D1.1
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is DNA replication?
DNA replication is the production of exact copies of DNA with identical base sequences.
Outline the purposes of DNA replication.
The primary purpose of DNA replication is to create an exact copy of a DNA molecule, ensuring that each new cell formed during cell division receives a complete set of genetic information
Describe the meaning of “semi conservative” in relation to DNA replication.
"Semi-conservative" in the context of DNA replication means that when a new DNA molecule is formed during replication, it consists of one strand from the original DNA molecule (the "parent" strand) and one newly synthesized strand, essentially "conserving" half of the original DNA information in each new molecule created
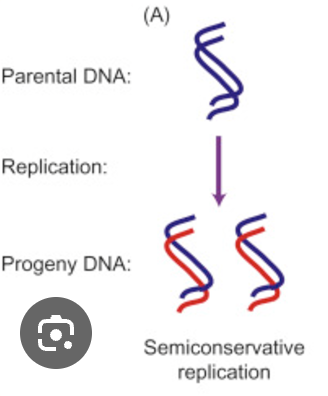
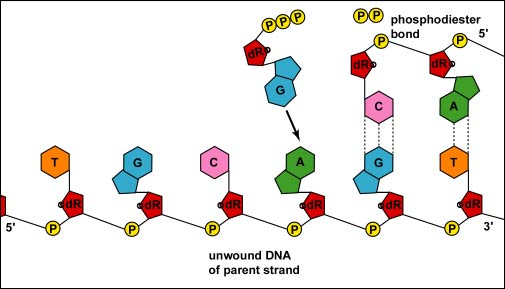
Explain the role of complementary base pairing in DNA replication.
Complementary base pairing ensures that the newly synthesized DNA strand is an exact copy of the original template strand, as it dictates which nucleotide is added next based on the complementary base pairing rules (A with T, and C with G), thus maintaining the genetic information fidelity during replication.
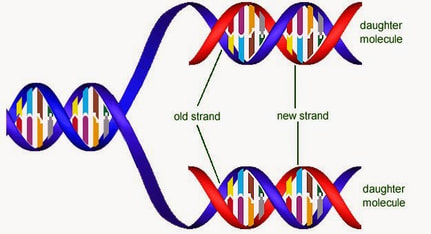
State why DNA strands must be separated prior to replication.
The two strands of the parent DNA molecule must separate so that each can serve as a template for the new DNA strands that are being built.
Outline the role of helicase in DNA replication.
Helicase, in DNA replication, breaks the hydrogen bonds that hold the double strand together to expose the single strands, in order to kickstart replication.
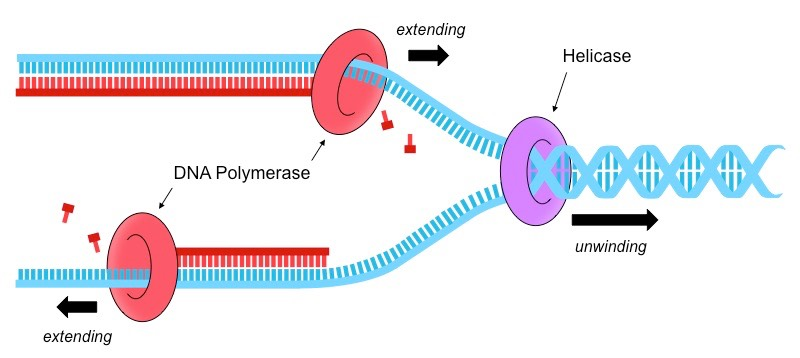
Outline the role of DNA polymerases in DNA replication.
DNA polymerases are responsible for synthesizing DNA: they add nucleotides one by one to the growing DNA chain, incorporating only those that are complementary to the template.
How many helicase enzyme(s) are there per instance of DNA replication?
One
How many DNA polymerase enzyme(s) are there per instance of DNA replication?
2; separate DNA polymerases are utilized for each strand of template DNA, allowing for simultaneous synthesis of the leading and lagging strands at the replication fork
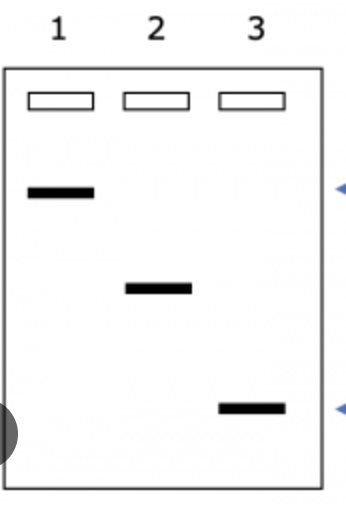
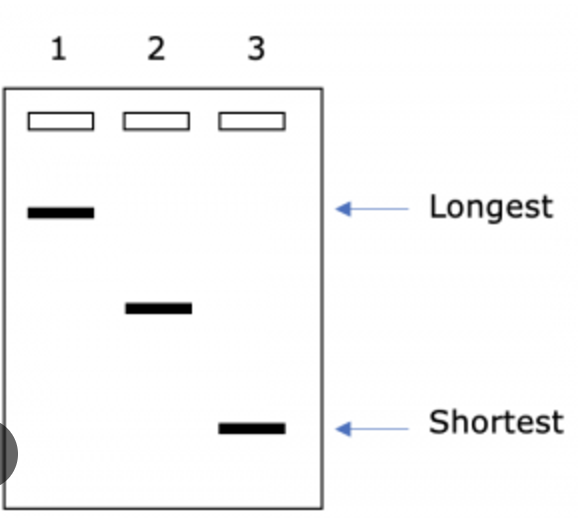
Which sample has the longest DNA fragments?
Sample 1 has the longest DNA fragments, as it has migrated the shortest distance (Sample 3 has the shortest DNA fragments, as it has migrated the furthest distance)
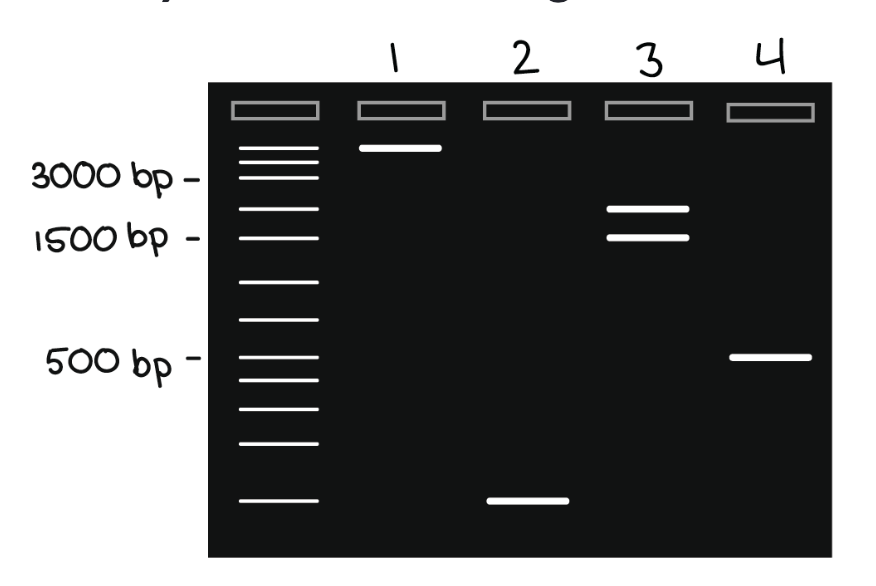
Which lane contains the 1500 bp fragment?
Lane 3
Outline the procedure for DNA electrophoresis.
DNA samples are loaded into wells (indentations) at one end of a gel, and an electric current is applied to pull them through the gel.
One well is reserved for a DNA ladder, a standard reference that contains DNA fragments of known lengths.
DNA fragments are negatively charged, so they move towards the positive electrode, and away from the negative end of the gel (where the wells are)
Small fragments move through the gel faster than large ones.
When a gel is stained with a DNA-binding dye, the DNA fragments can be seen as bands, each representing a group of same-sized DNA fragments.
Describe how and why DNA fragments separate during electrophoresis.
DNA is negatively charged, therefore, when an electric current is applied to the gel, DNA will migrate towards the positively charged electrode. Shorter strands of DNA move more quickly through the gel than longer strands resulting in the fragments being arranged in order of size
Outline the process of DNA profiling.
DNA profiling involves extracting DNA from a biological sample, then amplifying specific regions of interest using PCR, separating the amplified fragments by size using gel electrophoresis, and finally analyzing the resulting pattern to identify a unique DNA profile by comparing it to a known sample or database; this process is crucial in forensic science for linking individuals to crime scenes or for paternity testing.
List applications of DNA profiling.
Medical research, Forensic investigations, Paternity testing, Disaster victim identification, Genealogical research (anywhere where confirming an individual's identity is crucial)
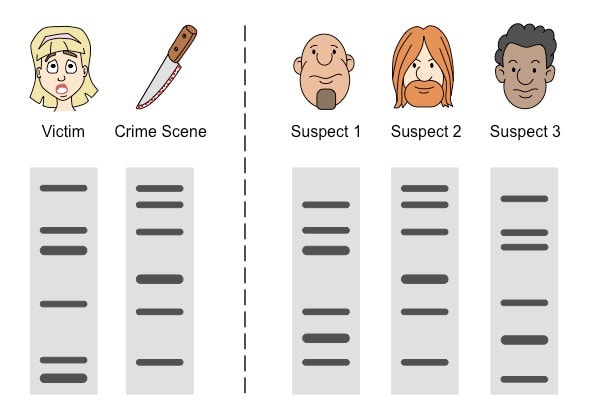
Based on DNA evidence, who did it?
Suspect 2— look at the DNA bands that are found at the crime scene, minus the bands belonging to the victim, then find the suspect who matches
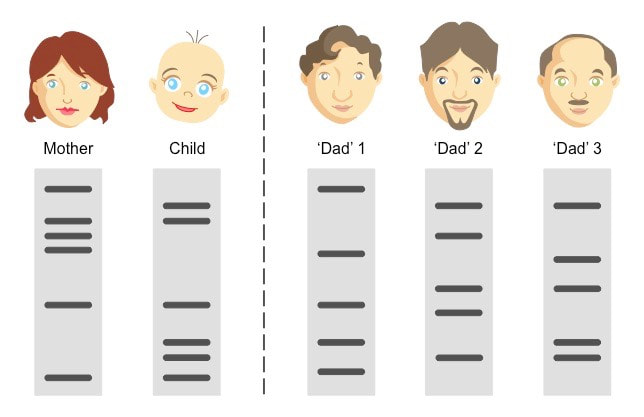
Based on DNA evidence, who’s the dad?
Dad 3— look at the baby’s bands, minus the mom’s bands, then find the dad who matches
List example sources of DNA that can be used in DNA profiling.
blood, saliva, semen, hair (particularly hair roots), skin cells, bone, teeth, tissue samples, buccal swabs (cheek swabs), fingernails, urine, and vaginal swabs