Physiological Psychology Final Exam
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Two Divisions of the Nervous System
Central Nervous System/CNS
Peripheral Nervous System/PNS
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
all the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord
Divisions of the PNS
Somatic
Autonomic
Somatic Division
voluntary subdivision of the PNS
Autonomic Division
regulates involuntary bodily functions. Broken up into the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
Sympathetic Division
Division of the autonomic nervous system commonly known as the “fight or flight” division
Parasympathetic Division
division of the autonomic nervous system commonly known as the “rest and digest” division
Efferent Neurons
motor and outgoing
Afferent Neurons
Sensory and incoming
Forms of Protection for the CNS
Blood-Brain Barrier
Meninges
Bones
Divisions of the adult human brain
Hindbrain
Midbrain
Forebrain
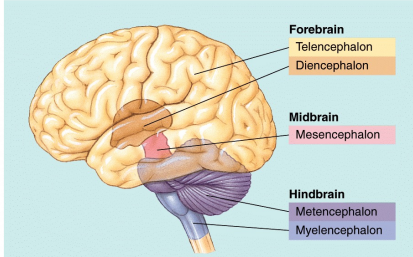
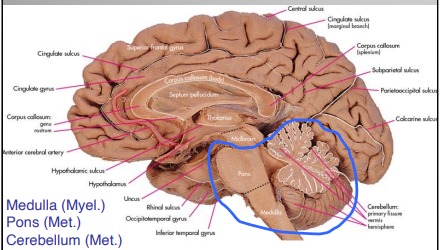
Substructures of the Hindbrain
Myelencephalon
Medulla
Metencephalon
Pons
Cerebellum
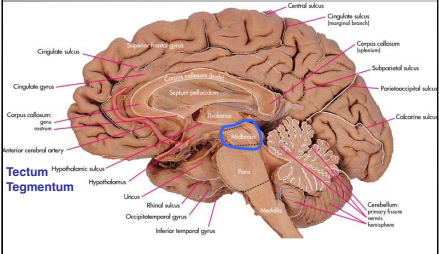
Substructures of the Midbrain
Mesencephalon
Tectum
Tegmentum
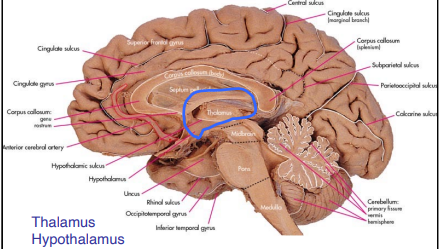
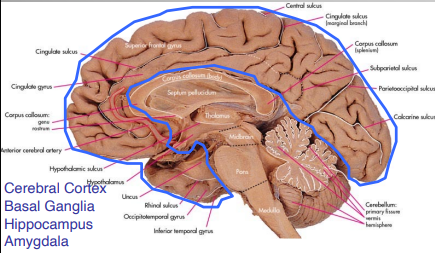
Substructures of the Forebrain
Diencephalon
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Telencephalon
Cerebral Cortex
Basal Ganglia
Hippocampus
Amygdala
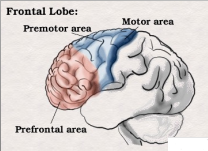
Frontal Lobe
Precentral Gyrus
Superior, middle, inferior gyri
Central Sulcus
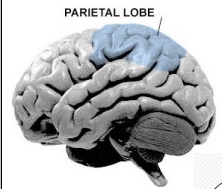
Parietal Lobe
Superior Parietal Lobule
Inferior Parietal Lobule
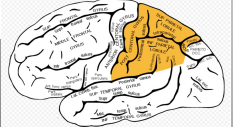
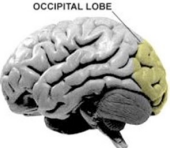
Occipital Lobe
Parieto-occipital Sulcus
Calcarine Fissure
Cuneus
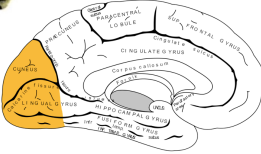
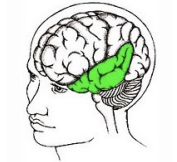
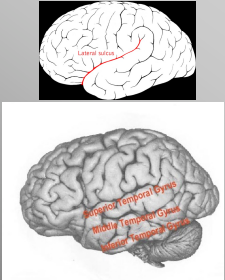
Temporal Lobe
Lateral Sulcus
Superior Temporal Gyrus
Middle Temporal Gyrus
Inferior Temporal Gyrus
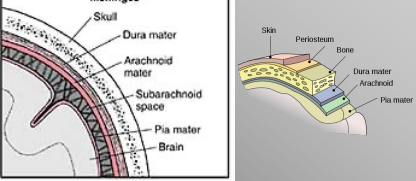
Meninges
Dura Mater
Arachnoid Mater
Pia Mater
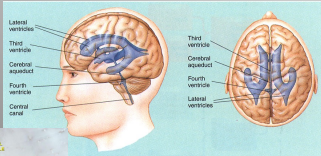
Ventricles
contain cerebral spinal fluid
Neurons
funcional cellular unit; transmit information via action potential & neurochemical release
Glia
provide structural and metabolic support for neurons (ex. modulate, support, and insulate neurons with myelin sheaths)
Macroglia
Astrocyte (CNS/PNS) (Physical and Nutritional Support)
Oligodendrocyte (CNS) (Myelin/Guidance)
Schwann Cell (PNS) (Myelin/Guidance)
Satelite Cell (PNS) (Physical Support)
Ependymal Glia
line the ventricles; only present in the CNS
Microglia
Present in the CNS and PNS; function in tissue repair, debris removal, and defense
Gray Matter
unmyelinated neurons and parts of neurons. Divided into “horns” (dorsal and ventral); some axons but mostly cell bodies
White Matter
myelinated parts of neurons and glia, surrounds central gray matter
Planes of Section of the Brain
Coronal Section
Sagittal Section
Horizontal Section
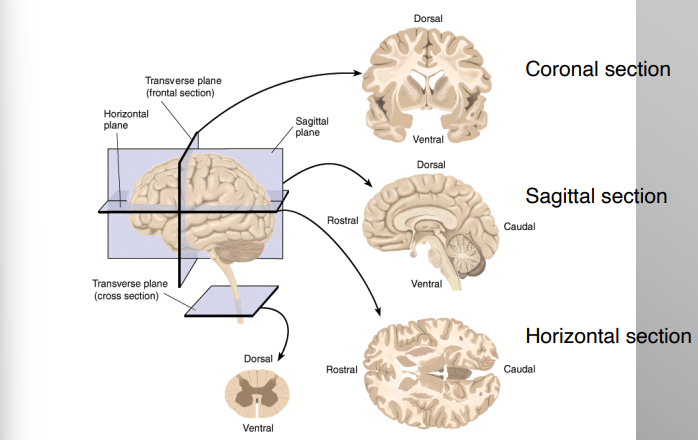
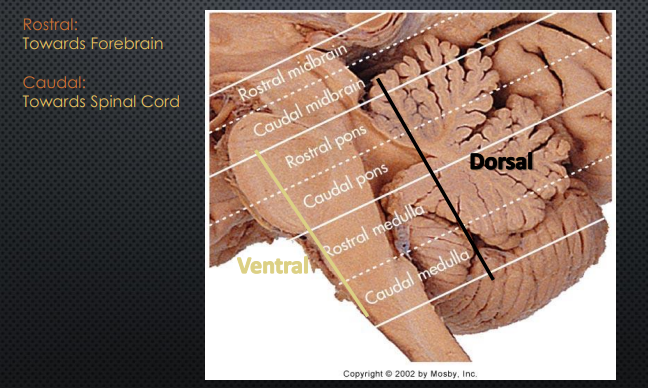
Human Brain Orientation
“hinged” horizontal to vertical at brainstem
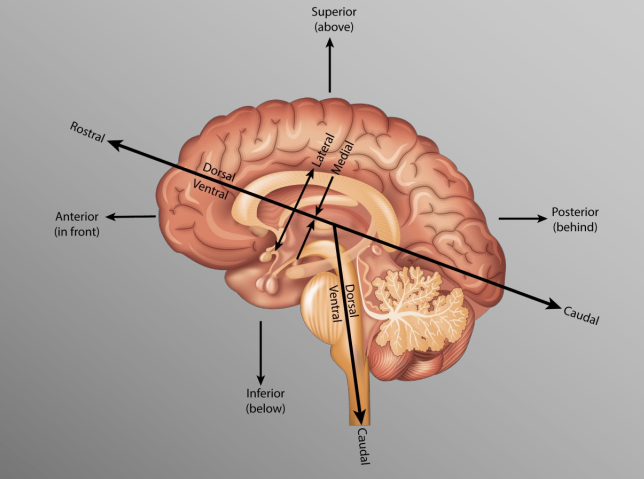
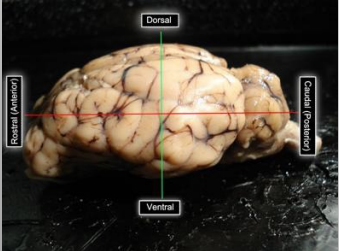
Sheep Brain Orientation
Differences in Cortical Folding
Skull imposes size limits on cerebral cortex
Overcome by folding into sulci (valleys) and gyri (hills)
Increases surface area, allowing for more compex processes
Lissencephalic
“smooth brain”
Steps in Histologic Preparation of Tissue
1) Fixing
2) Processing
3) Embedding
4) Slicing
5) Staining
Fixation
1) Blood is drained from the body (by means of saline)
2) Fixative solution (usually formalin) is pumped into vascular system to replace remaining fluid
3) The above steps ultimately stabilize the tissue, disable intrinsic molecules and enzymes to prevent degradation, and increase tissue strength for further processing
Processing
(does not occur when using a vibratome and is optional with cryostat)
1) Embedding in paraffin/wax (for microtome), or
2) Treatment with sugars to prevent cell damage during freezing for the cryostat
Slicing
1) Vibratome, can section unprocessed tissue
2) Cryostat is relatively fast and does not require embedding
3) Microtome provides high quality for thin sections/high mag resolution
Staining
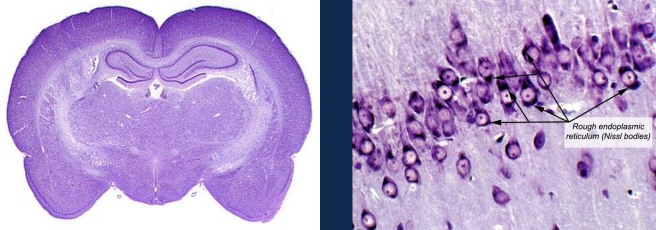
1) Nissl stain provides good general tissue contrast, stains cell bodies
2) Myelin stains affect white-matter only (ex. Luxol blue)
3) Golgi/Silver stains highlight just a few neurons in full detail
Nissl Stain
Luxol Blue Stain
Golgi (aka Silver) Stain
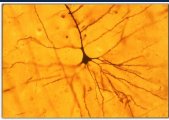
Staining with Cresyl violet - Nissl
Hydration helps the stain fix in the tissue because cell bodies are full of water
Dehydration with ethanol solutions help differentiate the Nissl stain by decoloring high myelinated areas of the brain
Done from less (70%) to more concentrated (100%) to avoid damaging the tissue due to dramatic changes in the environment where the tissue was previously exposed (distilled water and cresyl violet)
Epidural Space
Area outside of the meninges, mostly adipose tissue. Typically used to provide pain relief for the lower body (common for childbirth)
Subarachnoid Space
Area between the arachnoid mater and pia mater, contains CSF. Typically used to provide total body numbness/pain relief or check for bacteria in the CSF.
Cervical Vertebrae
8 (C1 - C8); send & receive info from the head, neck, shoulders, diaphragm
Thoracic Vertebrae
12 (Th 1 - Th 12); send & receive info from the trunk muscles, chest wall, and organs
Lumbar Vertrebrae
5 (L1 - L5); send & receive info from lower back, legs, feet.
Sacral Vertebrae
5 (S1 - S5); send & receive info from bowel, bladder, and sexual functions
Dermatome
an area of skin/the body associated with a single spinal cord segment (sensory and motor region)
Quadriplegia
loss of feeling in most of the body
Paraplegia
loss of feeling in the lower extremities
Decussation
the crossing of nerve fibers or tracts from one side of the body to the other (intersection for an X-shape)
Dorsal Root
sensory axons and interneuron cell bodies, ascending
Ventral Root
motor cell bodies, descending. Carries motor information from neurons to body’s muscles
Dorsal Horn
receives ascending sensory info from the body and carries this info to the brain
Ventral Horn
contains the cell bodies of the motor neurons. Receive input from other parts of the brain and spinal cords and send signals down their axons
Tract
a bundle of nerve fibers within the CNS that connects one area to another
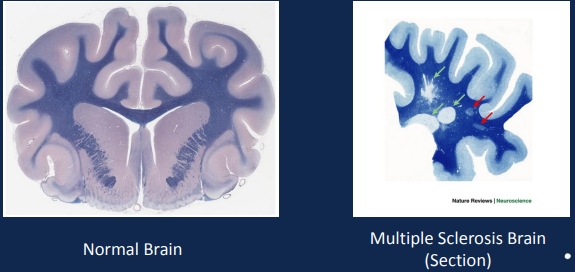
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Preferentially affects cervical spinal cord (dorsal areas)
Body’s immune cells attacking myelin leading to inflammation around nerves
Common symptoms: ascending numbness, starting in feet, bilateral hand numbness, numbness on one side of the body
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Loss of lower motor neurons in the ventral horn
Degredation of lateral column pathways in spinal cord
Muscle atrophy
No changes in intellect or memory
Meningitis
inflammation of the meninges. Symptoms include: headache, stiff neck, high fever. Massive immune response in CNS leads to swelling and cell death. Detected through a spinal tap to check for bacteria in the CSF. Also known as “Dorm Disease”
Encephalitis
inflammation of the brain tissue, often caused by an infection (like a virus) or sometimes the body’s immune system attacking the brain.
Spinal Segment
region associated with one vertebra and one dorsal/ventral nerve pair
Dorsal Route
Information comes from the body to the spinal cord via the dorsal root into the rootlets
Dorsal rootlets enter the cord at the posterolateral sulcus
Ventral Route
Information goes from the spinal cord to the body through the ventral rootlets into the ventral root
Ventral rootlets enter the cord at the anterolateral sulcus
Dorsal Root Ganglion Cells
“pseudounipolar neurons”, meaning they have one long axon with two branches
One branch extends peripherally (out of the CNS) to the muscles/skin
Ohter branch extends centrally (into the CNS) towards the spinal cord
Dorsal Column - Medial Lemniscus (touch)
Concious touch and proprioception from lower body (gracile) and upper body (cuneate)
Ascending (sensory) pathway
Somatosensory neurons in the dorsal root ganglia send axons into the dorsal column
These synapse which crosses (decussates) in the MEDULLA, slightly above motor crossing
Spinothalamic Tract
Ascending (sensory) Pathway
Lateral - Pain and thermal sensations
Anterior - light touch
1st Synapse: Neurons in the substantia gelatinosa send axons that decussate (cross midline) and travel down the spinal cord
Sensory crossing at the level of entry in spinal cord (no bundled decussation of tract)
Corticospinal Tracts
Descending (motor) Pathway
Principal pathway for the production of skilled volitional movements
Pyramid: corticospinal fibers forming a prominent fiber bundle on the ventral surface of the MEDULLA
Motor (pyramidal) decussation in Medulla, slightly below sensory decussation and visible “pyramids”
Upper motor neuron axon (in primary motor cortex) synapses with a cell body of a lower motor neuron in the ventral horn of the spinal cord
Lower motor neurons leave spinal cord through the ventral route to innervate muscles
General Functions of the Brainstem
Conduit Functions - passageway for information flow
Integrative Functions - integration point for information between higher and lower order structures
Cranial Nerve Functions - receive sensory and sends motor information to/from the head and vital organs
Divisions of the Brainstem
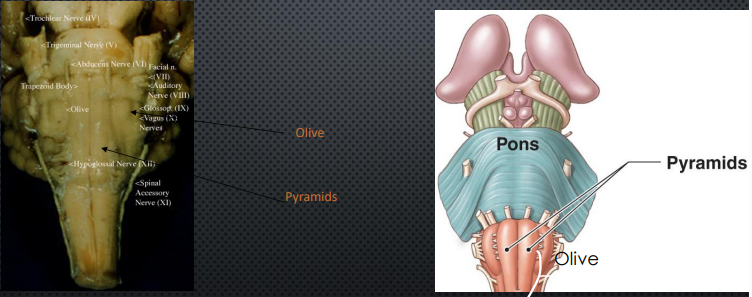
Key Ventral Structures of the Medulla
Superior Olive
Auditory perception
Inferior Olive
Cerebellar motor learning
Pyramids
Corticospinal tract
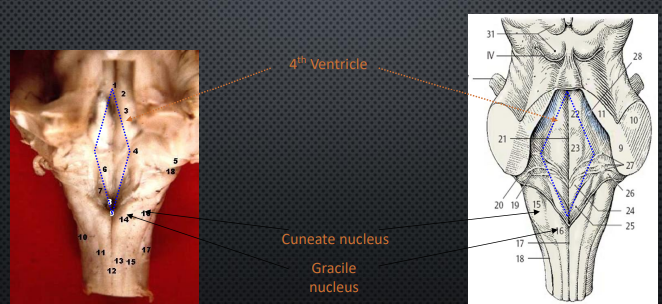
Key Dorsal Structures of the Medulla
4th Ventricle
Cuneate Nucleus
Upper Body
Gracile Nucleus
Lower Body
Key Ventral Structures of the Pons
Pontine Nuclei
Relay cortical input to the cerebellum and spinal cord
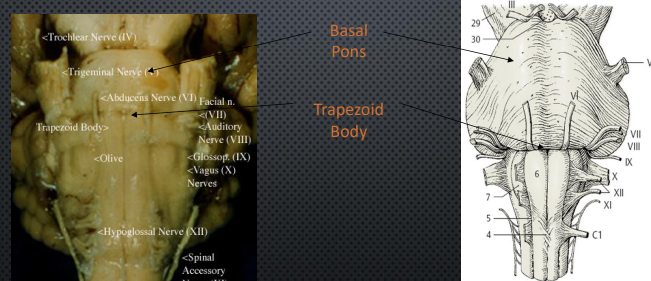
Basal Pons
“Bulge” that dominates this surface. Contains cell bodies of pontine nuclei the “middle men” in communication of motor information from cortex to cerebellum
Trapezoid Body
At junction of medulla and pons
Bundle of fibers involved in auditory processing
Key Dorsal Structures of the Pons
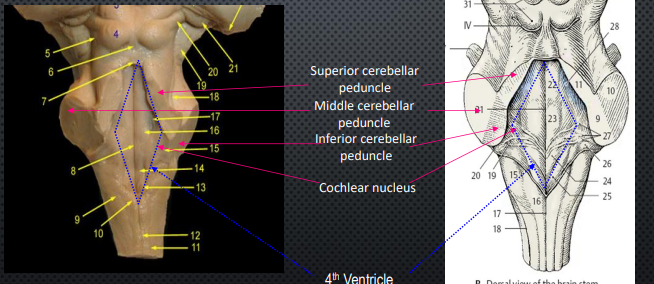
Cerebellar Peduncle
large white matter bundles connecting cerebellum to brainstem
Cochlear Nucleus
Auditory info to inferior colliculus
Fibers = trapezoid body
Key Ventral Structures of the Midbrain
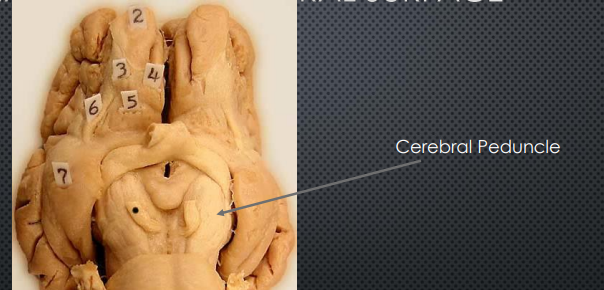
Cerebral Peduncle
Large white matter stalks; descending motor fibers from cortex to the brainstem
Key Dorsal Structures of the Midbrain
Superior Colliculi
Process visual info from retina
Detect and localize objects in visual field
Integrate visual cues with other sensory info
Coordinate complex motor functions such as reaching for objects or avoiding obstacles
Inferior Colliculi
Relay auditory info from cochlear nucleus to higher-order auditory areas
Coordinate acoustic-motor functions (ex. eye movements, head turns, etc. to auditory stimuli)
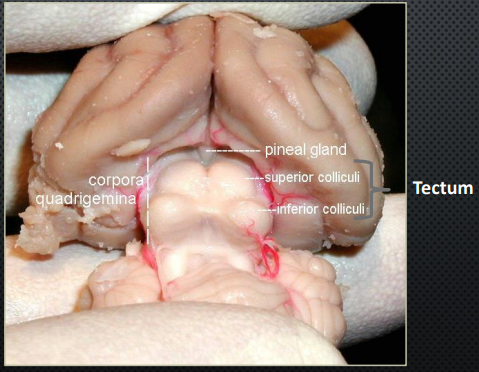
Tectum
“Ceiling” of the midbrain which contains the superior and inferior colliculi
Tegmentum
“ground” of the midbrain which contains the reticular formation, red nucleus, periaqueductal gray, and substantial nigra
Reticular Formation
Sleep/Wake Cycle
Central core of brainstem (passes through all 3 structures and weaves together functions)
Red Nucleus
Motor Coordination
Periaqueductal Gray
Modulation of pain (releases endogenous opioids)
Substantial Nigra
Movement
Recticular Activating System (RAS)
loops between reticular formation, thalamus, and cortex. Involved in control of arousal and conciousness. Always “on” must be inhibited by other areas for sleep
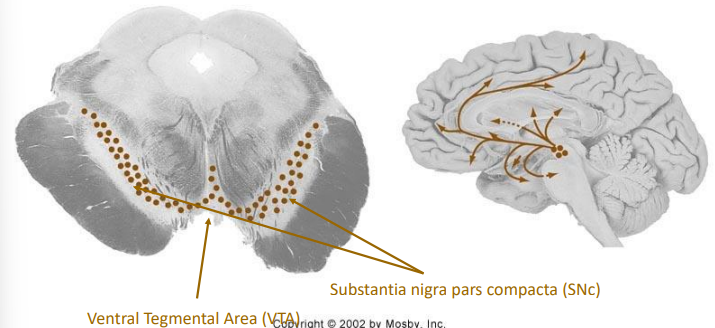
Dopaminergic Neurons in the Midbrain
Innervates amygdala, cingulate cortex, prefrontal cortex, & nucleus accumbens
VTA (Ventral Tegmental Area) : addiction, motivation, cognition
SNc (Substantia nigra pars compacta) : motor control, depleted in Parkinson’s disease
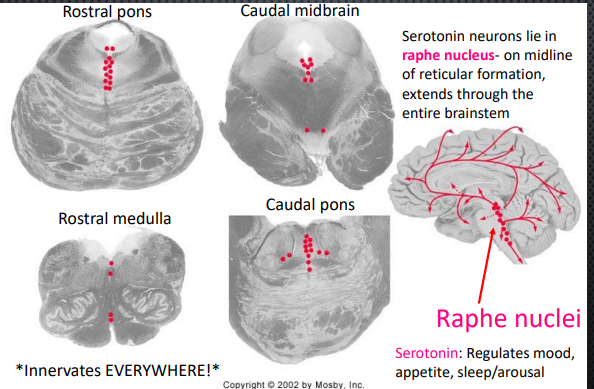
Serotonergic Neurons in the Brainstem
Raphe Nucleus
Where serotonin neurons lie
On midline of reticular formation, extends through the entire brainstem
Innverates Everywhere!!
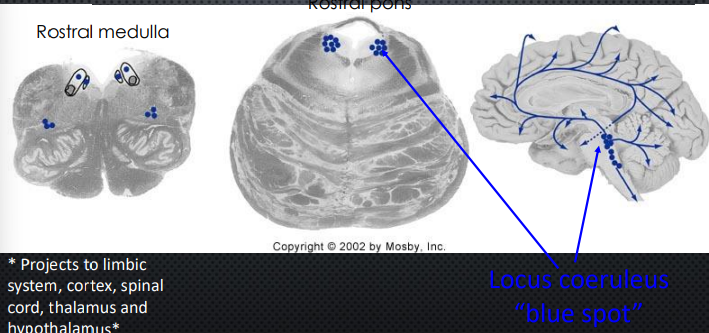
Norepinephrine Neurons in the Medulla and Pons
Projects to limbic system, cortex, spinal cord, thalamus, and hypothalamus
Locus Coeruleus
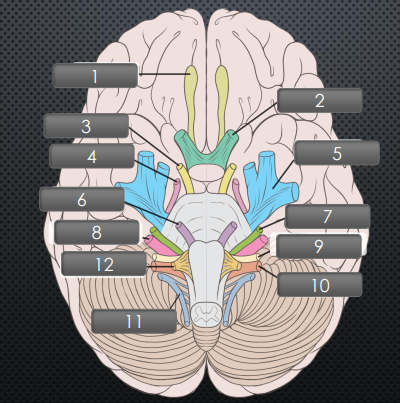
Cranial Nerves
(1) Olfactory
Originates in olfactory epithelium (in nose), and ends in olfactory bulb
(2) Optic
Originates in diencephalon
Midbrain
(3) Oculomotor
(4) Trochlear
Pons
(5) Trigeminal
(6) Abducens
(7) Facial
(8) Vestibulocochlear
Medulla
(9) Glossopharyngeal
(10) Vagus
(11) Acessory
(12) Hypoglossal
Olfactory Cranial Nerve
CN 1
Type: Sensory
Function: Smell
Optic Cranial Nerve
CN 2
Type: Sensory
Function: Vision
Oculomotor Cranial Nerve
CN 3
Type: Motor
Function: Eyelid/Eyeball/Lens/Pupil Movement
Trochlear Cranial Nerve
CN 4
Type: Motor
Function: Turn eyes down, lateral
Trigeminal Cranial Nerve
CN 5
Type: Sensory & Motor
Function: Face and mouth sensations; chewing
Abducens Cranial Nerve
CN 6
Type: Motor
Function: Moves eyes lateral
Facial Cranial Nerve
CN 7
Type: Sensory & Motor
Function: Facial Muscles, tears, saliva, taste
Vestibulocochlear Cranial Nerve
CN 8
Type: Sensory
Function: Sense of equilibrium, hearing
Glossopharyngeal Cranial Nerve
CN 9
Type: Sensory & Motor
Function: Taste
Vagus Cranial Nerve
CN 10
Type: Sensory & Motor
Function: Thoracic and abdominal sensation, controls speech, swallowing, gag reflex, heart rate
Accessory Cranial Nerve
CN 11
Type: Motor
Function: Head and Shoulder Movements
Hypoglossal Cranial Nerve
CN 12
Type: Motor
Function: Tongue movement, speech articulation