Midterm ANSC 4410
1/419
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
420 Terms
VCPR
Veterinary Client Patient Relationship; a formal relationship between a veterinarian and a client that establishes the veterinarian's responsibility for the patient's care.
What does VCPR stand for
V: veterinary
C: client
P: patient
R: relationship
What are the 5 VCPR requirements (defined by AVMA)
vet has assumed responsibility for making clinical judgements regarding the health of the patient and client has agreed to follow the vet’s instructions
vet has sufficient knowledge of the patient to initiate at least a general or preliminary diagnosis of the medical condition of the patient. This means that the vet is personally acquainted w/ keeping and care of the patient by virtue of a timely examination of the patient by the vet or medically appropriate and timely visits by vet to the operation where the patient is managed
vet is readily available for follow up evaluation or has arranged for the following: veterinary emergency coverage, and continuing care and treatment
veterinarian proves oversight of treatment, compliance, and outcome
patient records are maintained
What should a client portfolio contain?
Client name
Address
Phone number
Email address
Payment information
T/F: anyone can make medical decisions if they had some sort of relationship with the client
false
only the client listed on the records or listed on the charts can make medical decisions
Patient chart should include what 6 things
patient name
breed
sex
color
age
weight
Why is the description of the patient important
the context matters towards the diagnosis
T/F: Rounds always start with signalment to start the information with the team
true
What might client communication tell us
CC
ex: vomiting, vaccines, etc
Appointment
Estimate
History
travel history, vaccination history, etc
Vaccination status
which ones, doses, reactions, who administered
What does the client complaint (CC) tell us
tells us why they are here
T/F: Yes or no questions are sufficient to finding out more information
false
opt for open ended questions to gather more info
What is the appropriate order of triage
emergencies
appointments
walk-ins
AVMA
American Veterinary Medical Association; the organization that defines the requirements for VCPR.
Signalment
A summary of key patient information including name, breed, sex, color, age, and weight.
Triage
assignment of degrees of urgency to wounds or illnesses to decide the order of treatment of a large number of patients or casualties
Client Communication
The exchange of information between the veterinary staff and the client regarding the patient's health and care.
Why is the physical exam important
crucial for making medical decisions and evaluating
Documentation
The process of recording all aspects of patient care, which is crucial for legal and quality assurance purposes.
SOAP
An acronym for Subjective, Objective, Assessment, Plan; a method for organizing medical records and patient evaluations.
Differential Diagnosis (DDx)
A list of potential diagnoses that could explain the patient's clinical signs.
T/F: clients know everything you are saying in medical terms
false
they have no to little medical education so you need to modify terms or explanations to match their needs
Estimates matter because
clients need to know if they can afford the services
do not judge and give the same standard of care
give them everything you deem necessary (itemized list) w/ explanation
this give them option to opt out of some services and write their reasonings/what was not given for your own records
T/F: you can do surgery without written consent if they verbally tell you
False
ALWAYS requires written consent
phone consent requires 2 people to hear and write down that they heard it
Client care includes
communication
explain things in laymen’s terms
education
client handout
questions
payment for services rendered
T/F: Documentation is important and you should write everything down
true
Why is a medical record important
A medical record is a legal document
failure to document often leads to internal control problems, liability/forensic concerns, embarrassment of the practice or client , or a reduced value per pet seen
medical record keeping is everyone’s concern in the practice
in quality vet healthcare delivery is there’s always time to document everything
record everything that’s done, as it is done
charge for everything that’s done
Client Education
The process of informing and teaching clients about their pet's health, treatment options, and care requirements.
What does SOAP stand for
S: subjective
O: objective
A: Assessment
P: Plan
Subjective (SOAP)
Chief Complaint (CC): presenting problem
History (Hx): owner’s story
initial impression/observations
Clinical signs (CS) noted
Vomiting/ Diarrhea (V/D)
Coughing/ Sneezing
Patient’s attitude
Appetite
Past medical history
Objective (SOAP)
vital signs
findings of the physical exam
lab data and results
imaging (X-Ray) results
recognition, review and recording of other doctors’ results
any other diagnostic data
Assessment (SOAP)
consolidation of Subjective and Objective data
problems list
differential diagnosis (DDx) list
Diagnosis (Dx)
Prognosis (Px)
Plan (SOAP)
course of action RECOMMENDED to address the CC
Diagnostics
Treatments (Tx)
Procedures- include risks
advise
instructions
follow-up recommendations
Tips for Better Communication
Communicate Happiness
happiness @ work is most accurate predictor of life expectancy
take steps to make work more enjoyable
happiness (and unhappiness) is obvious to clients
smiling releases neurotransmitters that elevate mood
make conscious effort to think and act in a positive manner
if you show your clients that you enjoy your work, their pet, and them, they will reward you with affection and loyalty
Tips for Better Communication
Look and act professional
professional dress and behavior demands respect
dress and speak in an appropriate manner
clients will judge you on your appearance
your clients will only perceive your medicine as up-to-date if your dress, hairstyle, and hospital decor as well
impression are important
Tips for Better Communication
Listen to client, ask the right questions
client concerns are always valid
if they’re refusing care, ask them why
it takes time, effort, training, and rehearsals to get your staff to be “patient advocates”
questionnaires help streamline communication
helps determine what products and services that patient might need
leading questions
prompt owner to mention things they may not think are significant
Tips for Better Communication
Be honest and don’t surprise them
surveys show clients want to know the truth
less likely to sue if you tell the truth
accurate prognosis
accurate diagnosis
all options for care are explained to client
update clients when charges increase
as long as you acknowledge their comments or concerns, and even praise them for taking such good care of their pet, you’ll find that most of your clients keep coming back
Tips for Better Communication
Enthusiasm is contagious
show them how interesting and exciting medicine and physiology can be, and your enthusiasm for latest and greatest treatments
explain how complicated the body is and how sophisticated modern vet med can be
make learning about their care fun
give hospital tours
explain services available
Tips for Better Communication
remember diff people learn best in diff ways
be flexible in teaching habits
use Laymen’s terms
written material
verbal comms
models or diagrams
read body language
if you don’t see the little light bulb going off over their head when you’re trying to explain something, try a diff approach
ask them what they want your role to be
info presenter, advisor, decision maker
Tips for Better Communication
Repetition is key
avg person needs to hear something at least 5x to remember it
even motivated people remember less than 25% of what they hear
written material is crucial
quality, professional, easy to read
best clients are your most educated ones
takes 5 reps to make a sale
Tips for Better Communication
treat clients as they are what they should be
Don’t make pre-conceived judgements
most people will rise to level of our expectations
talk to them like intelligent adults who make intelligent decisions
give your clients info to make good treatment decisions for their pets
let them make a decision
clear up any concerns or misinterpretations
address $ concerns
be clear, be concerned, and be persistent
Tips for Better Communication
Entire staff should be good communicators
cannot handle all clients’ educational needs by yourself
invest in training for entire staff
receptionists, technicians, and assistants
income of practice is more dependent on skill lvl of staff than hours of operation
clients should hear consistent recommendations from ALL employees
Tips for Better Communication
only way you can help your patients lead long and healthy lives is to educate their owners
clients don’t have a degree in medicine or behavior
take time and make effort to teach them what they need to know
clients are decision makers
vet staff are recommenders
problems belong to client
vet staff are problem solvers
Medical Record
A legal document that contains all relevant information about a patient's medical history and treatment.
Enthusiasm
A positive attitude that can influence client perceptions and engagement in their pet's care.
Repetition
A key strategy in communication, emphasizing that clients may need to hear information multiple times to retain it.
Professionalism
The conduct, aims, or qualities that characterize a profession, including appropriate dress and behavior in veterinary practice.
Client Portfolio
A collection of information about a client, including contact details and payment information, used for managing client relationships.
Client Handout
Written materials provided to clients to help them understand their pet's health and care instructions.
Veterinary Staff
The team of professionals, including veterinarians, technicians, and receptionists, who work together to provide care for patients.
Follow-up Recommendations
Suggestions made by the veterinarian for ongoing care and monitoring of the patient's health after the initial visit.
Body Language
Non-verbal cues that can indicate a client's understanding or confusion during communication.
Sus scrofa
genus and species of domestic swine
Pig (piglet)
young porcine
hog
older porcine
Gilt
female porcine before farrowing
sow
female porcine after farrowing
farrowing
giving birth
parity
each birthing event
boar
male porcine
barrow
male porcine that has been castrated
stag
male porcine castrated late in life, after developing secondary sex characteristics
shoat
domestic porcine of either sex, usually bt 60-160#
feeder pig
domestic pig, either sex; refers to end prod of farrow-to-feeder pig operation 30-100+#
roaster pig
domestic pig 100-190# sold for slaughter
aka market pig
Characteristics of a pig
gregarious
strict social structure
playful, curious, highly intelligent
trained easily w/ positive reinforcement (i.e marshmallows)
when frightened or confused: get excited, struggle and vocalize veraciously
v similar anatomic/physiologic structures to humans
popular biomed science animal model
preferred animal for supplemental organs and tissues
Safety around pig
sow w/ litter
strong maternal protective instinct
may attack- use caution when processing piglets
boars
well developed canines/tusks
slashing motion when attacking (should be trimmed every 6M)
knees
be aware of those running towards you
hearing
high decibel screams
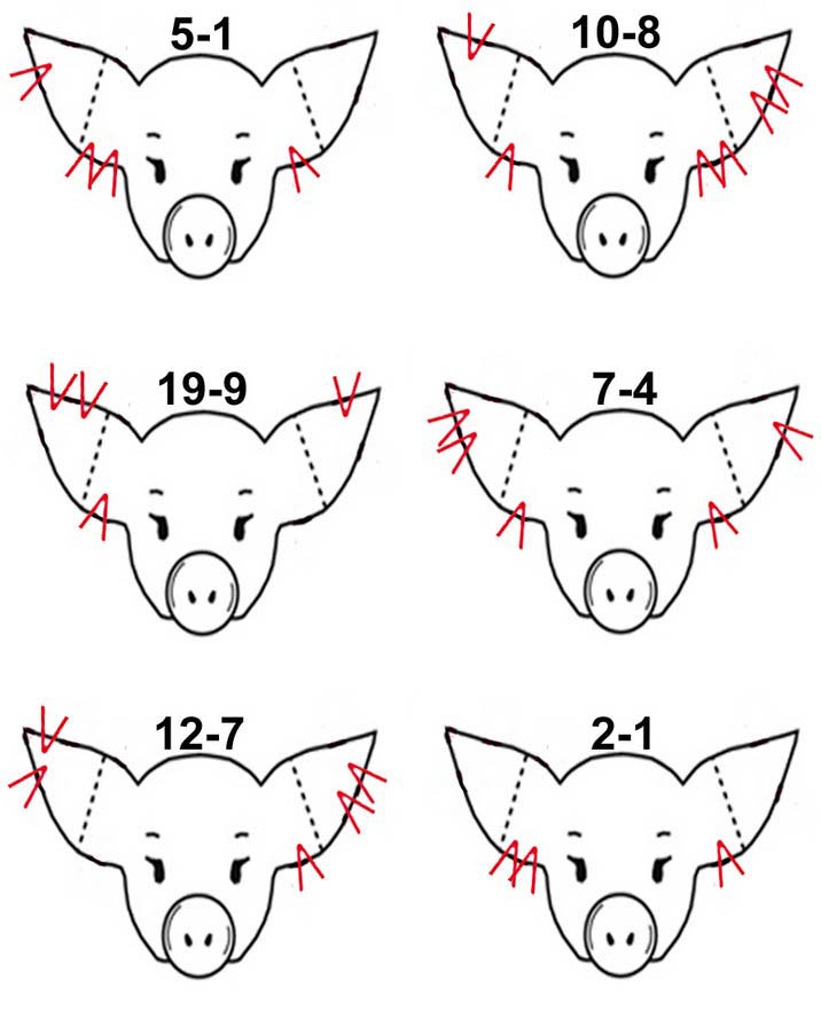
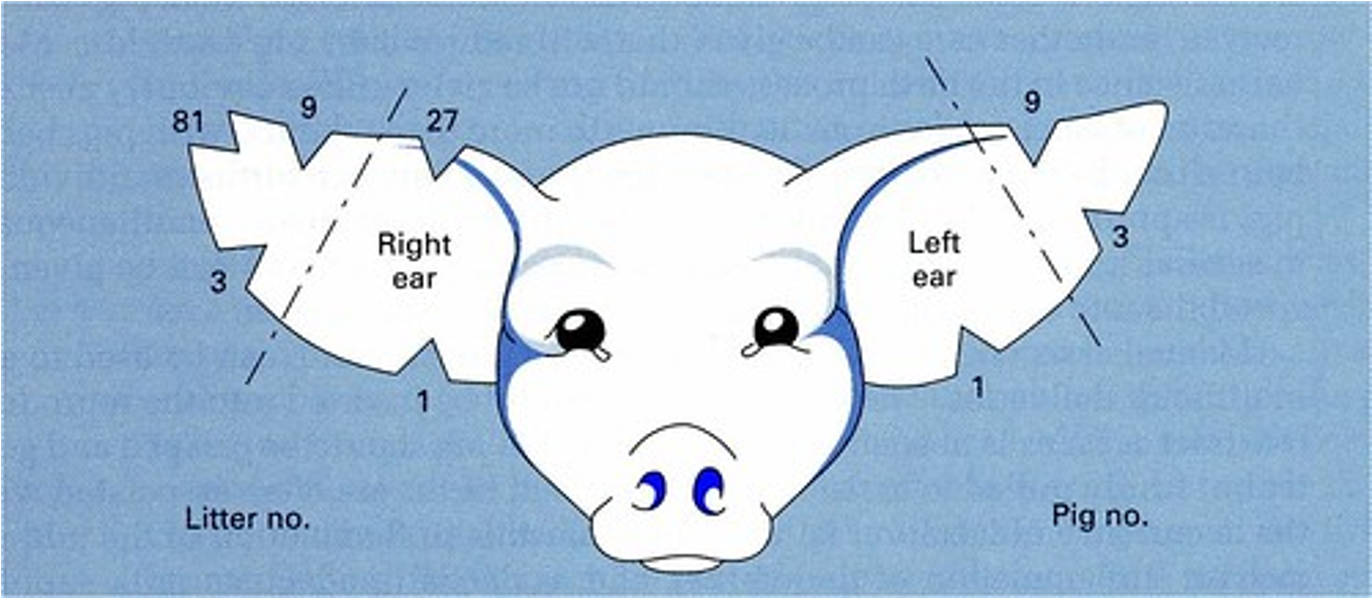
Identification of a pig (Ear Notches)
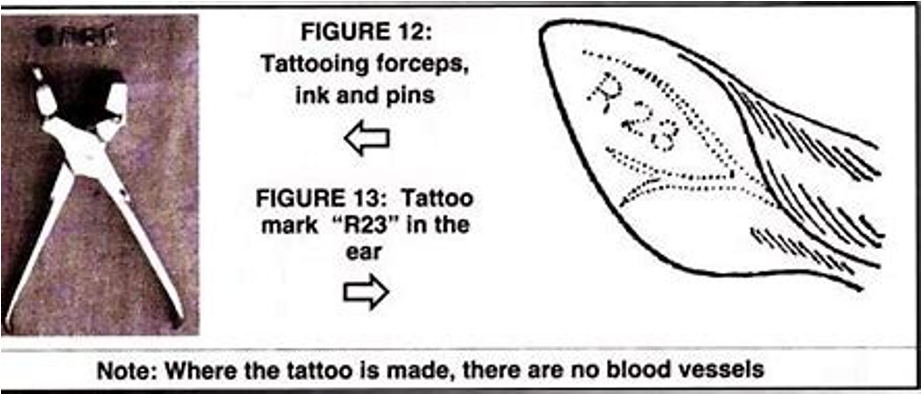
Pig ID through ear tags
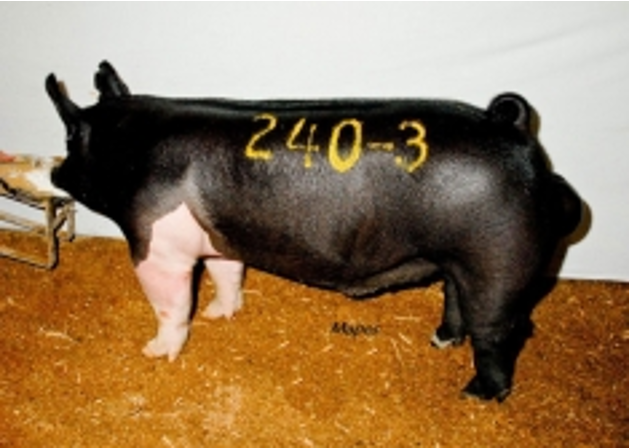
Pig ID through temp ID

Handling/Restraint
small pen
hurdles/parturition
let their natural curiosity take them
never abuse/punish
Hand Restraint
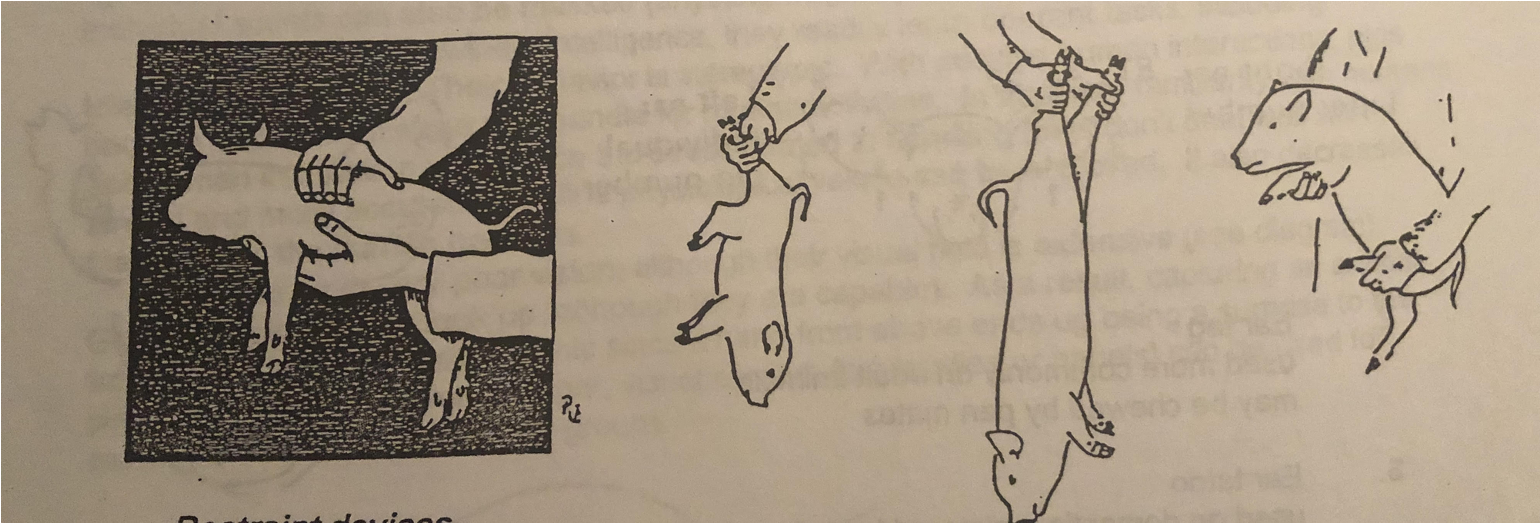
Restraint Devices

Chemical Restraint
Telazol
Ketamine
Anased

Risks of anesthesia (w/ Tx)
malignant hyperthermia
uncontrolled pyrexia (condition where body temperature is higher than normal)
muscle rigidity
acid-base changes
Tx
terminated ax administration
IV procaine or dantrolene
ccs
hyperventilate
sodium bicarb
aggressive body cooling
IM injection sites
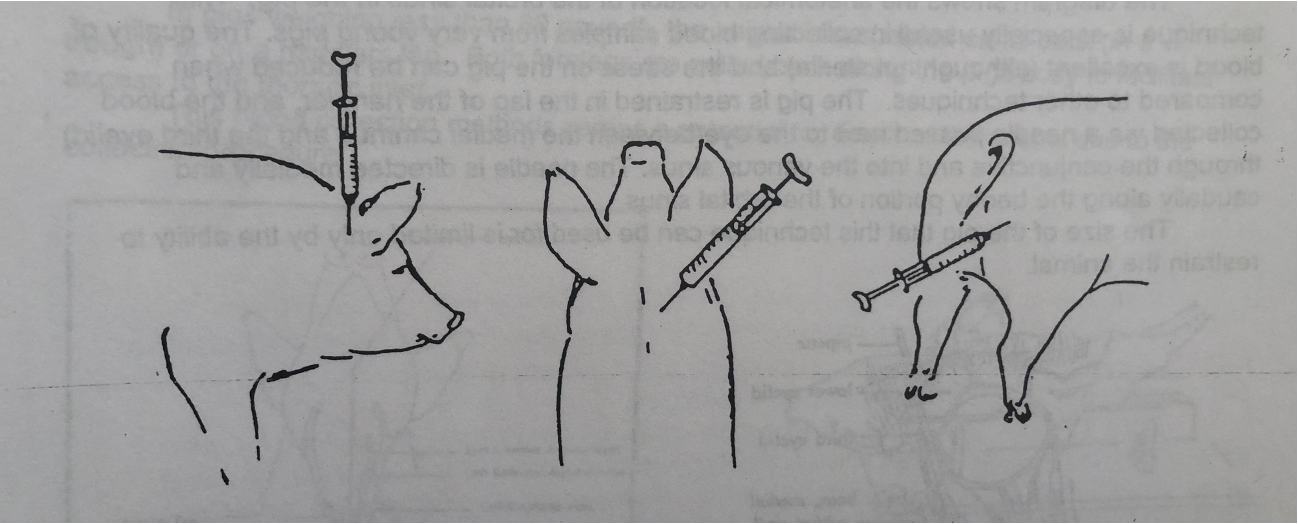

IV Injection sites

IV (<80#) injection sites
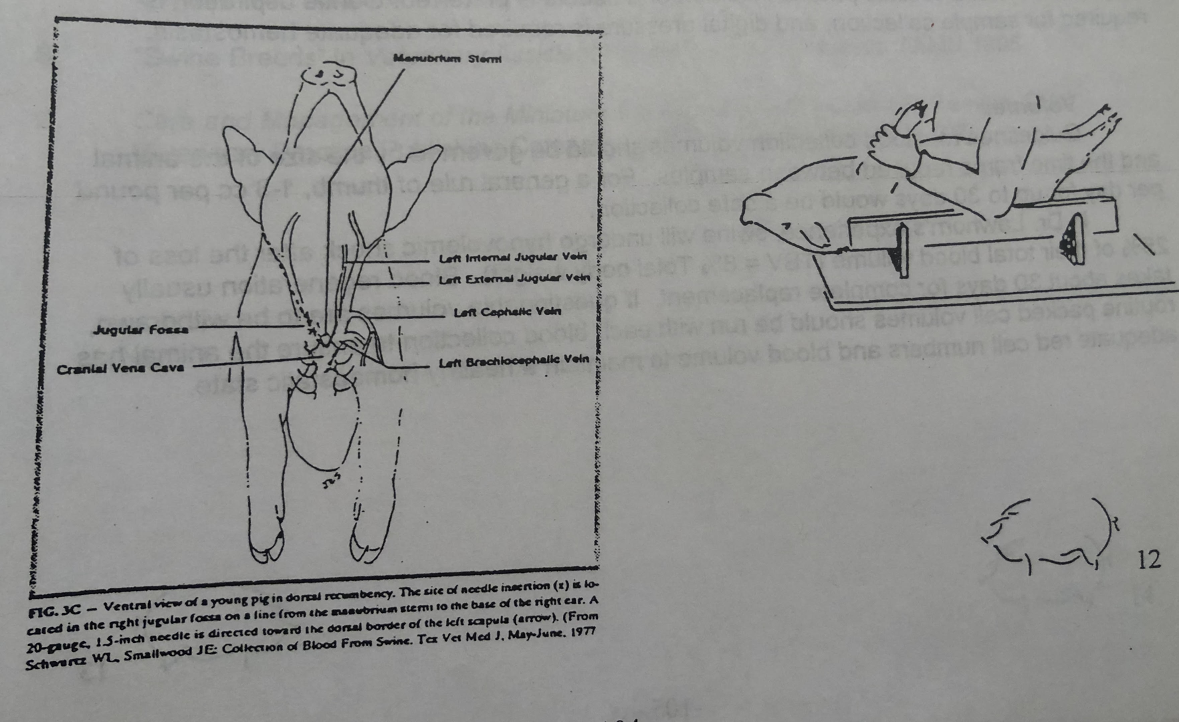
IV subcutaneous injection sites
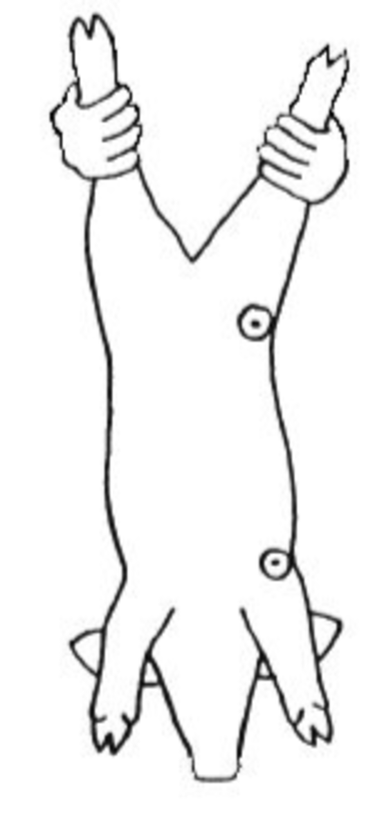
Processing a pig
ear notches
tail docking
clipping needle teeth
injections
castration
vaccines
Tail docking prevents what
tail biting behaviors
Needle Teeth (Pros and Cons)
Pros
helps prevent injury to sows udders
helps prevent face and body injury of other piglets that occur when piglets fight or attempt to establish a “peck” order
Cons
clipping teeth too short and causing damage and/or infection to the gums
time and labor required to carry out procedure
Processing (injections)
Fe Dextran
IM injections to prevent anemia from indoor raised piglets
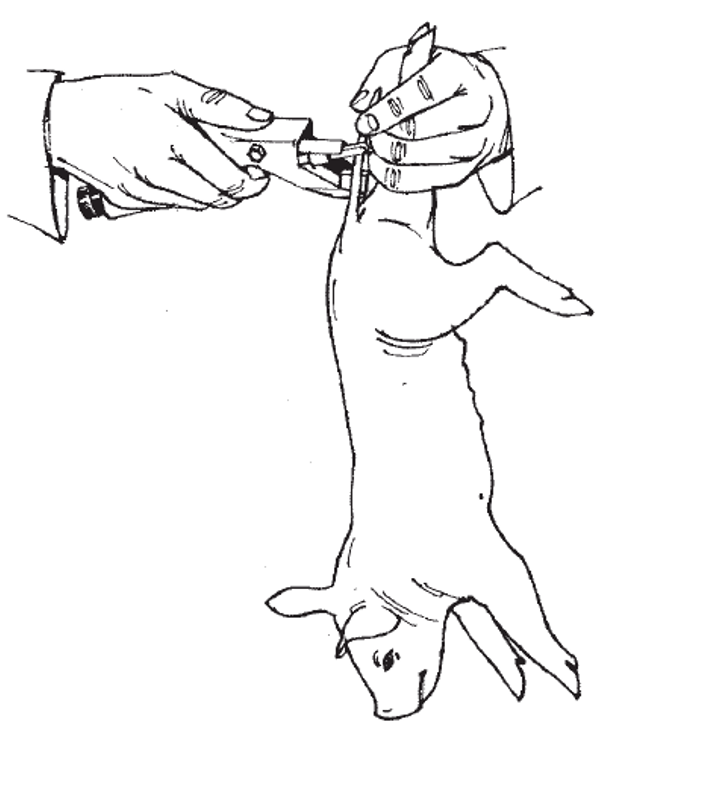
Castration (processing)
hold piglet by both hind legs w/ its head down
using thumb, push up on both testicles
make an incision through skin of scrotum over each testicle in direction of tail
be sure incisions are made low on scrotal sac to allow for fluid drainage
doesn’t matter if you cut through white membrane on each testicle or not
pop testicles through each incision and pull on them slightly
pull each testicle out while pressing your thumb against piglet’s pelvis
thumb pressure on pelvis is important to ensure that testicular cords break off at point of your thumb rather than deep inside body, which may promote development of a hernia
if necessary, testicle may be cut free of cord using scraping motion
cut away any cord or connective tissue protruding from incision and spray wound w/ antiseptic
Vaccine protocol
circovirus
diarrhea
mycoplasma
joint infection
rhinitis
atrophy of snout
influenza
What info should the receptionist get from a new client
name
address
phone number
email address
payment preference
Apppointment
receptionist
schedules either work-up or brief appointment
day
time
doctor
chief complaint: recent wt loss (for freddy)
requests estimate prior to exam but willing to perform diagnostics
Signalment (for Freddy Flores)
8 yo
male intact
pitbull
blue brindle
What was the chief complaint for Freddy Flores
recent wt loss
History of Freddy Flores
taken by tech
O owned p since a puppy
no vaccine history
never neutered (cost)
not on F/T prevention but haven’t seen any ticks
not on HW prevention
eats Blue Diamond kibble and ppl food
recently eating less
no V/D, no coughing, no sneezing, no itching
water intake/ urination wnl
Physical Exam (Freddy Flores)
BAR
T: 103
P (pulse): 160
R (respiration): pant
haircoat: dull, lusterless
BCS: 3/9
Wt: 42.4# → 19kg
Dry crustular nasum
OU: sunken orbits, protruding third eyelids, injected sclera
oral: missing few teeth, numerous worn teeth
MM: pale, tacky
LN (lymph nodes): NSF
M/S: thin, no observable lameness, stiff on ambulation
Neuro: CN wnl, proprioception wnl, withdrawals intact
CV (cardiovascular): heart beats strong and regular, clear lung sounds in all fields
Abd Palp: firm round soft tissue mass in the caudal ventral abdomen
GI: NSF
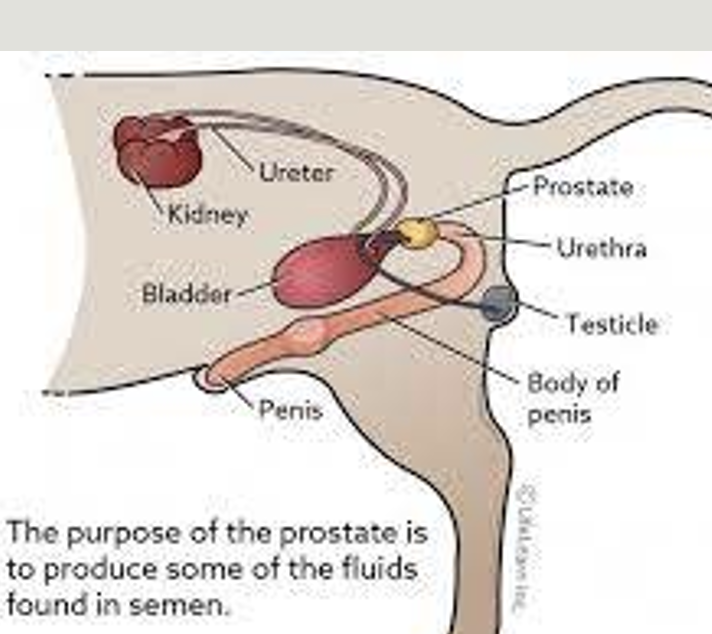
Repro/Renal: unilateral cryptorchid, R retained testicle
Rectal exam (Freddy Flores)
prostatic enlargement
Diagnostic plan for Freddy Flores
CBC/CHEM/USUA
urine culture
HWTAE
Fecal floatation
abdominal radiographs
abdominal ultrasound
CT scan
Estimate for Freddy Flores
OV (40$): Vet exam
CBC/CHEM/USUA (200$)
U/S guided cystocentesis (25$)
fecal floatation (25$)
HWTAE (45$)
abdominal radiographs (55$ initial; 50$ per rad)
Ultrasound (120$ in house; 400$ referred)
CT scan (800$ + anesthesia)
Owner declines
add rads
referred U/S
CT scan
Sample collection
Venapuncture
EDTA purple top
Serum red top
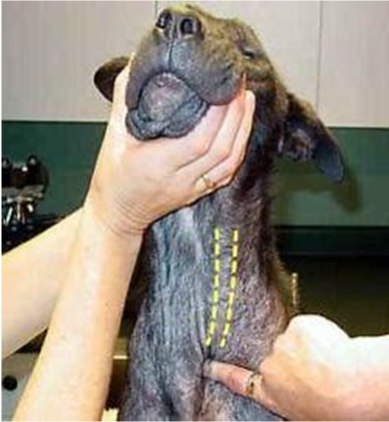
Ultrasound Guided Cystocentesis
white top
Fecal loop
fecal float tube

ALB (CHEM panel)
albumin
major protein found in body
carries various substances through blood and important in maintain pressure within vessels
high lvls = dehydration
low lvls = chronic inflammation, liver disease, kidney disease, starvation and blood loss
ALP (CHEM panel)
alkaline phosphatase
ALKP
important in metabolism and found in liver cells
high lvls = bile duct obstruction, cushing’s, liver disease, certain cancers and may be due to certain drugs such as steroids or phenobarbital
low lvls = starvation/malnutrition or end stage liver disease
ALT (CHEM panel)
alanine aminotransferase
important in metabolism of nitrogen and most often assoc w/ liver
high lvls = liver damage, toxin ingestion, Cushing’s disease, and various metabolic disorders
low lvls = starvation/malnutrition or end stage liver disease
AMYL (CHEM panel)
Amylase
secreted by pancreas
important in normal digestion of starch
high lvls = pancreatic inflammation or cancer, kidney disease, prostatic inflammation, diabetic, ketoacidosis, and liver cancer
low lvls = malnutrition or starvation