Active Transport
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
active trans
cell uss bond energy from ATP to move solutes across mem
active trans mechanisms
primary active and secondary
→ solute “pumps” (proteins) that move ions uphill/against concentration gradient
→ low to high
primary active
energy directly from hydrolysis of ATP
→ selective
→ hydrolysis of ATP= phosphorylation of tarns protein to change configuration so pump bound solute againts concentration gradient (ATP powers the pump → pump changes shape → molecule is moved against its gradient.)
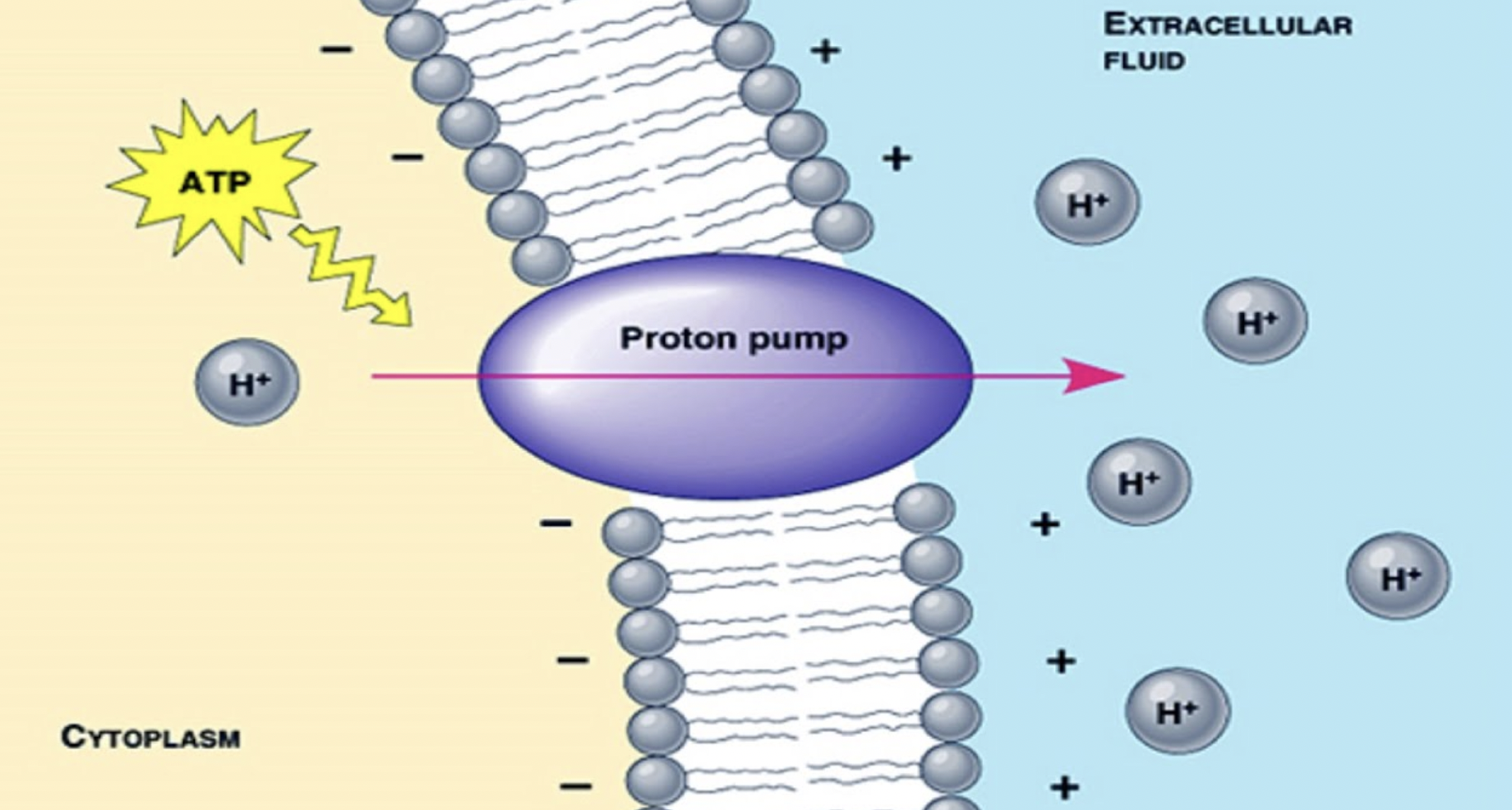
primary active trans
why sodium potassium pump essential
concentration differences essential for cell to maitain fluid volume and for excitable cells
sodium potassium pump
primary active ver important
every ATP pumps 3 Na OUT and 2 K IN
‘high K inside high Na outside
unequal causes electrical charge
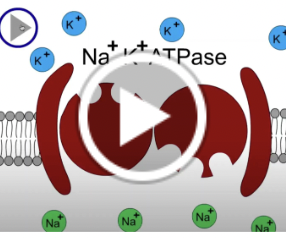
sodium potassium pump
secondary active
cannot happen wt out primary
ATP used in primary to set up ability to do secondary
→ NOT USED DIRECTLY
what energy in secondary
energy stored in form of an ion concentration (usually Na) to drive other substances against gradient
AKA co trans bc 2 substances cross mem at the same time
1. symporters
2. antiporters
antiport
Na in, down gradient
Ca out, against gradient
opposite directions
symport
glucose in, along gradient
Na in, against gradient
same direction
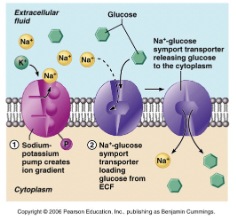
secondary active
mem pump of trans protein allows cell to be
selective abt what allows cross mem
vesicular trans
large particles macromolecules fluids
energized by ATP
endocytosis, exocytosis
vesicle
small membranous sac formed by budding off from existing mem
exocytosis
mem enclosed structures called secretory vesicles that form inside the cell fuse wt the plasma me and release their contents into the ECF
hormone secretion, neurotransmitter release, mucous secretion, ejection of wastes
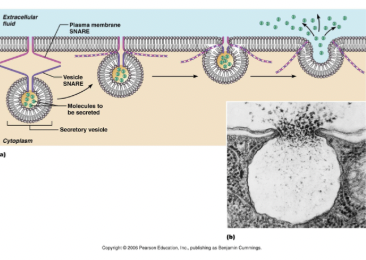
exocytosis
endocytosis
cell eating
Phagocytosis
pinocytosis
receptor-mediated endocytosis
surface area of plasma mem remains constant bc plasma mem removed by endocytosis is replaced by that gained during exocytosis
phagocytosis
reaching out adn grabbind smt solid
reaching= dathern protein
solid= bacterium or particle
pinch
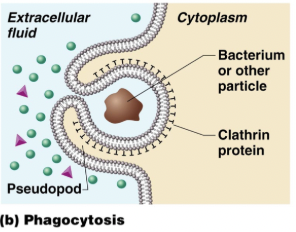
phagocytosis
pinocytosis
forms a pit
liquids
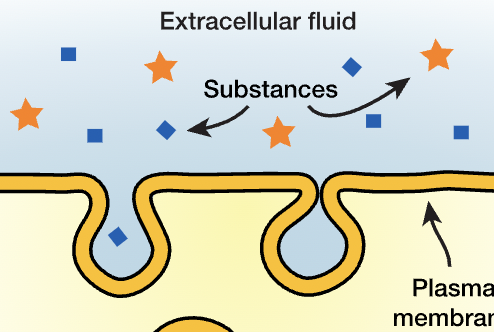
pincytosis
receptor mediated
grabs substances
“Y”
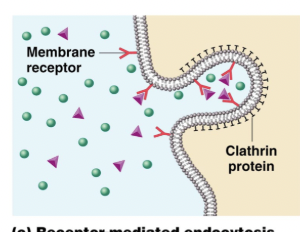
receptor mediated