All Unit 1 Knowt
1/189
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP Euro Topic 1 Terms AMSCO
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
190 Terms
Capital
money or property that is used for investment to make more money
Capitalism
an economic and political system in which a country's trade and industry are controlled by private owners for profit.
means of production
the factories, machines, tools, raw materials, land, and financial capital needed to make things
means
a way to get something accomplished
market economy
Economic decisions are made by individuals or the open market, rather than the government
Entrepreneur
A person who organizes, manages, and takes on the risks of a business.
Medici
A powerful Italian family of bankers and merchants whose members effectively ruled Florence for much of the 15th century
Fuggers
leading banking family of Germany during the 15th and 16th century
money economy
an economic system based on money rather than barter
barter economy
economic system in which one set of goods or services is exchanged for another
double-entry bookkeeping
Bookkeepers record all transactions in two places so they can check one list of transactions against the other for accuracy.
joint-stock company
A company made up of a group of shareholders. Each shareholder contributes some money to the company, sharing the risk with others and receiving some share of the company's profits in exchange
stock
A share of ownership in a company
Dividends
payments of cash from a corporation to its stockholders
Dutch East India Company
a trading company established by the Netherlands in 1602 to protect and expand its trade in Asia
British East India Company
A joint stock company that controlled most of India during the period of imperialism. This company controlled the political, social, and economic life in India for more than 200 years.
Genoa
A seaport town in Italy
Amsterdam
Major trading port and financial center in the Netherlands
London
Capital of England and the center of Banking and Stock Exchange in England
commerce
the buying and selling of goods and services; trade
hierarchy
a system or organization in which people or groups are ranked one above the other according to status or authority.
Manor
A large estate, often including farms and a village, ruled by a lord.
landlord
owner of rental property
Peasants
people who worked the land or served the nobles
Serfdom
Institution in which a peasant is attached to a feudal estate and is not free to leave
subsistence agriculture
Agriculture designed primarily to provide food for direct consumption by the farmer and the farmer's family, rather than to sell in a market for profit
Little Ice Age
A century-long period of cool climate that began in the 1590s. Its bad effects on agriculture in northern Europe were notable.
Great Plague
Recurrence of the Black Death in England 1665-1666
open-field system
division of large fields into long, narrow strips that are each then farmed by individual peasants.
the commons
land or resources belonging to the whole of a community. Such as a grazing field for animals.
crop rotation
The planting of different crops in a field each year to maintain the soil's fertility.
two-field system
planting crops on only half of the cultivated land, leaving the other half to lie fallow (unplanted) for a year to recover its fertility
three-field system
A rotational system for agriculture in which one field grows grain, one grows legumes, and one lies fallow.
fallow
a plowed field that is not planted in order to let the soil "rest".
Inflation
A continuous rise in the price of goods and services
Price Revolution
increase in prices in 16th century-inflation-increased demand for goods-in part because of an influx of gold and silver from the Americas
Commercial Agriculture
Agriculture undertaken primarily to generate products for sale off the farm for a profit.
Enclosure Movement
practice of fencing or enclosing common lands into individual holdings, which happened in the 18th c in England.
agricultural commodities
staple crops and animals produced or raised on farms or plantations to be sold in the market for a profit
Migrants
people who leave their homes to work for a time in other regions or countries
Portugal
First European Country to engage in African Slave Trade
Planter Society
Stretching from the Chesapeake Bay (mid-Atlantic) to Brazil and in other parts of the world that produced crops, especially sugar, cotton and tobacco using slave labor on large estates.
Demographics
the characteristics of a population with respect to age, race, and gender.
Demographic Catastrophe
a high mortality rate in a particular portion of the population (such as Native Americans)
increased demand
when a need for a product goes up, leading to attempts to create more of something (such as cotton or sugar)
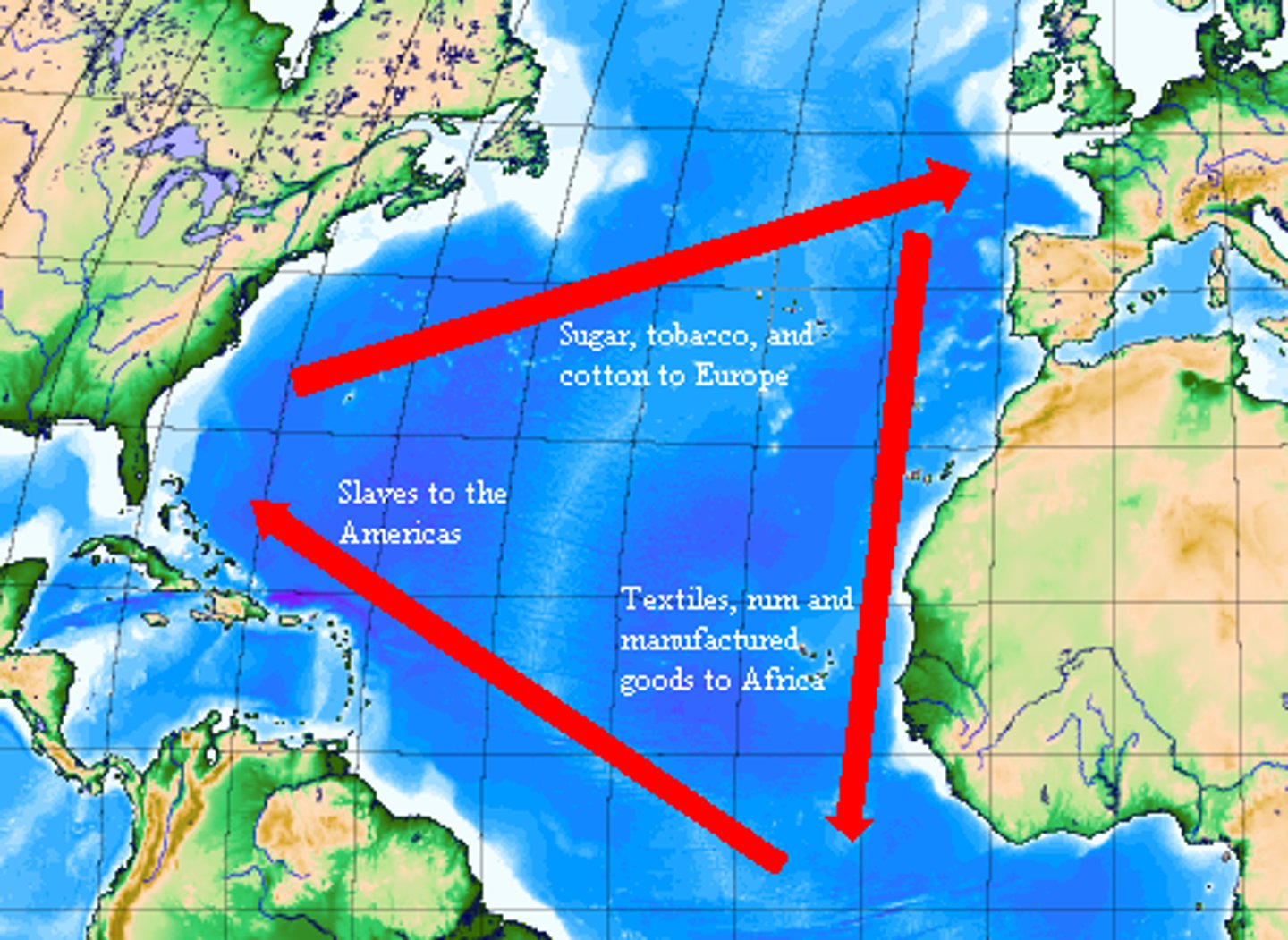
Triangle Trade
the extensive exchange of slaves, sugar, cotton, and furs between Europe, Africa, and the Americas that transformed economic, political, and social life on both sides of the Atlantic
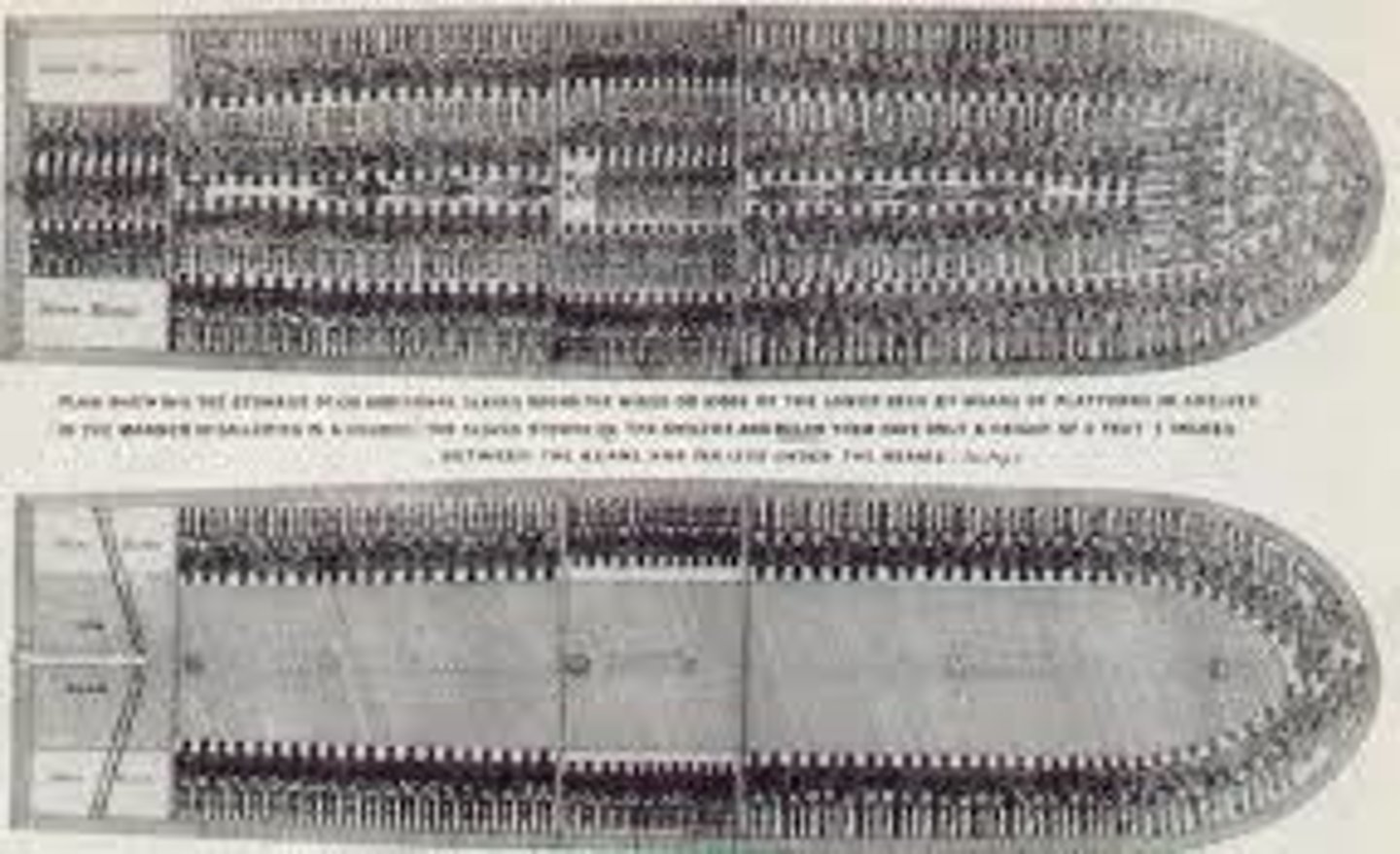
Middle Passage
the horrific sea journey undertaken by slave ships from West Africa to the West Indies.
Forced Migration
Human migration flows in which the people moving are not doing so because of their own choice (such as the slave trade).
Olaudah Equiano
An antislavery activist who wrote a famous account of his enslavement.
Chattel Slavery
A system of bondage in which a slave has the legal status of property and so can be bought and sold like property.
Prince Henry the Navigator
(1394-1460) Prince of Portugal who established an observatory and school of navigation and directed voyages that spurred the growth of Portugal's colonial empire.
Gold Coast
Southern coast of West Africa where Portugese fleets sponsored by Prince Henry the Navigator discovered and stole new source of gold.
Bartolomeu Dias
Portuguese explorer who rounded the tip of Africa
Vasco da Gama
the first European to reach India by sea sailing around the tip of Africa.
Pedro Alvares Cabral
Portuguese leader of an expedition to India; blown off course in 1500 and landed in Brazil (talk about failing upward!)
Plantation
A large farm in tropical and subtropical climates that specializes in the production of one or two cash crops for sale. Often used slave labor.
Lisbon
Capital of Portugal
Antwerp
A city in Flanders that became the centre of banking and commerce during the 16th century.
Amsterdam
Capital of the Netherlands
Bristol
English port city center of 16th and 17th c trade
London
Capital of England
Columbian Exchange
The exchange of plants, animals, diseases, and technologies between the Americas and the rest of the world following Columbus's voyages.
small pox
Disease spread by Europeans in the Americas. Led to the deaths of millions of Native Americans in North and South America
measles
Disease spread by Europeans in the Americas that led to the death of millions of Native Americans in North and South America.
immunity
the ability of an organism to resist a particular infection--since indigenous peoples of the Americas did not have this, many died.
cash crop
a crop produced for its commercial value rather than for use by the grower. (cotton, sugar, tobacco, for example).
Christopher Columbus
Mistakenly discovered the Americas in 1492 while searching for a faster route to India.
West Indies
Caribbean Islands
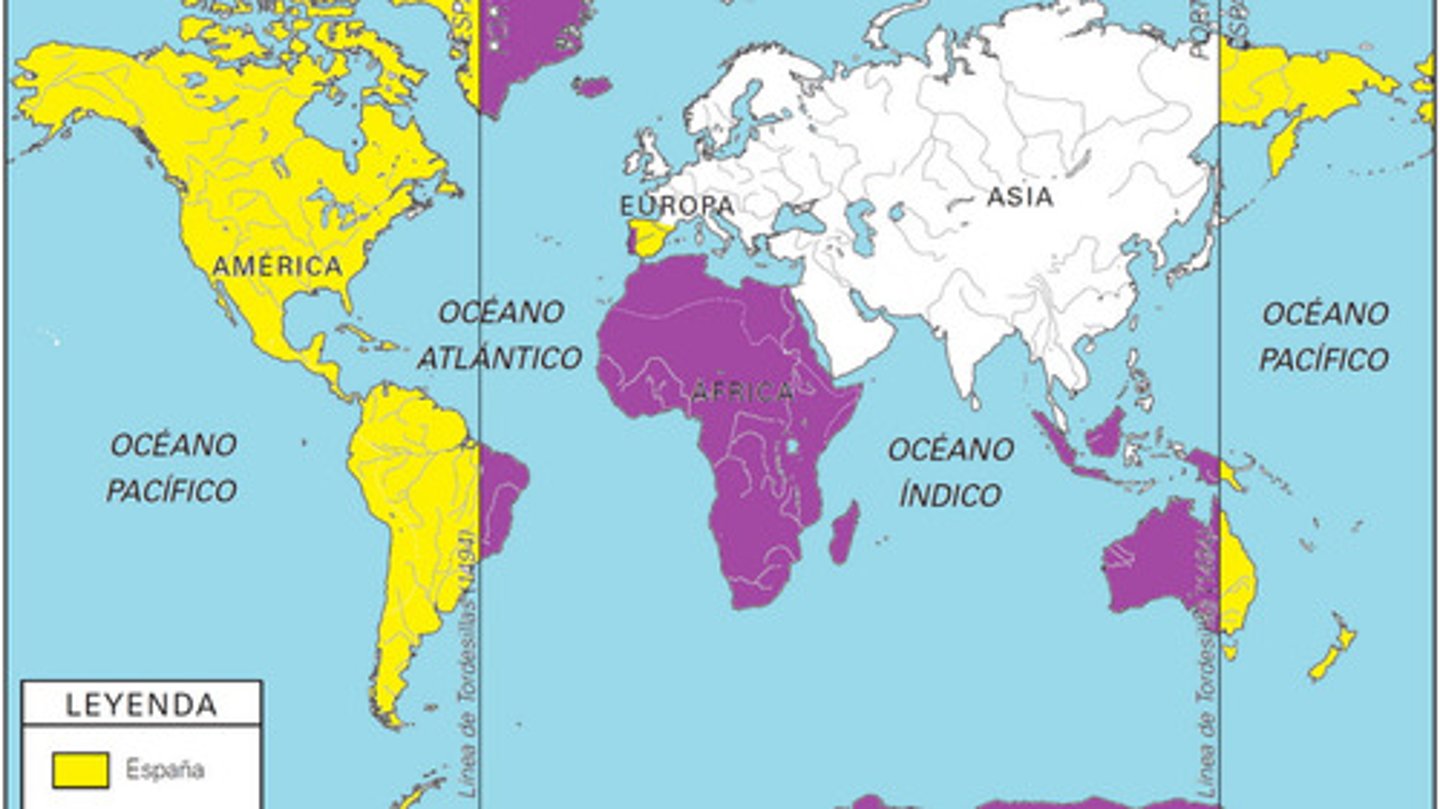
Treaty of Tordesillas
set the boundary established in 1493 to define Spanish and Portuguese possessions in the Americas.
Amerigo Vespucci
A mapmaker and explorer who said that America was a new continent, so America was named after him.
New World
the name given by Europeans to the Americas, which were unknown to most Europeans before the voyages of Christopher Columbus
conquistadors
Spanish soldiers and explorers who led military expeditions in the Americas and captured land for Spain
Hernan Cortes
Spanish conquistador who defeated the Aztecs and conquered Mexico (1485-1547)
Aztec Empire
Central American empire constructed by the Mexica and expanded greatly during the fifteenth century during the reigns of Itzcoatl and Motecuzoma I.
New Spain
Spanish colonial possessions in Mesoamerica; included most of central Mexico;
encomienda
a grant by the Spanish Crown to a colonist in America giving them the right to demand tribute and forced labor from the Indian inhabitants of an area.
Bartolome de las Casas
Dominican priest who spoke out against mistreatment of Native Americans
asiento
a slave trade treaty between other countries and Spain which allowed other countries to supply slaves to Spanish colonies
Vasco Nunez de Balboa
Spanish explorer who discovered the Pacific Ocean
Francisco Pizarro
Spanish explorer who conquered the Incas in what is now Peru
Inca Empire
The vast and sophisticated empire in modern day Peru, South America, that was at its peak from 1438 until 1532 when the Spanish defeated it
Ferdinand Magellan
Portuguese explorer who found a sea route to the Spice Island by sailing around the American continent. His crew was the first to circumnavigate the world.
Spice Islands
Europeans' name for the Moluccas, islands rich in cloves and nutmeg-- modern day Indonesia south of Asia.
New Amsterdam
Dutch colonial settlement that served as the capital of New Netherland. This later became "New York City" when the British took it over.
John Cabot
1497 claimed Canada for England
Jacques Cartier
French explorer who explored the St. Lawrence river and laid claim to the region for France (1491-1557)
Samuel de Champlain
Founded Quebec
New France
French colony in North America, with a capital in Quebec, founded 1608. New France fell to the British in 1763.
War of the Spanish Succession
a conflict, lasting from 1701 to 1713, in which a number of European states fought to prevent the Bourbon family from controlling Spain as well as France.
Seven Years' War
worldwide struggle between France and Great Britain for power and control of land in North America and India.
coercion
the use of force to get others to do what you want
Jesuits
Also known as the Society of Jesus; founded by Ignatius Loyola (1491-1556) as a teaching and missionary order to resist the spread of Protestantism.
Marco Polo
13th Century Venetian Italian explorer who wrote about his travels to Central Asia and China inspiring interest in trade with the East
Ottoman Empire
A Muslim empire based in modern day Turkey that lasted from the 1300's to 1922. Blocked trade routes to East, forcing ocean exploration.
mercantilism
An economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by selling more goods than they bought
Favorable Balance of Trade
an economic situation in which a country sells more goods abroad than it buys from abroad, it is essential for Mercantilism
Exports
Goods and Services sold to other countries
Imports
goods and services purchased from other countries
colony
a country or area under the full or partial political control of another country, typically a distant one, and occupied by settlers from that country.
Jean Baptiste Colbert
Chief Minister of Finance under Louis XIV, huge supporter of Mercantilism.