Speciation and Reproductive Isolation Mechanisms
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Species
A group of interbreeding natural populations.
Speciation
The process by which new species form.
Biological Species Concept
Species defined by reproductive isolation.
Pre-zygotic mechanisms
Prevent mating or fertilization before zygote forms.
Post-zygotic mechanisms
Prevent hybrid offspring from developing or reproducing.
Geographic isolation
Physical barriers separate populations.
Ecological isolation
Different habitats prevent species from mating.
Temporal isolation
Species breed at different times.
Behavioral isolation
Differences in mating behaviors prevent interbreeding.
Mechanical isolation
Morphological differences prevent successful mating.
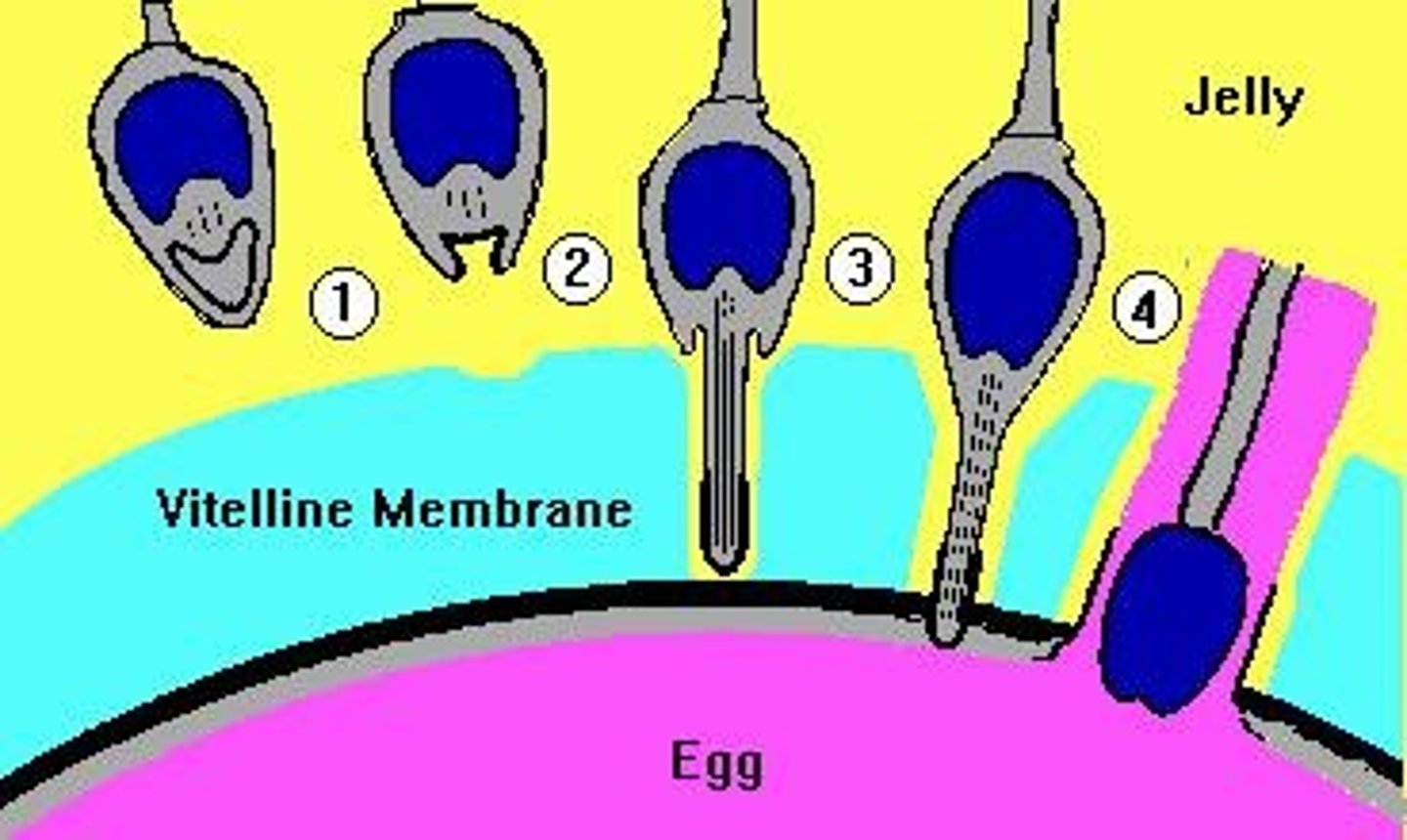
Prevention of gamete fusion
Sperm and egg proteins must match.
Hybrid zygote dies
Zygote fails to develop after fertilization.
Hybrid individual dies
Hybrid survives briefly but does not reproduce.
Hybrid sterility
Hybrid offspring are unable to reproduce.
Allopatric speciation
Speciation due to geographic separation.
Sympatric speciation
Speciation occurs within the same geographic area.
Polyploidization
Increase in chromosome number leading to speciation.
Microevolutionary forces
Mutation, drift, and selection drive divergence.
Reinforcement of reproductive isolation
Natural selection strengthens isolating mechanisms.
Carduelis pinus
Example of a species within the finch family.
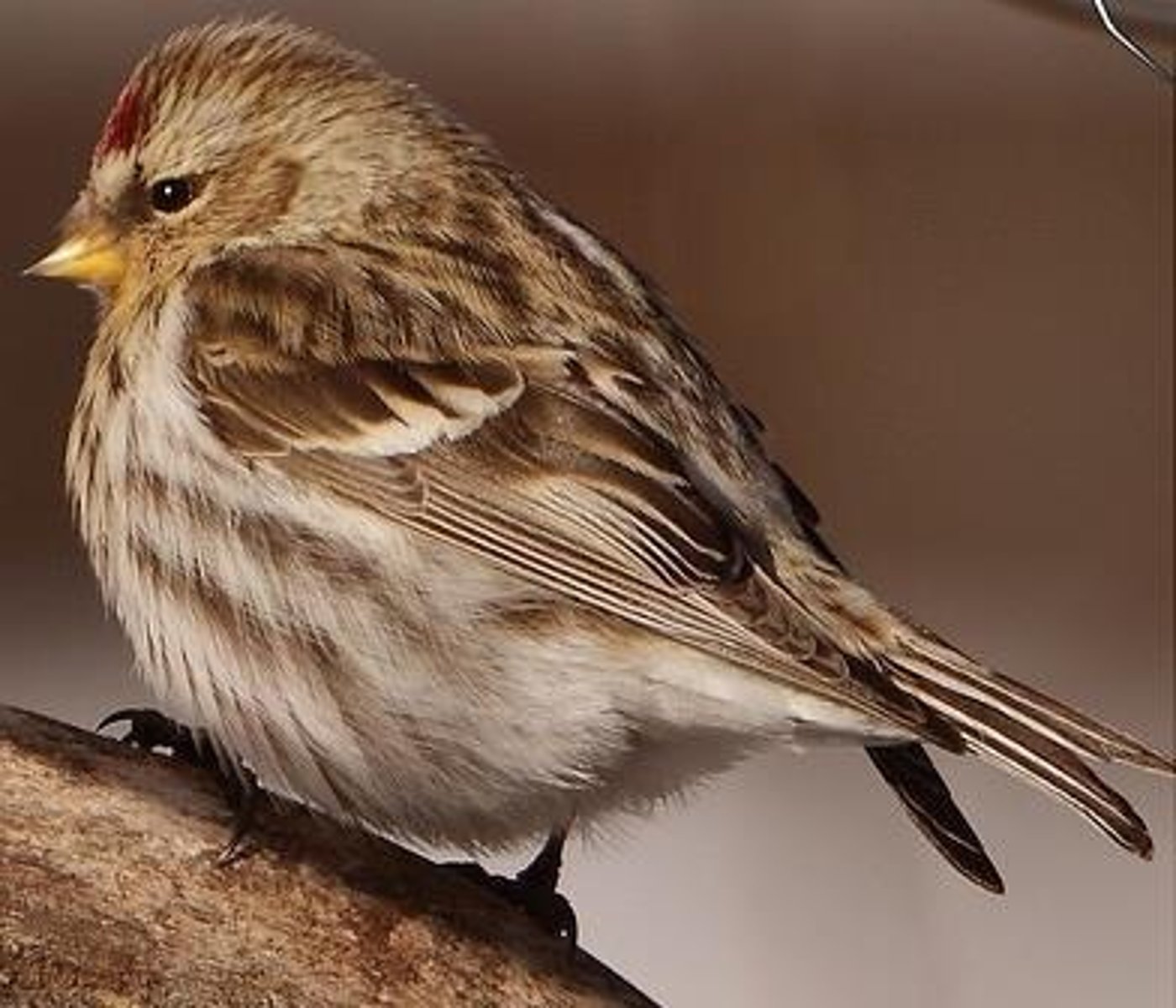
Carduelis flammea
Common redpoll, another finch species.

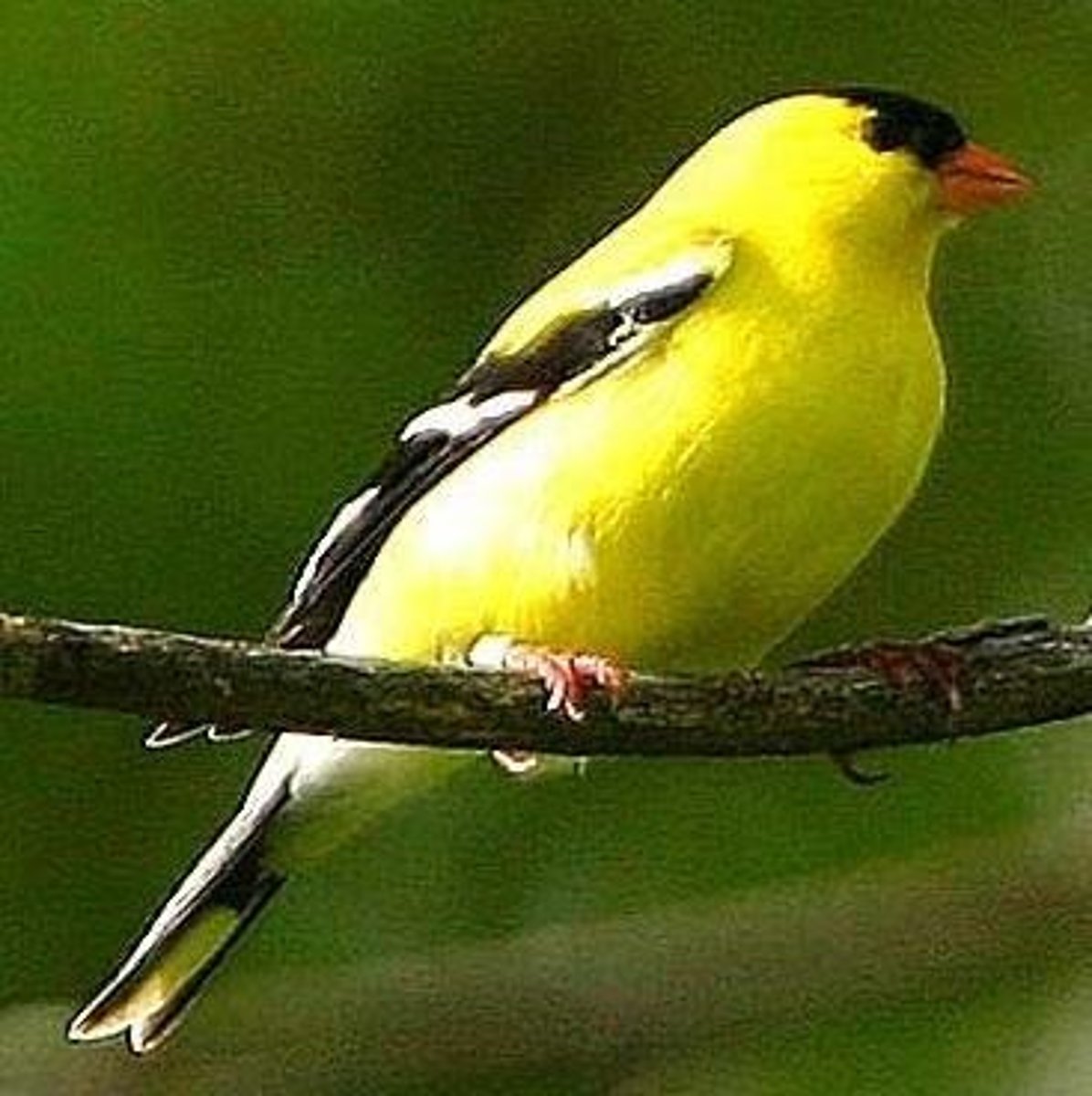
Carduelis tristis
American goldfinch, distinct species.

Ernst Mayr
Proposed the Biological Species Concept.
Gene flow
Movement of genes between populations.
Discrete units
Distinct species recognized in nature.
Mule
Hybrid of donkey and horse, sterile.
Murres
Example of species with hybridization issues.
Canids
Wolves and coyotes, can interbreed.
Mussels
Example of species that hybridize frequently.
Lactuca canadensis
Wild lettuce species flowering in summer.
Lactuca graminifolia
Wild lettuce species flowering in early spring.
S. arcticus
Species with disjunct distribution.
S. maritimensis
Another species with geographic isolation.
Tiglon
Hybrid between tiger and lion.
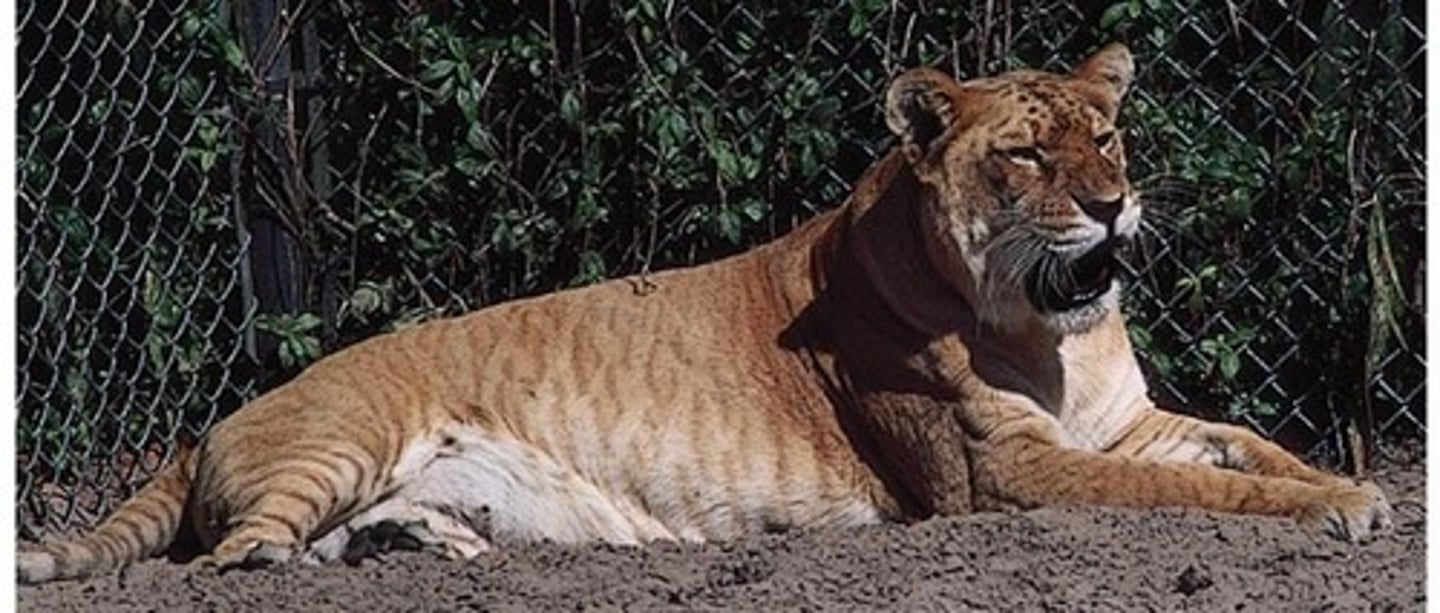

Liger
Hybrid between lion and tiger.
Hybrid embryos
Embryos resulting from interspecies mating.
Spontaneous abortion
Natural termination of a pregnancy.
Morphological variation
Differences in physical form among species.
Birds of Paradise
Example of behavioral isolation in mating.
Secondary contact
When previously separated species meet again.
Extinction of intermediate populations
Loss of populations that connect two species.