BIOL 2020: Lecture 8 (golgi apparatus)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Secretory pathway
the route through which proteins and lipids are synthesized, processed, and transported to their final destinations, either within the cell or for secretion outside the cell.
translates from mRNA in the ribosomes in the cytoplasm
enters the ER lumen
goes from the ER to the golgi in a vesicle
transits the golgi
leaves the golgi in a vesicle
the vesicle fuses the cell membrane
it is outside
Vesicular transport
transport vesicles bud off from one compartment and fuse with another
as they do, they carry material as cargo
these buds are called coated vesicles, which have a distinctive cage of proteins

Endocytic pathway
the series of steps a cell uses to internalize substances from its surface
leads inwards from the plasma membrane, whereas secretory pathway leads outwards from the ER towards the golgi, and cell surface
Coated vesicles
vesicles which bud off from one compartment to fuse with another, all while carrying material as cargo
have a distinctive cage of proteins
4 well-characterized types, each used for different transport steps:
clathrin-coated
COPI-coated
COPII-coated
able to accomodate large cargos by assembling tubes instead of vesicles
retromer-coater
Coats
geometrical structures that assemble into vesicle cages
coated vessicles
Rab proteins
guide transport vesicles to their target membrane
all transport vesicles display surface markers that identify them and target membranes display complementary receptors
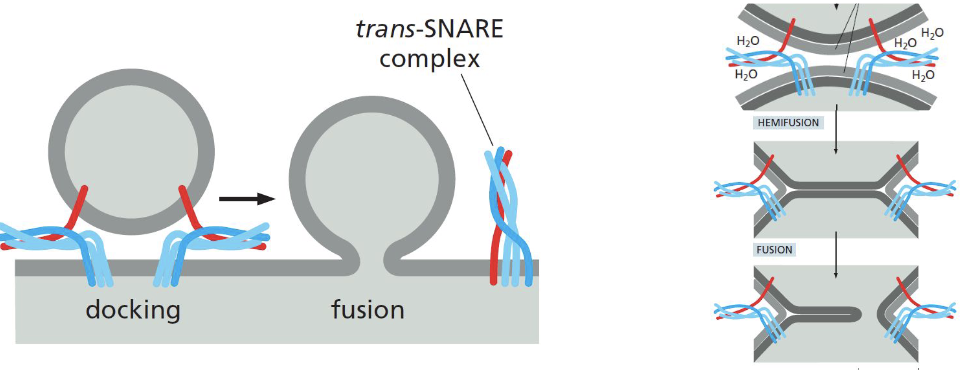
SNARE proteins
mediate membrane fusion by putting membranes in close proximity
ERES
ER exit site
where proteins leave the ER via COPII-coated transport vesicles
Cargo receptors
inside vesicles there are cargo receptors which ensure that the vesicles are loaded
Golgi apparatus
consists of a collection of flattened, membrane-enclosed compartments
cisternae
in some species, cisternae are not stacked
glycosylation and phosphorylation at the golgi are destination codes
transport through golgi occurs by 2 mechanisms:
vesicle transport mechanism
cisternal maturation mechanism
evidence of this through both fixed samples, and fluorescent live imaging
Vesicle transport mechanism
vesicle transport of molecules between cisternae

Cisternal maturation mechanism
cisternal mature from cis to trans together with cargo molecules
COPI vesicles
form of transport-vesicles
bring ER proteins back from the golgi
KDEL sequence/receptor
ER proteins have the KDEL sequence
KDEL receptor initiates vesicle formation
Non-selective constitutive secretory pathway
mechanism which transports most other proteins directly to the cell surface
no specific signal yields the secretion of protein
default pathway
specific signals are needed to direct secretory proteins into secretory vesicles and lysosomal proteins into different specialized transport vesicles.
Parts of the golgi
cisternae
flattened, sac-like membrane compartments that make up the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the Golgi apparatus.
cisternae are organized in stacks and are responsible for modifying, packaging, and transporting proteins and lipids.
CisGN
"forming," face of the Golgi apparatus, which receives proteins and lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
It is located on the convex side of the Golgi stack, facing the ER. Its function is to receive these materials and prepare them for further modification as they move through the medial and trans compartments of the Golgi before they exit
TransGN
final sorting and dispatch station of the Golgi apparatus, where proteins and lipids are packaged into vesicles for delivery to their final destinations, such as lysosomes, the cell membrane, or secretion outside the cell.
located on concave side of the Golgi stack
