Lecture 11: Great Recession 2007-2009
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
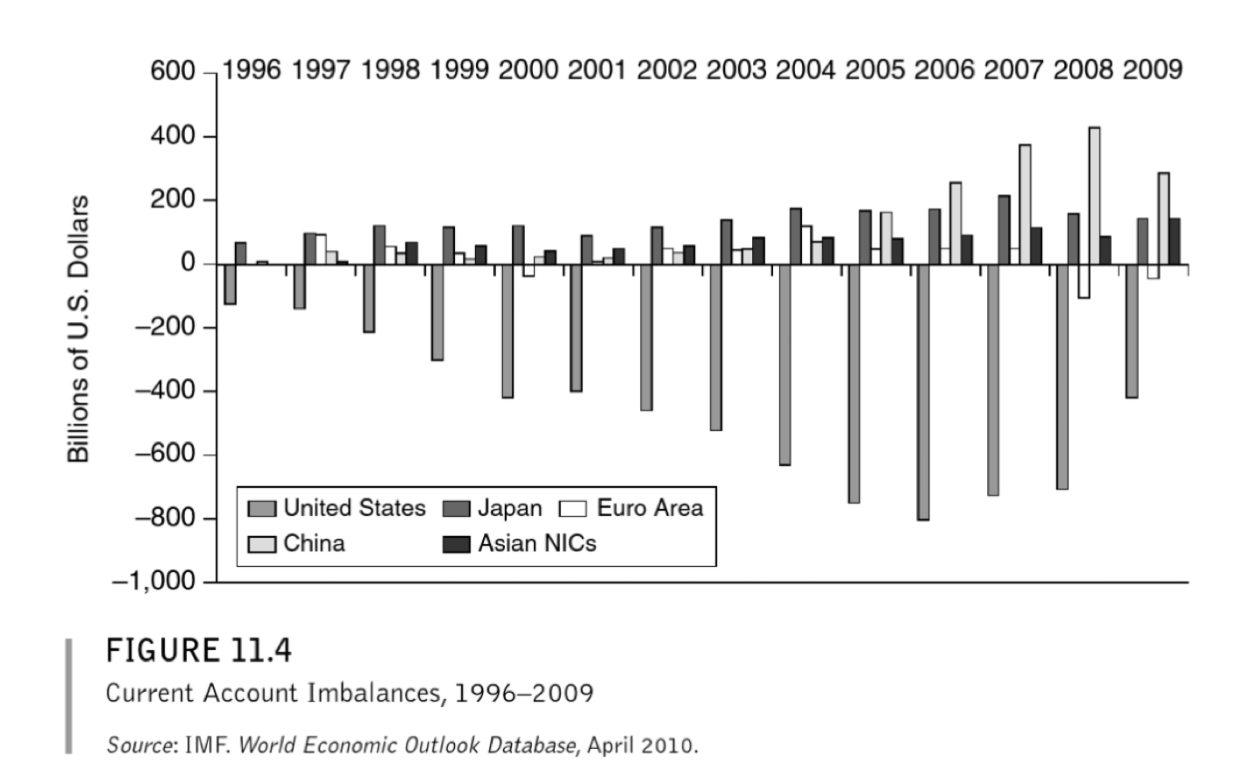
Global Imbalances
The lessons that Asia learned from their crisis leads to this huge imbalance
Buying up US currency to put into their reserves
Exports more to US than US exports to them
Global imbalances: international bargaining failure → US blames…
Savings Glut (saving too much)
Bush administration tries to push China to expand consumption and allow RMB to appreciate against dollar
Tries to shift IMF's attention to China Unsuccessful
presses European governments (Germany) to reduce their Current Account surpluses
Global imbalances: international bargaining failure → Govs in surplus counties blames …
US, demand American policy changes instead
EU says that its not saving too much, US is spending too much
Europeans blame US federal gt's budget deficit following 2001 tax cut for US CA deficit
EU argued not their issue, since overall Euro area in CA deficit
As a whole the EU is in balance
China adopts more flexible peg in 2005, but otherwise also demands US balance its budget instead
Global imbalances: international bargaining failure Result
no action, flow of cheap and plentiful credit from the surplus countries to the US
Cheap Credit in the US fuels real estate bubble
Real estate prices rose 60% btw 2000 and 2006
Mortgage-backed securities: bundles of different risk in a single security
Easier and easier to get loan for a house
Low interest rate
No credit check
Little check on you in general
Prices rose bc more buyers in system
Financial institutions discounted risk of nationwide collapse of real estate prices, worst case scenario planned for: regional collapse
2007: real estate prices fall by almost 25 percent nationwide, mortgage default rates rise sharply
Banks taking a lot of risks and underestimating the risks in the real estate market
Planned for regional default
Did not plan for national default
Fewer and fewer people are able to afford their homes bc the mortgages can’t be paid
Securities suffered large losses, many bought with debt - debt-service problems entire financial system
Crisis becomes international
Great Britain, Ireland and Spain, had their own real estate bubbles that collapsed
Copied the US business model
European financial institutions had purchased mortgage-backed securities in large quantities - suffer same losses
Freezing of global credit markets after bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers in fall of 2008 made it difficult for all financial institutions to secure credit for their activities
Banks lend a lot to each other to keep each other/system going
Usually with low interests rats
Credit dries up -> interest rates on inter-bank lending grow sharply
Policy reactions
Bank bailouts
Monetary policy
International cooperation
Policy reactions: bank bailouts
Initially US government regulators close some failing banks, arrange sales
E.g. Bear Stearns sold to JP Morgan
failed to find buyer for Lehman Brothers
Banks deemed too big to fail got bailouts in both the US and the EU
Ireland with the largest bailouts in the EU => creates debt problems in the Eurozone debt crisis
Policy reaction: monetary policy
Central Banks inject liquidity → As much money as possible
August 2007: ECB, Bank of England, and Fed inject $200 billion into markets, again in December 2007
Lower interest rates to 0
Eventually: Unconventional monetary policy - asset purchasing to stimulate the economy = "Quantitative Easing"
Quantitative easing
Creation of money to try and fix economy
Creation of new/more money —> not printing but digital
Increase money supply
CB decreasing money supply
Abandoned safe investment and go more for riskier ones (goal)
Long run will lead to inflation (hindsight- not the case)
Short run - stopped a deep recession
At the time untested policy, no other choice —> no action will lead to catastrophe
Put more money into the system but commercial banks were keeping more in
Policy reaction: International cooperation
Shift from importance of G-7 to G-20 (with emerging markets) to coordinate response
Governments agreed to coordinate fiscal stimulus measures to boost economic activity
Try to grow out of the crisis
Expanded IMF lending capacity
Financial Stability Board charged with coordinating and monitoring efforts on reform of financial regulation
Current account balances today
Global imbalances stubbornly large
US continues to have CA deficits
Trump (largely unsuccessfully) pressured China and Germany to change their policies (sound familiar?)
How to prevent banking/financial crisis for banks
Regulation!
Increase Reserve requirements - share of deposits/liabilities a bank has to hold as reserves
Need to have more in reserve
Less that they can lend out
Deposit insurance - the government insures bank deposits
Learned from Great Depression
Need people to believe that their money is safe otherwise bank run = bankruptcy
Division between risky investment & retail banking
Regulatory Oversight
Limit risk
How to prevent banking/financial crisis for governments
Governments can try (but often fail) to prevent the global imbalances that drive financial crisis
Coordinate monetary and fiscal policy —> happens rarely (too self interested)
How to prevent banking/financial crisis for both
Lenders of Last Resort
Institutions that lend money in a crisis to provide emergency liquidity (although beware of moral hazard!)
Central Banks, IMF
Good idea to have a lender of last resort —> prevent moral hazards
Saves you from things like bank-runs —> good for banks
Trust in system
Pair lender of last resort with good/strong regulatory oversight