BIO 111 Exam 2 Practice
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Crystal Lattice
A crystal lattice is a three-dimensional arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline solid
Liquid Water
H bonds break and reform, and molecules are constantly moving even though they are densely packed.
Solid Water (Ice)
less dense than water
has a crystal lattice structure
Hydrophillic
“water-loving”
polar molecules form H bonds with H2O (bonding onto the O)
ions are attracted to partial charges
ex.) glucose and NaCl
Hydrophobic
“water-hating”
non-polar molecules, often Carbon and Hydrogen
repelled by water
cant form H bonds
ex.) oil
Octane
Acids
Any substance that gives up H+ (protons) during a chemical reaction.
provide hydrogen ions (H+) and lower pH
pH < 7
Bases
Any substance that acquires H+ (protons) during a chemical reaction.
provide hydroxide ions (OH–) and raise pH
pH > 7
Buffers
Help maintain homeostasis
a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components
pH Scale
0 - 14
a change of 1 unit of the pH scale means a 10x change in [H+]
lower pH has a higher amount of H+ than a higher pH
Organic Molecules
A molecule that contains a Carbon and at least 1 Hydrogen.
4 Major Categories of Organic Molecules Important to Life
proteins
nucleic acids
carbohydrates
lipids
Functional Groups
there are 6 function groups
5 groups are hydrophilic, 1 hydrophobic
all behave predictably and consistently
given unique properties to a molecule
often the site of chemical reactions
Amino Group
family: amines
formula: NH2
amino acids = compounds w/ both amino and carboxyl group
acts as a base, tends to attract a proton to form NH3
Carboxyl Group
family: carboxyl acids
formula: COOH
amino acids = compounds w/ both amino and carboxyl group
acts as an acid, tends to lose a proton to form
-COO-
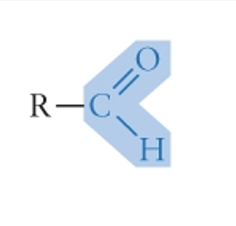
Carbonyl Group
formula in picture
family: aldehydes, ketones
Hydroxyl Group
formula: R-OH
family: alcohols, end in ol
ionized: R-O^-
highly polar; acts as a weak acid, donating a proton
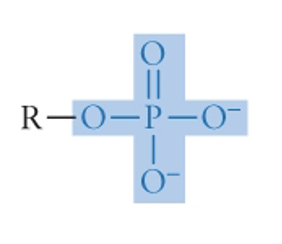
Phosphate Group
family: Organic phosphates
formula in picture
Sulfhydryl Group
formula: R-S-H
family: thiols
S = C in terms of electronegativity, leading to nonpolar covalent bonds; hydrophobic
can for disulfide bonds contributing to protein structure. (S-S)
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy is neither created nor destroyed; it just changes form.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Entropy always increases
cells are working against this
Entropy
measures the amount of energy in a physical system that is not available to do work
polymer
a chain of monomers
monomer
molecule of any of a class of compounds, mostly organic, that can react with other molecules to form very large molecules.
polymerization
Monomers combine chemically to produce a very large chainlike or network molecule, called a polymer.-
defies the second law of thermodynamics
Condensation Reactions/ Dehydration Synthesis
A reaction in which two molecules combine to form a single molecule.
creates a peptide bond between amino acids
Hydrolysis
Water breaks polymers into monomers.
no energy required
Polypeptide chains
a sequence of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
N Terminus to C Terminus
Oligopeptide
A smaller and shorter chain of peptide bonds
4 Levels of Protein Structure
Primary (1°)
Secondary (2°)
Tertiary (3°)
Quaternary (4°)
Primary (1°) Structure
Unique structure of amino acids creates a polypeptide
R groups don’t interact
Secondary (2°) Structure
Due to the number of bonds within one peptide chain, alpha(α) helices and beta(β) pleated sheets form so O and H can interact.
Tertiary (3°) Structure
determined by interactions between R groups on amino acids
Quaternary (4°) Structure
when two or more polypeptide chains form one more macromolecule
macromelcule
a molecule containing a very large number of atoms, such as a protein, nucleic acid, or synthetic polymer.
anthropatic
has both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts.
allows proteins to integrate into the lipid bilayers
prions
proteins that act as infectious, disease-causing agents
due to the misfolding of proteins
sickle-shaped red blood cells
when hemoglobin is folded incorrectly, which can clog blood vessels
(Glu) is usually spot 6 in the polypeptide chain but is changed to (Val) due to mutation in DNA instruction
Glutamate (Glu)
correct placement in the polypeptide chain
has a (-) charge due to its side chain
polar; hydrophilic
Valine (Val)
incorrect placement in the polypeptide chain
has no charge
nonpolar; hydrophobic
Denaturation
the process of ribonuclease proteins being unfolded
caused by heat, pH, [salt], solvents, and chemicals
1° structure still remains 2°,3°, and 4° are lost
Nucleic Acids
first molecules of life and can self-replicate or synthesize using RNA
Function 1: information storage if genetic material
chromosomes and genes are made of DNA
DNA codes the order of amino acids in the primary (1°) structure.
Sickle sell results in….
amino acids sticking together, making a fiber, changing the cell shape and amount of oxygen carried by the blood cells
Nucleotides
monomers of nucleic acids
each monomer has three parts
phosphate functional group
5-carbon pentose
Nitrogenous base
Nitrogenous Bases
DNA:
cytosine (C)
thymine (T)
adenine (A)
guanine (G)
RNA:
uracil (U)
Pyrimidines
single six-membered ring
cytosine (C)
thymine (T)
uracil (U)
nitrogenous Base
Purines
six-membered ring + five-membered ring (double)
adenine (A)
guanine (G)
nitrogenous Base
Nitrogenous Base Pairings
TA, AT
GC, CG
AU, UA
Ribose
found in ribonucleotides
reactive
2’=OH
RNA
Deoxyribose
found in deoxyribonucleotides
stable
2’ = H
DNA
How to build a nucleic acid:
3’ and 5’ of to different nucleotides react releasing a molecule of water through condensation reactions
phosphodiester linkage
holds nucleotides together
creates the sugar-phosphate backbone of RNA
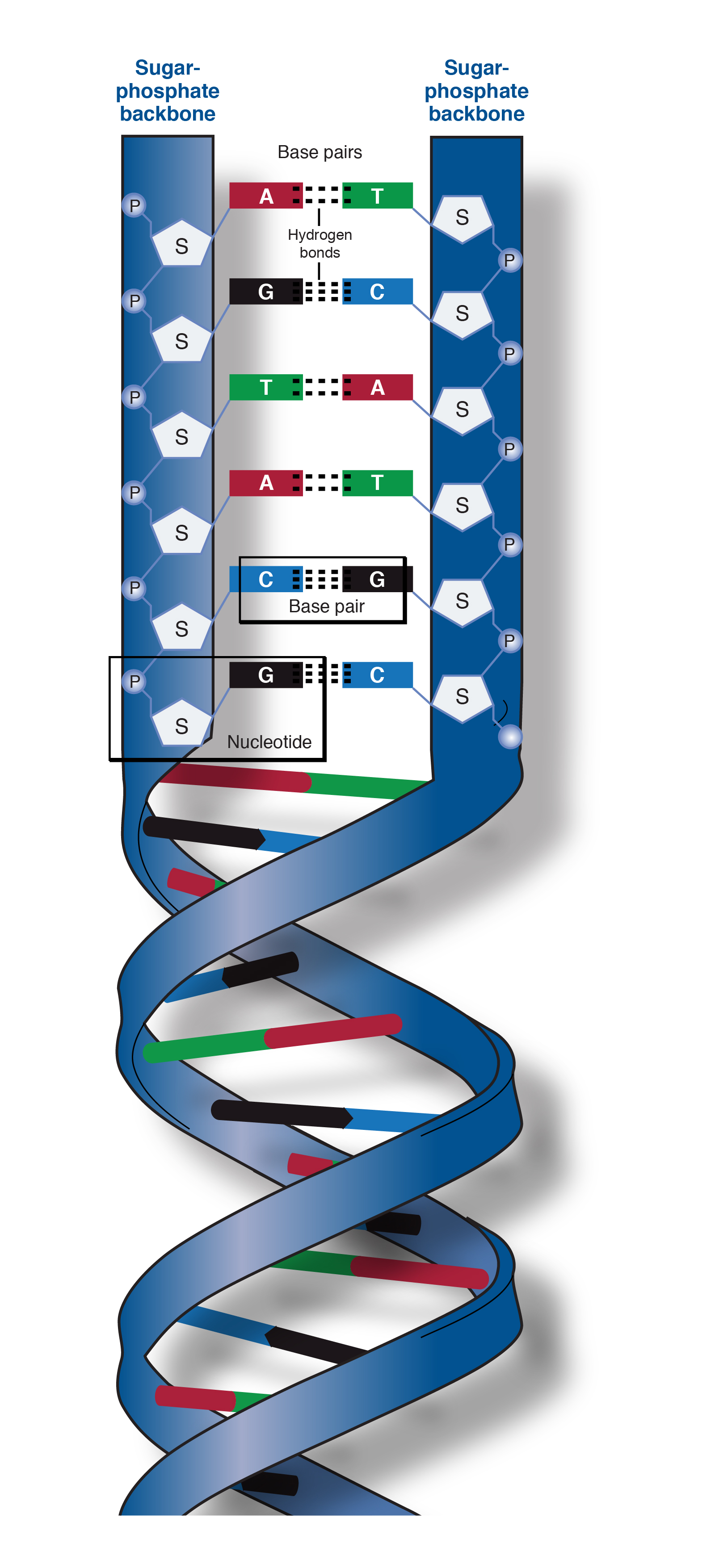
sugar-phosphate backbone
the portion of the DNA double helix that provides structural support to the molecule.
hydrophobic
Standard Orientation of Nucleic Acids
5’C to 3’C
Standard Orientation of Proteins
N - C Terminus
1º Structure of DNA within nucleic acids
contains deoxyribose
contains (T)
Double-stranded
1º Structure of RNA within nucleic acids
contains ribose
contains (U)
The presence of the –OH group on
the 2’ C of ribose makes RNA much
more reactive and less stable than
DNA.
usually Single-stranded
(Erwin) Chargaff’s Rules:
(1) The total number of purines = total # of pyrimidines in DNA
(2) The # of Adenines = # of Thymines, and the # of Guanines = # of Cytosines in DNA
X-ray crystallography
Franklin & Wilkins
a tool used for determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal.
Watson and Crick Model
Complementary base pairing
hydrogen bonds form between nitrogenous bases
purine - pyrimidine
GC = triple H bond
AT = double H bond
strands are antiparallel
Antiparallel
opposite orientations of the two strands of a DNA double helix
DNA Replication
1: Strands separate when H bonds between complementary base pairs are broken
2: base-pairing w/ template (each new strand created on the 5’ to 3’ orientation)
3: polymerization; the original molecule has been copied
Stem-and-Loop Hairpin
single RNA strand folds in on itself by H bonds
forms a loop
Cellulose
(cell wall) = gives cell structure
Starch
stored in plant cells
energy storage
monosaccharides
“one sugar”
monomer
end is ose
oligosaccharides
“few sugars”
small polymers
help cell-cell recognition and signaling
polysaccharides
“many sugars”
large polymers
Storage:
1. starch (plants)
2. glycogen (animals)
Structural
1. cellulose (plants)
2. Chitin (animals & fungi)
3. peptidoglycan (bacteria)
aldose
carbonyl group at the end of a carbon chain
ketose
carbonyl group in the middle of a carbon chain
Glycosidic Linkages
monomers of carbohydrates and monosaccharides join to form polysaccharides
α-glucose
hydroxyl is below the ring on the 1’C
β-glucose
hydroxyl is above the ring on the 1’C
α-glycosidic linkages/ β-glycosidic linkages
Two α-glucose links through the process of a condensation reaction or dehydration synthesis
forms an α-1,4-glycosidic linkage or β-1,4-glycosidic linkages
α- bond is downward
β- bond is upward
Storage polysaccharide linkage
α-1,4-glycosidic linkages
a strong bond but it is easy to hydrolyze when sugars are needed
Structural polysaccharide linkage
β-1,4-glycosidic linkages
The similar structure of these enables their function
Strong bond, but fairly easy to hydrolyze when sugars are needed
Graham Stain in Bacteria Cell Wall structure
purple = Graham positive (+) cell wall is
thick and holds onto dye
penicillin works to fight against these bacteria
pink = Graham negative (-) less peptidoglycan
so most dye washes away
erythromycin works to fight against these bacteria
Organic molecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins contain relatively weak covalent bonds and thus have
high potential energy
Lipids
don’t form polymers
are hydrophobic
make cell membranes possible
have no standard orientation
Types of Lipids
Fats - contain fatty acids
steroids - contain no fatty acids
phospholipids- contain fatty acids
main 3
waxes - contain fatty acids
Fatty Acids
make up most lipids but are not monomers b/c they can’t be built into a chain
can be saturated or unsaturated
Saturated Fatty Acids
All carbons are single-bonded
only one reaction can happen
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Carbons are single-bonded, but at least one is double-bonded
only one reaction can happen
has a (kink)
Fats form via?
ester linkages
glycerol reacts with a fatty acid through a condensation reaction/ dehyd.
3 fatty acids complete the fat, forming triglycerides
Ester linkages
formed between the oxygen molecules of glycerol and the hydroxyl molecules of fatty acids
Unsaturated Fat Heat Exposure
Can become trans fatty acids when exposed to heat, then act like saturated fats.
Steroids
no fatty acids, recognized by by 4 carbon rings
Cholesterol
Hydrophilic OH piece with amphipathic properties
4 ring
Phospholipids
composed of glycerol + phosphate group + 2 fatty acid tails (joined by ester linkages)
has a polar “head” (hydrophilic)
hydrophilic tail
are in constant motion
Fatty Acids Affect on Cell Membranes
saturated fats:
lower permeability and fluidity b/c of how tightly packed it is
unsaturated fats:
high permeability and fluidity b/c the kinks in the tails create more space between the phospholipids.
Enzymes
a special category of proteins that end in ose.
Function:
acts as a catalyst that helps chemical reaction take place
lowers the activation energy of the reaction
increases the rate of the reaction
Substrate
a molecule that an enzyme reacts with
Active Site
Site where substrates bind to the enzyme
Induced Fit
The enzyme closes around the bound substrate to make it tighter.
Competitive Inhibition
Regulatory molecules bind to the enzyme, blocking the true substrates from binding to the enzyme.
Allosteric Attraction
A regulatory molecule binds to the enzyme, changing the shape of the enzyme to make it available for the substrates to bind to the active site.
Allosteric Inhibition
A regulatory molecule binds to the enzyme, making the enzyme change shape and making the active site unavailable to substrates.