Cell Signaling
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
what are ligands
signaling molecules that bind to other molecules to create a complex that transmits signals
ligand’s shape must be ___ to the receptor
complementary
what is autocrine signaling
secreted molecules trigger a response in the cells that secrete them
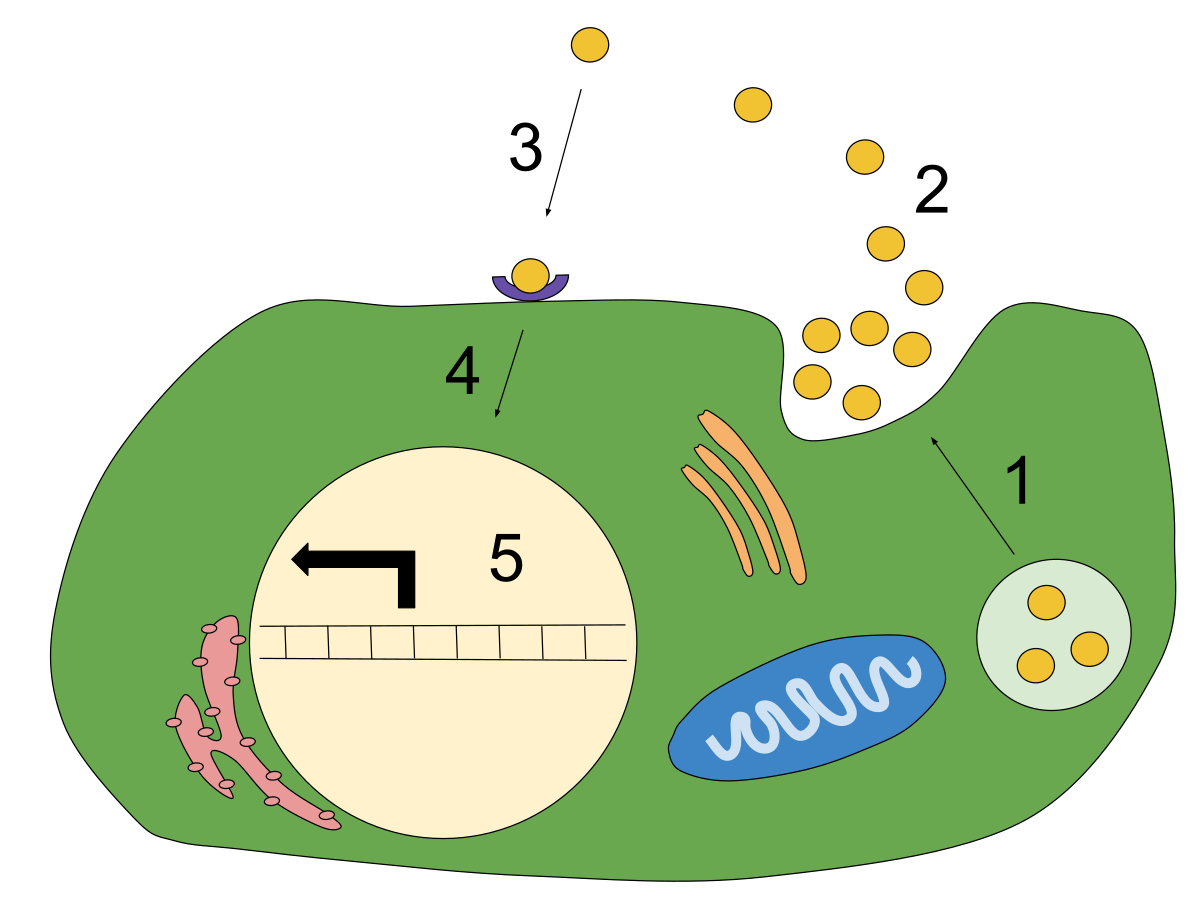
example of autocrine signaling
some cancer cells release their own growth factors, allowing tumors to grow more rapidly
what is juxtacrine signaling
cells communicate via direct contact
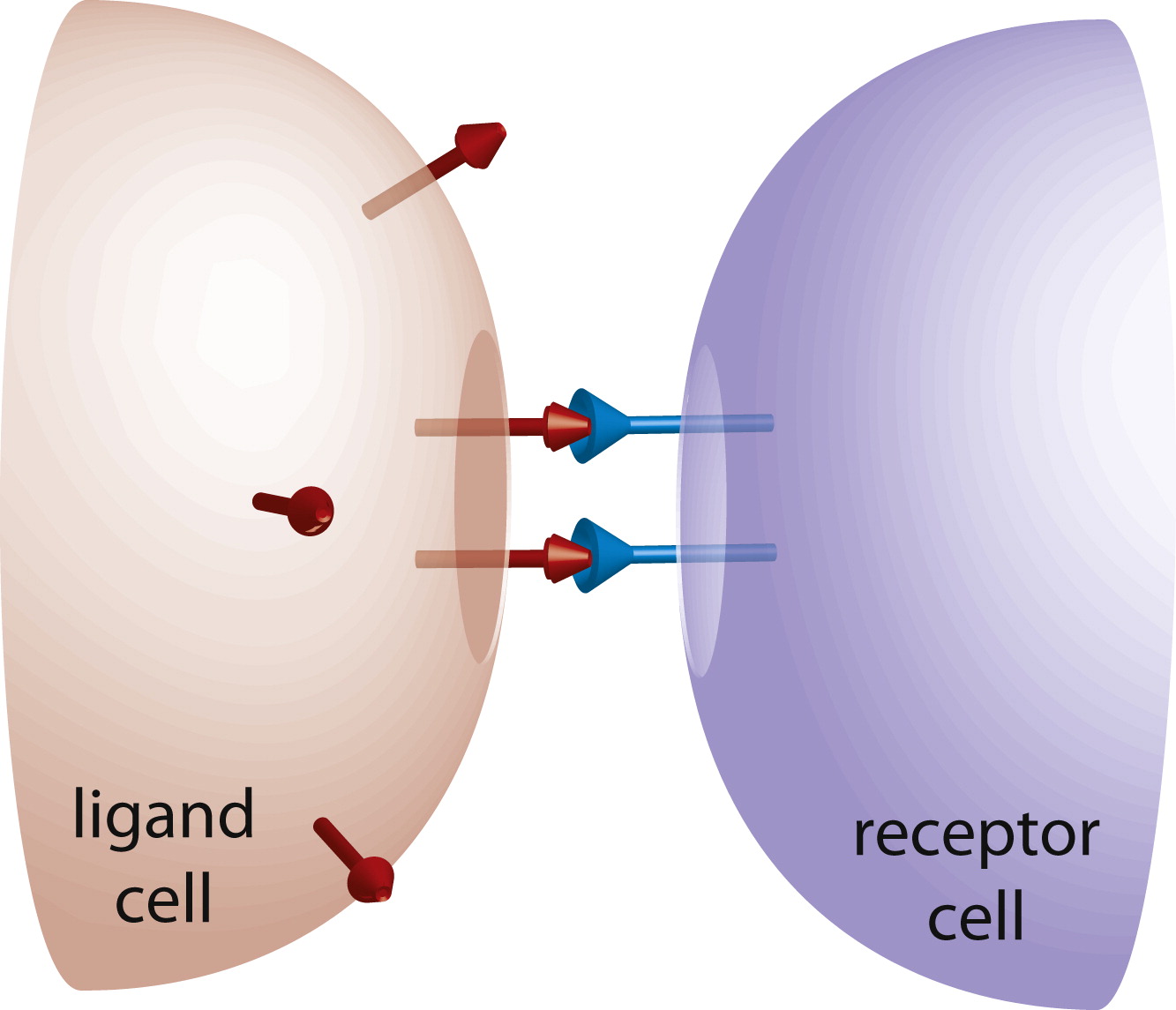
example of juxtacrine signaling
muscle cells of the heart are linked by gap junctions- this allows all the cells of the heart to contract at the same time. or, some immune cells interact through direct contact
what are gap junctions
cytoplasmic channels between animal cells
what is plasmodesmata
cytoplasmic channels between plant cells
what is paracrine signaling
secreted molecules trigger a response in nearby cells
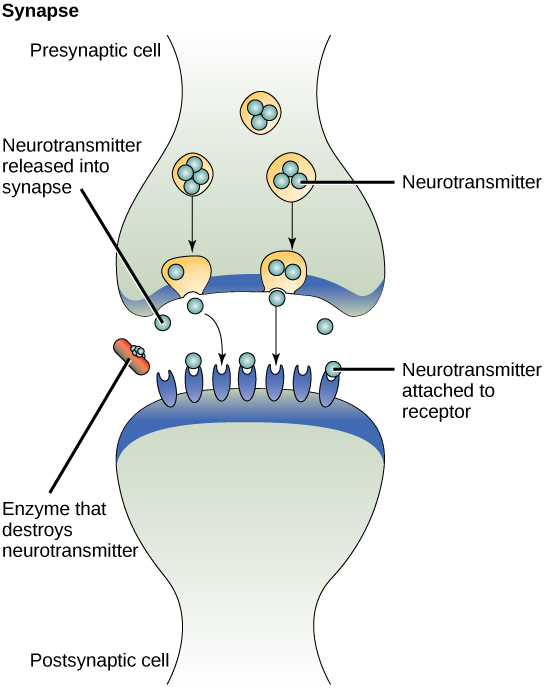
example of paracrine signaling
quorum sensing in bacteria, induction during development
what is quorum sensing
signal molecules are produced by individuals; if enough bacteria are present, lots of signal molecules are produced, resulting in a response that would only be beneficial if large numbers of bacteria are present
example of quorum sensing
dental plaque
what is induction
signals from neighboring cells cause changes in gene expression, causing cells to differentiate
what is endocrine signaling
molecules (hormones) secreted into the bloodstream, affects cells anywhere only if they have the appropriate receptors

steroid hormones function
affect DNA expression to initiate long-term changes to the target cell, bind to intracellular receptors
examples of steroids
testosterone and estrogens
steroid hormones are ____ soluble
lipid soluble
first step of steroid action
hormone diffuses across cell membrane of all cells
second step of steroid action
hormone binds to receptor
third step of steroid action
hormone-receptor complex diffuses into the nucleus, binds to DNA, and act as a transcription factor
fourth step of steroid action
transcription factor causes specific genes to make new proteins
steroid hormones alter…
gene expression
water soluble hormones function
affect enzyme activity to initiate short-term changes in a cell
examples of water-soluble hormones
epinephrine, melatonin, insulin
mechanism of water-soluble hormone action
signal-transduction pathway
what is a signal-transduction pathway
a series of steps where signaling molecule binding results in a cellular response
what are G-proteins
a protein activated when bound to GTP, inactivated when bound to GDP
what are G protein coupled receptors
binds and activates G protein when activated by ligand
what is protein kinase
enzyme that transfers phosphate group from ATP to a protein, activating the enzyme via phosphorylation
what are second messengers
small molecules/ions that act as intermediaries between activated receptor and activation of other proteins
first step of signal-transduction pathways
epinephrine binds to G protein coupled receptor
second step of signal-transduction pathways
receptor activates G protein by allowing it to bind to GTP
third step of signal-transduction pathways
activated G protein activates an enzyme, converting ATP to cAMP, a second messenger
result of signal-transduction pathways
a signal cascade: cAMP activates kinase, which activates another, and another, until the target enzyme is reached. then, glycogen is broken down into glucose by the target enzyme
signal-transduction pathways always have…
reception, transduction, and response
description of reception
signal molecule binds to a receptor
description of transduction
bound receptor stimulates another molecule, then another, this result is known as amplification
description of response
cell change
define amplification
enzyme activates many other enzymes in the next step
function of tyrosine kinase receptors
binding of ligand makes two receptors join together, causing phosphorylation and initiating a transduction pathway
function of ion channel receptors
ligand binding causes these channels to open, thus allowing ions to enter and exit the cell
examples of second messengers
inositol triphosphate and ca2+