MedChem Exam 2
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Transporters, Reaction Types, Phase 1-2 enzymes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
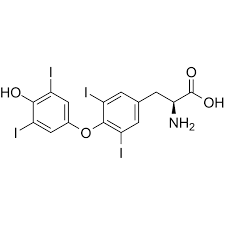
What Transporters does this drug taken up?
Paracellular Transporter
e.g. Levothyroxine (40-80% BA)
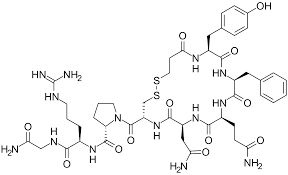
What Transporters does this drug taken up
Paracellular Transporter
e.g. Desmopressin (0.16% BA)
Carrier-mediated or Active Transport can take up drugs in the ___ or _____, where uptake of ______________
gut or intestinal epithelial cells
uptake of endogenous nutrients, ions, and occasionally drugs (looks like endogenous nutrients, ions, amino acids, oligopeptides, phosphate).
What Transporters does this drug taken up?
Amino Acid transporter (active transporters)
What Transporters does this drug taken up?
Amino Acid transporter (active transporters)
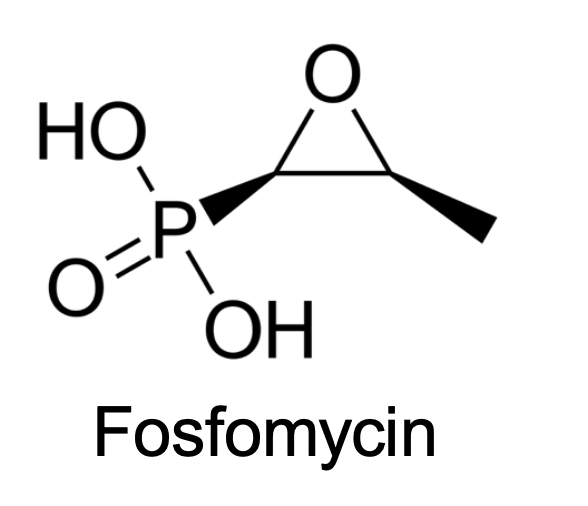
What Transporters does this drug taken up?
Phosphate transporter (active transporters)
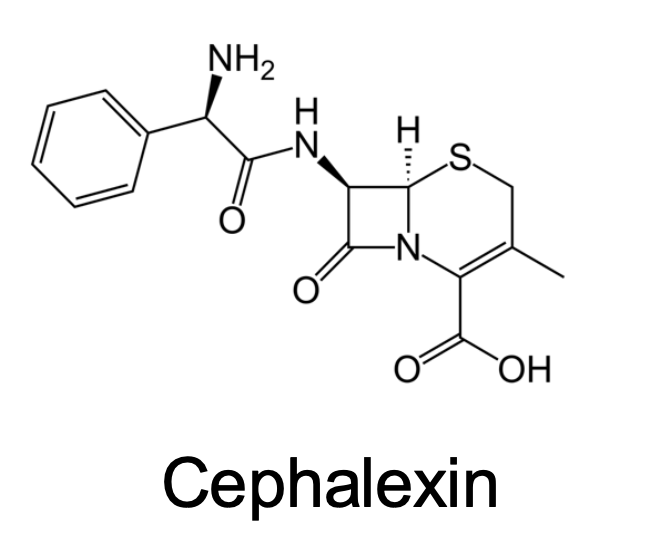
What Transporters does this drug taken up?
Oligopeptide Transporter (active)
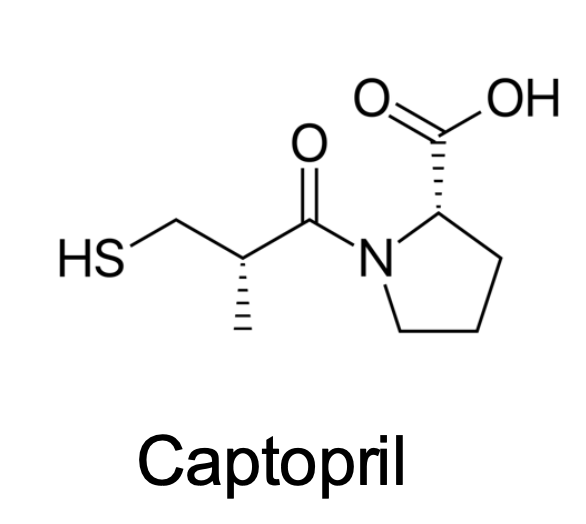
What Transporters does this drug taken up?
Oligopeptide Transporter (active)
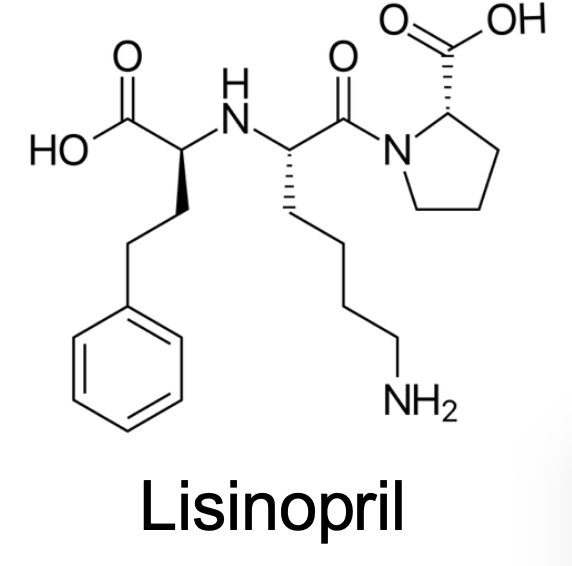
What Transporters does this drug taken up?
Oligopeptide Transporter (active)

After the calculation, what percent of drugs can passively diffuse? Is it effective?
Using the same logic as above:
b. At pH 7 = 10% is neutral and can cross by passive
diffusion
c. At pH 10 = 99% neutral and can cross by passive
diffusion


After the calculation, what percent of drugs can passively diffuse? Is it effective?
Using the same logic as above:
b. At pH 7 = 0.1% is neutral and can cross by passive
diffusion
c. At pH 10 = 0.0001% is neutral and can cross by passive
diffusion

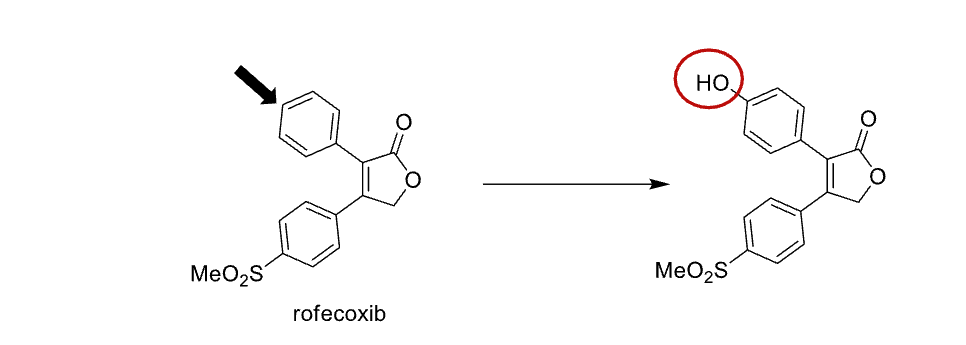
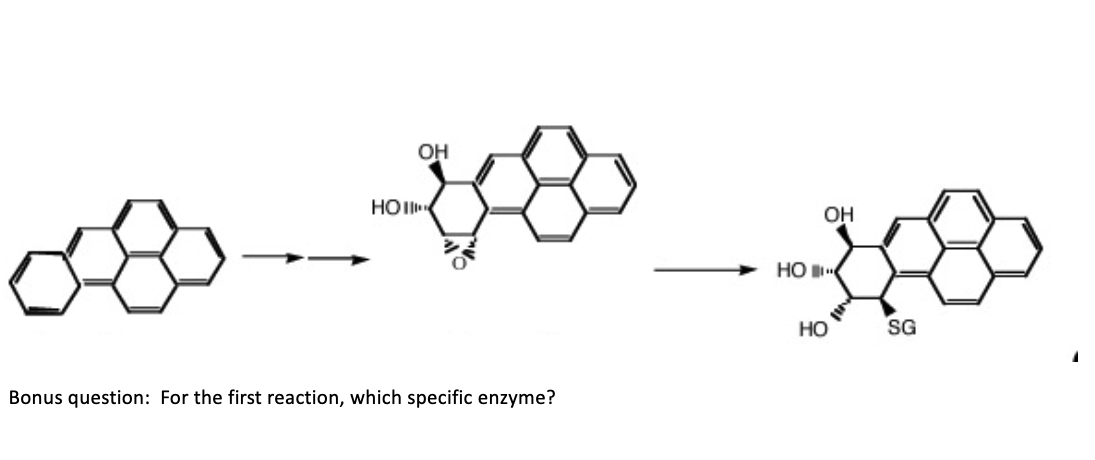
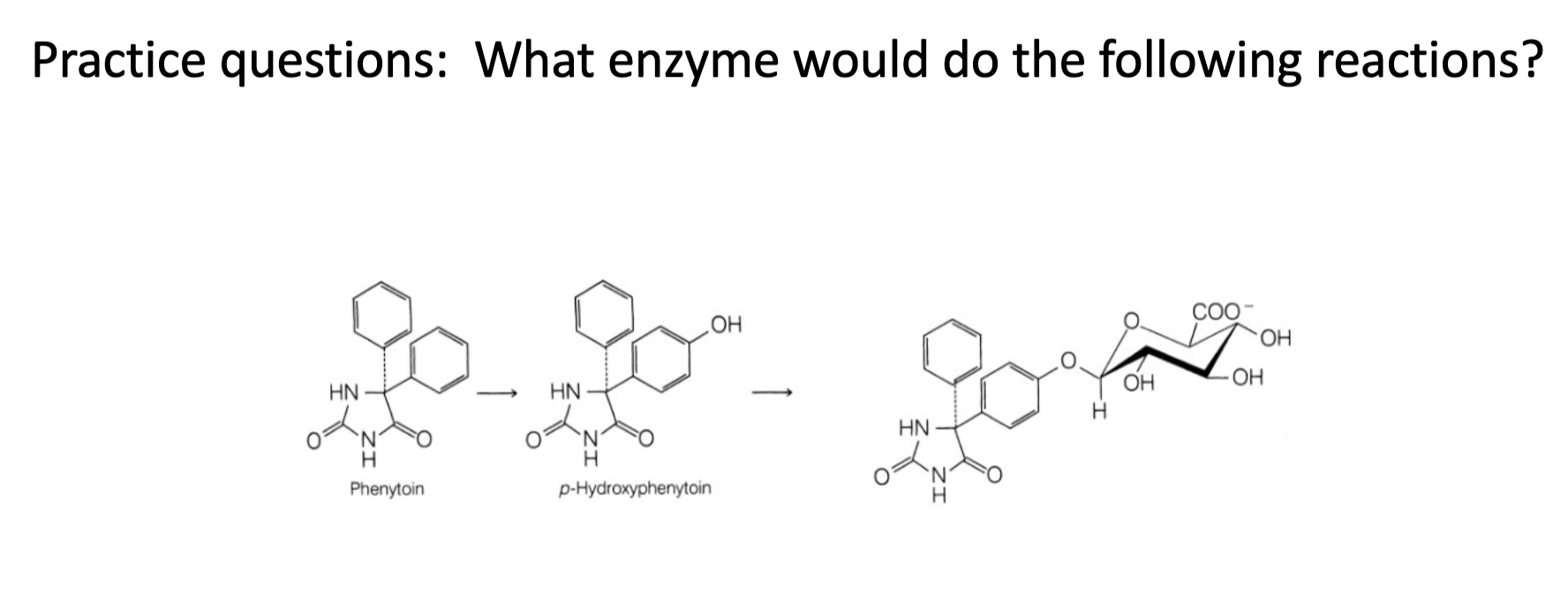
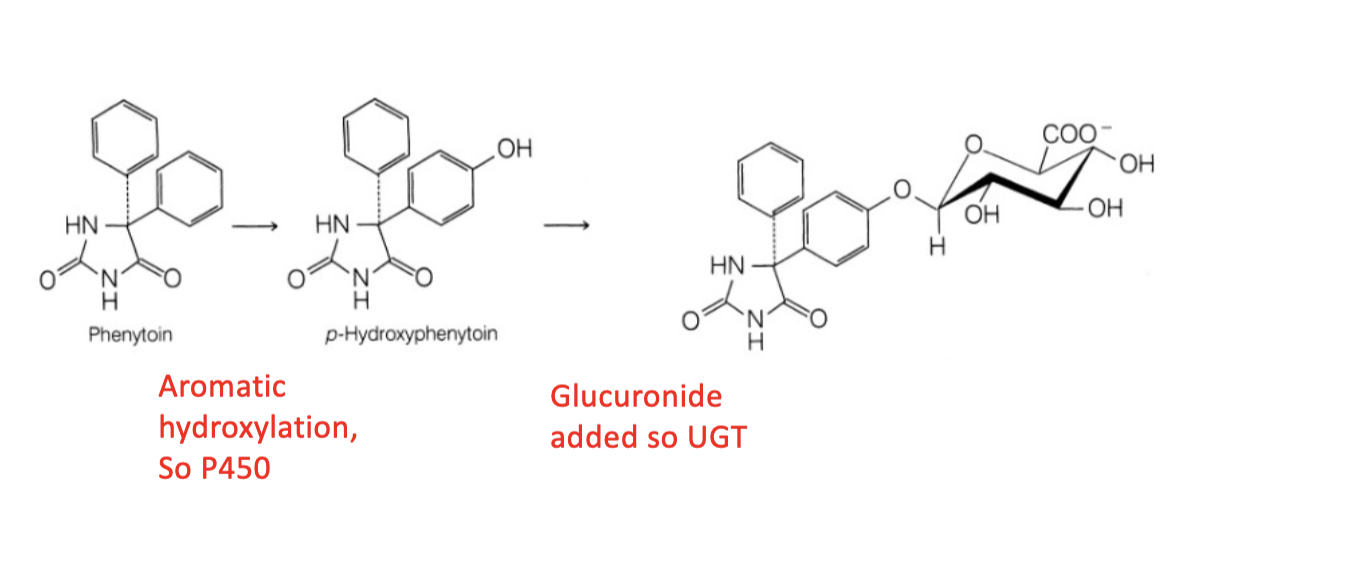
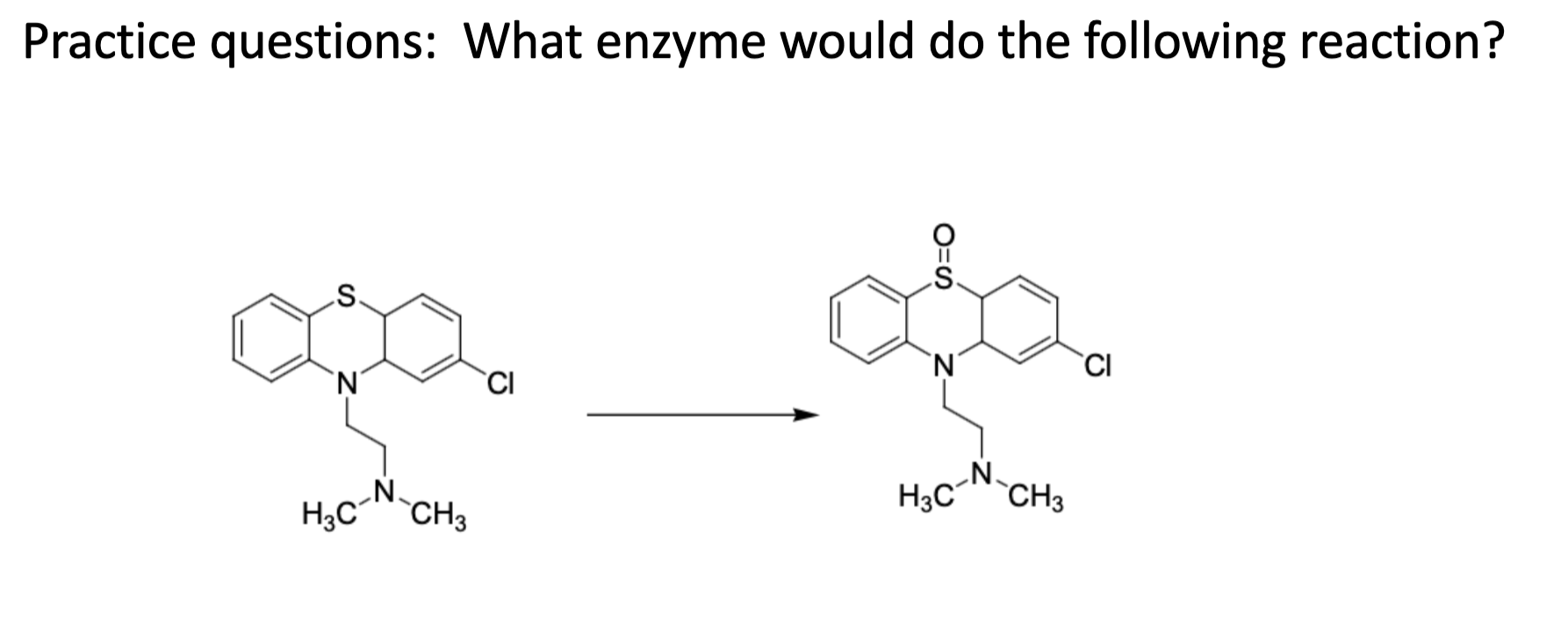
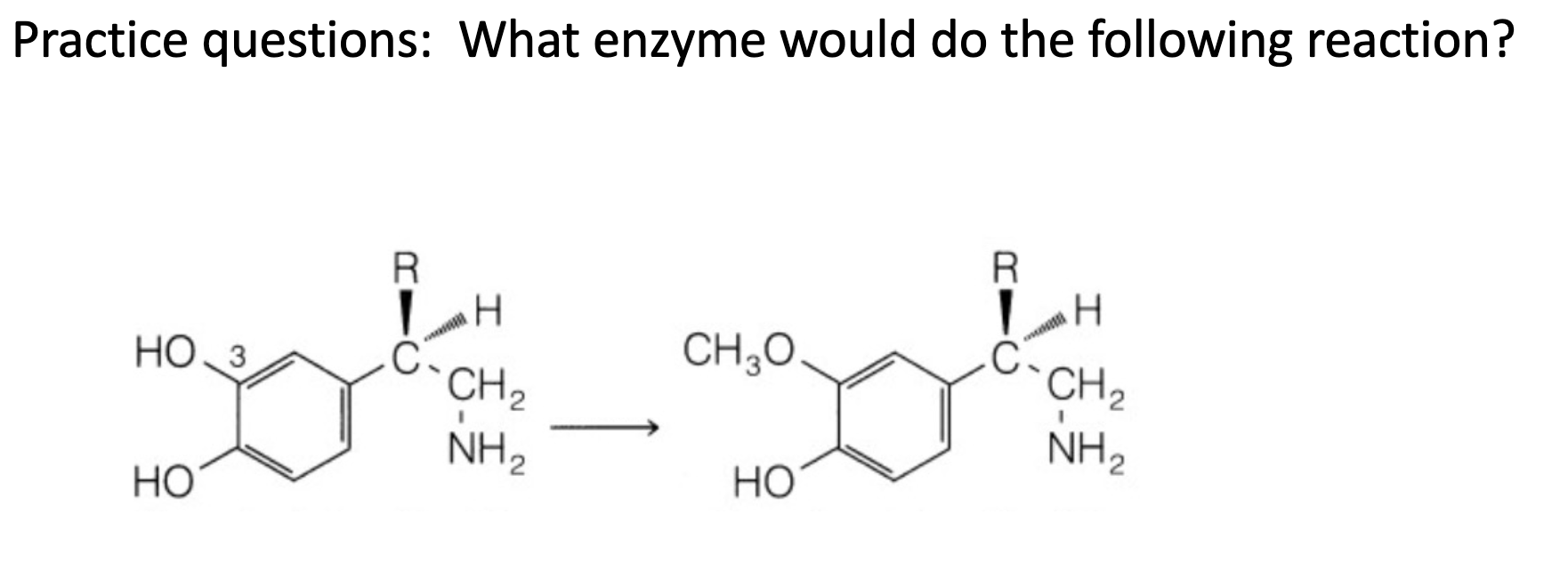
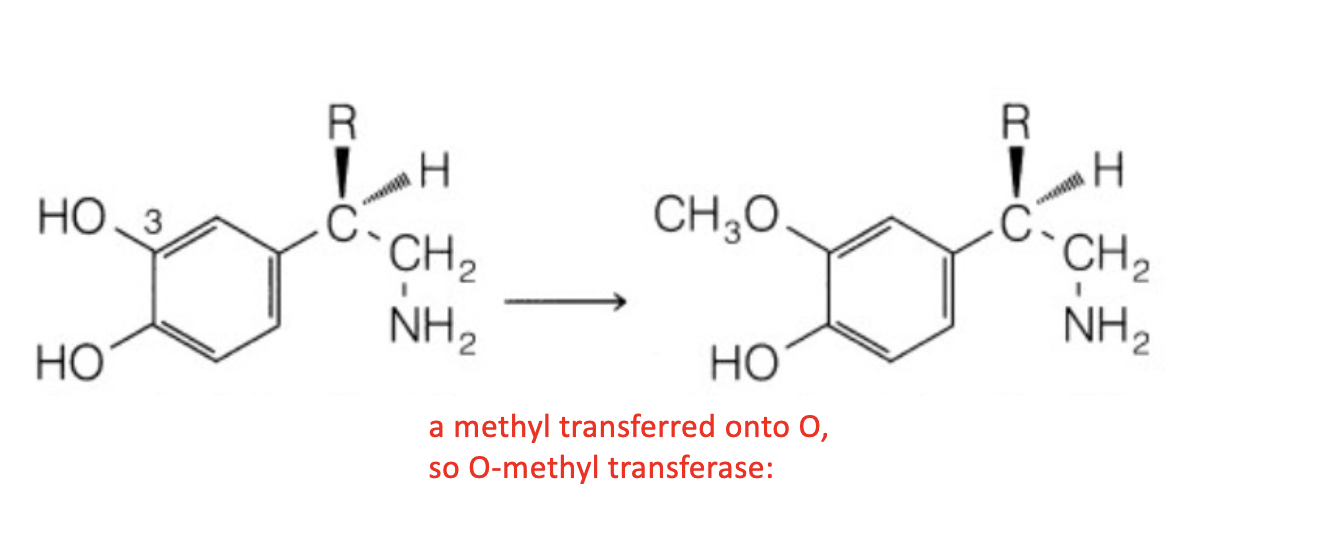
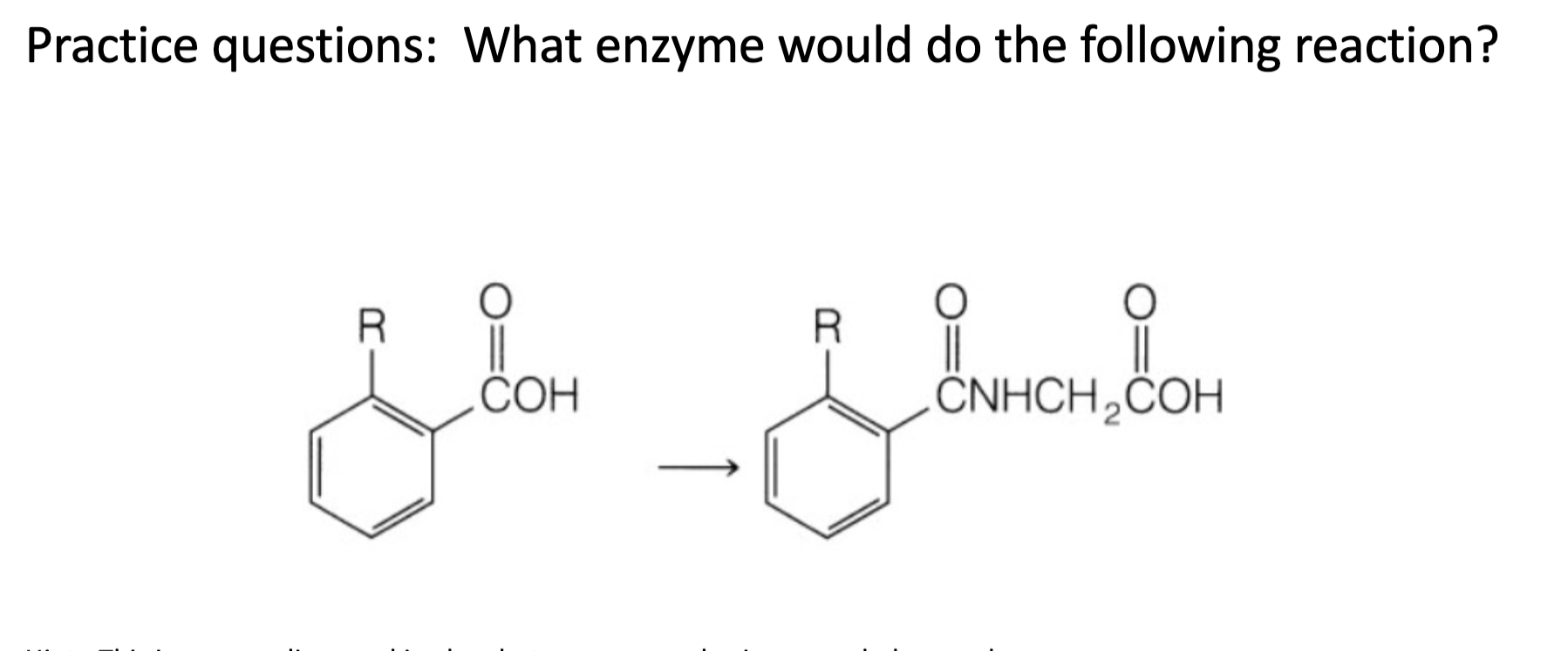
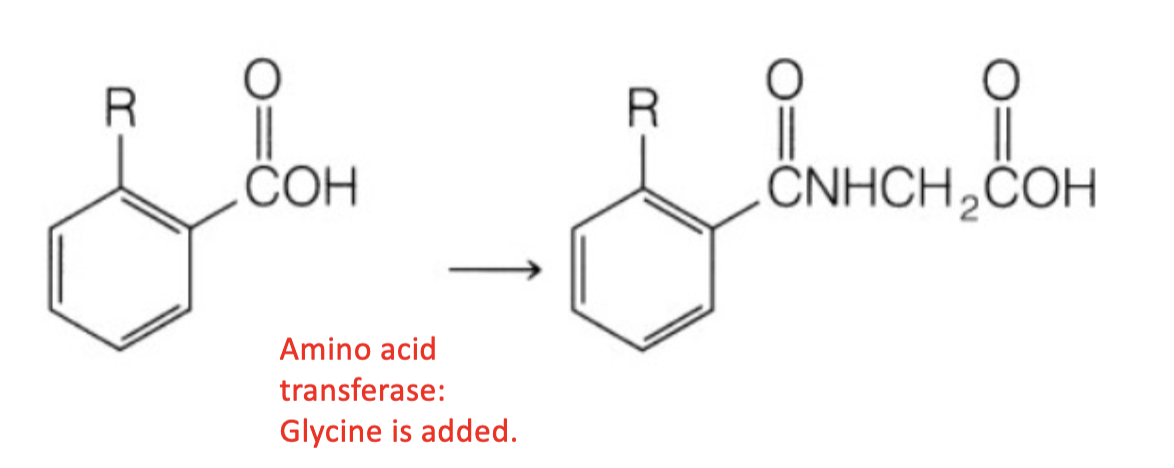
Name reaction and enzyme
Aromatic hydroxylation & CYP 450
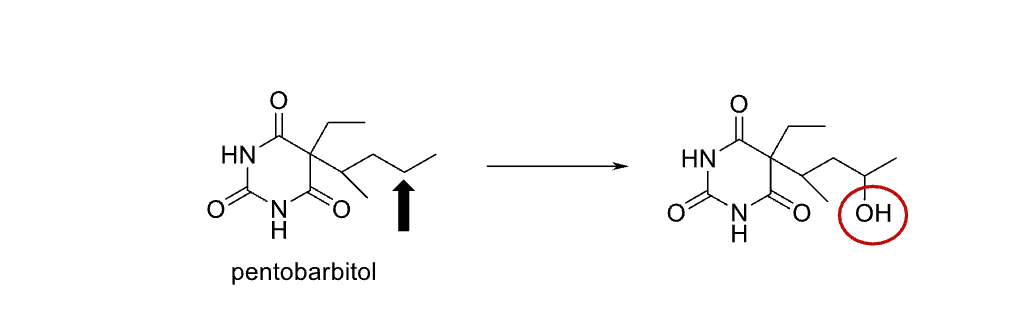
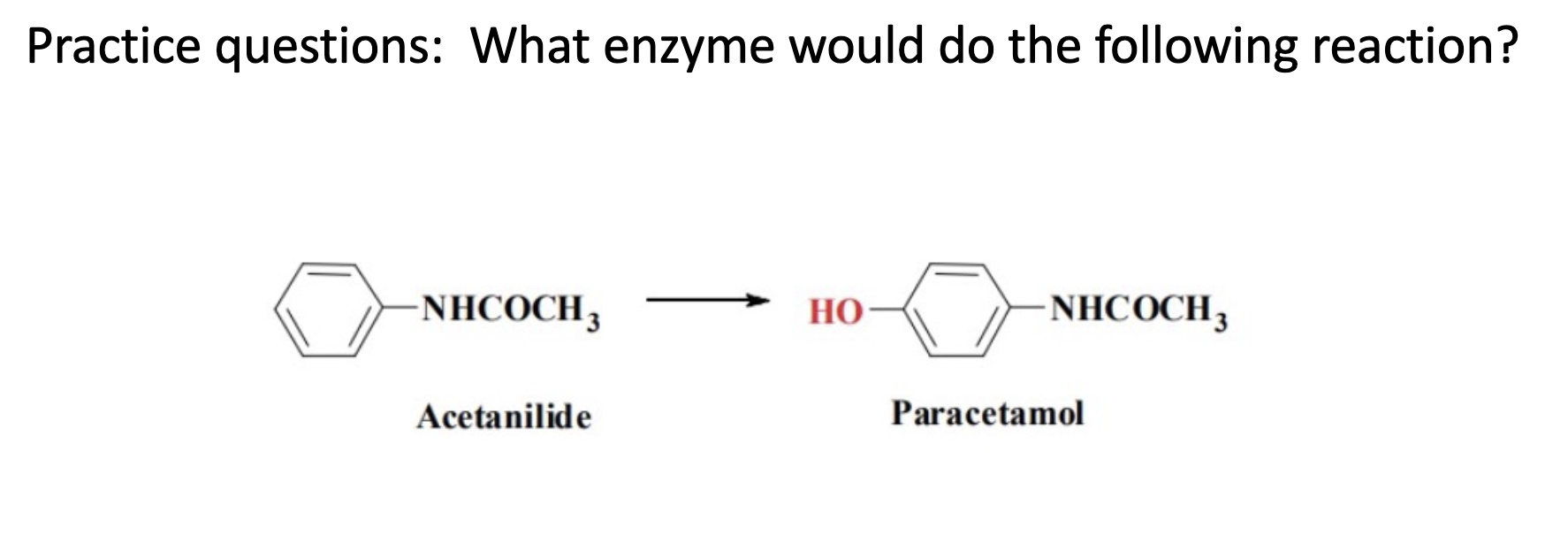
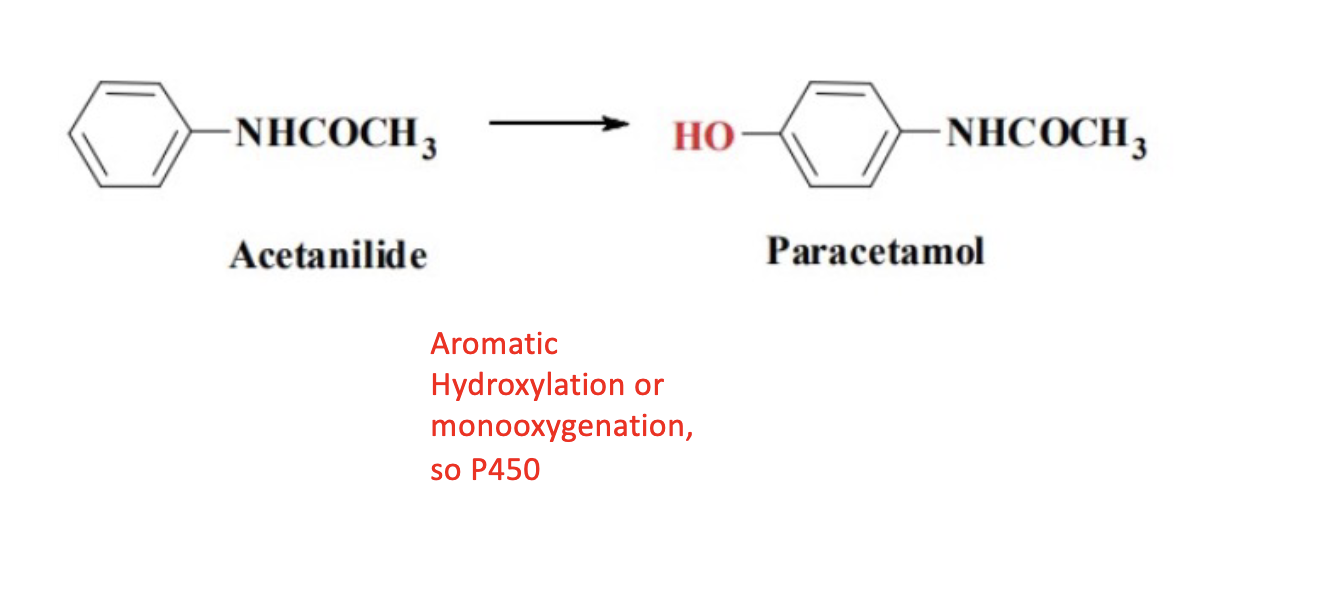
Name reaction and enzyme
Aliphatic Hydroxylation;CYP 450
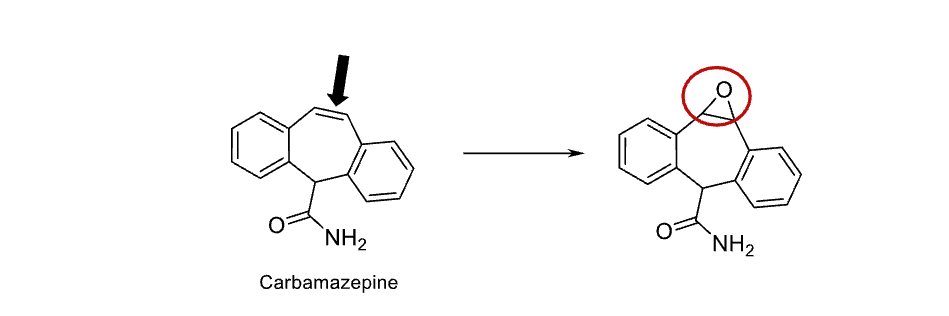
Name reaction and enzyme
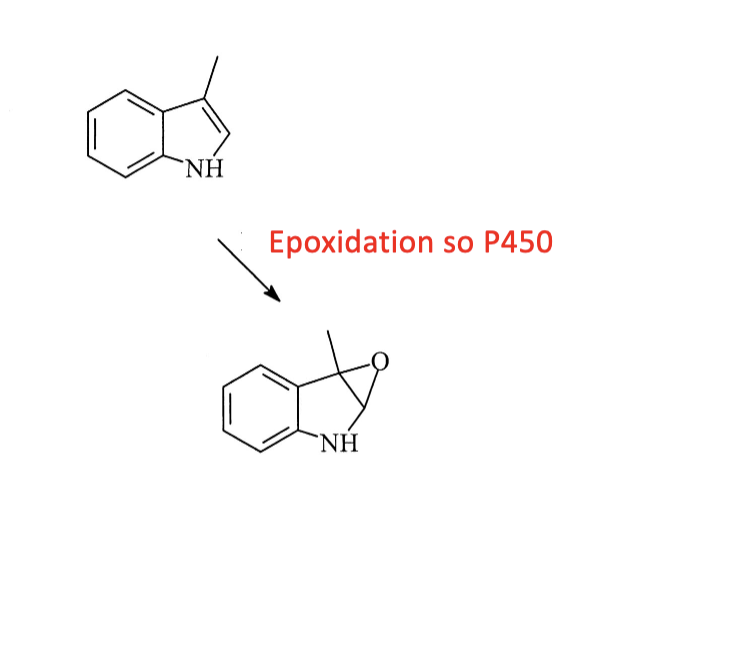
Epoxidation; CYP 450
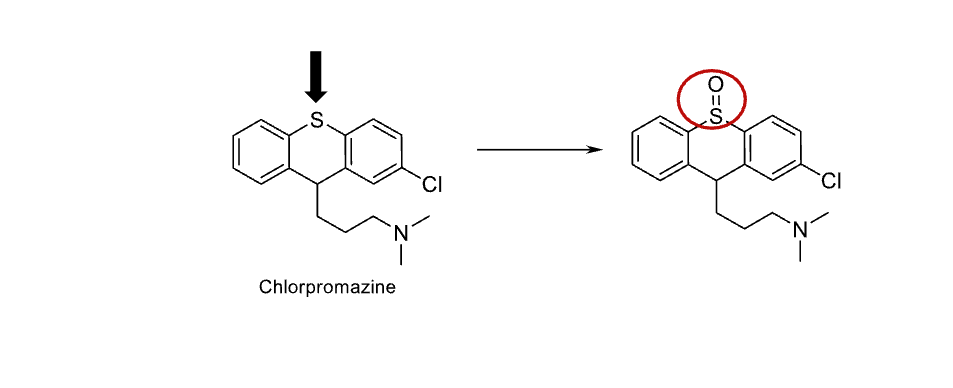
Name reaction and enzyme
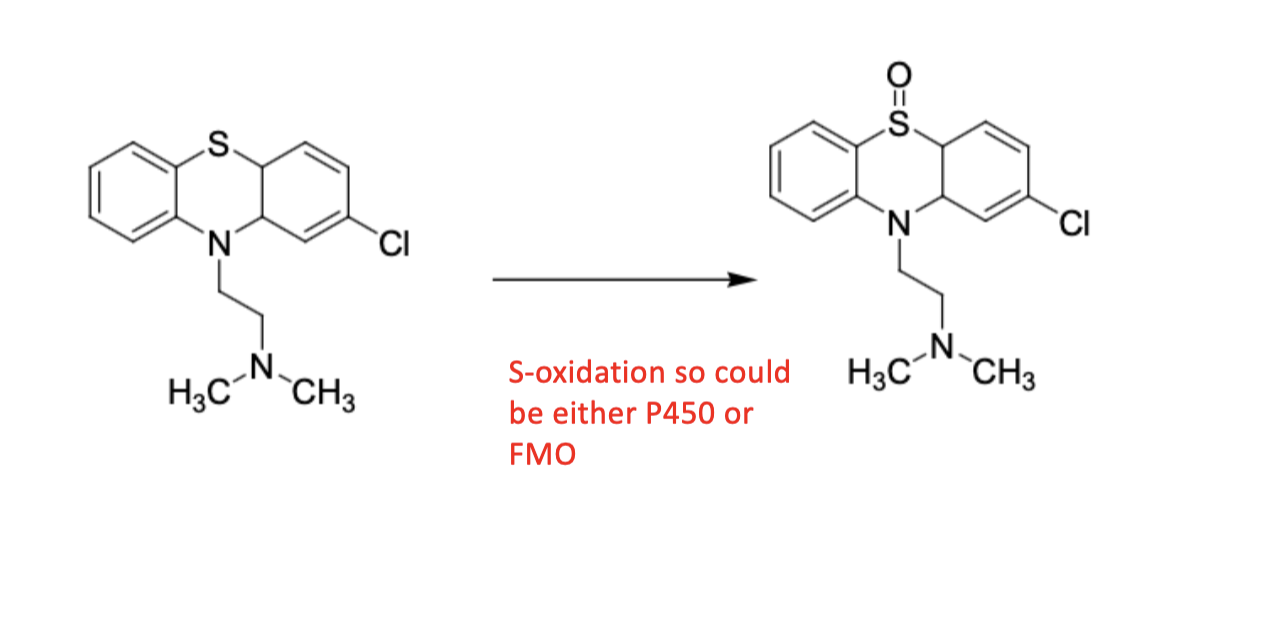
S-oxidation; CYP 450
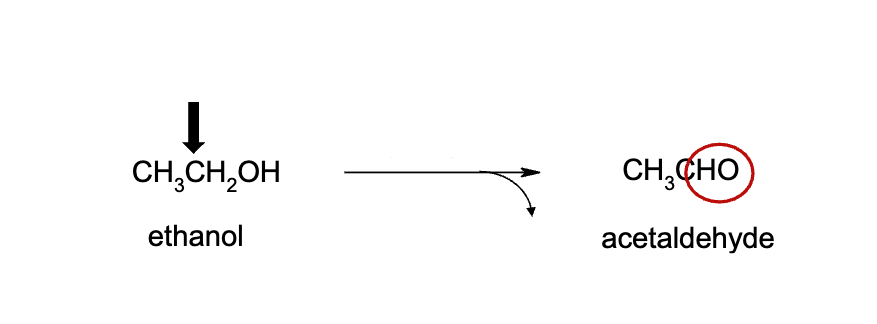
Name reaction and enzyme (Cofactor)
Alcohol Oxidation; alcohol dehydrogenase or CYP 450 & H2O as side product
Cofactor: NAD+
acetaldehyde
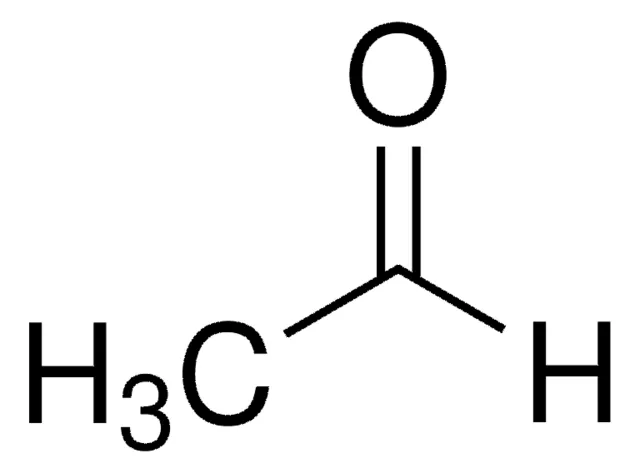
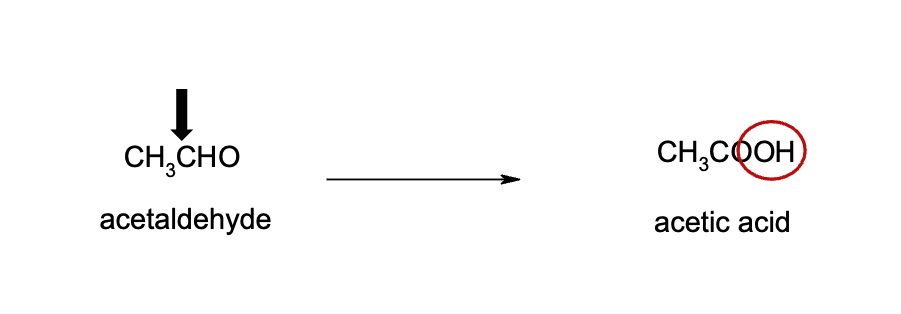
Name reaction and enzyme (Cofactor)
Aldehyde Oxidation; aldehyde dehydrogenase or CYP 450
Cofactor: NAD+
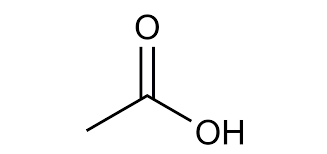
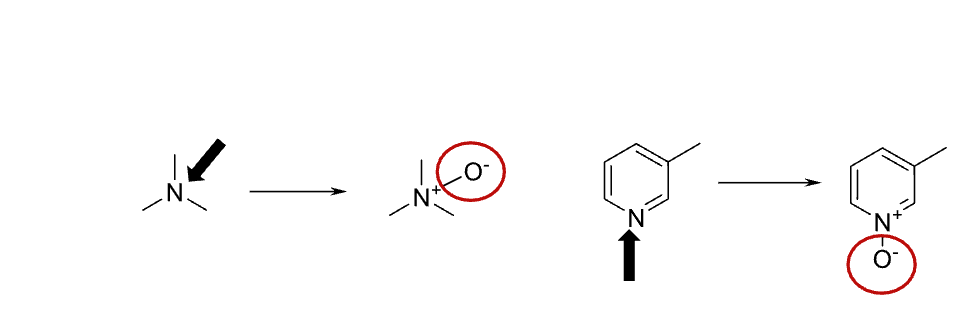
Name reaction and enzyme
N-oxidations; CYP 450 or FMO
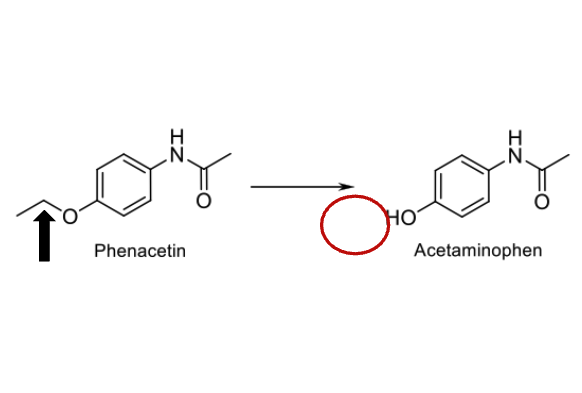
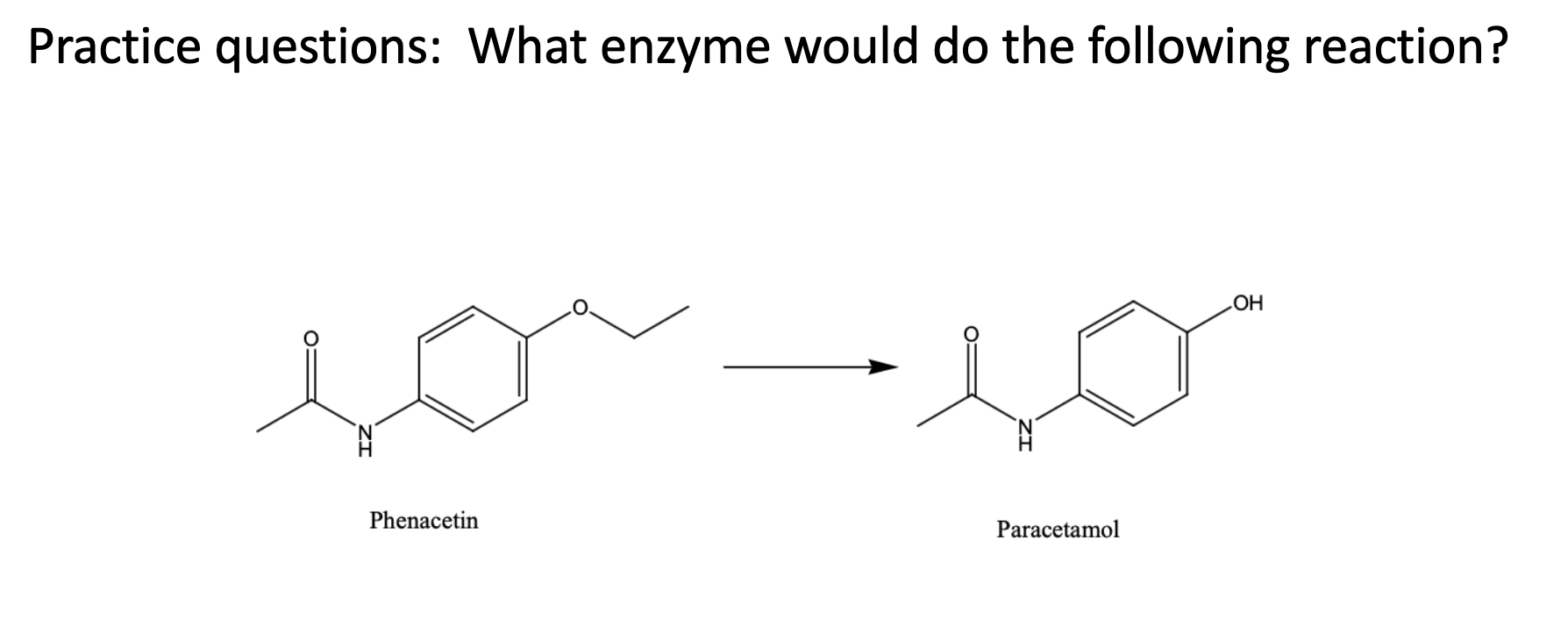
Name reaction and enzyme
O-dealkylation; cyp 450
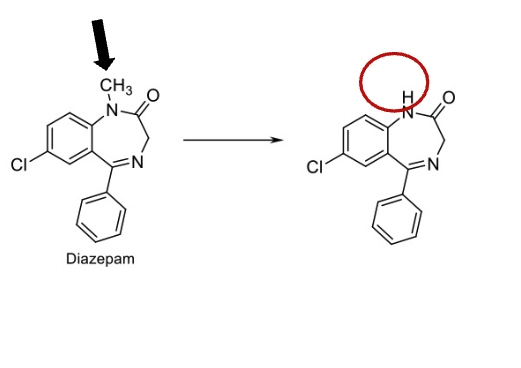
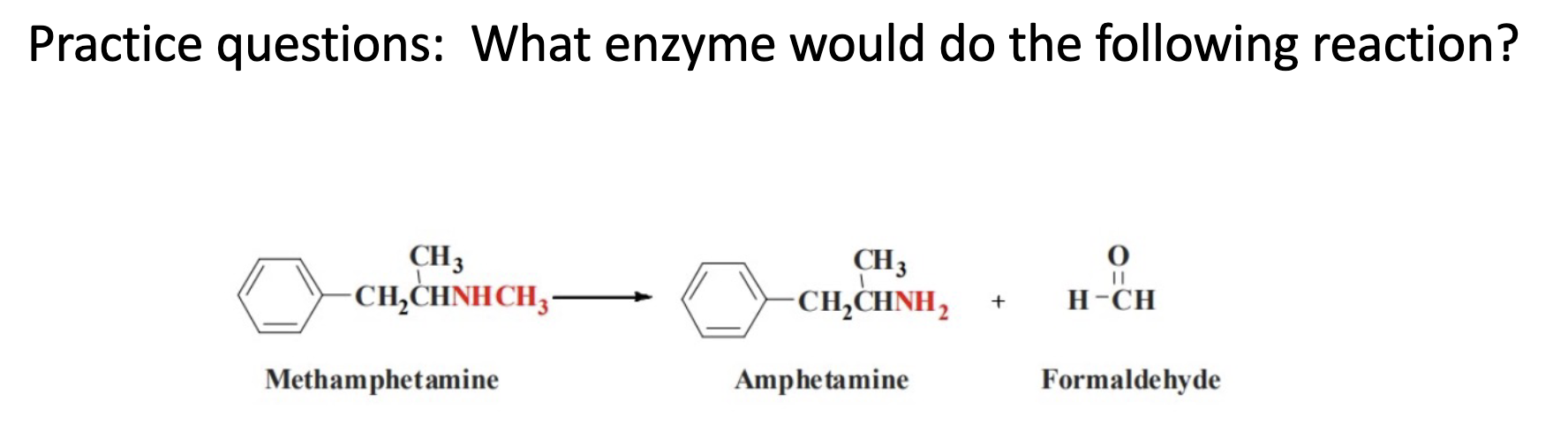
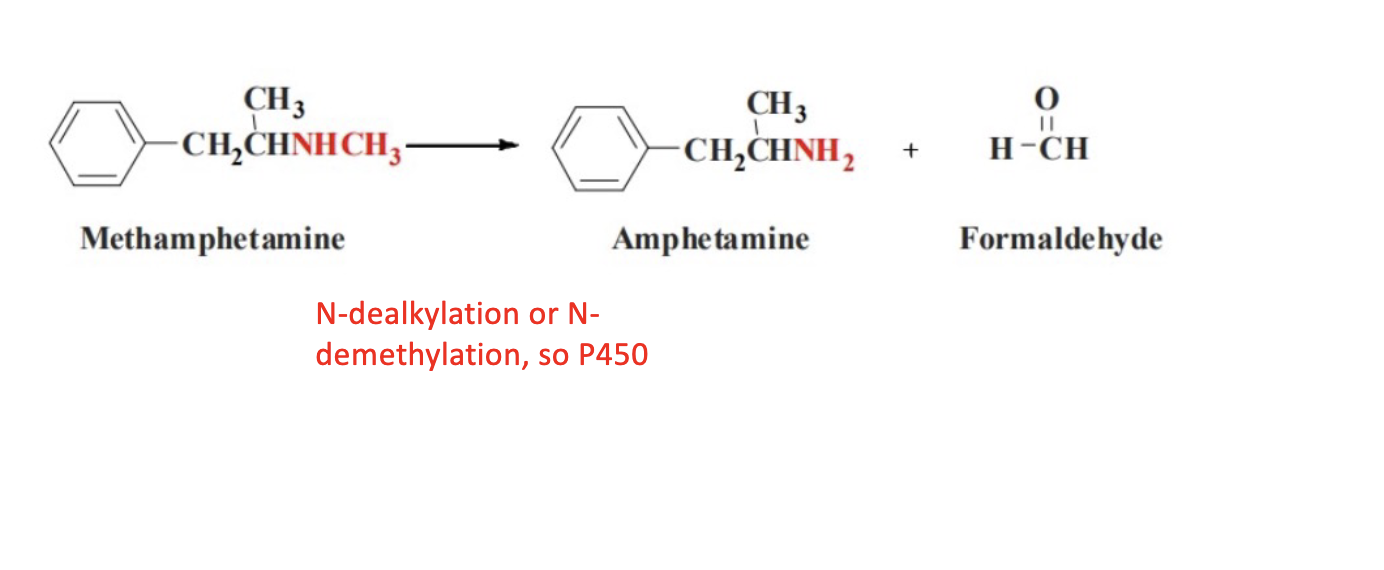
Name Reaction and Enzyme
N-dealkylation; cyp 450
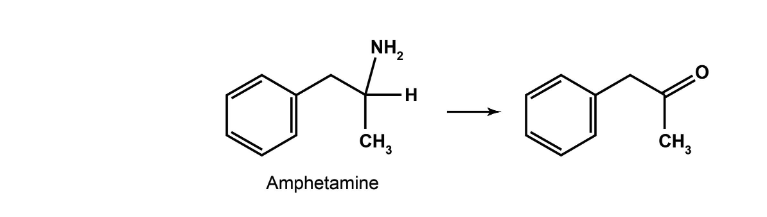
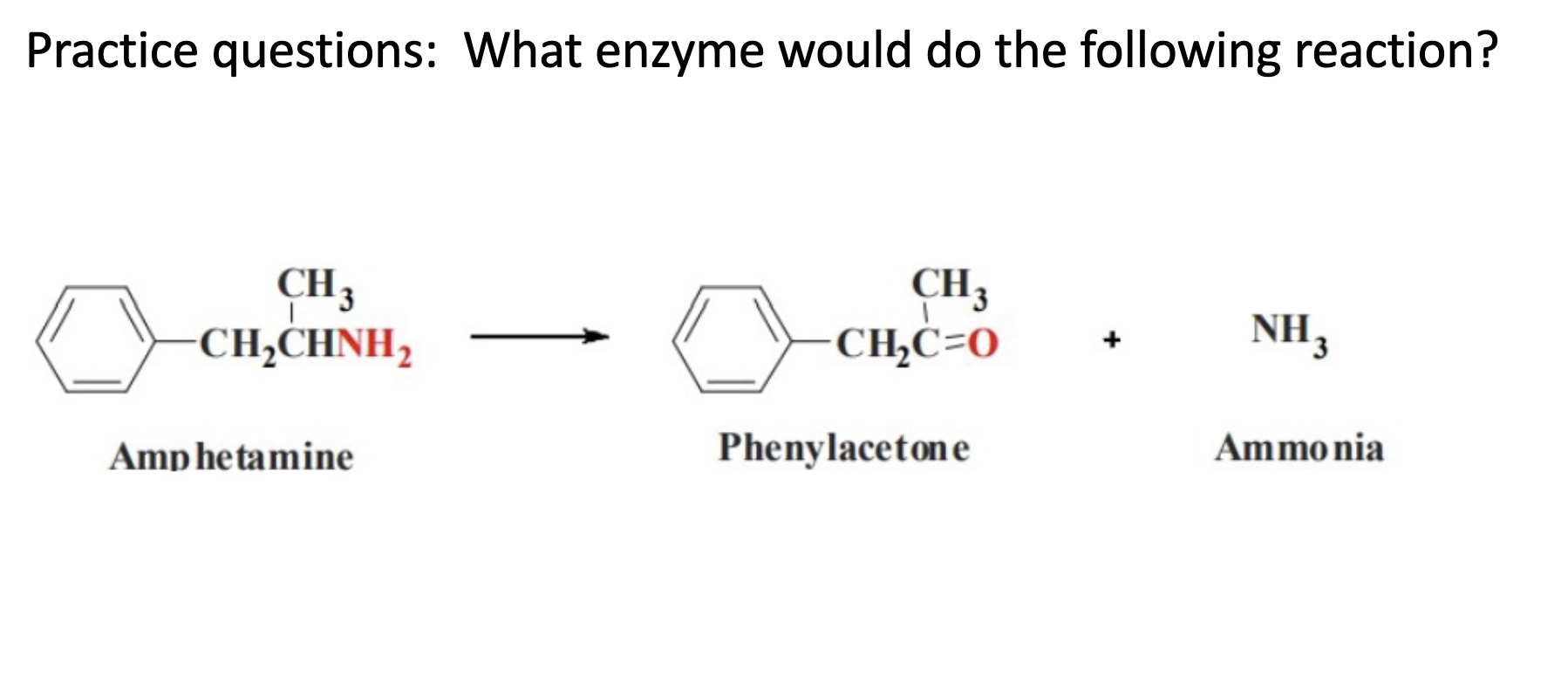
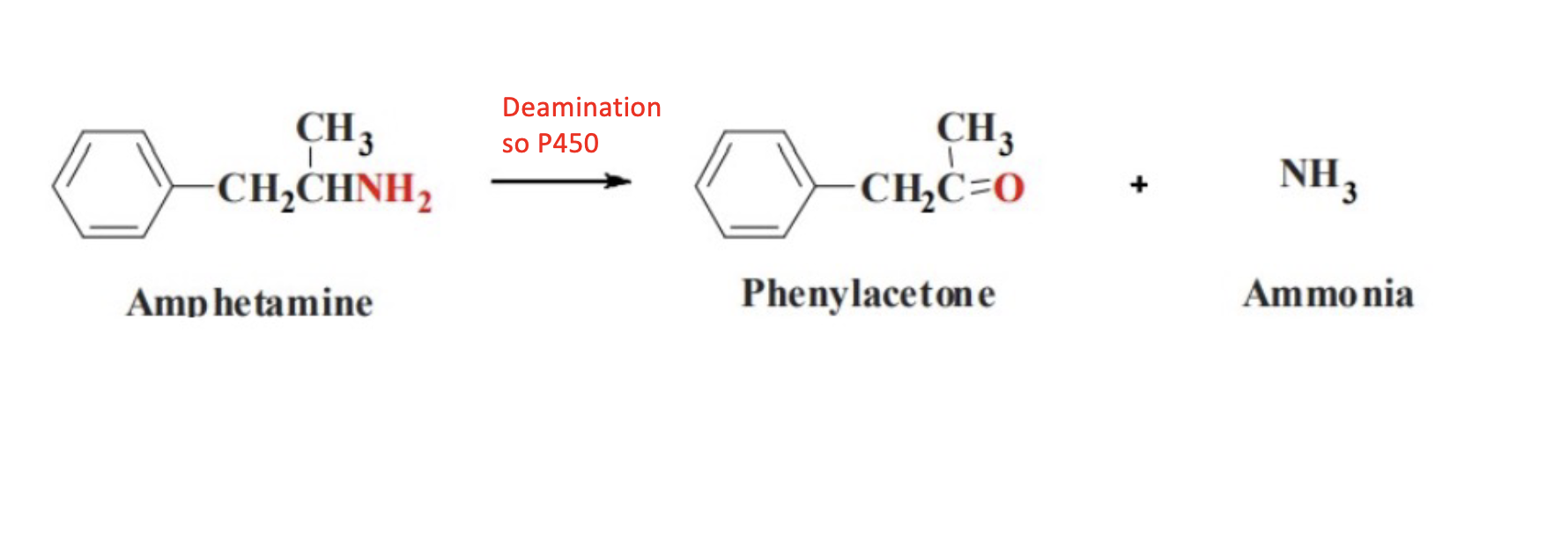
Name Reaction and Enzyme
Oxidative Deamination; CYP 2D6
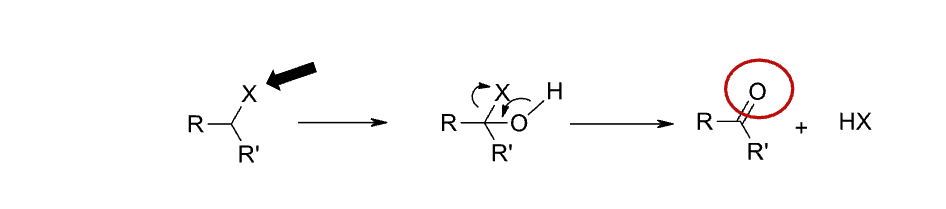
Name reaction and enzyme
Dehalogenation; CYP 450
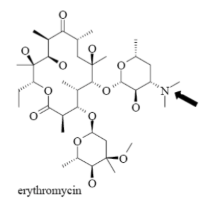
Name Enzyme
3A4: high volume, lipophilic, structurally diverse, 1-2 H bond donors/acceptors at 5.5-7.5 Å and 8-10 Å from the site of metabolism
numerous lipophilic Phe residues around the site of metabolism
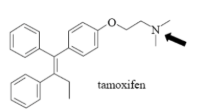
Name Enzyme
3A4: high volume, lipophilic, structurally diverse, 1-2 H bond donors/acceptors at 5.5-7.5 Å and 8-10 Å from the site of metabolism
numerous lipophilic Phe residues around the site of metabolism
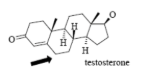
Name Enzyme
3A4: high volume, lipophilic, structurally diverse, 1-2 H bond donors/acceptors at 5.5-7.5 Å and 8-10 Å from the site of metabolism
numerous lipophilic Phe residues around the site of metabolism
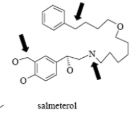
Name Enzyme
3A4: high volume, lipophilic, structurally diverse, 1-2 H bond donors/acceptors at 5.5-7.5 Å and 8-10 Å from the site of metabolism
numerous lipophilic Phe residues around the site of metabolism
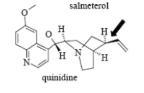
Name Enzyme
3A4: high volume, lipophilic, structurally diverse, 1-2 H bond donors/acceptors at 5.5-7.5 Å and 8-10 Å from the site of metabolism
numerous lipophilic Phe residues around the site of metabolism
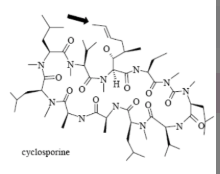
Name Enzyme
3A4: high volume, lipophilic, structurally diverse, 1-2 H bond donors/acceptors at 5.5-7.5 Å and 8-10 Å from the site of metabolism
numerous lipophilic Phe residues around the site of metabolism
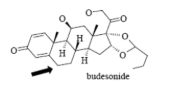
Name Enzyme
3A4: high volume, lipophilic, structurally diverse, 1-2 H bond donors/acceptors at 5.5-7.5 Å and 8-10 Å from the site of metabolism
numerous lipophilic Phe residues around the site of metabolism
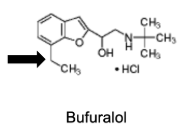
Name Enzyme
2D6: away from basic (nitrogen), relatively hydrophilic, a H-bond donor/acceptor at 5-7 A from site of metabolism
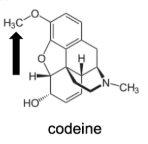
Name Enzyme
2D6: away from basic (nitrogen), relatively hydrophilic, a H-bond donor/acceptor at 5-7 A from site of metabolism
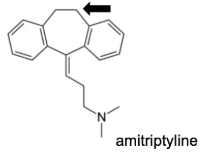
Name Enzyme
2D6: away from basic (nitrogen), relatively hydrophilic, a H-bond donor/acceptor at 5-7 A from site of metabolism
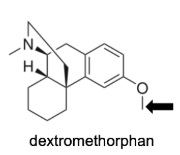
Name Enzyme
2D6: away from basic (nitrogen), relatively hydrophilic, a H-bond donor/acceptor at 5-7 A from site of metabolism
Most CYP2D6 substrates are characterized by a basic nitrogen atom located approximately 5 to 7 Å from the site of oxidation.
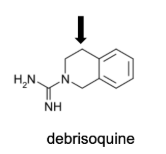
Name Enzyme
2D6: away from basic (nitrogen), relatively hydrophilic, a H-bond donor/acceptor at 5-7 A from site of metabolism
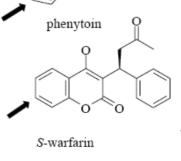
Name Enzyme
2C9: weakly acidic, lipophilic, 1 or 2 H-bond donor/acceptor at 5-8 Å from the site of metabolism
Interact with COO- /COOH
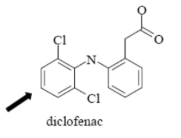
Name Enzyme
2C9: weakly acidic, lipophilic, 1 or 2 H-bond donor/acceptor at 5-8 Å from the site of metabolism
Interact with COO- /COOH
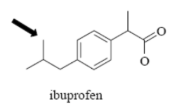
Name Enzyme
2C9: weakly acidic, lipophilic, 1 or 2 H-bond donor/acceptor at 5-8 Å from the site of metabolism
Interact with COO- /COOH
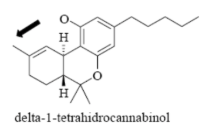
Name Enzyme
2C9: weakly acidic, lipophilic, 1 or 2 H-bond donor/acceptor at 5-8 Å from the site of metabolism
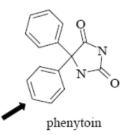
Name Enzyme
2C9: weakly acidic, lipophilic, 1 or 2 H-bond donor/acceptor at 5-8 Å from the site of metabolism
imide group (two carbonyl stabilize the molecule, resulting more acidic than amide)
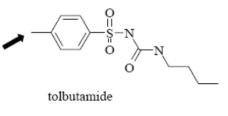
Name Enzyme
2C9: weakly acidic, lipophilic, 1 or 2 H-bond donor/acceptor at 5-8 Å from the site of metabolism
Electron-withdrawing effect of the sulfonyl group: A sulfonyl group contains two oxygen atoms, which are highly electronegative. This creates a strong electron-withdrawing effect
Name Enzyme and Reaction
Aromatic Hydroxylation; CYP 2D6
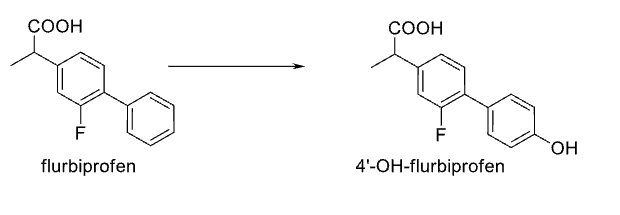
Name Enzyme and Reaction
Aromatic Hydroxylation; CYP 2C9
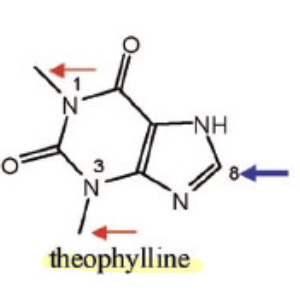
Name Enzyme
1A2: planar aromatic and/or heterocyclic amines and amides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, neutral or basic, lipophilic, preferably with one H-bond donor (XH) group
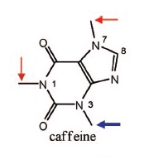
Name Enzyme
1A2: planar aromatic and/or heterocyclic amines and amides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, neutral or basic, lipophilic, preferably with one H-bond donor (XH) groupv
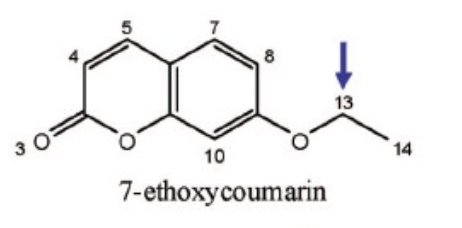
Name Enzyme
1A2: planar aromatic and/or heterocyclic amines and amides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, neutral or basic, lipophilic, preferably with one H-bond donor (XH) group
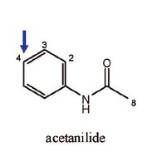
Name Enzyme
1A2: planar aromatic and/or heterocyclic amines and amides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, neutral or basic, lipophilic, preferably with one H-bond donor (XH) group
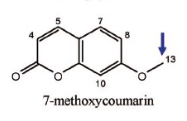
Name Enzyme
1A2: planar aromatic and/or heterocyclic amines and amides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, neutral or basic, lipophilic, preferably with one H-bond donor (XH) group
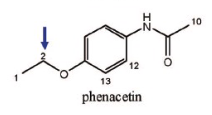
Name Enzyme
1A2: planar aromatic and/or heterocyclic amines and amides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, neutral or basic, lipophilic, preferably with one H-bond donor (XH) group
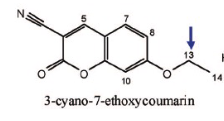
Name Enzyme
1A2: planar aromatic and/or heterocyclic amines and amides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, neutral or basic, lipophilic, preferably with one H-bond donor (XH) group
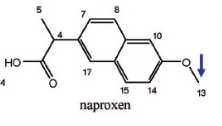
Name Enzyme
1A2: planar aromatic and/or heterocyclic amines and amides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, neutral or basic, lipophilic, preferably with one H-bond donor (XH) group
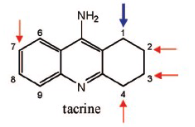
Name Enzyme
1A2: planar aromatic and/or heterocyclic amines and amides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, neutral or basic, lipophilic, preferably with one H-bond donor (XH) group
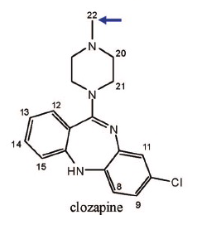
Name Enzyme
1A2: planar aromatic and/or heterocyclic amines and amides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, neutral or basic, lipophilic, preferably with one H-bond donor (XH) group
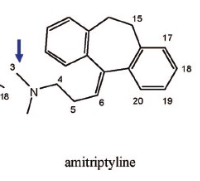
Name Enzyme
1A2: planar aromatic and/or heterocyclic amines and amides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, neutral or basic, lipophilic, preferably with one H-bond donor (XH) group
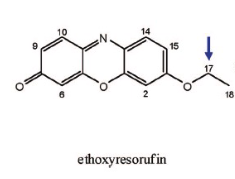
Name Enzyme
1A2: planar aromatic and/or heterocyclic amines and amides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, neutral or basic, lipophilic, preferably with one H-bond donor (XH) group
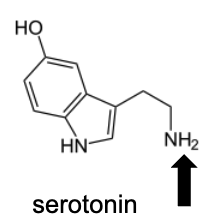
Name Enzyme
MAO: monoamine oxidase ; neurotransmitter
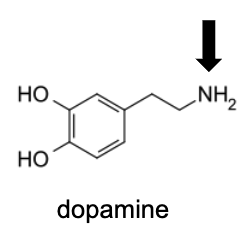
Name Enzyme
MAO: monoamine oxidase ; neurotransmitter
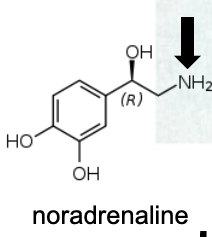
Name Enzyme
MAO: monoamine oxidase ; neurotransmitter
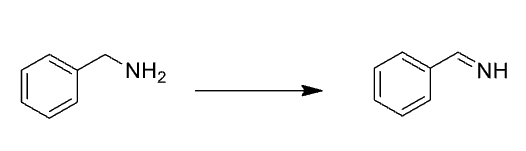
Name Enzyme
MAO: monoamine oxidase ; neurotransmitter
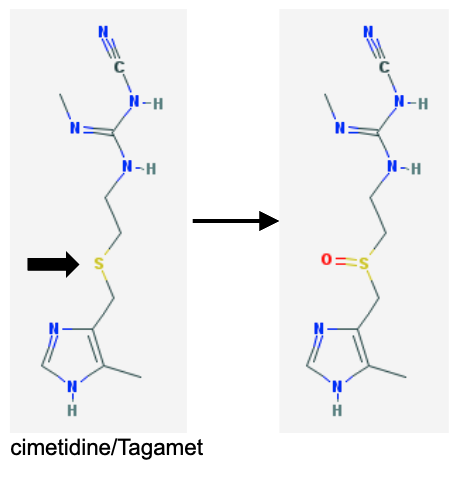
Name Enzyme
FMO: Flavin monooxygenase
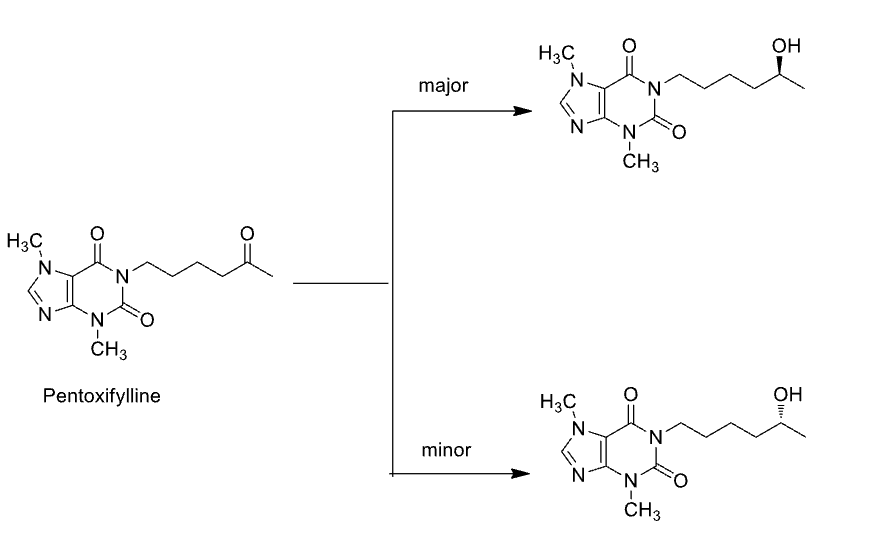
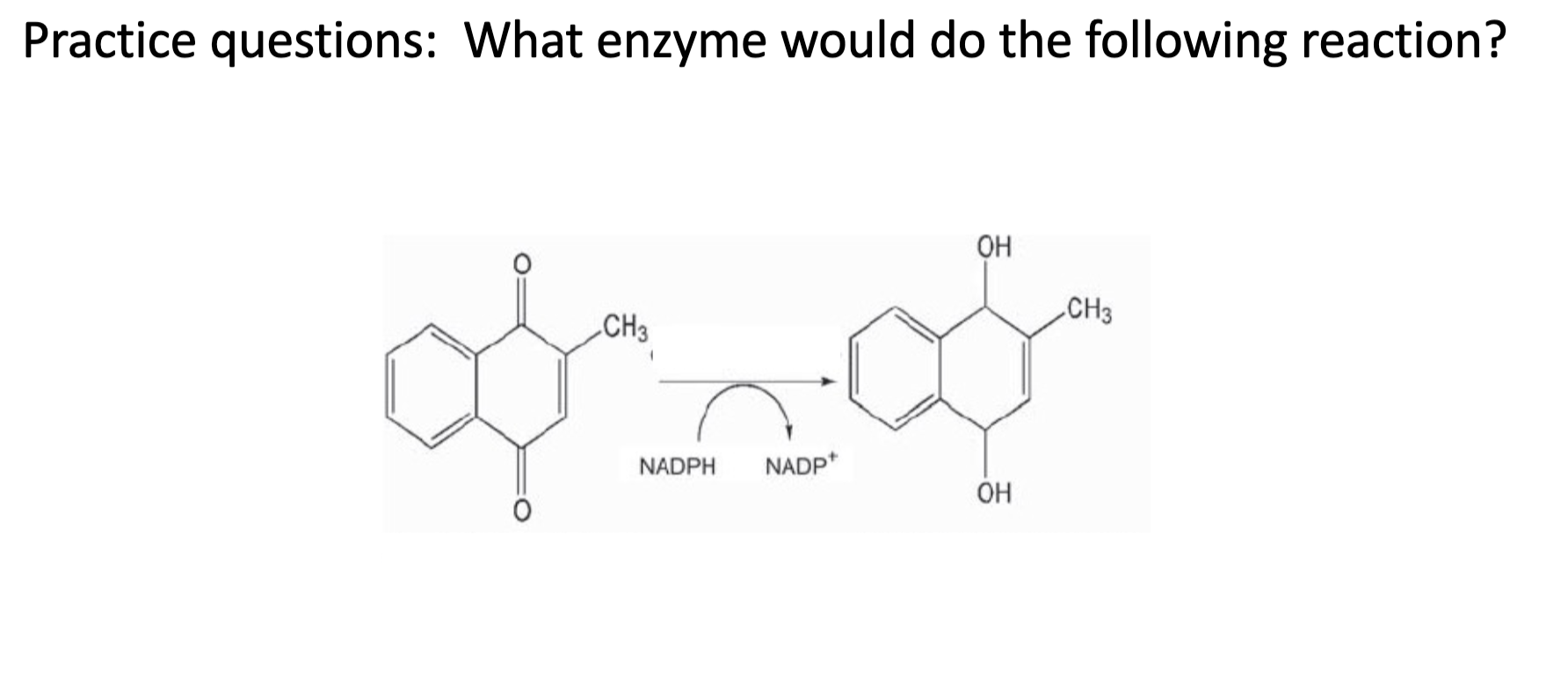
Name Enzyme
Carbonyl Reductase (carbonyl to OH)
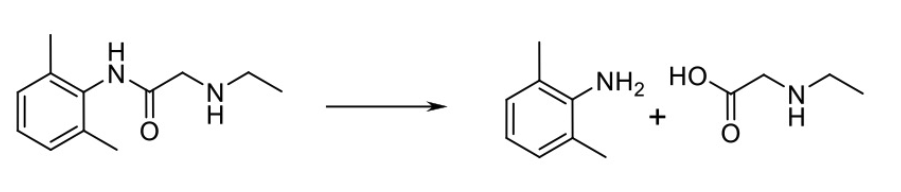
Name Enzyme
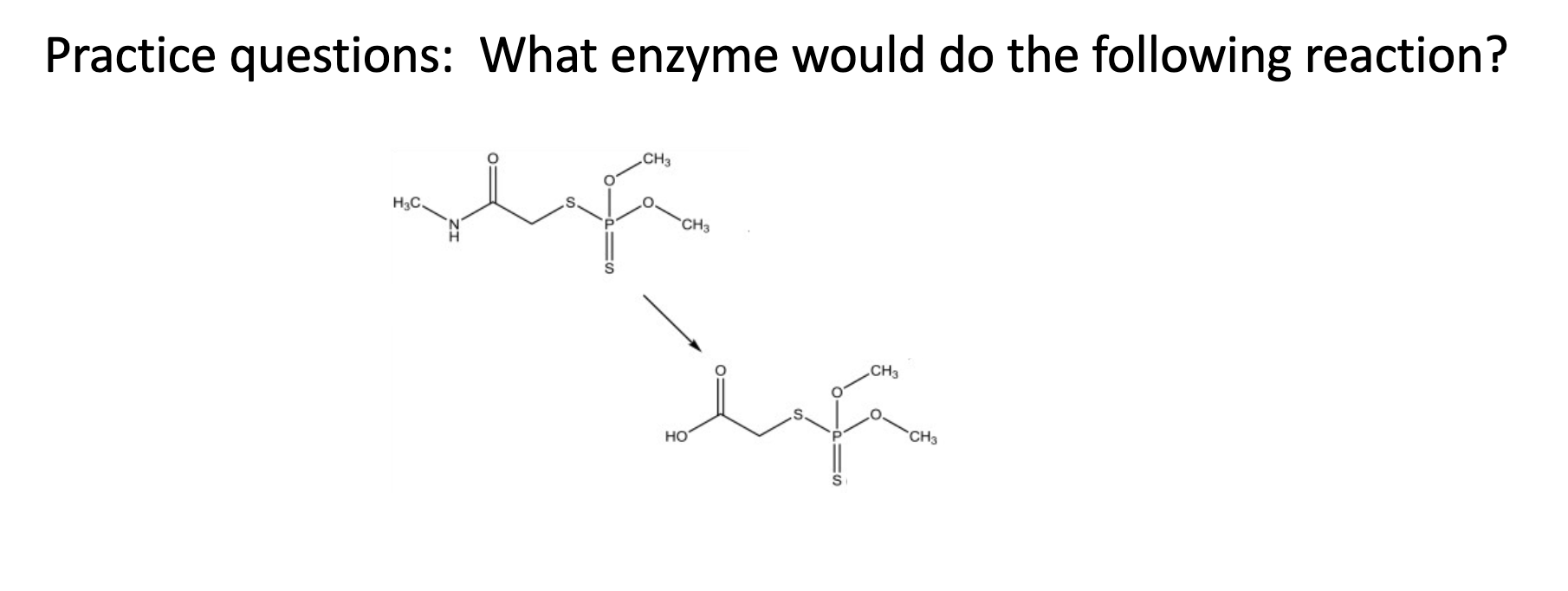
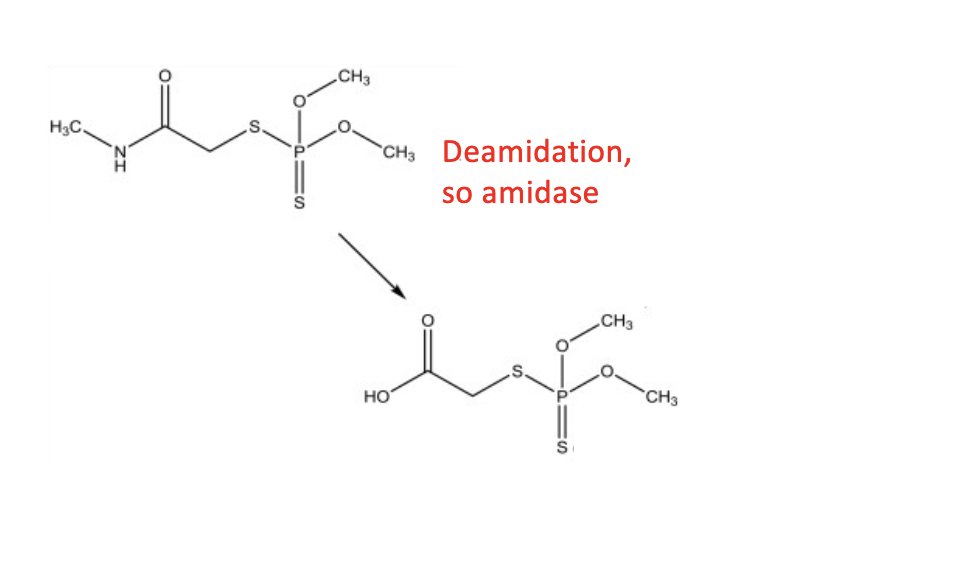
amidase (amine to carboxylic acid
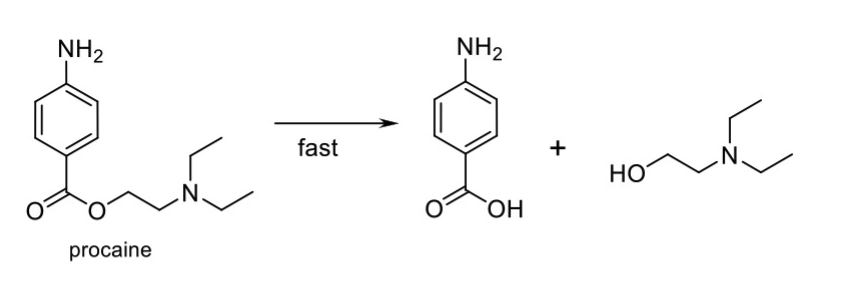
Name Enzyme
Esterase (ester to carboxylic acid and amides)
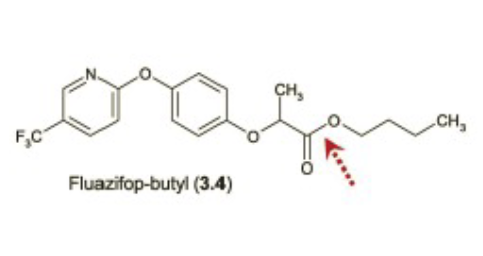
Name Enzyme
Carboxylic Esterase (carboxylic acid)
Overlapping substrate specificities (i.e. fairly promiscuous)
• Ubiquitously expressed
• Commonly counted on to convert prodrugs to active drugs
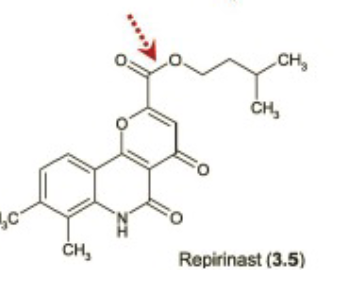
Name Enzyme
Carboxylic Esterase (carboxylic acid)
Overlapping substrate specificities (i.e. fairly promiscuous)
• Ubiquitously expressed
• Commonly counted on to convert prodrugs to active drugs
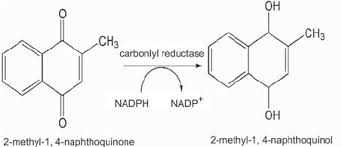
Name Enzyme
Carbonyl Reductase ( carbonyl to OH)
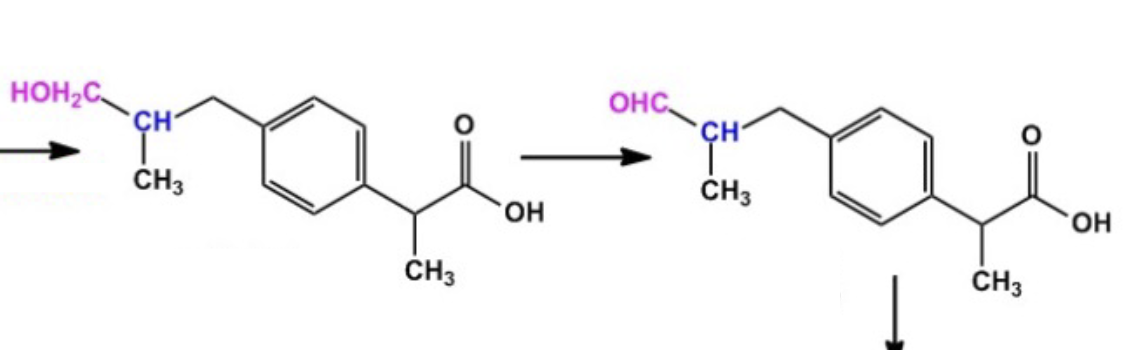
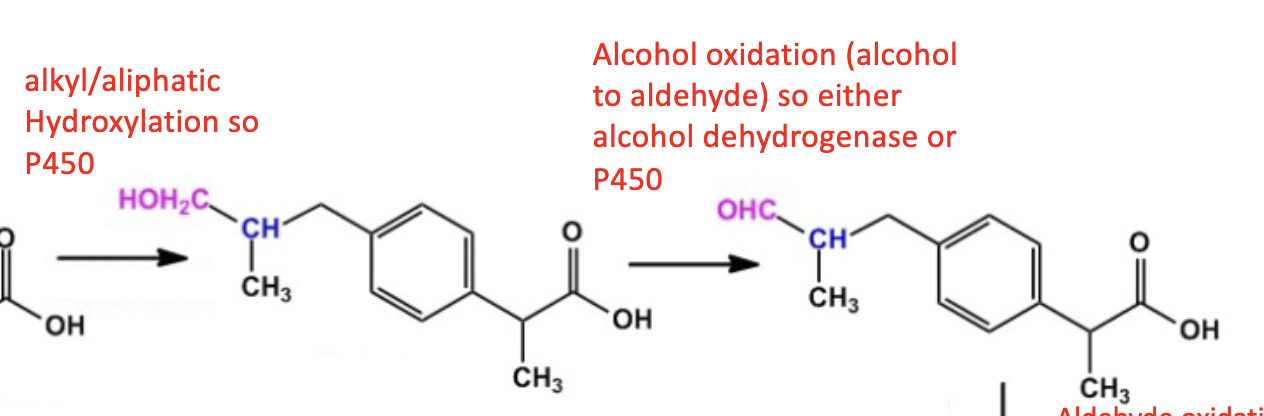
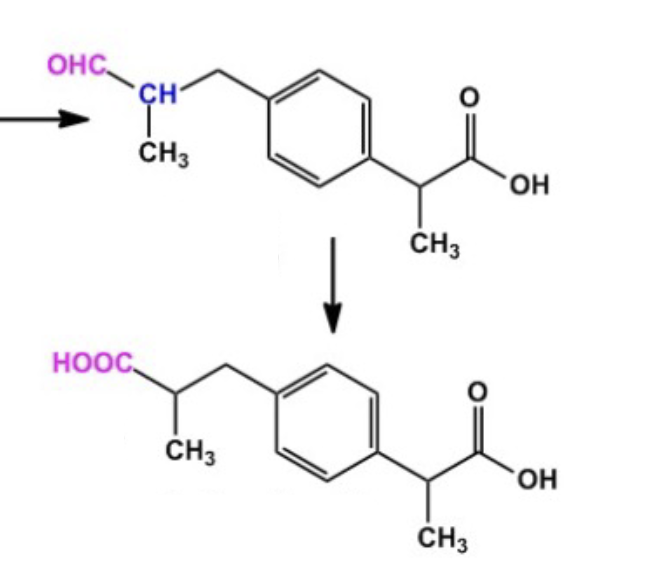
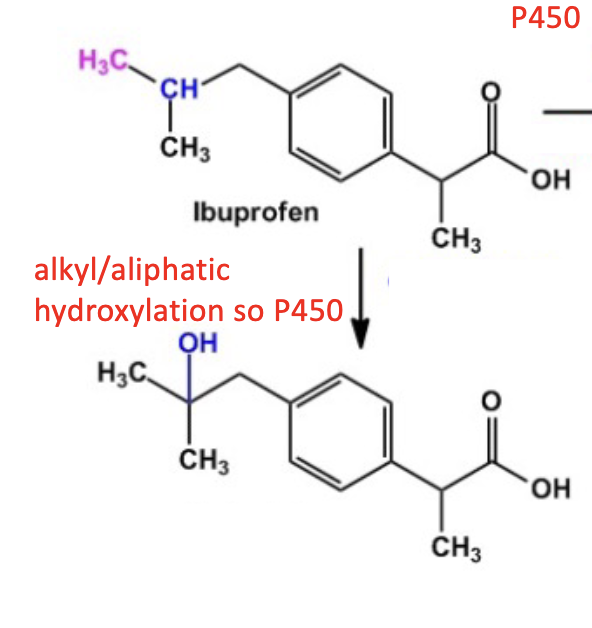
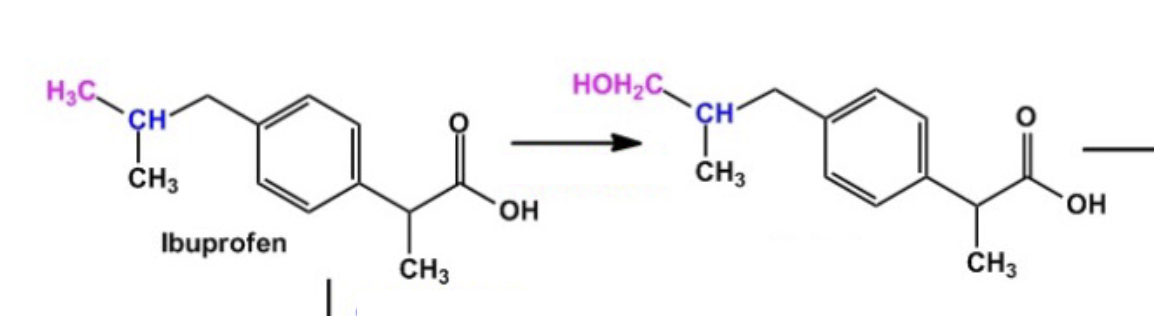
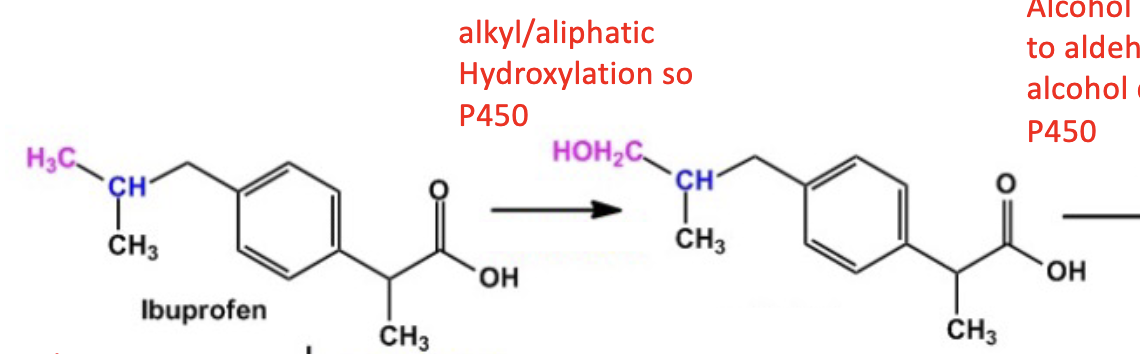
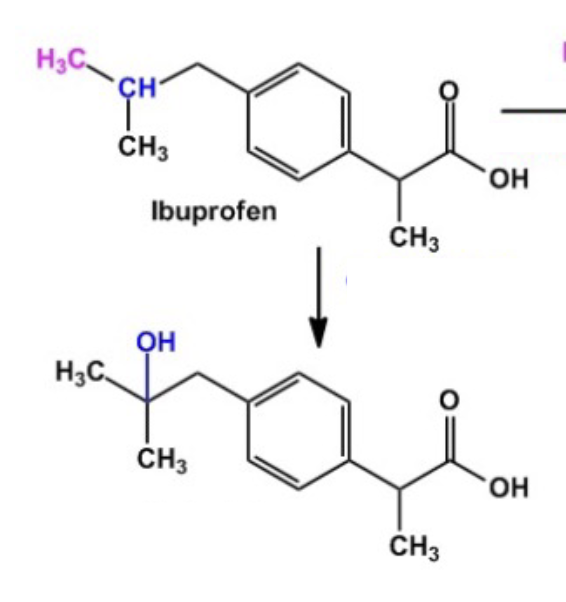
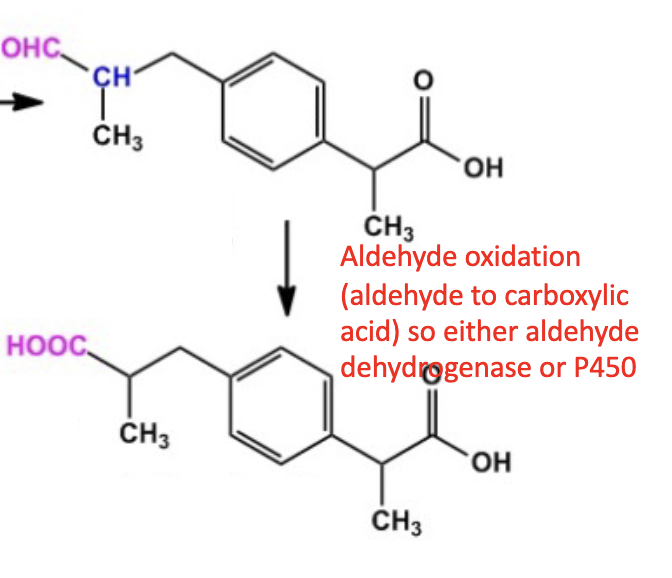
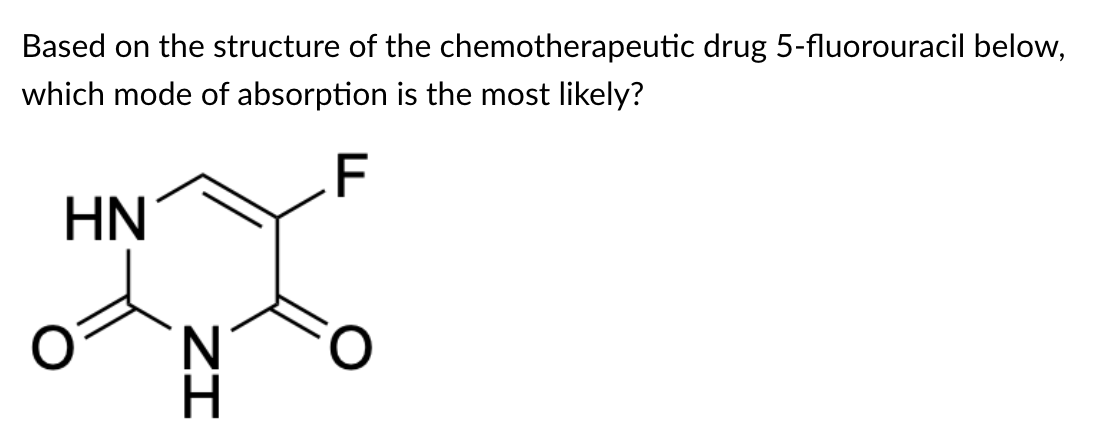
Active Transporter

At pH 5.4, 50% of the drug is protonated and 50% unprotonated.
At pH 6.4, 10% of the drug is protonated and 90% unprotonated.
At pH 7.4 (bloodstream pH), 1% of the drug is protonated and 99% unprotonated.
This molecule is described as an acid and a protonated acid (HA) is uncharged and can passively diffuse. But the unprotonated form of an acid (A-) is charged and cannot passively diffuse.
Thus only 1% of the drug can passively diffuse across a membrane.
Alternatively you could have used the Henderson-Hasselback equation to arrive at essentially the same answer.
Make sure you could do this 1) for either an acid or base and 2) that you could recognize an acid or base if given the structure instead of being told which the compound was.
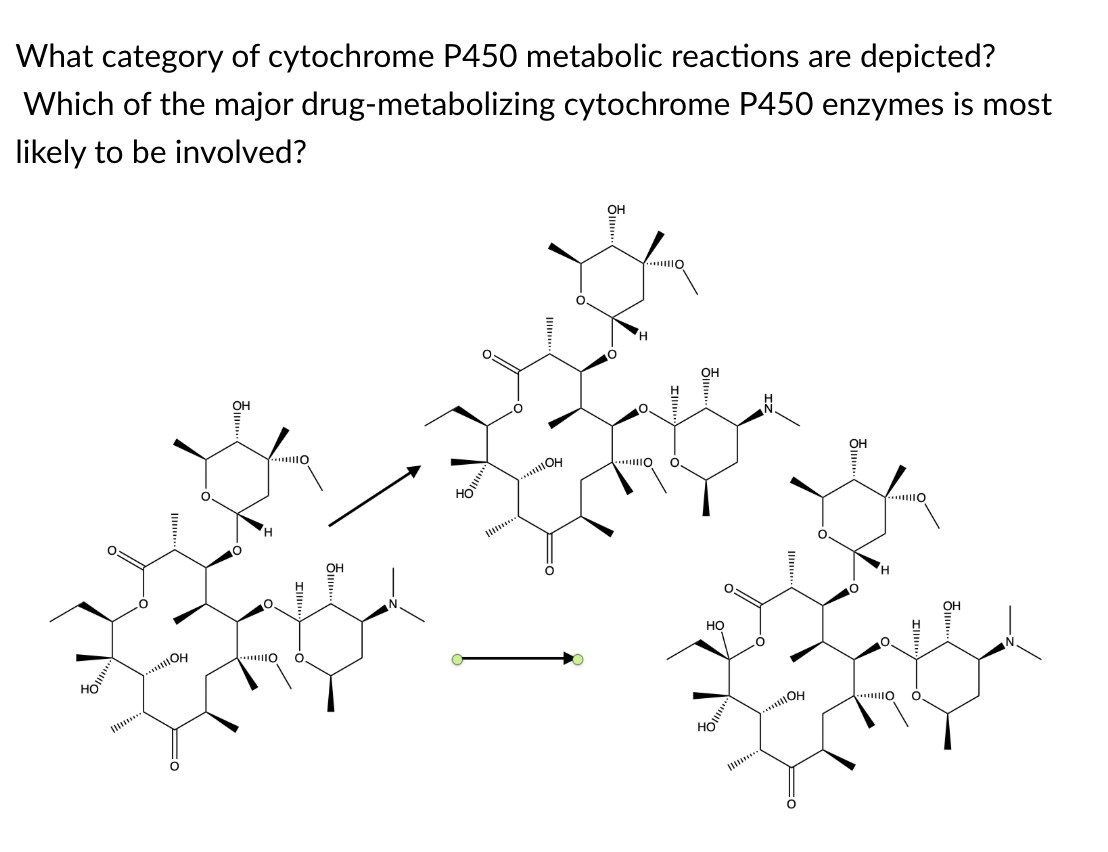
hydroxylation and N-demethylation; CYP3A4
This large macrolide antibiotic named clarithromycin (left) is biotransformed to both an N-demethylated metabolite (top) and a hydroxylated metabolite (bottom right). The size and flexibility of this compound suggests that CYP3A4 is the most likely CYP enzyme to perform these reactions.
Because of differences in drug metabolism, elderly patients may require medication doses that are ______ compared to young adults.
Less frequent or lower dose
Elderly patients tend to metabolize some drugs more slowly than young adults (see "(Some) Factors Affecting Drug Metabolism"). Since these drugs remain in the bloodstream longer, less frequent dosing may be appropriate.
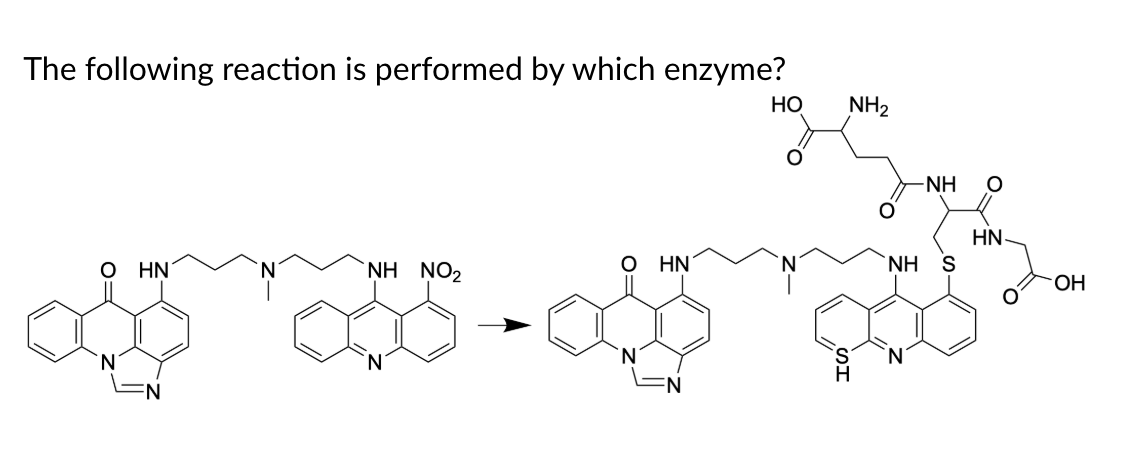
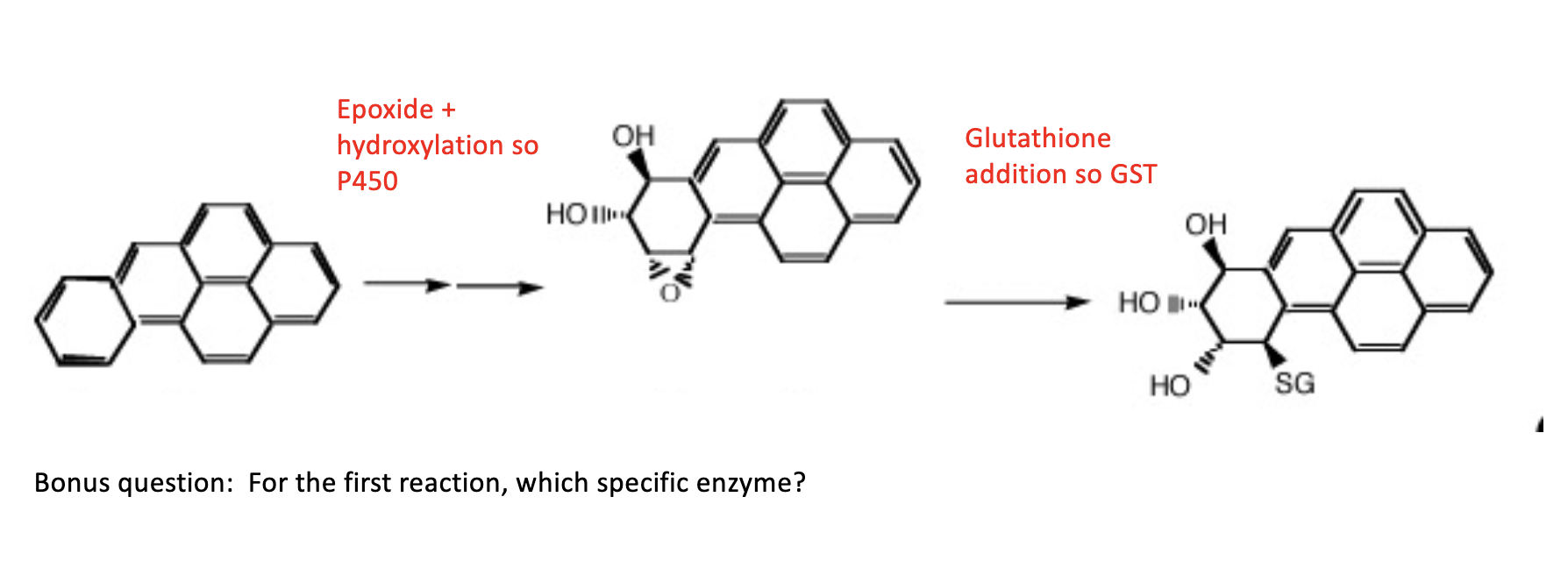
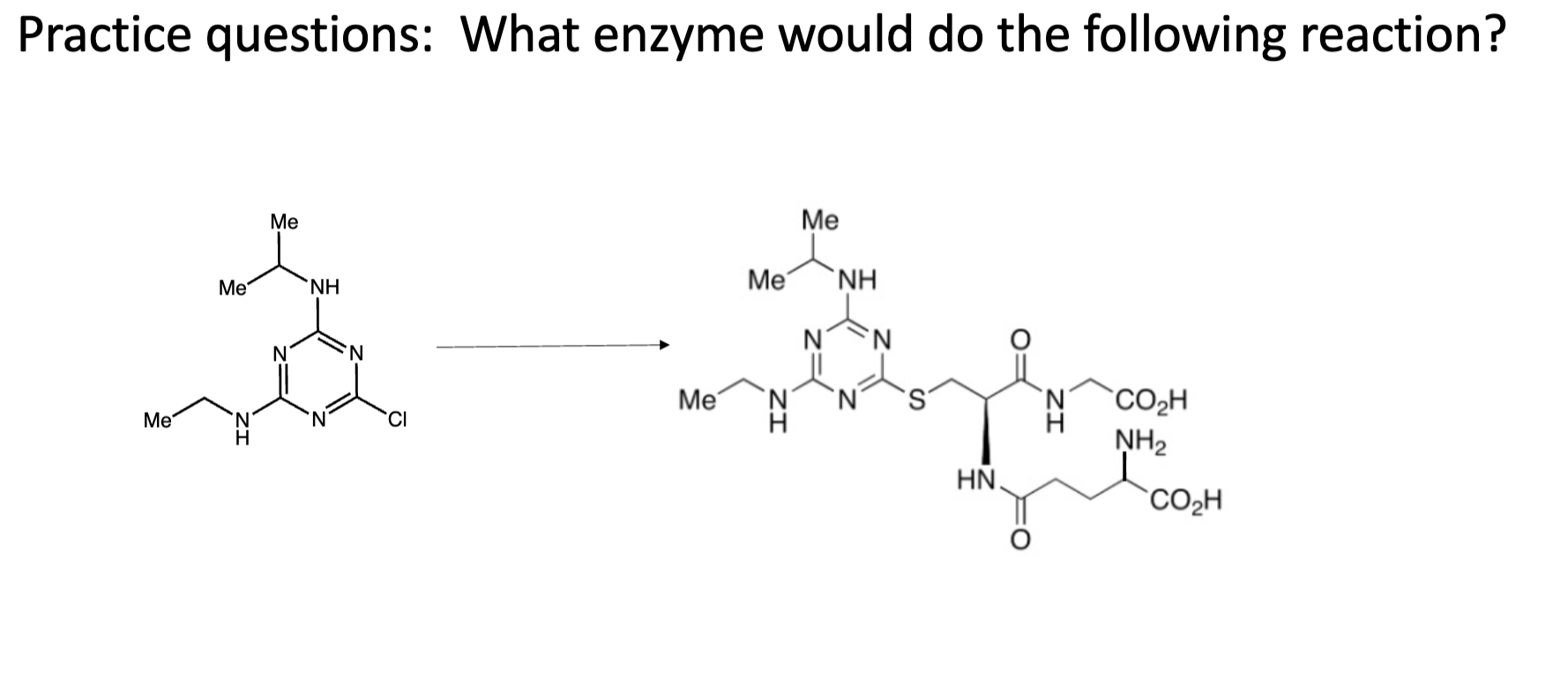
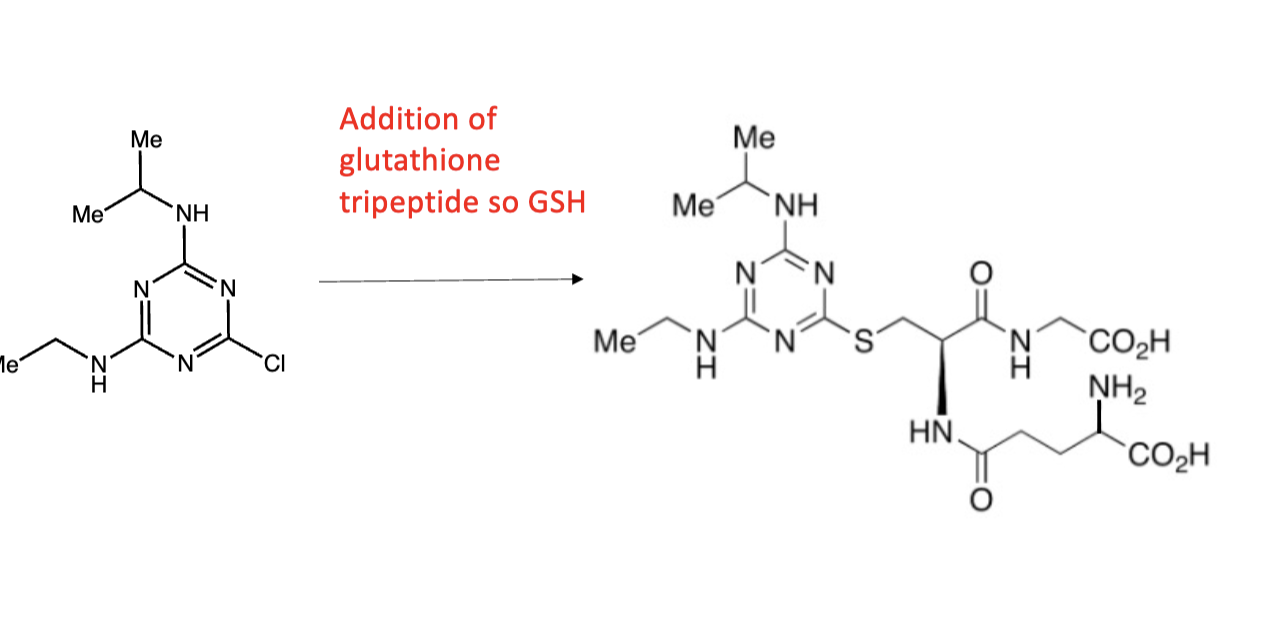
GST
GST is glutathione S-transferase, which adds glutathione. Glutathione is a 3-amino acid peptide composed of glutamine-cysteine-glycine where the glutamine is connected to Cys via the Gln side chain and not the normal backbone connection.
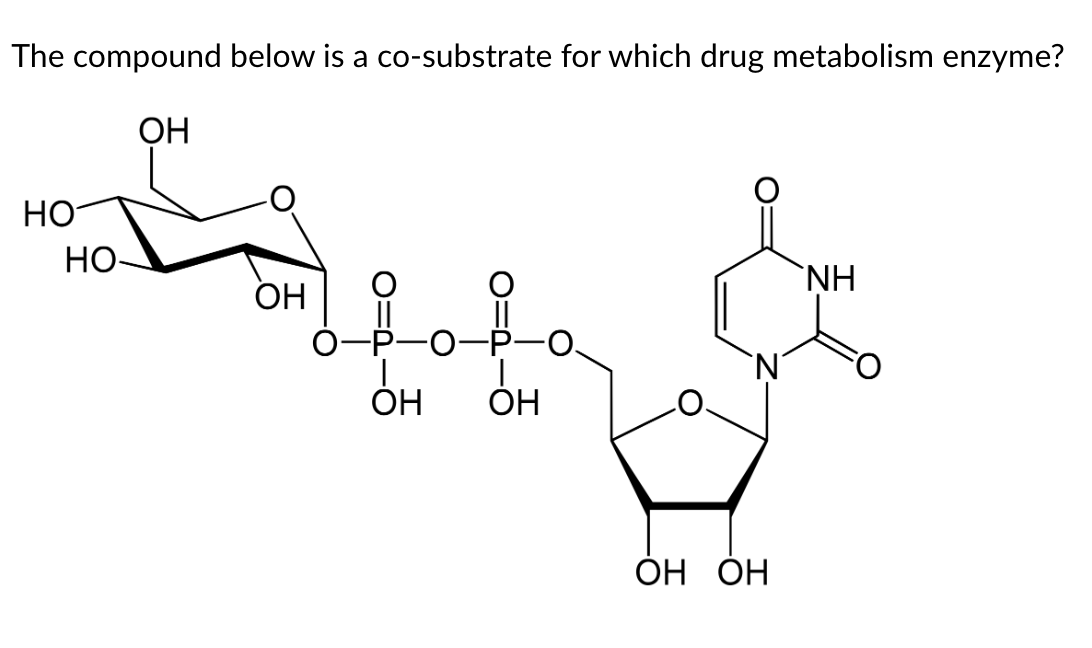
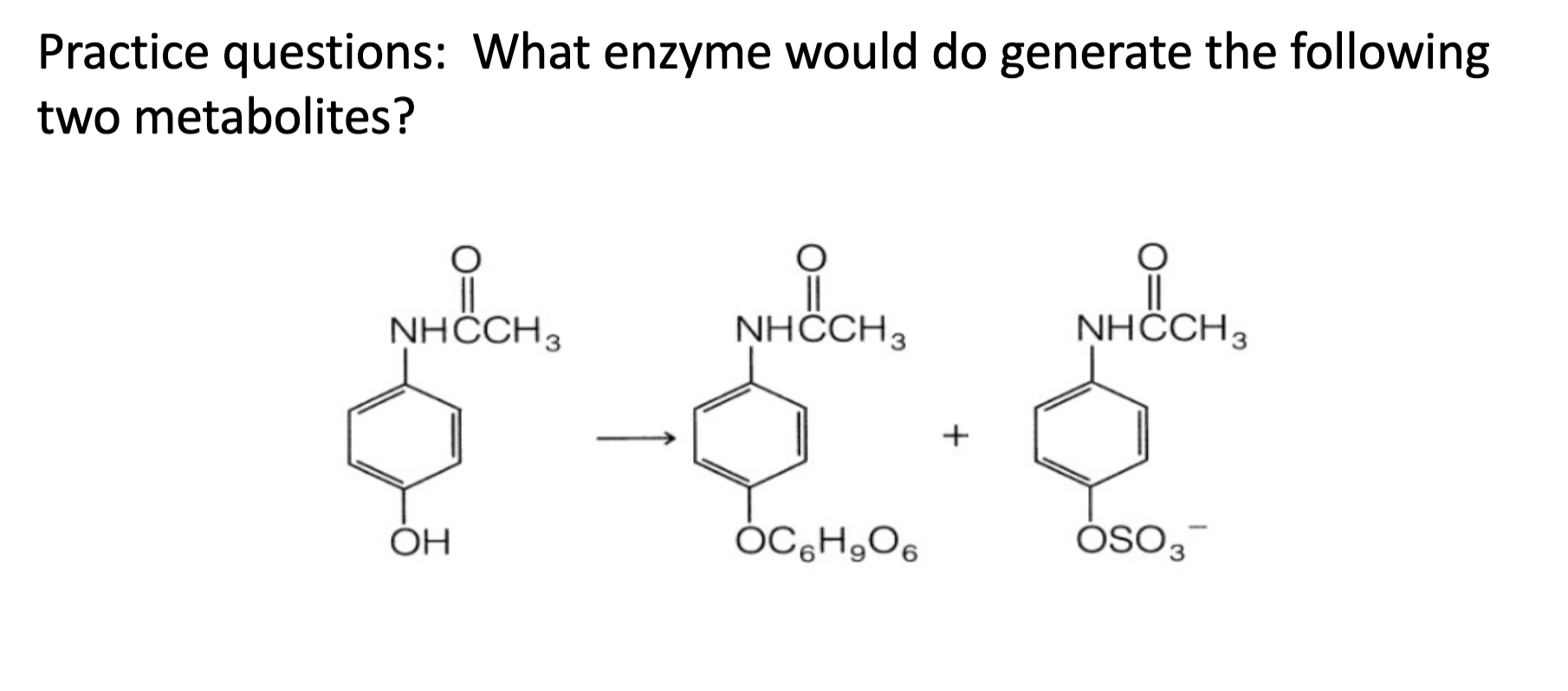
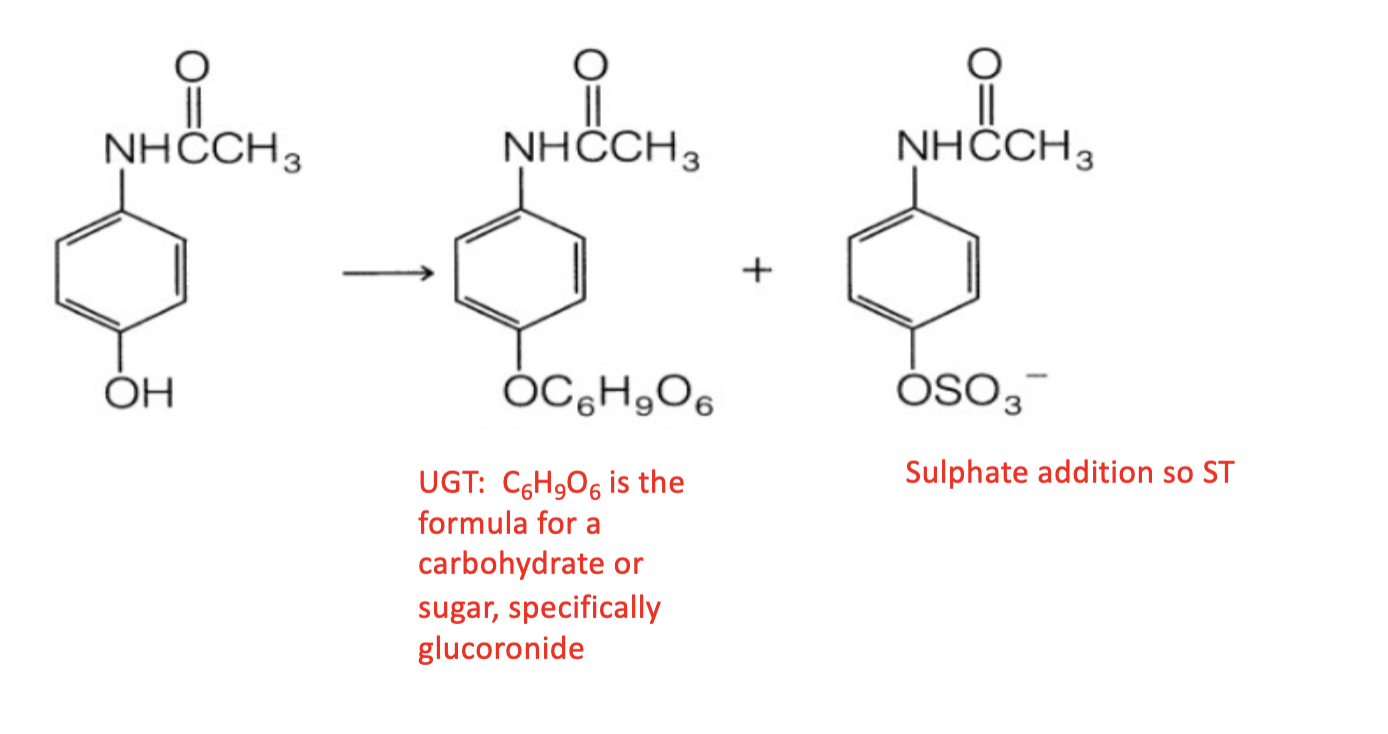
UGT
You should recognize this structure as the nucleotide uridylate (uridine base + ribose sugar + two phosphates) with a sugar (carbohydrate) added to the terminal 5' phosphate, which is UDP-glucose. UDP-glucose is used by UDP-glucuronyl transferase (UGT) to add the sugar part to a drug substrate.
Which enzyme shares the following characteristics with ALDH: uses NAD+ and is a dehydrogenase.
ADH is alcohol dehydrogenase, which is obviously a dehydrogenase and it uses NAD+ to perform this reaction.

The drug will be more slowly metabolized.
Which of the following transporter superfamilies is primarily responsible for the efflux of drugs and their metabolites out of cells?
ABC superfamily primarily involves in the efflux of drugs from cell
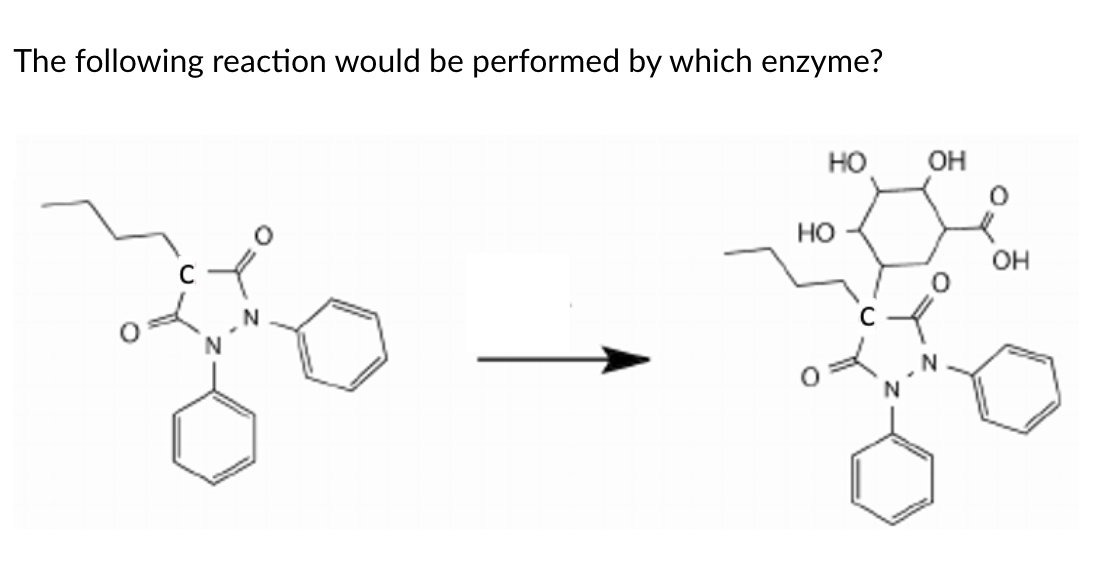
UGT
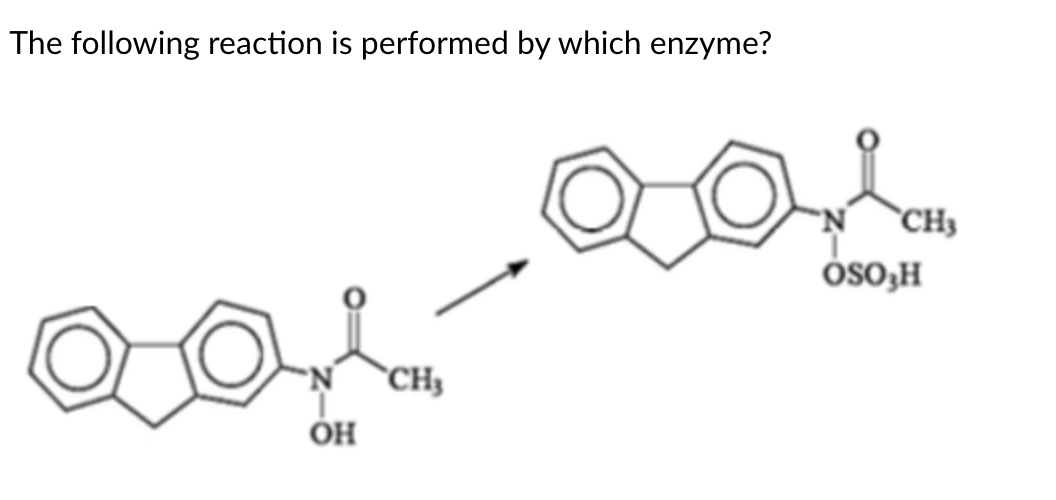
SULT
Which of the following is primarily involved in the drug or small molecule efflux from cells?
PGP or P-glycoprotein or ABCB1 or MDR1 is a member of the ABC (ATP-binding cassette) superfamily which is primarily involved in efflux from cells.
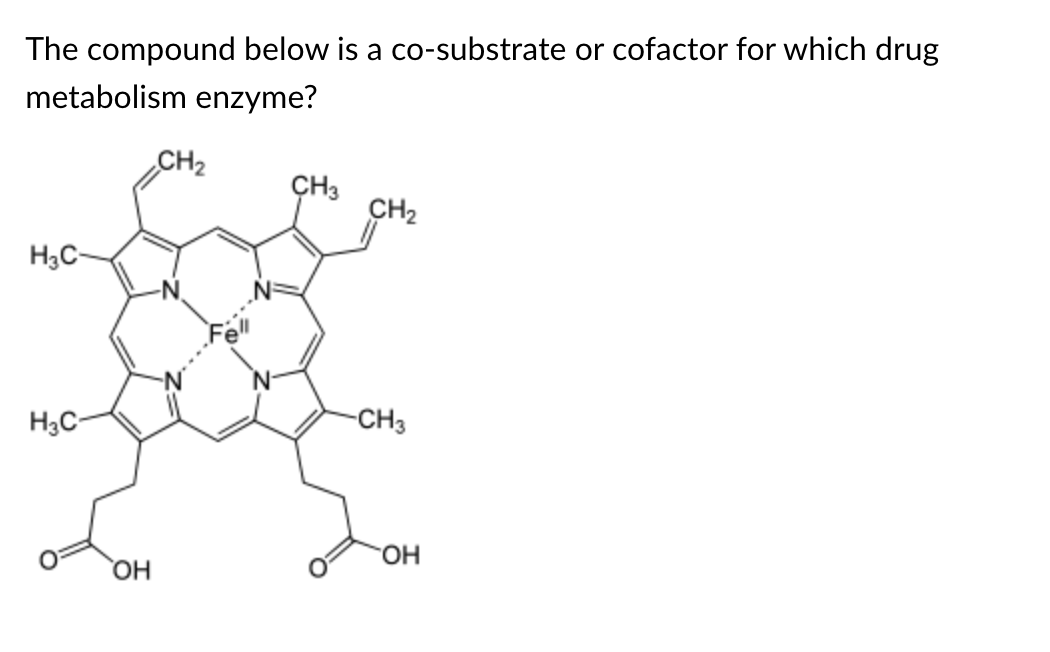
P450
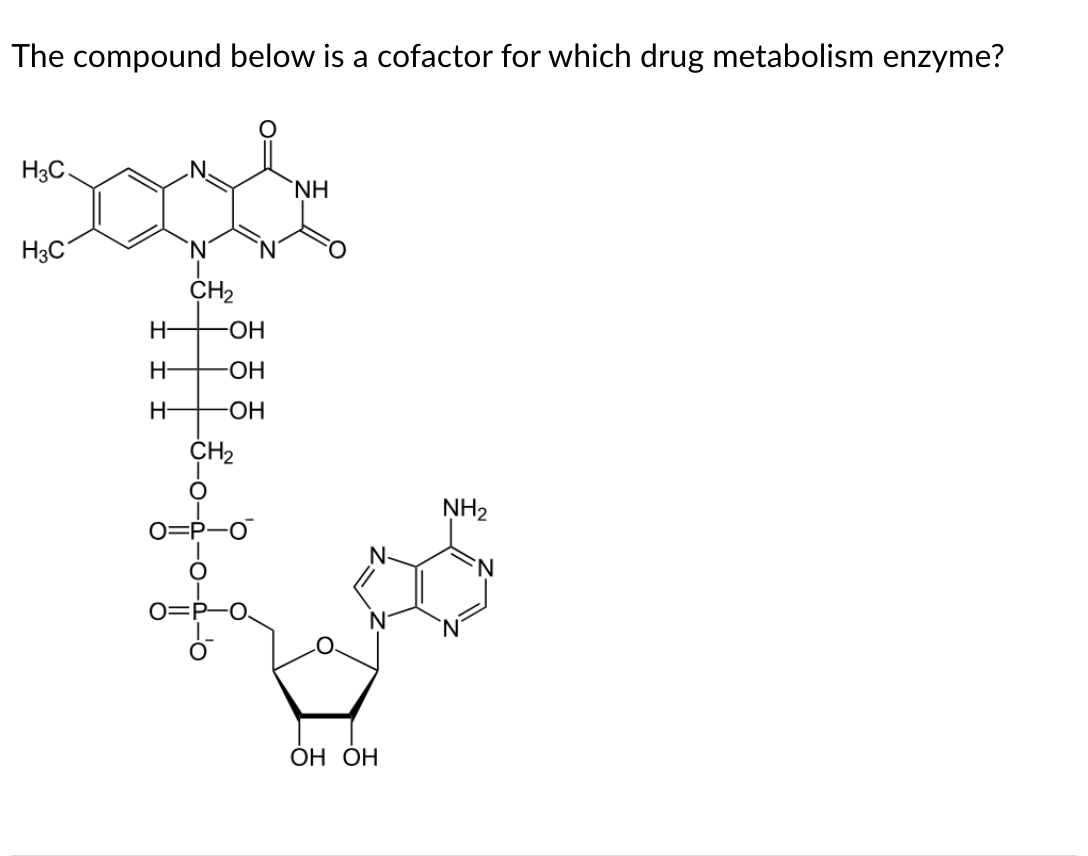
Flavin
The structure consists of the adenylate nucleotide linked to a flavin, and thus is flavin adenine dinucleotide or FAD. The only metabolism enzyme we studied that uses FAD is flavin monooxygenase or FMO.
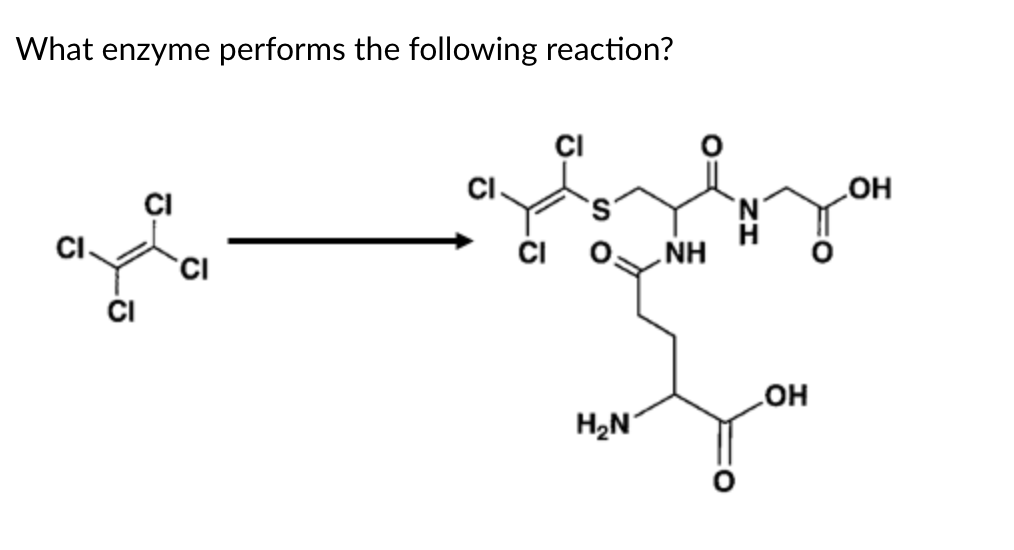
GST
A patient is prescribed a drug that is primarily inactivated by CYP3A4. The patient is also taking a second medication that is a known inducer of CYP3A4. What is the expected outcome?
The drug will be cleared more quickly, potentially falling below the therapeutic level.
A prodrug is prescribed that is activated by a CYP3A4. The CYP3A4 inhibitor ritonavir is concurrently prescribed. What is the expected outcome?
less pharmacological effect from the prodrug
the prodrug will work the same as if ritonavir was not also being dosed
increased pharmacological effect from the prodrug
Ritonavir would be metabolized faster than ususal
less pharmacological effect from the prodrug