Descriptive Statistics
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
null hypothesis
-assertion that there is no relationship between exposure and disease
alternative hypothesis
-assertion that there is some relation between exposure and disease
significance testing
-play of chance- must always be considered alternative explanation
-tells likelihood of finding results because of play of chance
p value
-all tests of statistical significance lead to probability or p value
-usually set at 0.05
-if probability = or < 0.05, then you can safely reject the null hypothesis
-if p value > 0.05, chance cannot be excluded as likely explanation and the null is not rejected, state findings not statistically significant
alpha, type I error
-false positive
beta, type II error
-false negative
-most common error in dental literature
-1- beta (power) = probability of correctly concluding that groups differ
statistical power
-power = 1-beta
-higher the power, better the chances of finding the tx benefit if there is one
-increase number of subjects, increase power
-influenced by: determining factors (size of tx, alpha error (0.05), beta error (0.2)), interrelationship of alpha/beta error, impact of sample size (overpowered for large sample size, underpowered for small sample size), meta-analysis (increase statistical power)
incidence
-number of new cases of specific disease occurring in a defined population during a specified time period
-gives clues to the research into etiology and pathogenesis of disease
-helps with study of distribution of disease and taking action to control disease
-useful in evaluating the efficacy of preventative and therapeutic measures
prevalence
-how common is some factor at a given time
-typically measured in cross-sectional sample
-useful in estimating the magnitude of disease or health problems in a community
-identify potential high-risk populations
-useful in administration and planning purposes
-prevalence = incidence * mean duration
positive skew, negative skew, normal curve
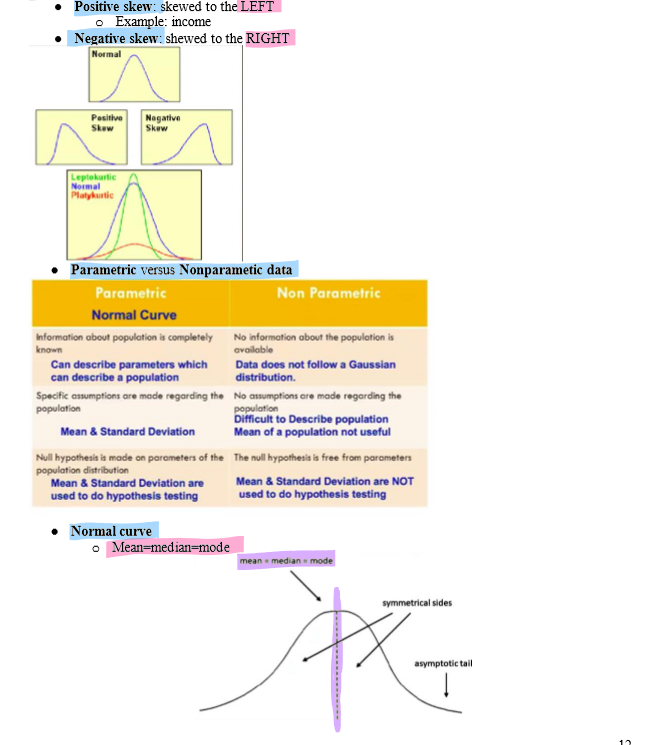
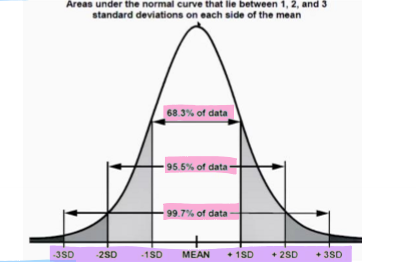
standard deviation
-measure of variability of sample
standard error
-variability in the mean within the whole population
-SE = SD/square root of N
-tighter range than SD
dependent v independent variable
-dependent- outcome variable
-independent- factor manipulated in experiment, cause
types of variables
-categorical/nominal: non-ranked, dichotomous (binary)
-ordinal: have directionality
-numerical/continuous: have directionality, values have numeric sense