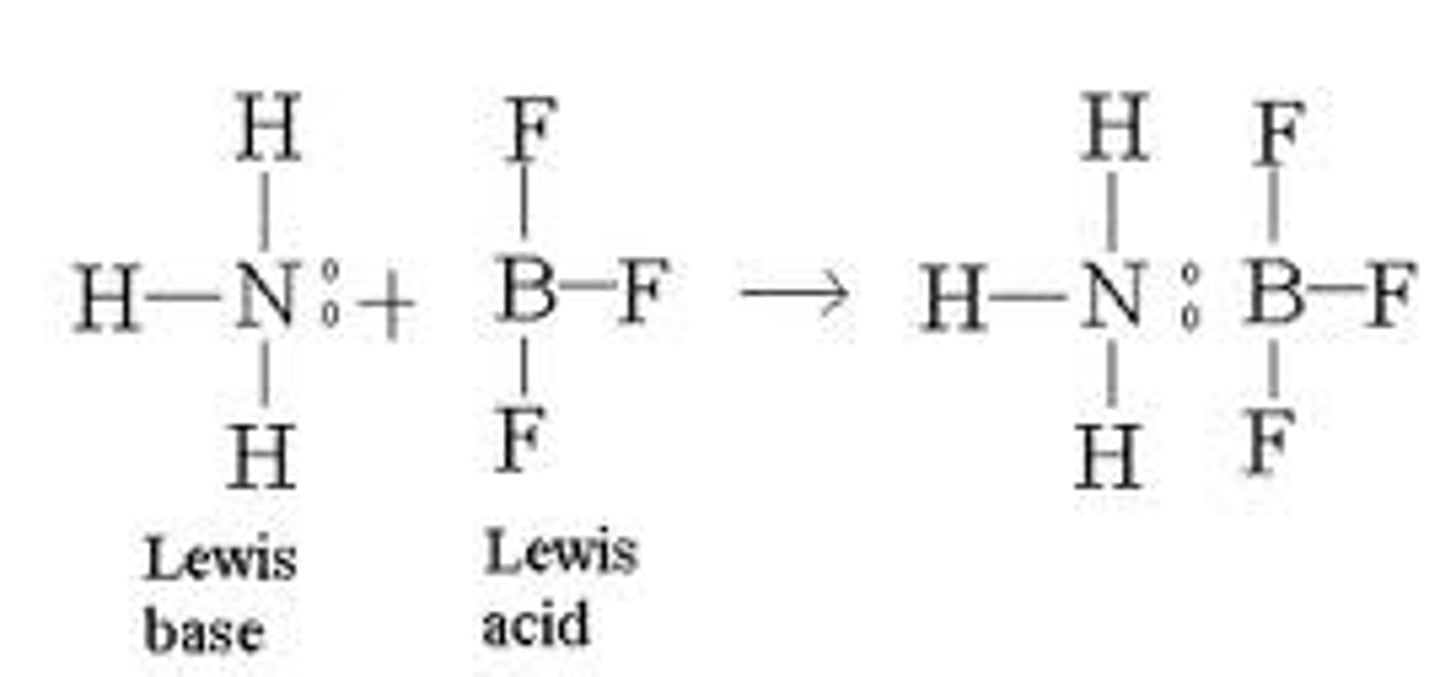
coordinate covalent bond
forms when one atom donates a pair of electrons to be shared with an atom or ion that needs two electrons to become stable
Most often found in Lewis acid-base chemistry.
-nucleophilic, electrophilic reaction
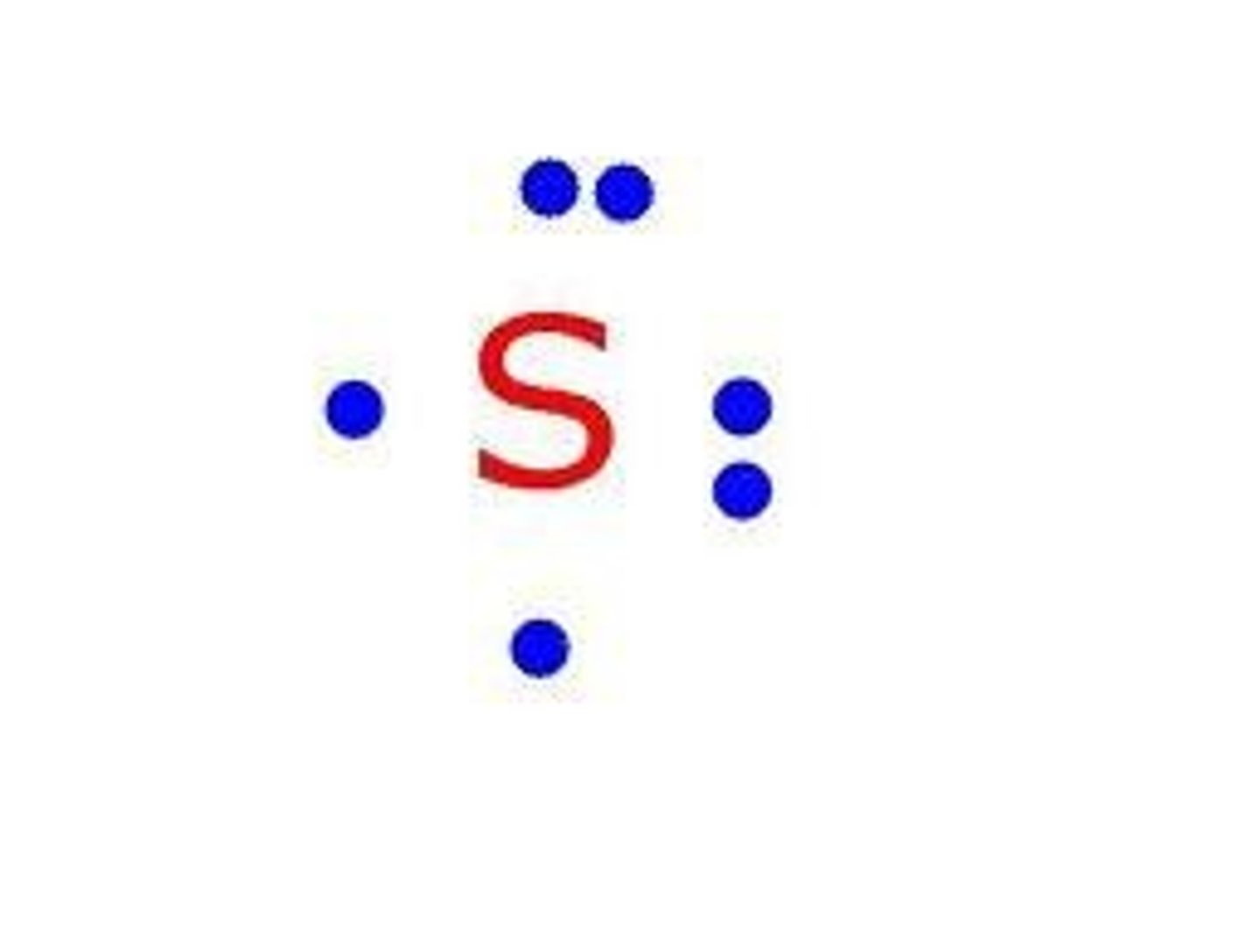
nonbonding electrons
e- in valence shell not involved in covalent bonding
lewis structure
A structural formula in which electrons are represented by dots; dot pairs or dashes between two atomic symbols represent pairs in covalent bonds.
formal charge
The number of valence electrons in an isolated atom minus the number of electrons assigned to the atom in the Lewis structure
Formal Charge = valence e! − dots − sticks
Dots: Nonbonding e-
Sticks: Pair of bonding electrons
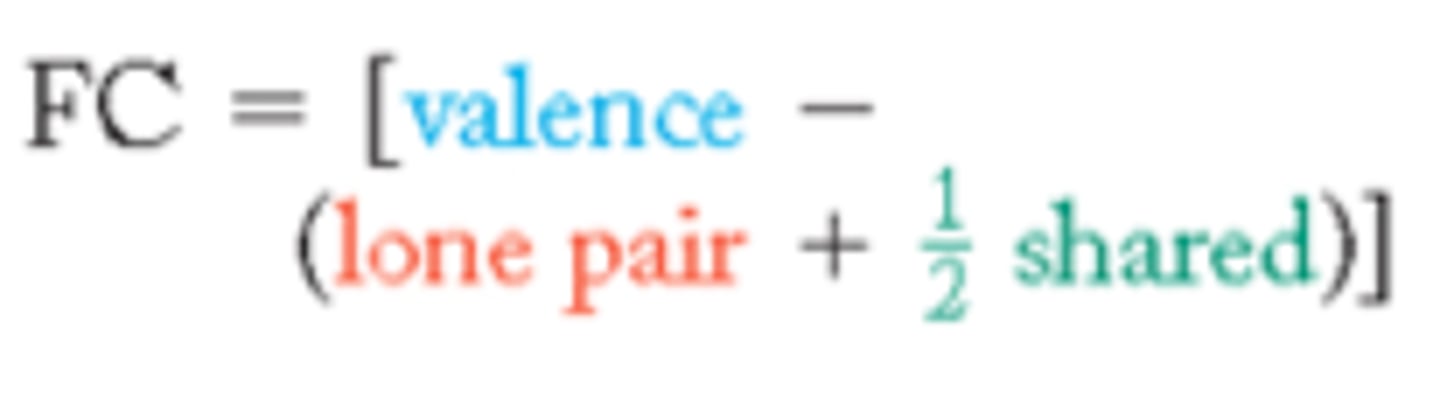
lewis dot diagram
Diagram of an atom, ion or molecule in which each dot represents a valence electron
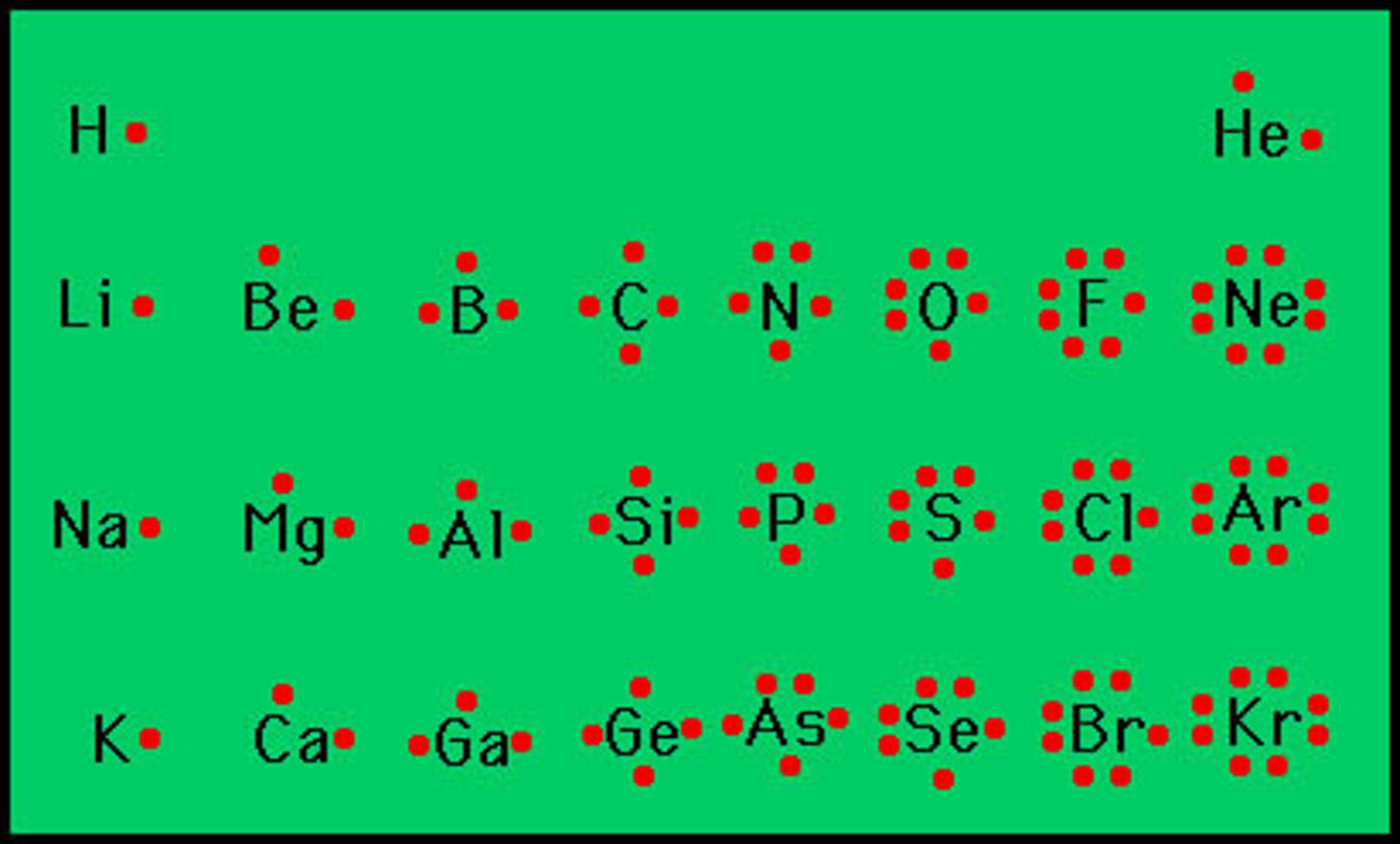
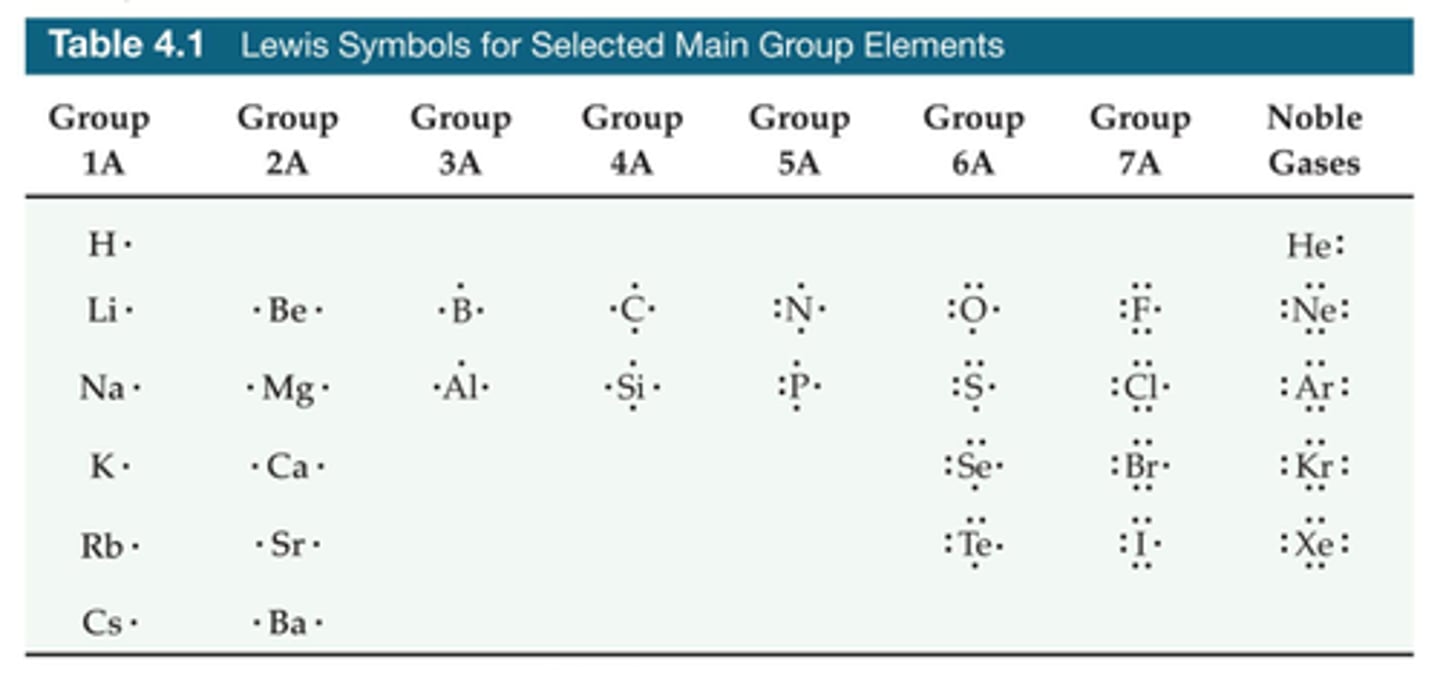
Lewis symbols for period 2 elements
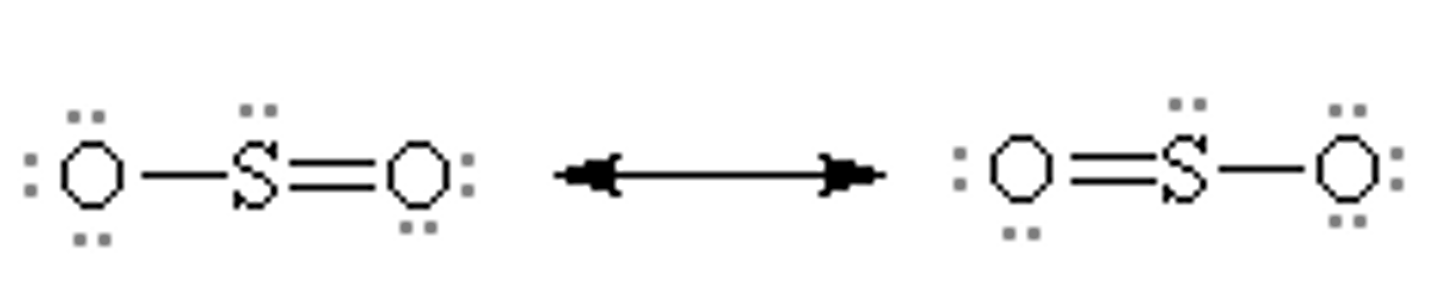
resonance structure
one of the two or more equally valid electron dot structures of a molecule or polyatomic ion
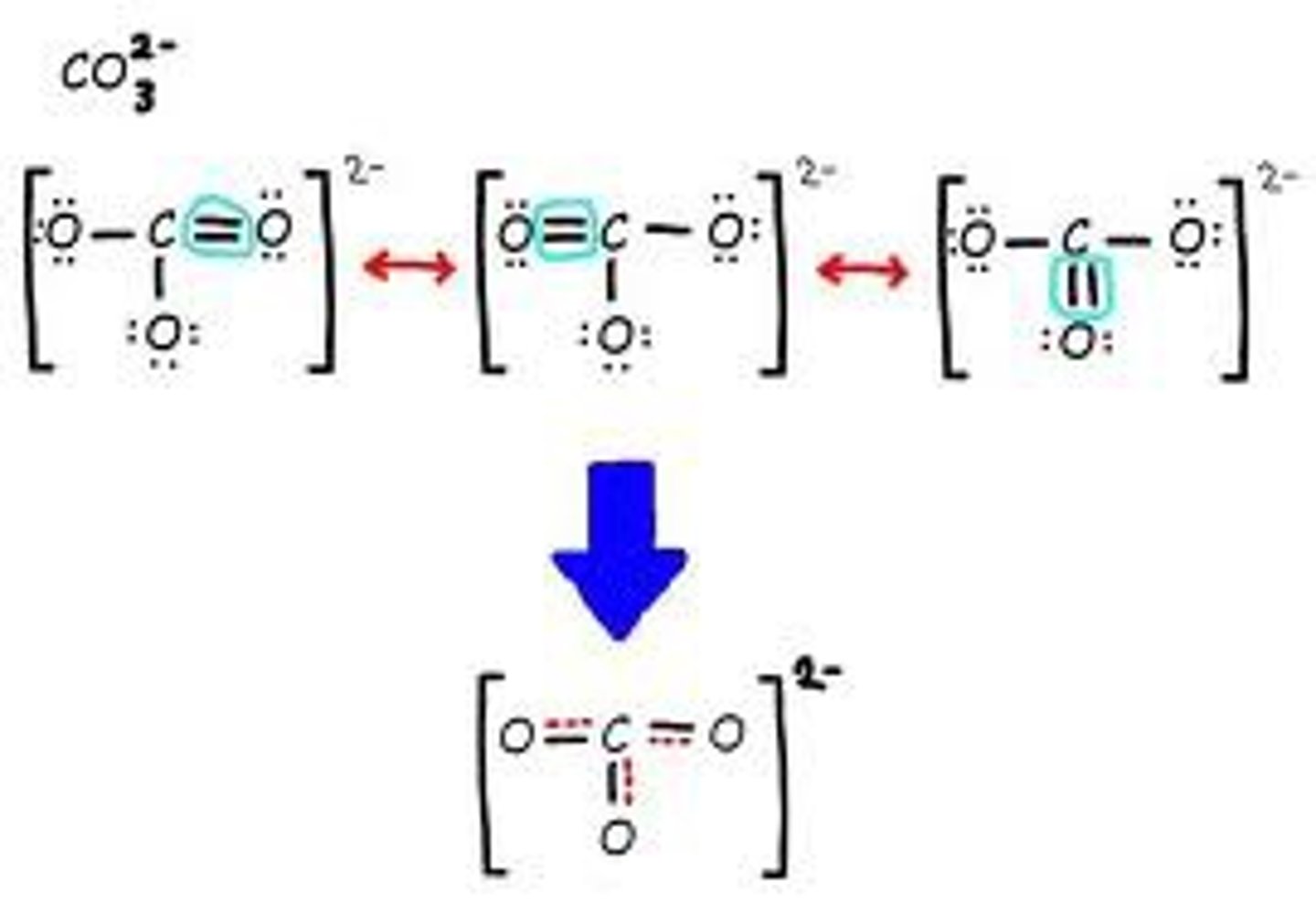
resonance structures for so2
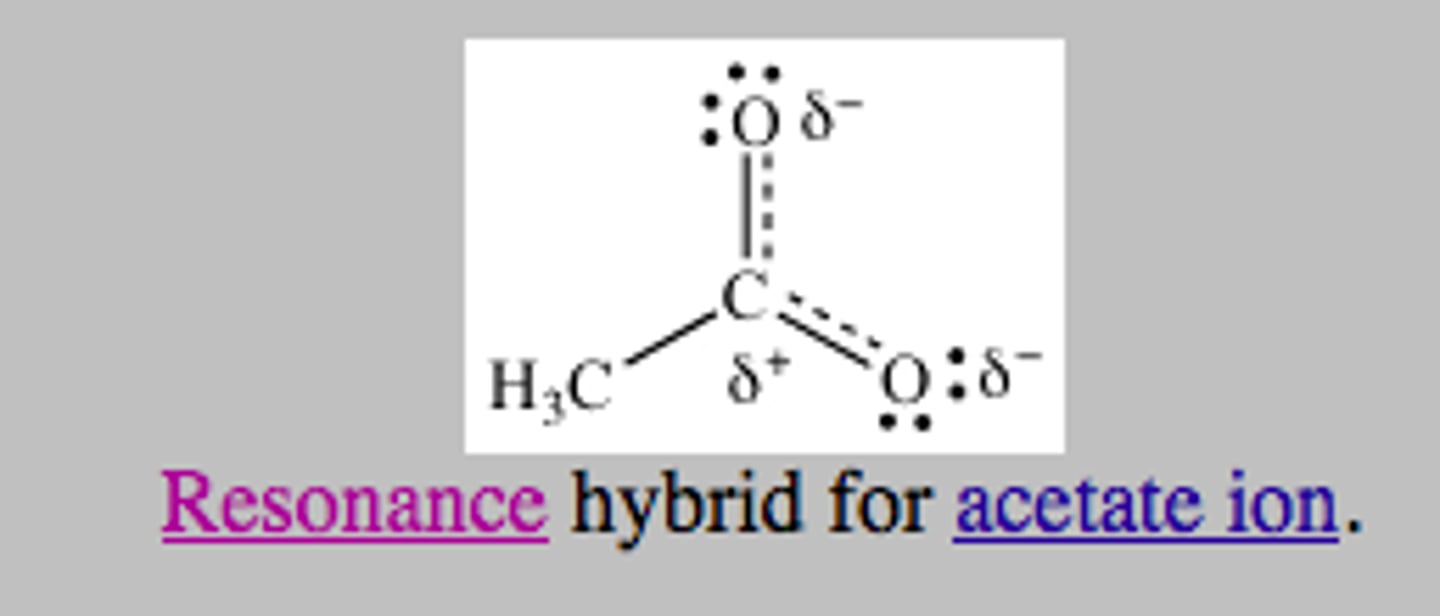
resonance hybrid
-structure of a compound whose electronic distribution is made of all of the possible resonance structures
-the more stable the structure, the more it contributes to the hybrid
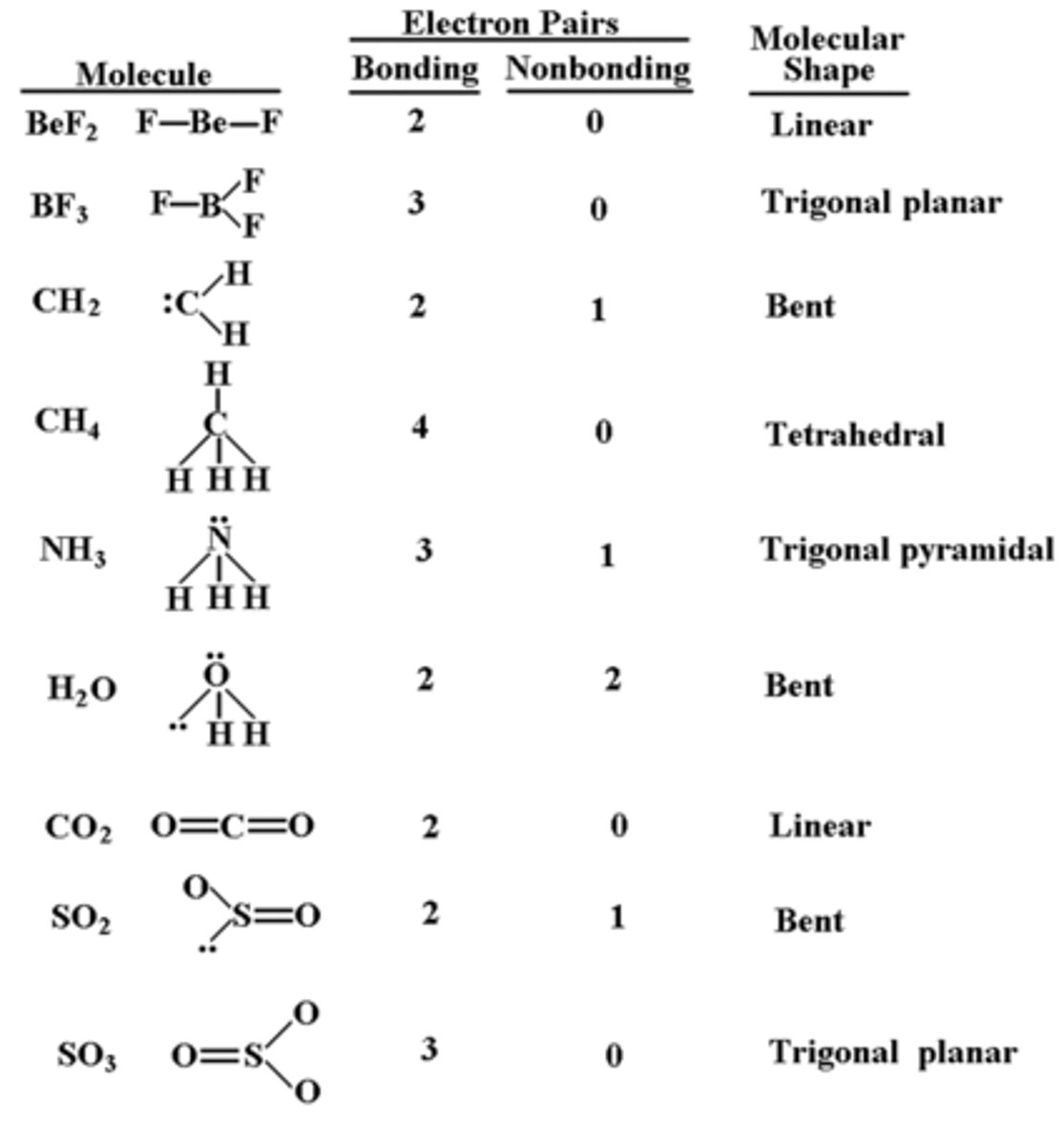
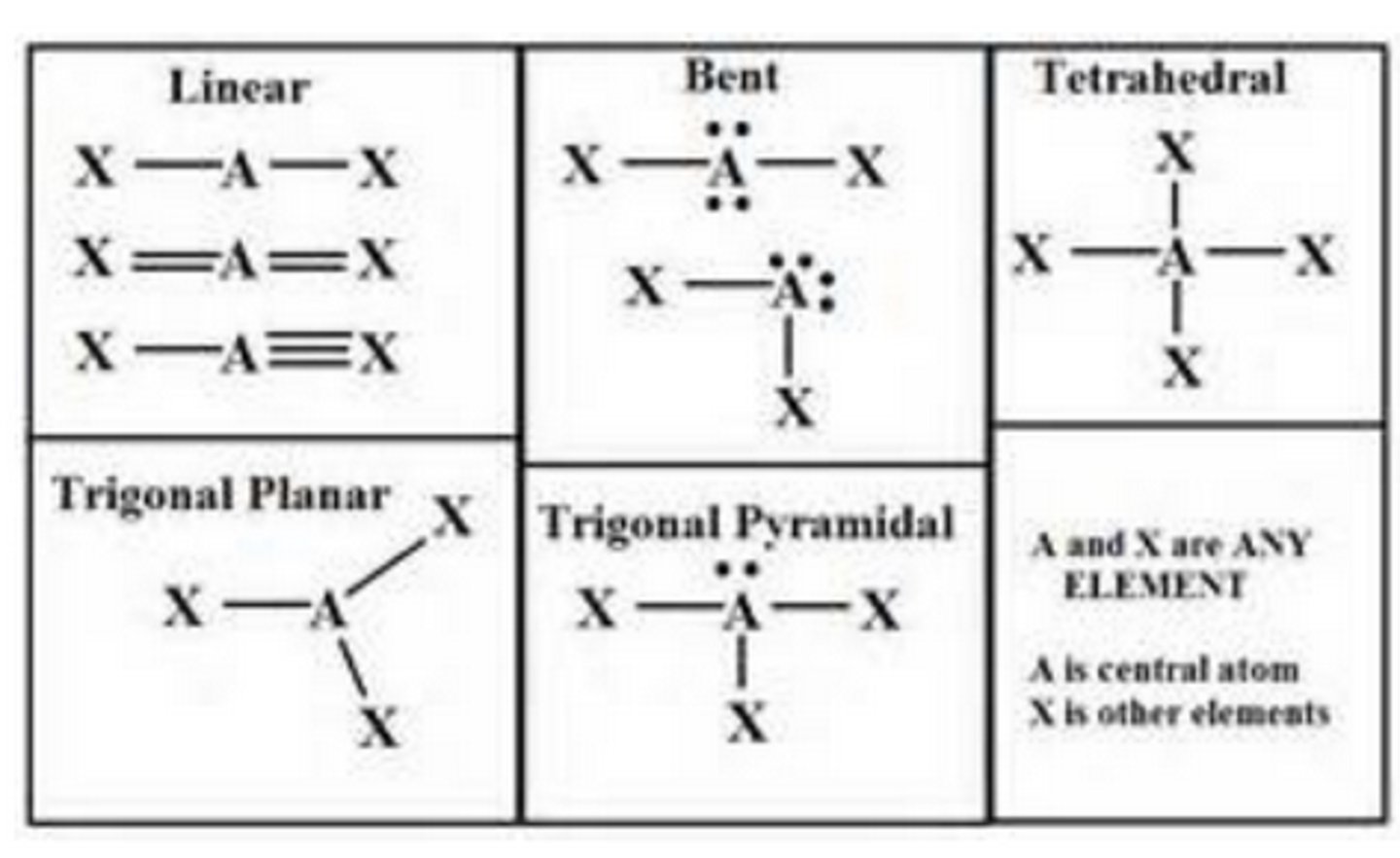
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory
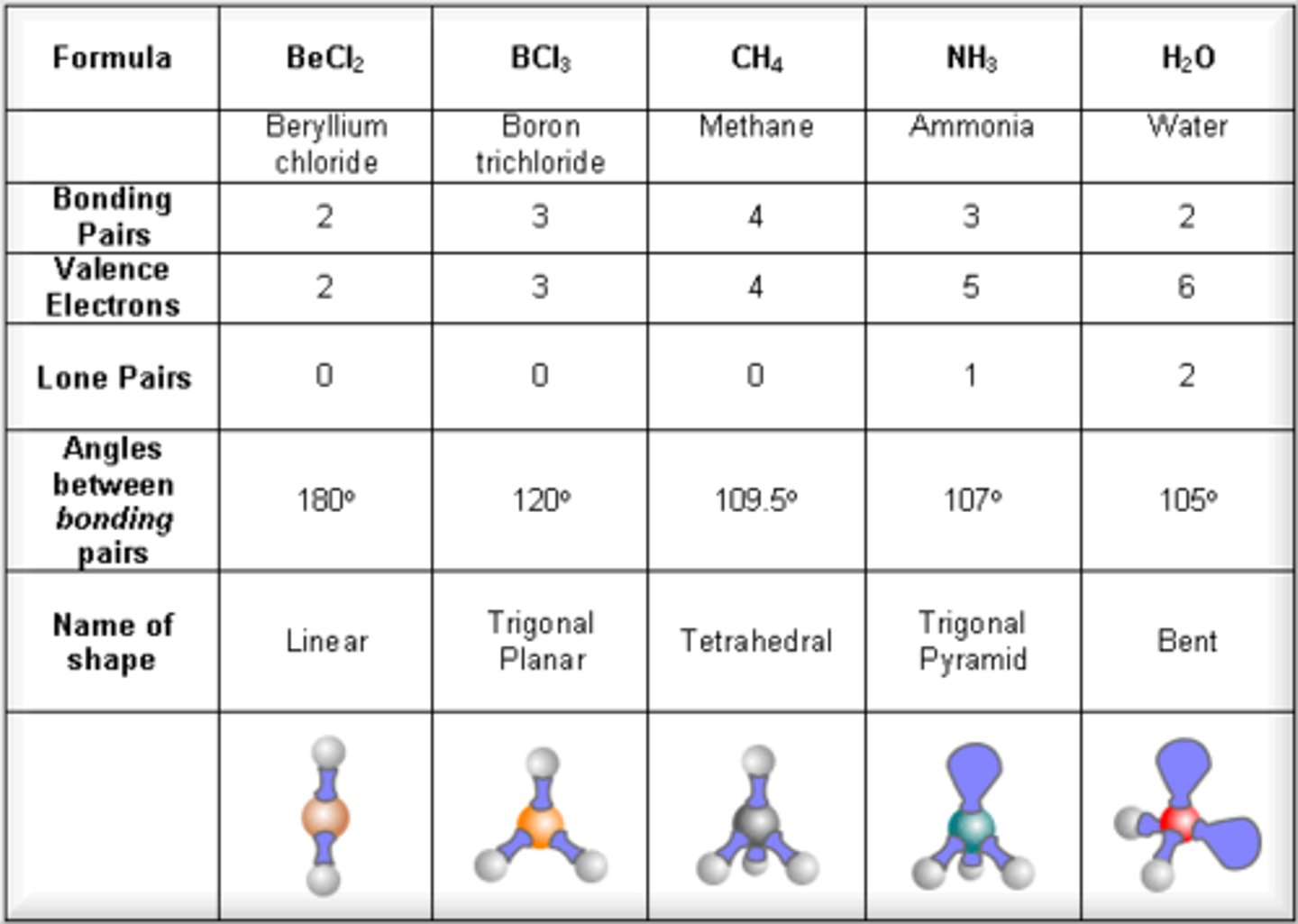
VSEPR theory
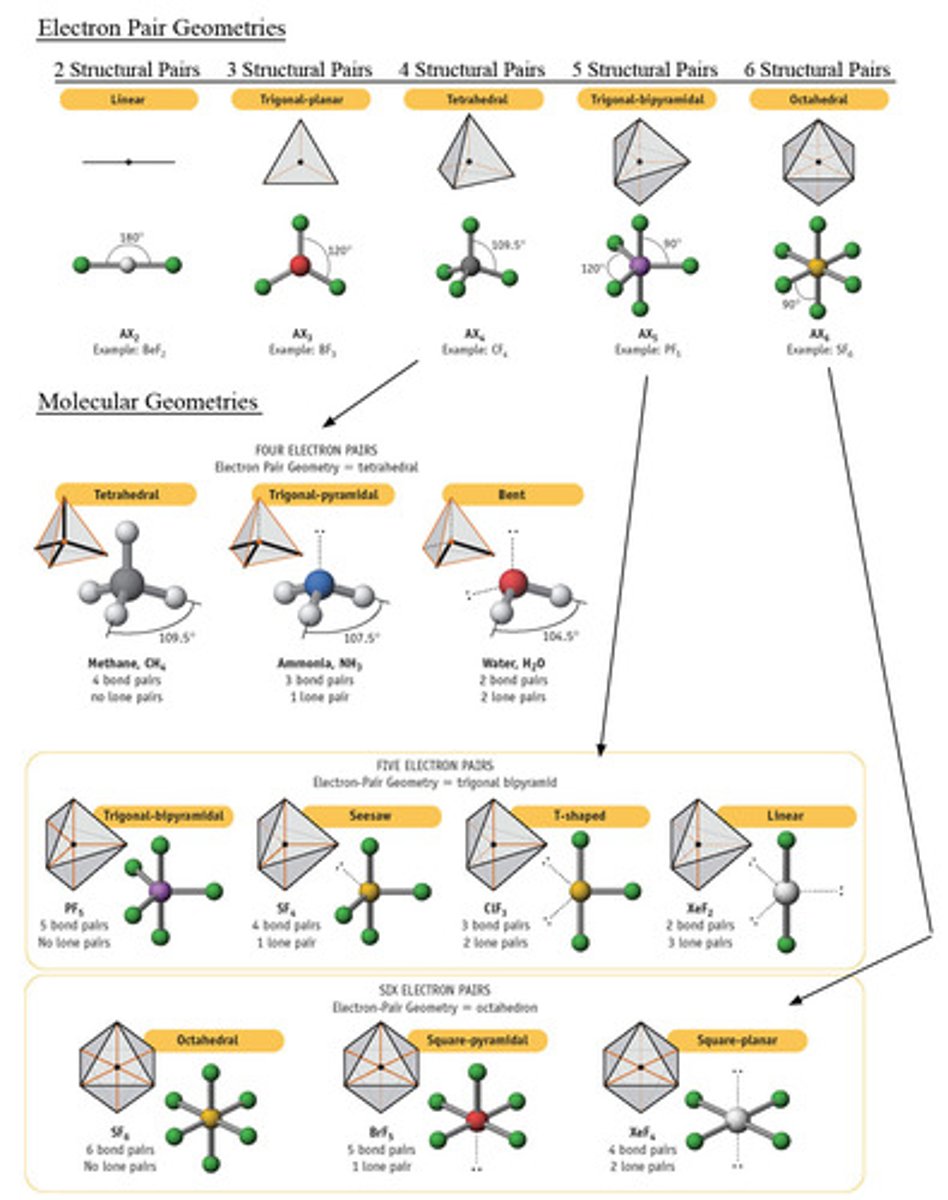
electronic geometry vs molecular geometry
ex. NH3
Electronic Geometry: Bonded and lone pairs treated the same.
Molecular Shape: Lone pairs take up less space than a bond to another atom.
ex. NH3
electronic G= tetrahedral
molecular G= trigonal pyramidal
electronic geometry
-spatial arrangement of all pairs of e- around central atom (both bonding e- and lone pairs of e-)
(linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral etc.)
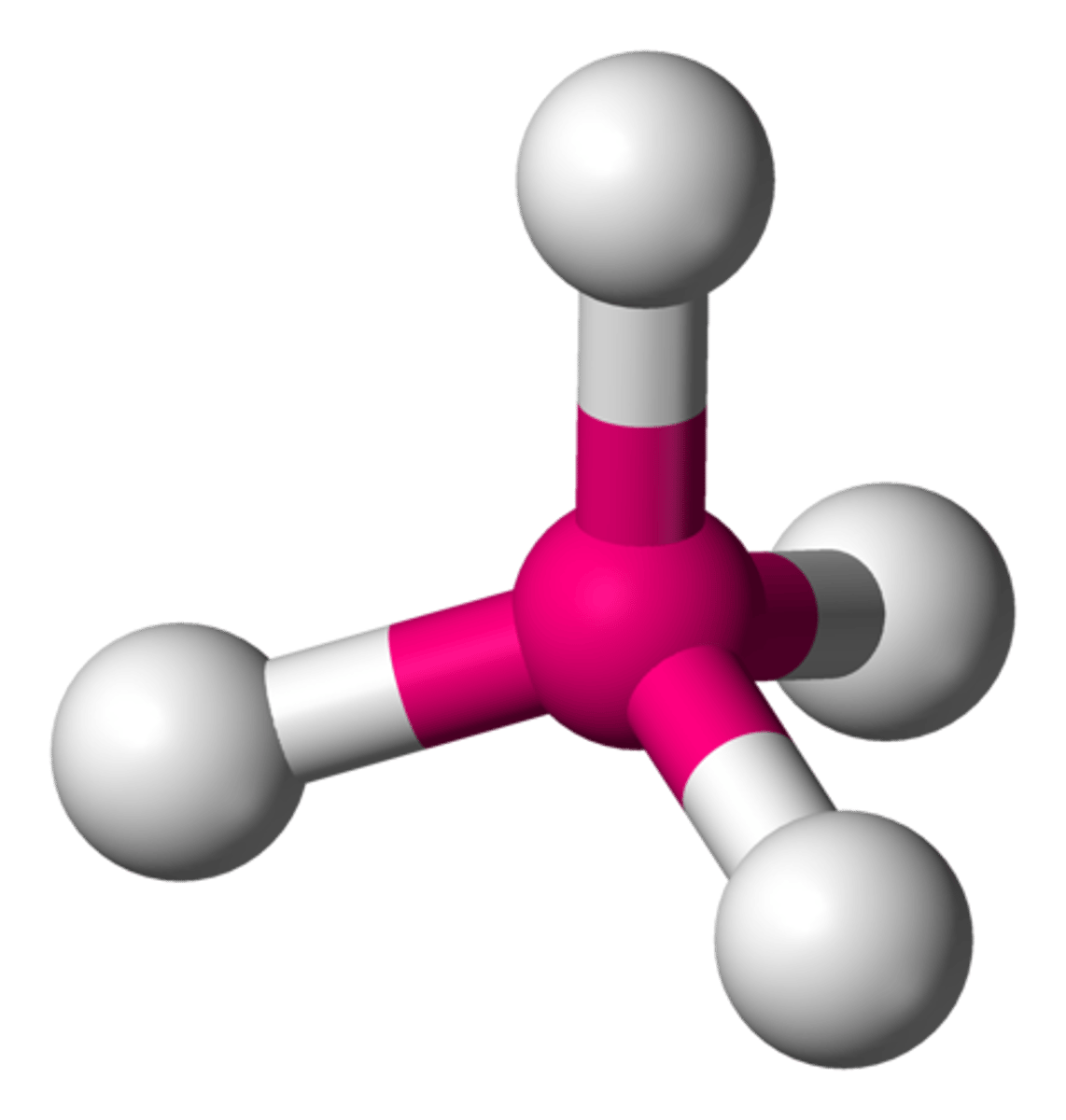
molecular geometry
The arrangement of atoms determined by the arrangement of bonding electron pairs and lone pairs around the central atom in a molecule.
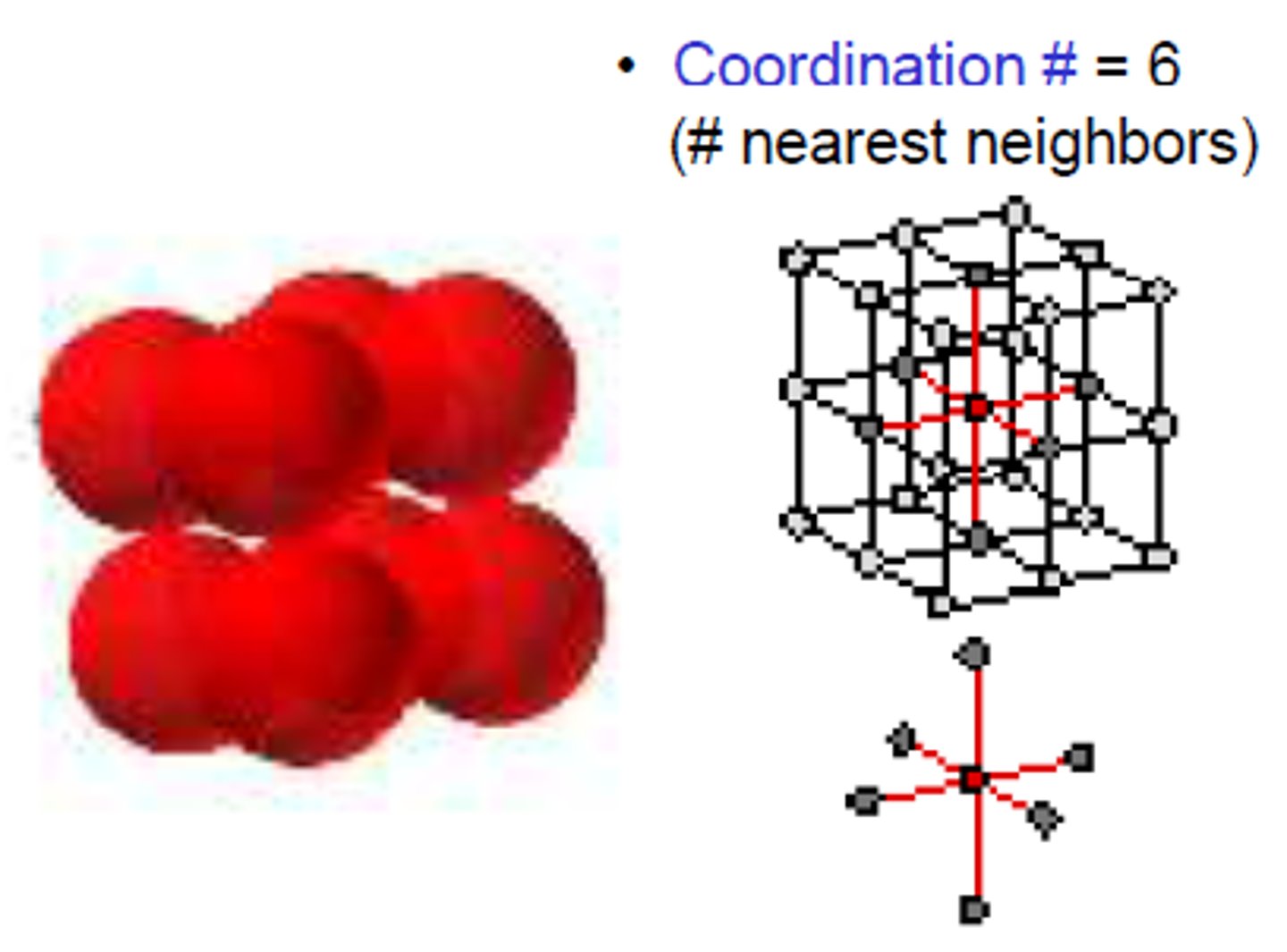
coordination number
the number of ions of opposite charge that surround each ion in a crystal
ideal bond angle
-determined by electronic geometry
-lone pairs of e- are closer to the nucleus so they exert more repulsion
-presence of lone pairs of e- makes ideal angle smaller
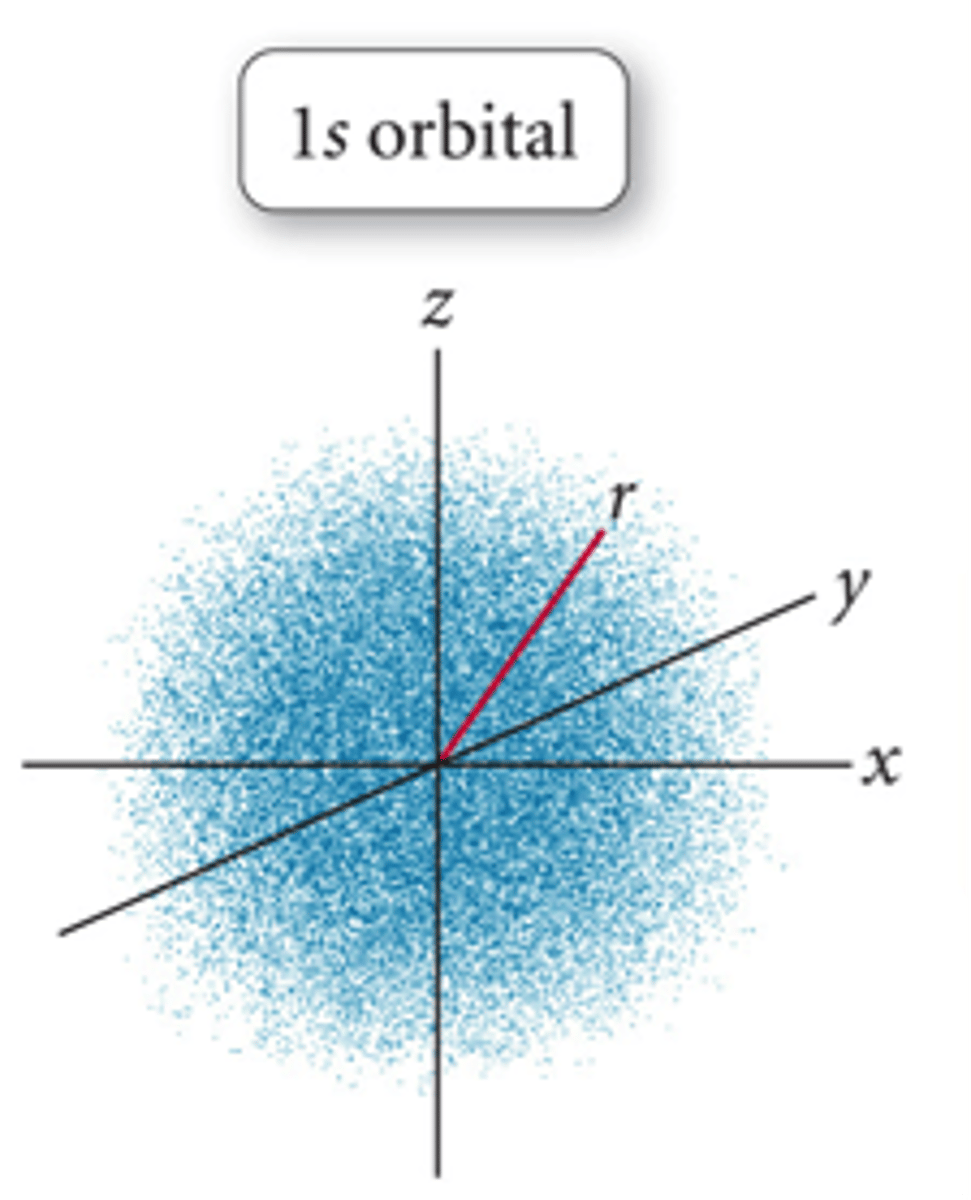
1s orbital
it describes the hydrogen electron's lowest energy state (the ground state)
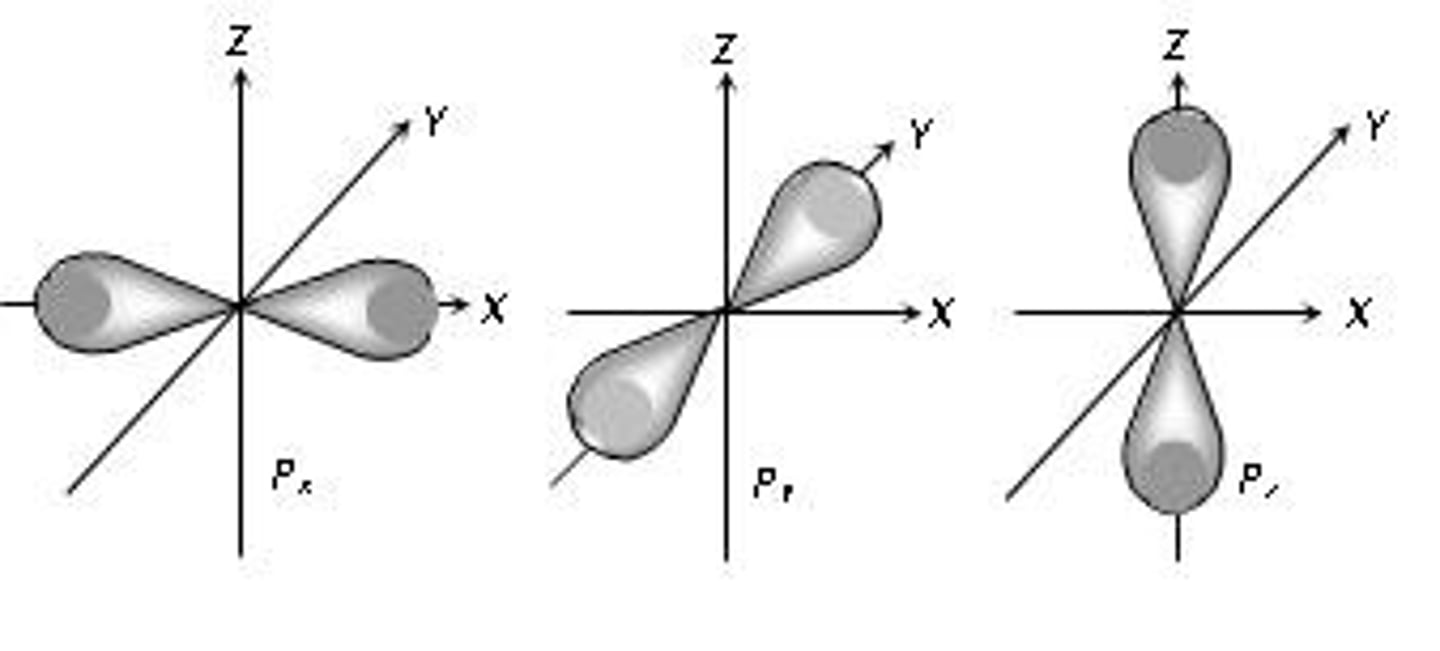
p-orbitals
molecular orbital
Region in a molecule where atomic orbitals overlap, resulting in either a stable low-energy bonding orbital or an unstable high-energy antibonding orbital.
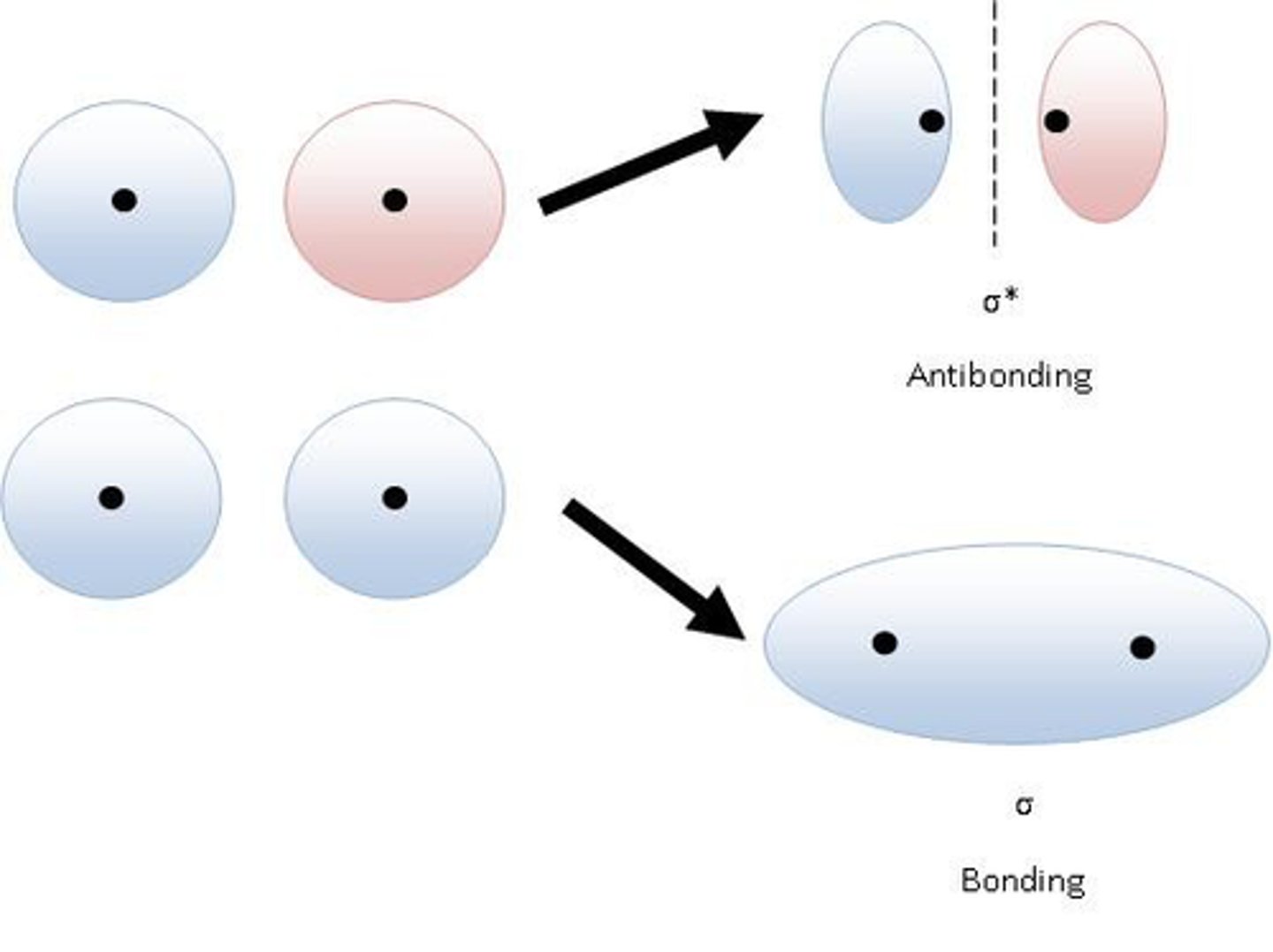
bonding orbital
a molecular orbital that can be occupied by two electrons of a covalent bond
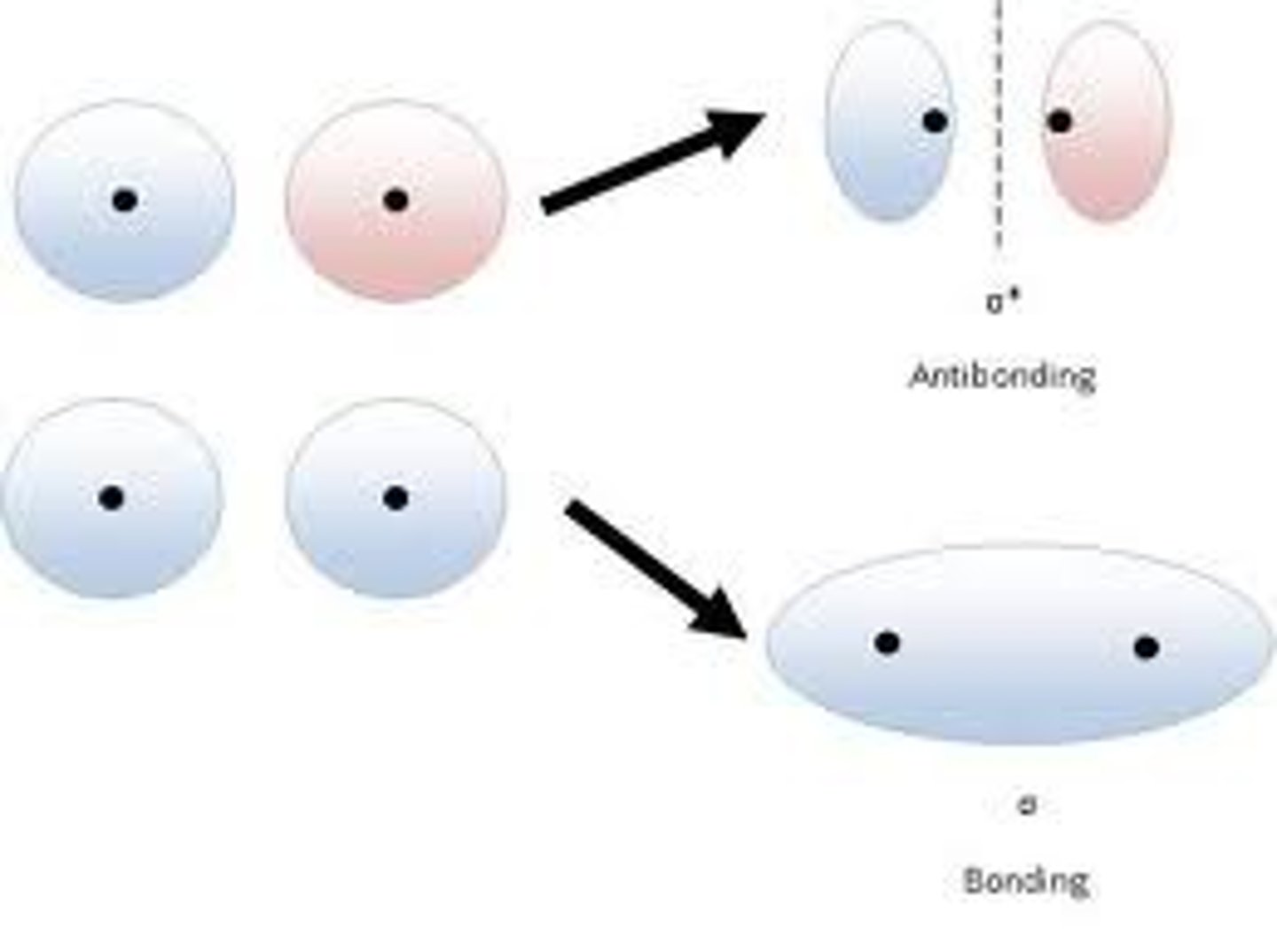
antibonding orbital
a molecular orbital that is higher in energy than any of the atomic orbitals from which it was formed
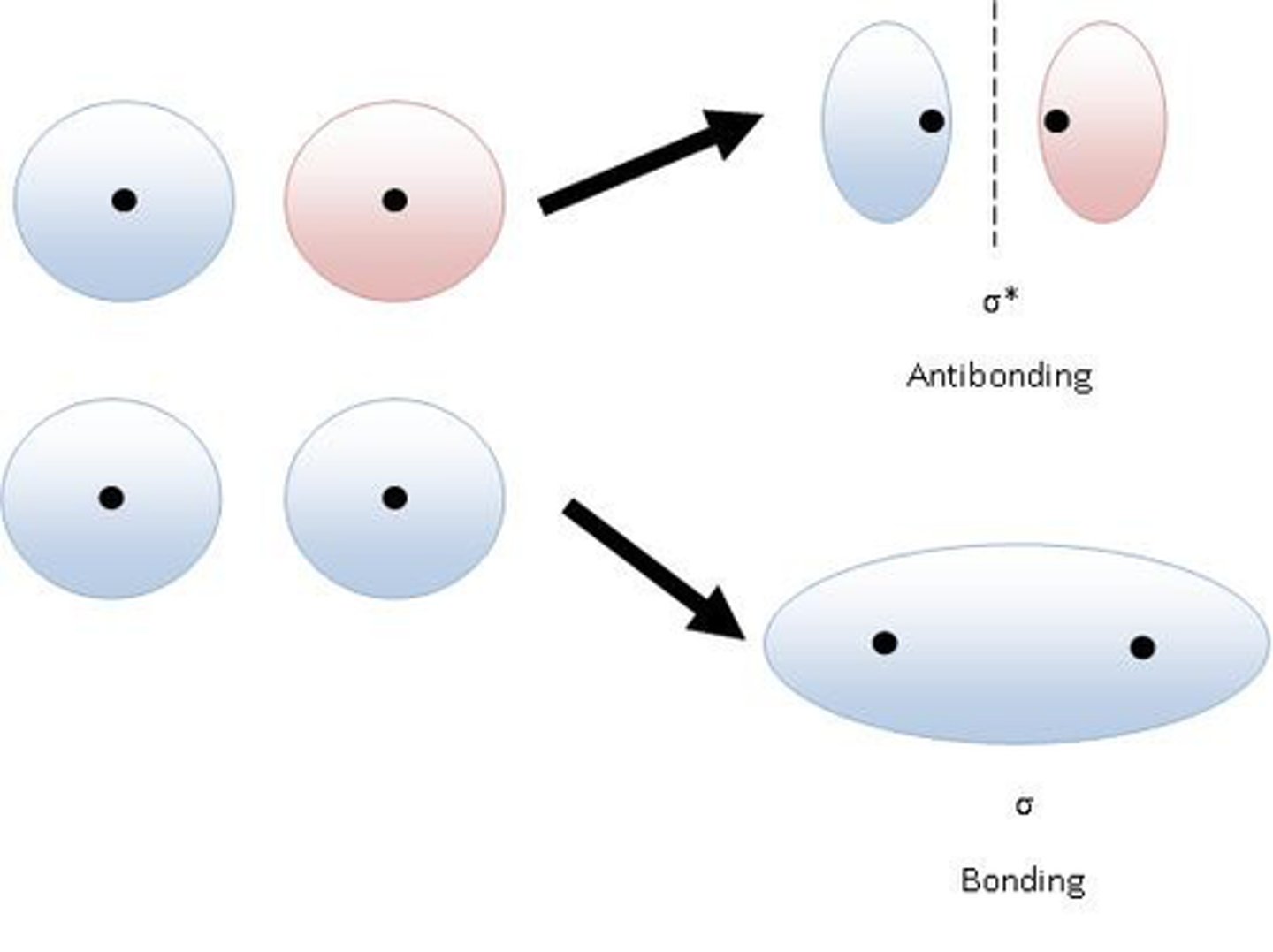
sigma bond
a bond formed when two atomic orbitals combine to form a molecular orbital that is symmetrical around the axis connecting the two atomic nuclei
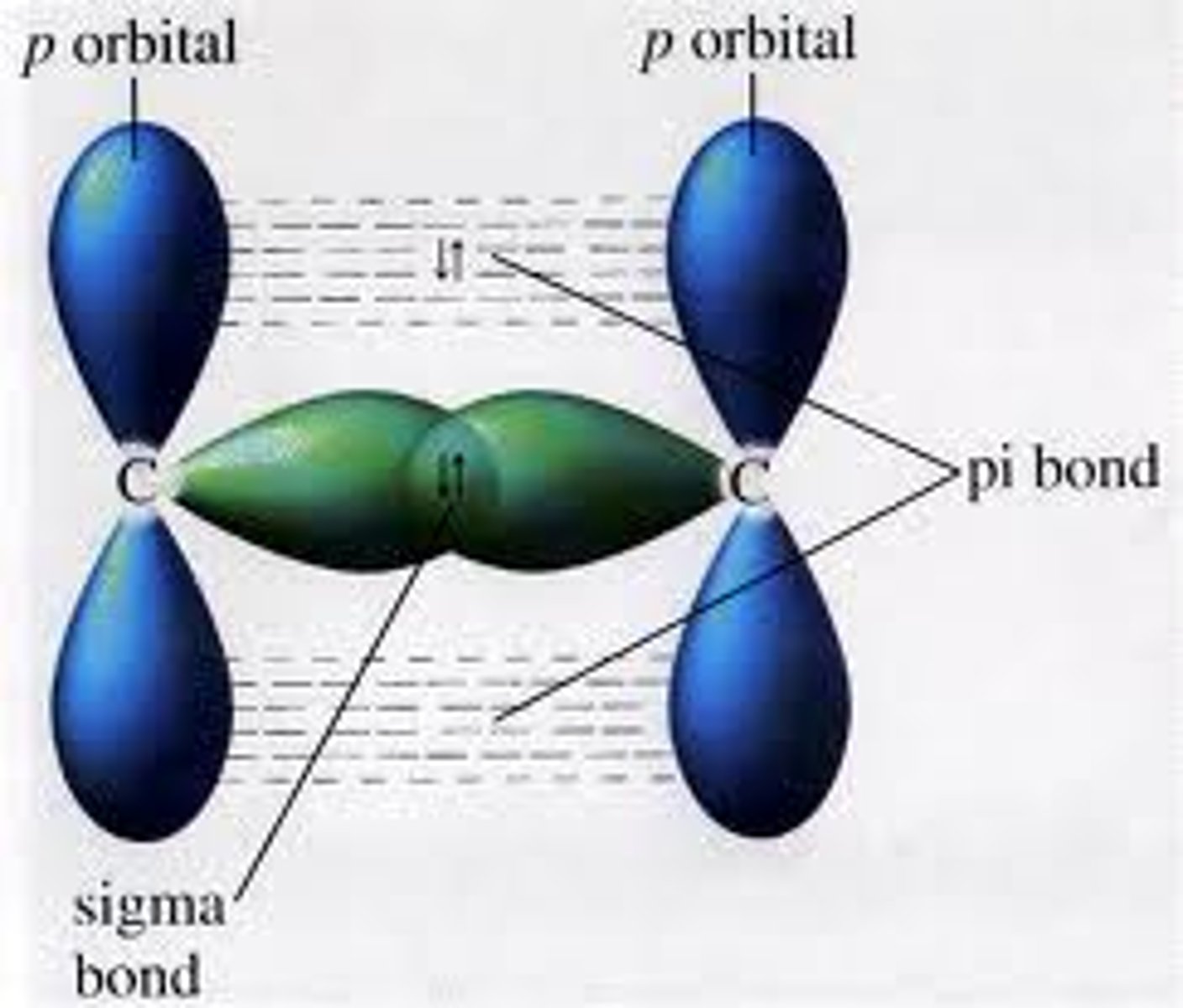
pi bond
a covalent bond in which the bonding electrons are most likely to be found in sausage-shaped regions above and below the bond axis of the bonded atoms
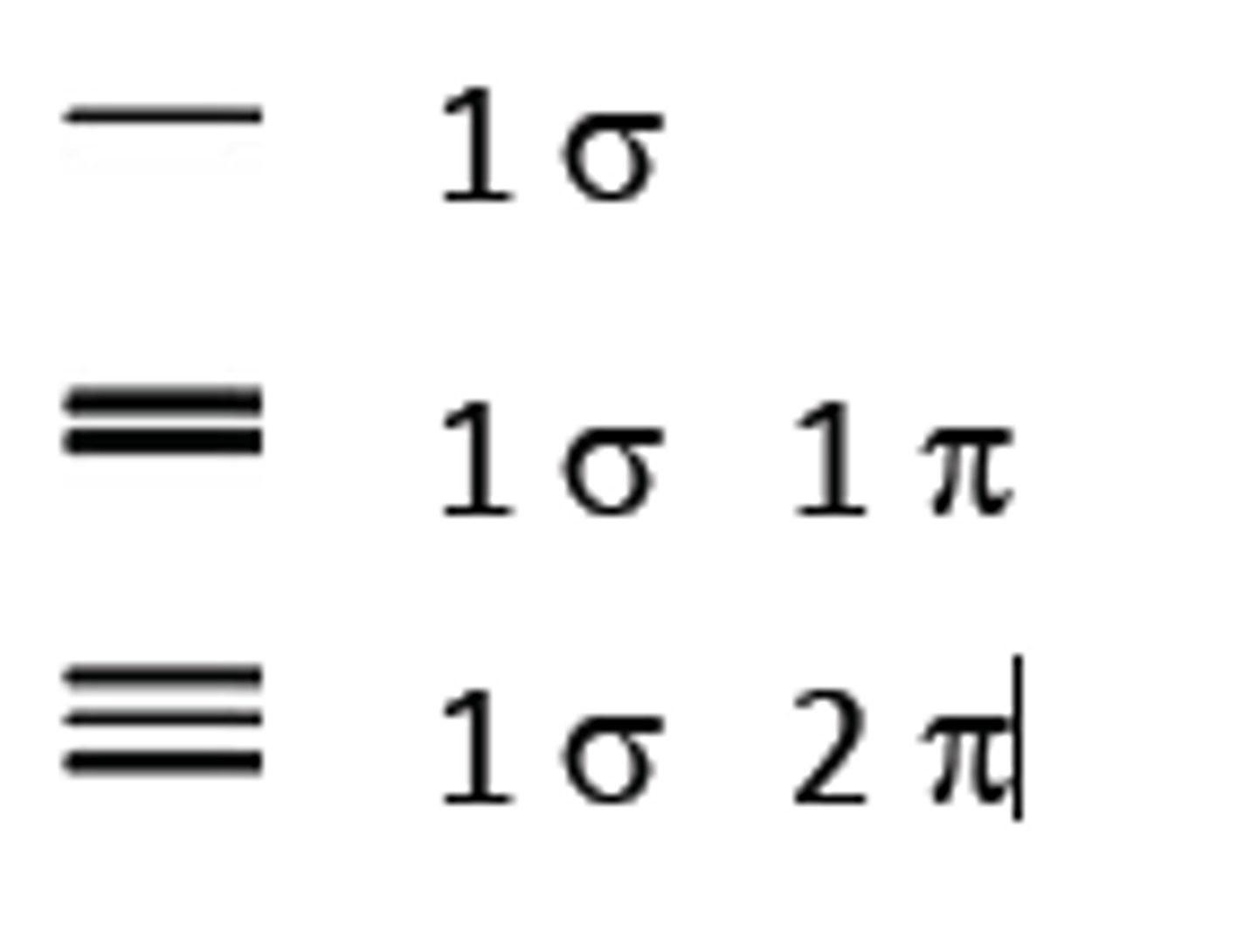
intermolecular forces
forces of attraction between molecules
(Strongest to Weakest)
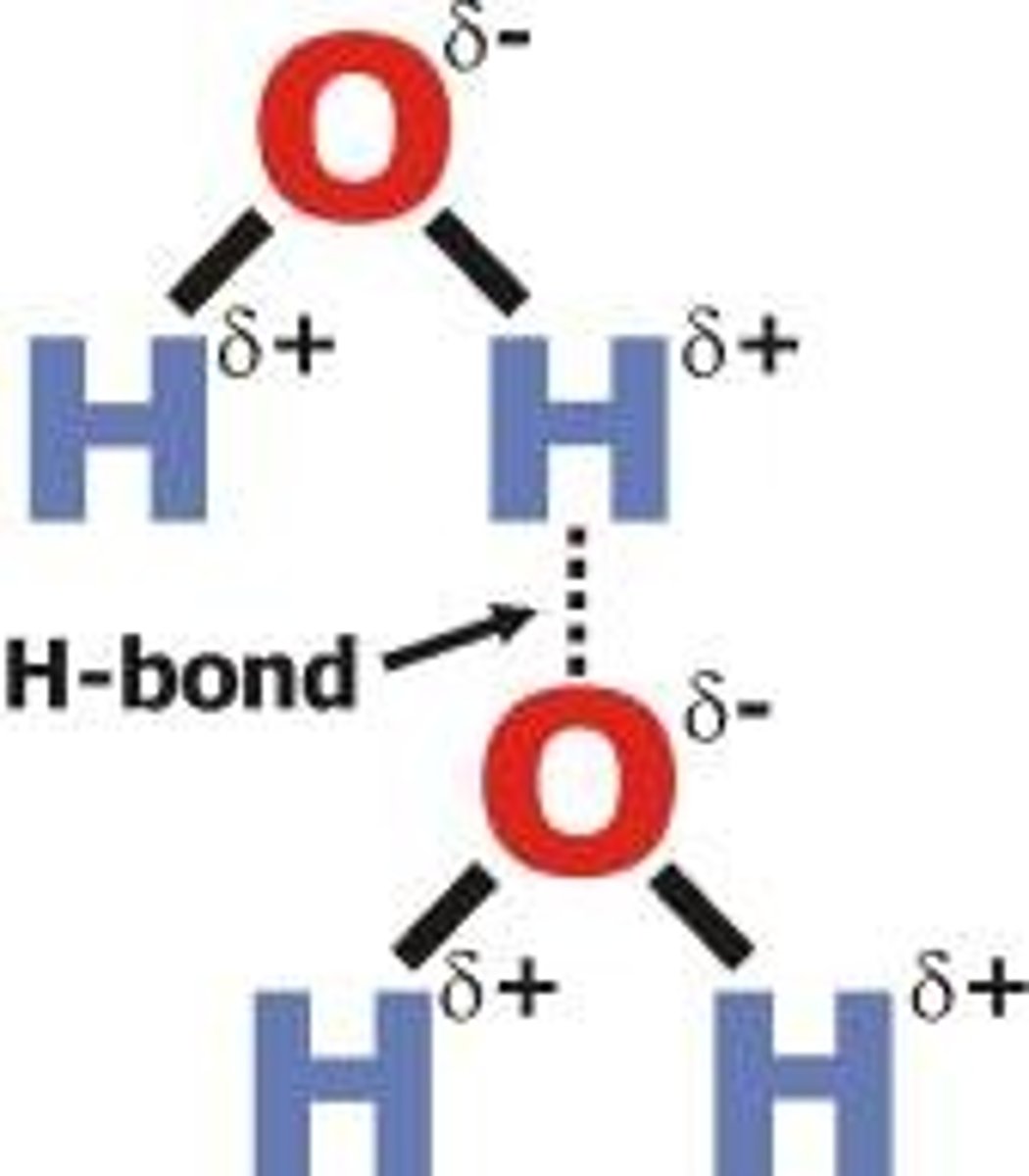
Hydrogen O-H, N-H, F-H
Dipole-Dipole
London Dispersion
Van de Waals Forces is a general term that includes
Dipole-Dipole forces and London Dispersion forces.
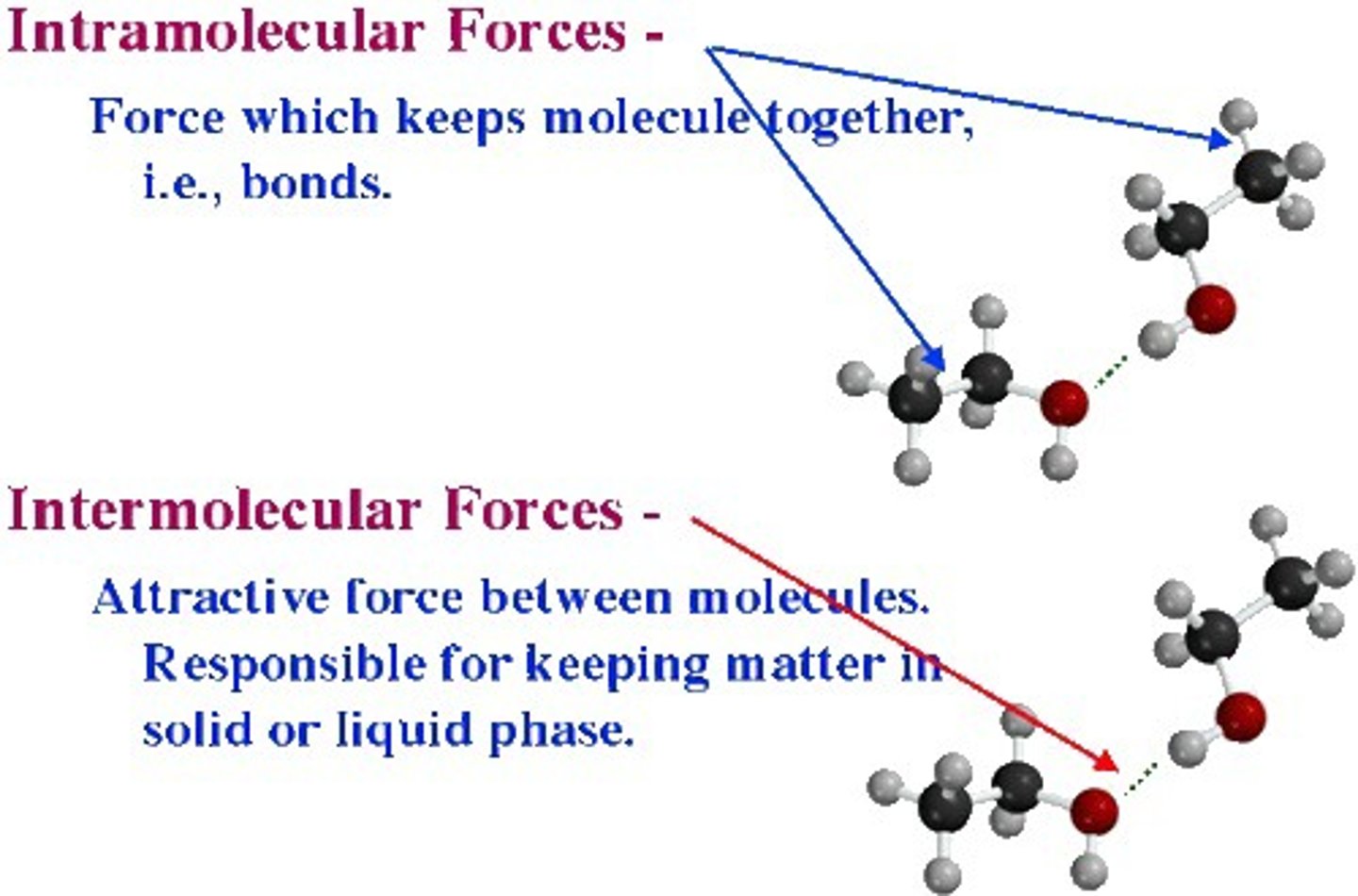
hydrogen bond
Attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom and a slightly negative atom.
Hydrogen O-H, N-H, F-H