8.2 Alkenes in Nature and in Industry
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is another common name for alkenes?
Olefins
Why are alkenes called “olefins”
Because early chemists observed that they form oily compounds when reacting with halogens
Where are alkenes found in nature?
They are abundant in plants, pheromones, and natural products such as terpenes and fatty acids
What makes alkenes distinct in structure compared to alkanes?
They contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond (C=C)
What are acyclic alkenes?
Alkenes that do not contain any rings (open-chain structures)
What are cyclic alkenes?
Alkenes that contain a ring structure with one or more C=C bonds within it
Define bicyclic alkene
A compound containing two fused or bridged rings that include at least one double bond
Define polycyclic alkene
A compound containing three or more interconnected rings with one or more double bonds
What is the simplest alkene?
Ethane (ethylene), CH₂=CH₂
Why are alkenes considered important in organic synthesis?
They serve as versatile precursors for producing alcohols, halides, polymers, and other functionalized molecules
What determines whether an alkene is cyclic or acyclic?
The presence or absence of a ring structures in the carbon framework
If an alkene contains no rings and one double bond, how would it be described?
As a simple acyclic monoalkene
What happens to bond angles around carbons in an alkene?
They are approximately 120°, consistent with sp² hybridization
What does the prefix “poly-” in “polycyclic” indicate?
The molecule contains multiple ring systems
If asked, “What structural feature defines all alkenes?”
All akenes contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond (C=C)
Describe these pictures
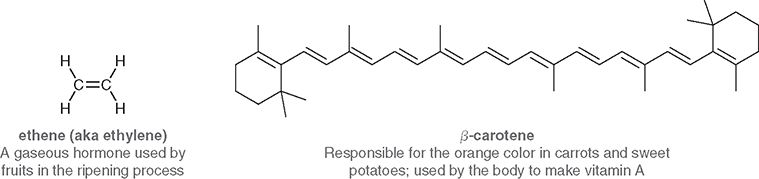
Describe these pictures
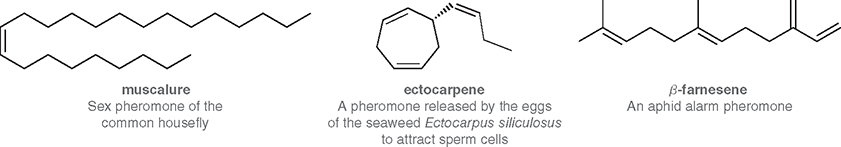
Where are double bonds often found in biological molecules?
In the structures of pheromones and many natural products
What are pheromones?
Chemical signals released by living organisms to trigger specific behavioral or physiological responses in members of the same species
What is the purpose of alarm pheromones?
To warn other members of the species of danger or threat
What is the purpose of sex pheromones?
To attract members of the opposite sex for mating
Why do pheromones often contain C=C double bonds?
The double bonds influence the molecule’s shape, volatility, and reactivity—key factors for receptor recognition and signal strength.
How does the alkene functional group affect pheromone volatility?
It increases volatility, allowing the compound to evaporate easily and travel through air to reach other organisms