Blood bank exam 4 review session
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
What is the cause of HDFN?
Typically an IgG antibody from mom crosses the placenta and has contact with fetal cells
The ONEG mother with an APOS baby, also has a positive fetal bleed screen. Circle all tests that could be used to determine the volume of fetal maternal bleed.
Fetal F flow cytometry or Kleihauer Betke
Evaluate the following results. What is baby's blood type? What is the next step to determine if a fetal maternal hemorrhage occurred?
Mom
anti-A | anti-B | anti-D | A cell | B cell |
4+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4+ |
Baby
anti-A | anti-B | anti-D | D ctrl | Weak D | Weak D ctrl | DAT IgG | DAT ctrl |
4+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2+ | 2+ | 2+ | 0 |
Baby is type A, Rh IND; request Kleihauer Betke to be performed on mom
What is the source of fetal antigens that mom may have antibodies against?
The baby's father
ABO incompatibility generally occurs in a group __ mother with a group __ baby.
O; A or B
ABO incompatibility is an issue in the first pregnancy, or in sequential pregnancies?
First pregnancy
Rh incompatibility is an issue in the first pregnancy, or in sequential pregnancies?
Sequential pregnancies
When doing Rhogam studies, what tests are performed on the cord sample?
ABO/Rh (only the front type)
Weak D if baby is Rh neg
DAT (only IgG)
When doing Rhogam studies, what tests are performed on the mom's sample?
ABO/Rh
Fetal screen if indicated by baby's sample
If mom and baby are both Rh neg, is Rhogam indicated?
No
If mom is Rh neg and baby is Rh pos or weak D pos, what is the next step?
Perform a fetal bleed screen
If a fetal bleed screen is negative, what is the next step?
Administer one dose of Rhogam to mom
If a fetal bleed screen is positive, what is the next step?
Perform weak D testing on mom. Then perform quantitative testing (such as KB) to determine the appropriate dose of Rhogam.
If mom is Rh neg and baby is Rh undetermined, what is the next step?
Quantitative testing (fetal F flow and kleihaurer betke)
What do you suspect if a fetal bleed screen result is strongly positive?
Large bleed, or technical error (accidentally using cord cells)
How much blood does one dose of Rhogam cover?
30 mL
How do you calculate a Rhogam dose for a 5% bleed?
0.05 * 5000 mL = 250 mL
250 mL/30 mL = 8 + 1 = 9 doses of RhIg
When should Rhogam be administered?
within 72 hours after delivery
In Rhogam studies, if you have no sample from the baby, how do you proceed?
Assume the baby is Rh positive.
When is Rhogam routinely given?
For Rh neg moms, Rhogam is given at 28 weeks gestation, regardless of the baby's blood type.
What will the antibody screen look like for a mom who has been given Rhogam?
The screen will be positive, and it will look like an anti-D
What are the requirements for blood used for an intrauterine transfusion?
Washed
Higher hct
Fresh as possible
Irradiated
Leukocyte reduced
CMV neg
Hgb S negative
O neg blood
Antigen negative
Compatible with mom
How is a fetus's blood type determined?
Percutaneous sample
Amniocentesis
Chorionic villus
What are titers used for?
Monitor HDFN
Characterize HTLAs
What titer values are considered clinically significant?
Two blank tubes difference between the previous titer and the current titer
What is a short cold used for?
ABO discrepancy
What is a eluate used for?
positive DAT IgG
What are enzymes and chemicals used for?
enhance/destroy antigens (Anti-Fya, M or N) in order to do more rule outs, such as when there are multiple antibodies, antibodies to high frequency antigens, and sometimes ABO discrepancy.
What is neutralization used for?
used to confirm an antibody, Binds antibody with soluble antigen so that a clinically significant antibody underlying can be detected.
What is prewarm technique used for?
Remove a cold-reacting antibody interference to reveal a warm-reacting allo or auto antibody
What is a cold or warm adsorption used for?
auto antibodies
What is saline replacement used for?
Rouleaux
What do you run a titer against?
A cell that is homozygous for the antigen for which the patient has an antibody. A homozygous cell has more antigen sites for the antigen of interest than a heterozygous cell.
For example, the patient has anti-Jka. Run the titer against a cell that is homozygous for Jka.
What cells are ran in a short cold?
A1, A2, B, SC I, SC II, cord cells, auto control
What is the purpose of the SC I and SC II cells ran in a short cold?
Looking for allo antibodies
What is the purpose of the cord cells ran in a short cold?
Looking for big I or little i
What is the purpose of the auto control cells ran in a short cold?
Looking for auto antibodies
What are some reasons that a patient might have an ABO discrepancy?
cancer: down regulation of back type
transfusion: mixed field
age: very old and very young- no back type
bone marrow tx: different blood type being made
Acquired B antigen: perforated bowel
Preanalytical errors: misidentification of patient
Cold autoantibody
Rouleaux
Cell suspension is too concentrated
Wharton's jelly: cord cells (wash to remove)
A subgroups: do the back type with A2 cells
Cold allo-antibodies
What blood group antigens are enhanced by enzymes?
Kidd, Rh (C,c, E,e), Lewis, I/i, P1
What blood group antigens are destroyed by enzymes?
Duffy, M, N, sometimes S
What is the sequence of steps if the antibody screen is positive?
Positive ABSC --> ABID --> phenotype patient --> phenotype donor --> crossmatch AHG
Why might you perform a DAT?
Cord cells
Positive auto control
Included with AHG XM
What are significant IgM blood group antibodies?
ABO, M, N
What are significant IgG blood group antibodies?
Kell, Kidd, Duffy
What does ficin do?
Destroys Duffy, M, N, (S)
Reduces sialic acid
Reduces zeta potential
What does AET do?
Destroys Kell, Le, Lw
What does ZZAP do?
Destroys Kell, Lu, Duffy, M, N, S
Enhances Rh, Kidd, Lewis
What does chloroquin do?
Removes bound IgG to make cell DAT negative
What does DTT do?
Destroys disulfide bonds
Destroys Kell, Lu, Lw
What does 2-ME do?
Destroys Kell, Lu, Lw
Unexpected reactions in either the forward, reverse or both in ABO typing are caused by what types of errors
• Misidentification of the patient (pre-analytical)
• Technical (analytical)
• Tech
• Reagents
• Equipment
• Incorrect entry (post-analytical)
First step in solving ABO discrepancyis to
repeat testing
What is the most likely cause of the discrepancy below?
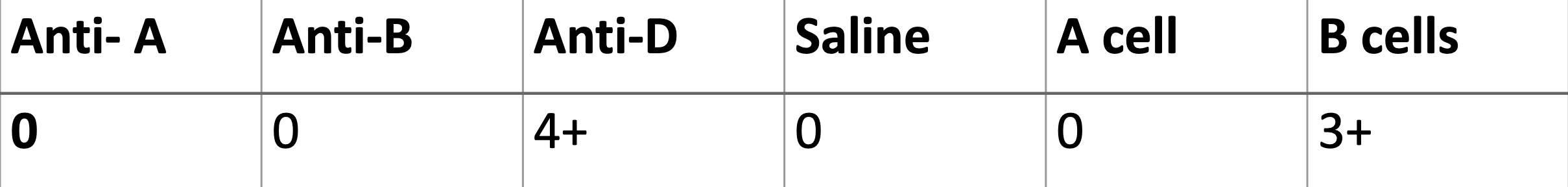
From a healthy 25-year-old donor.
A sub group
•What is the most likely cause of the discrepancy below?
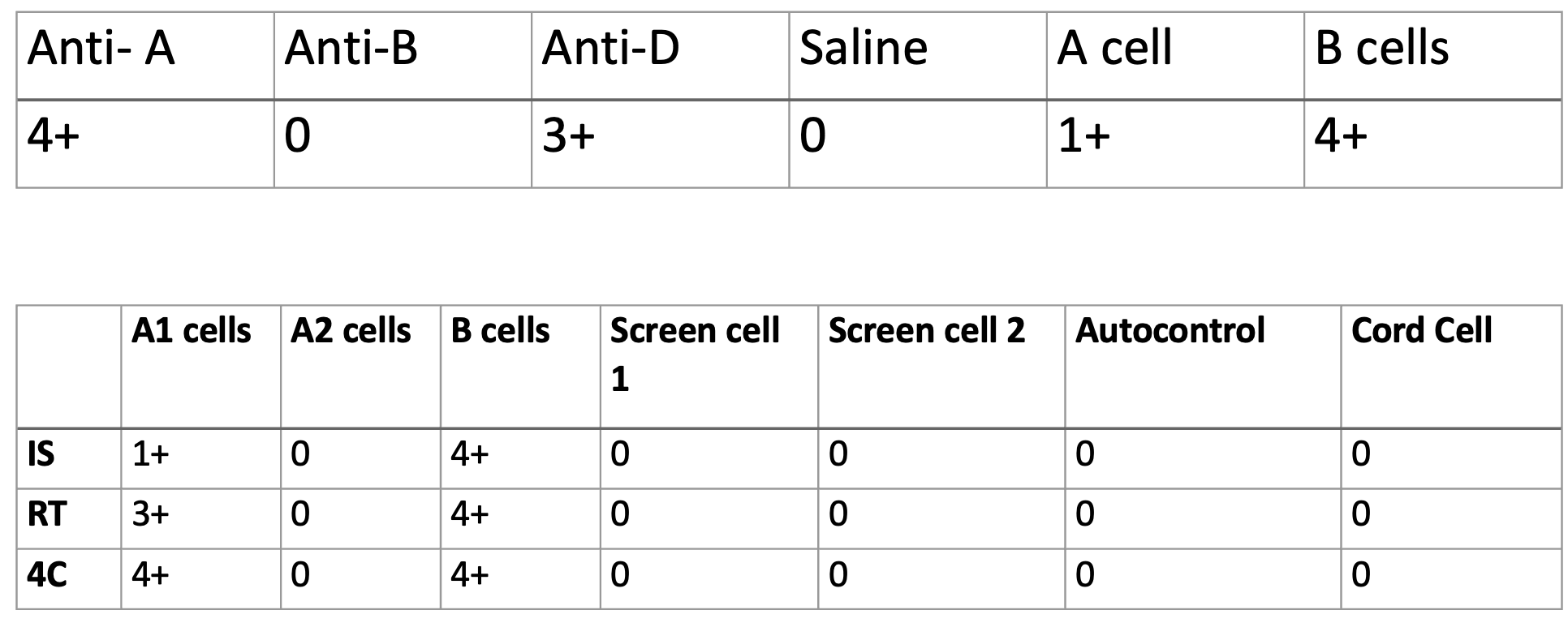
A2 subgroup with an Anti-A1
•What is the most likely cause of the discrepancy below?
Cold autoantibodies
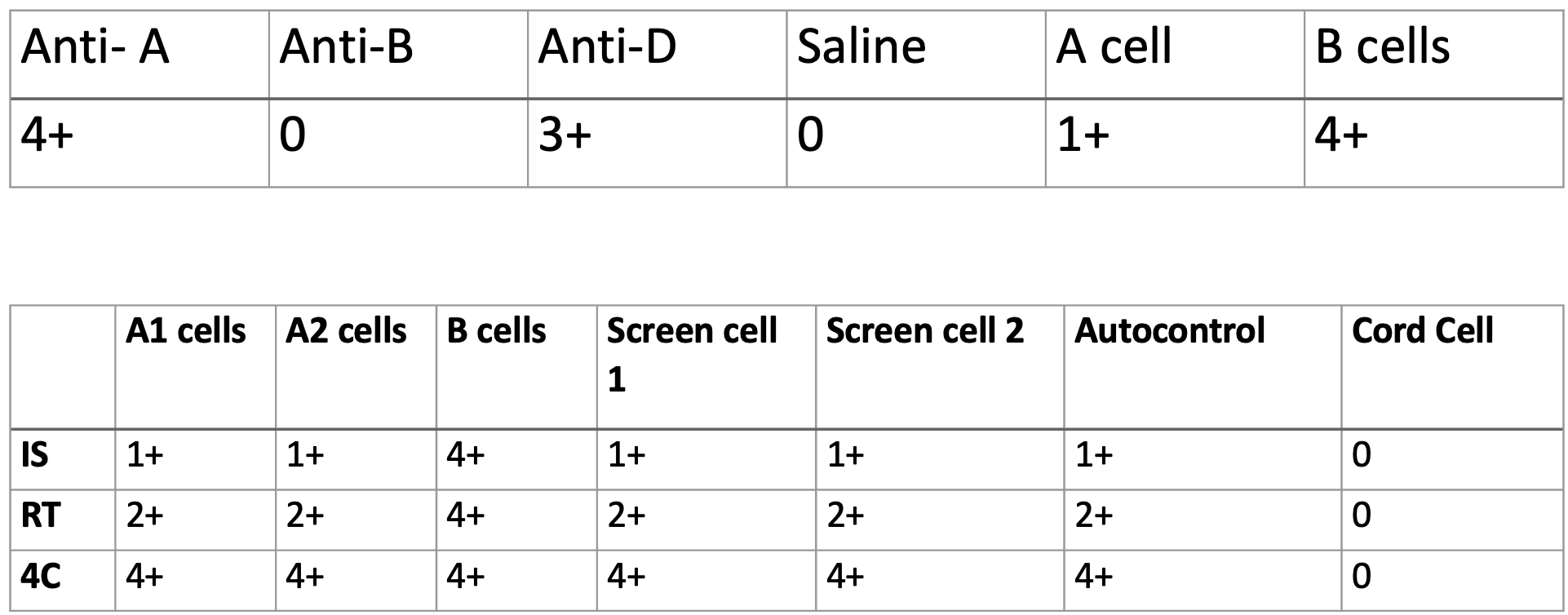
patient has an Anti-M , what is the most likely cause of the discrepancy below? What would fix it?
Interference in the back type from the cold reacting Anti-M. Fix with A cell and B cell negative for M antigen.
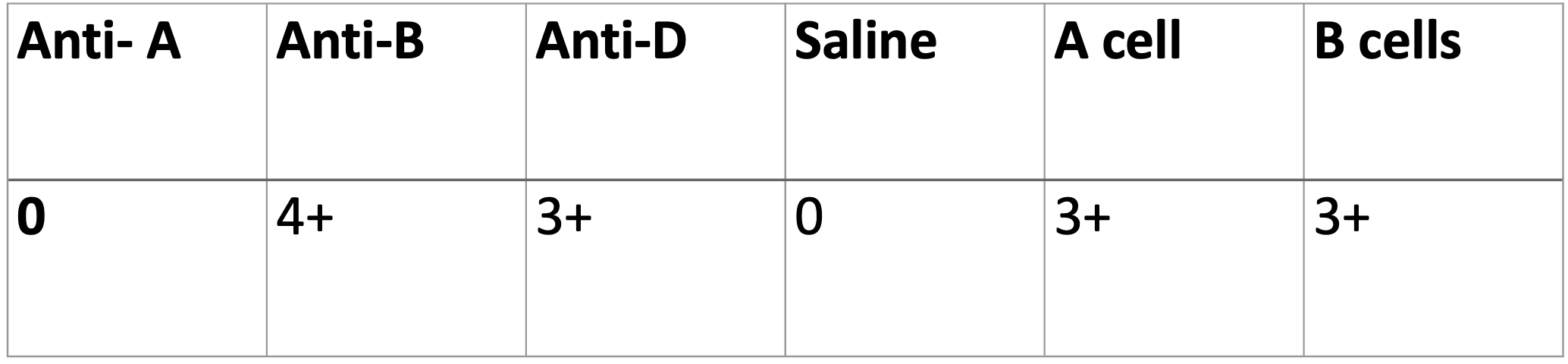
What is the most likely cause of the discrepancy below? What part of the body do you think of when you have this type of discrepancy?
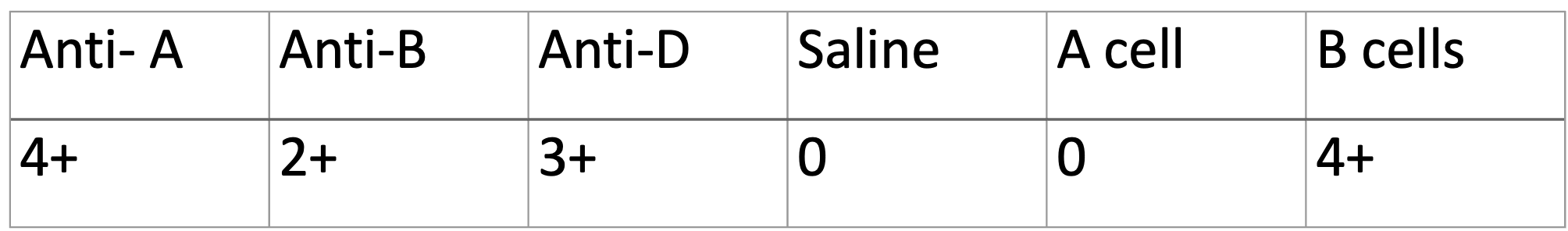
Acquired B – rectum or colon
What antibodies are clinically significant for causing HDFN? Which one is most common?
•Most common Anti-D
• Anti-D, Anti-C, Anti-c, Anti-E, Anti-e, Anti-K, Anti Jka, Anti-Jkb, Anti-Fya, Anti-Fyb, Anti-S, Anti-s
How do we monitor prenatal antibody activity?
Titer
Rh Immune Globulin (RhIg) is given to who?
Rh negative pregnant women
How can we test blood type of a fetus in utero?
Blood draw from amniocentesis
When selecting blood for an intrauterine transfusion, what attributes should it have?
•O neg, Antigen negative for moms antibodies, CMV neg, irradiated, fresh , <5 days, Hgb S neg
Fetal bleed screens are done on Rh ____ moms who give birth to Rh _____ babies.
negative; positive
What is a fetal screen (rosette test)?
•A test that screens for fetal cells in moms circulation. Anti D reagent in kit attaches to Rh positive fetal cells, once incubated and washed indicator cells are added to show agglutination of fetal cells in moms blood. They look like rosettes.
What test is a follow up for a positive fetal bleed screen?
Kleihauer Betke or Fetal Flow
Which antibody is stronger a passive Anti-D from RhIg administration or a real Anti-D?
Real Anti-D
Is HDFN caused by ABO incompatibility clinically significant? How is it usually treated?
•Usually not clinically significant, can occur in first pregnancies. Treated with phototherapy.
Kleihauer-Betke stain results on a postpartum mother indicate that there has been a fetal maternal bleed; 1.5% of the cells counted are fetal cells. Assuming the woman has a blood volume of 5000mL, please calculate the proper RhIg dosage.
0.015 x 5000mL = 75mL 75mL/30mL = 2.5 round up to 3 and add a dose
4 vials
The results of a Kleihauer-Betke stain indicate that a fetal maternal bleed of 60 cells whole blood has occurred. How many vials of RhIg is required?
60 cells/2000 cells = 0.03 x 5000 mL = 150 mL/30mL = 5 and add a dose
6 vials
Cold panel
Enhance cold reactive antibody
elution
Strip bound IgG of RBCs for ID of its specificity
What indicates the endpoint of a titer?
•The last 1+ reaction.
What is the purpose of the A1 and A2 cells ran in a short cold?
Looking for A sub
What is the purpose of the B cells ran in a short cold?
Looking for allo antibodies
What antibodies are most common?
Anti-D, Anti-E, Anti-K
Which antibodies are not clinically significant?
Anti-M, Anti-N, Anti-Lea, Anti-Leb, Anti-Lua, Anti-P1
Who is most likely to have an Anti-U? Is it clinically significant
Black population, yes it is clinically significant
What antibodies are enhanced by cold?
•Anti-M, Anti-N, Anti-Lea, Anti-Leb, Anti-Lua, Anti-P1
What population is likely to develop a Lewis antibody?
•Pregnant
Fill in the following table for the relationship between Lewis, secretor and ABO.
Genes | Antigens in Secretions | RBC phenotype |
Le, Se, HH, AA
| Lea, Leb, A, H | |
lele, Se, HH, BB
| B, H, Le (a-, b-) | |
Le, sese, Hh | Lea | |
lele, sese, HH, AO | None | A, H, Le (a-, b-) |
Le, sese, hh, AB |
| Oh, Le (a+, b-) |
Genes | Antigens in Secretions | RBC phenotype |
Le, Se, HH, AA
| Lea, Leb, A, H | A, H, Le(a-, b+) |
lele, Se, HH, BB
| B, H | B, H, Le (a-, b-) |
Le, sese, Hh | Lea | H, Le (a+, b-) |
lele, sese, HH, AO | None | A, H, Le (a-, b-) |
Le, sese, hh, AB | Lea | Oh, Le (a+, b-) |
Blood group antigen | Neutralizing agent |
P1 | |
Lewis | |
Sda | |
Chido Rogers (Ch/Rg) |
|
Blood group antigen | Neutralizing agent |
P1 | Pigeon egg whites |
Lewis | Saliva |
Sda | Urine |
Chido Rogers (Ch/Rg) | Plasma |
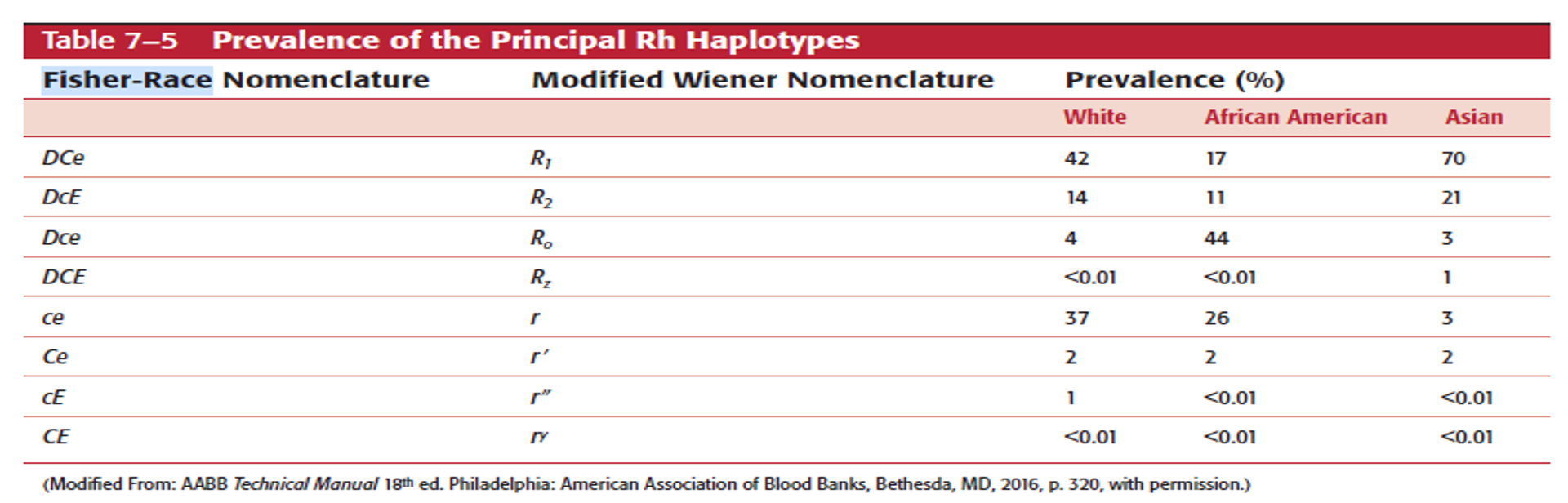
Using Rh antigen frequencies for Weiner phenotypes (Table 7-5 pg. 155 in the text). What would be the most common Weiner type for the following races?
white:
Black:
Asian
White: R1r
Black: R0r
Asian: R1R2
After you've done a panel, performed your ruling out process, and identified what antibody most likely present in a patient sample, what test should you generally do on the patient's RBC?
•Phenotyping