Prostaglandins and Leukotrienes
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
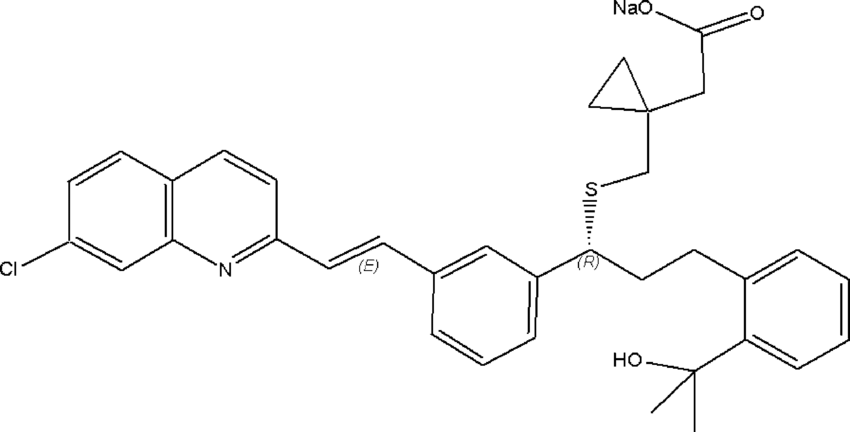
Structure of Prostacyclin
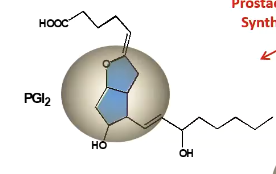
Structure of PGE2
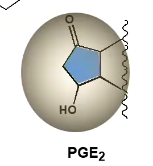
Structure of PGF2a
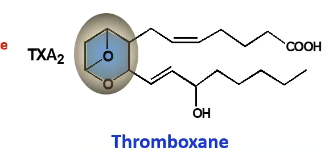
Structure of TXA2
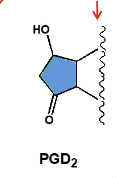
Structure of PGD2
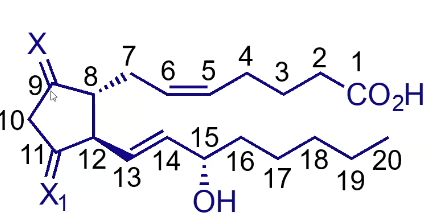
What groups do prostaglandins have?
Oxygenated cyclopentane/pentene ring
Heptenoic/heptanoic acid side chain
Octenol side chain
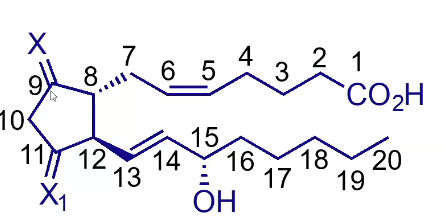
Are prostaglandin side chains cis or trans
Two side chains are trans to each other
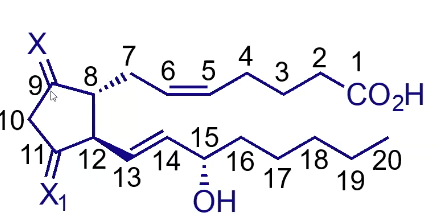
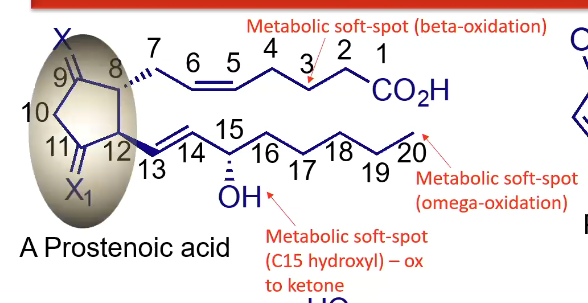
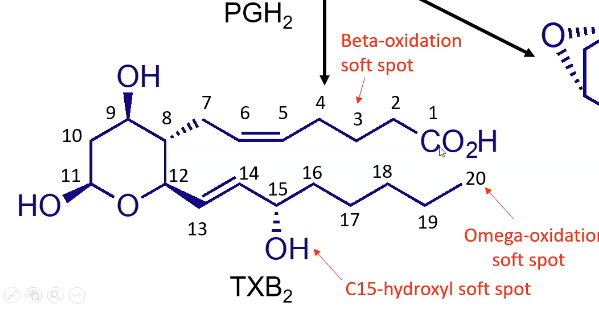
Soft spots of Prostenoic acid?
What is thromboxane derived from? What membered ring does it have?
Derived from PGH2
Six membered ring
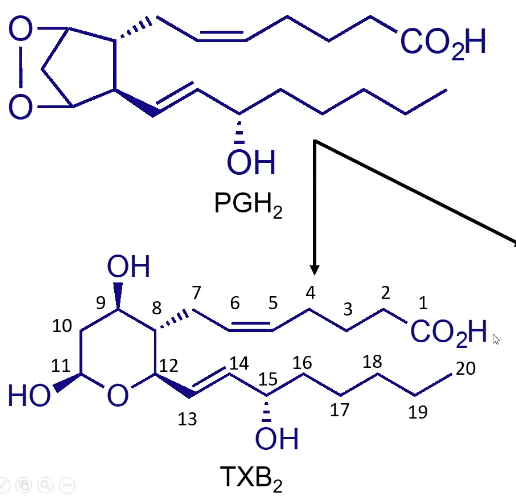
Soft spots of thromboxane (TXB2)
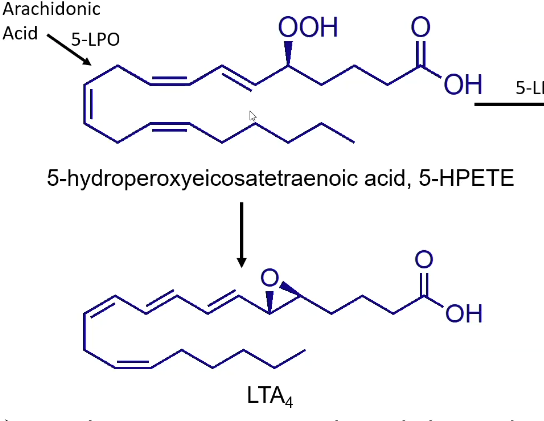
What are leukotrienes derived from? Which pathway do they follow? Do they have rings?
Derived from 5-HPETE
Lipoxygenase pathway
NO RINGS
Subscript: Number of double bonds
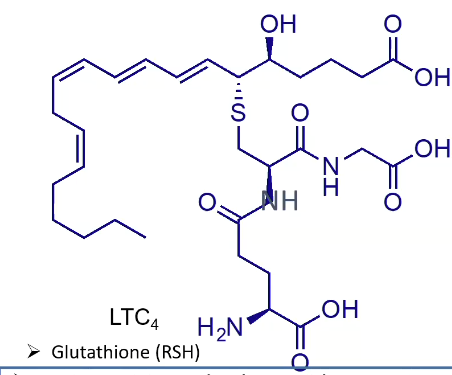
Where does LTC4 and LTD4 come from?
LTA4
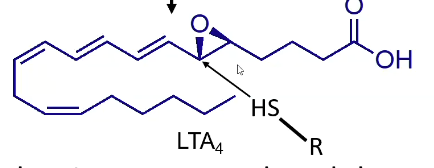
What functional group does LTA4 contain? What does it mean in terms of activity?
Epoxide
Electrophilic (delta +) → thiols will open this
Opens, creates trans product
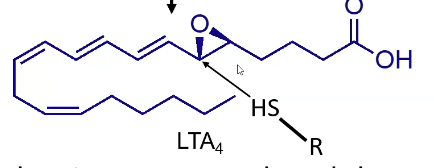
What is LTC4?
Glutathione (Trans)
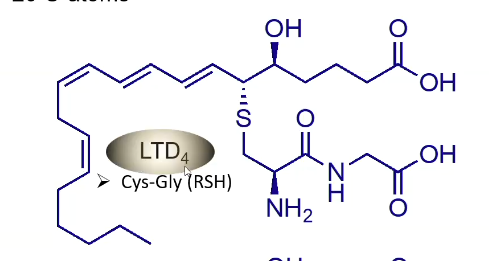
What is LTD4?
Cysteine + Glycine
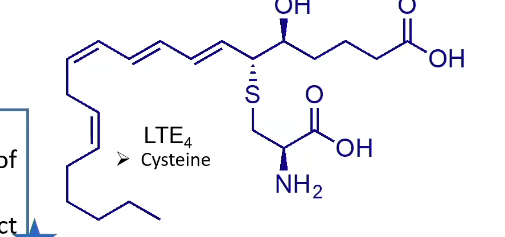
What is LTE4?
Cysteine
What are important points about LTC4-LTE4
Thiol epoxide trapping of LTA4
Leukotrienes → produced through 5-LPO on arachidonic acid
Epoxide ring → gives trans product
Which receptors does PGE2 bind to?
EP1, EP2, EP3, EP4
What receptors does PGF2a bind to?
FP receptors
What receptors does PGI2 bind to?
IP receptors
What receptor does TXA2 bind to?
TP alpha, beta
What receptors do PGD2 bind to?
DP1 and DP2
What receptors does LTB4 bind to?
LTB4R1 and LTB4R2
What receptors do LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4 bind to?
CysLTR1 and CysLTR2
Biological functions of PGD2
Mast cell maturation, vasodilation, neuroprotection
Biological functions of PGE2
Vasodilation, labor induction
Biological functions of PGF2a
Uterine, vascular, respiratory contraction, decrease of intraocular pressure
Biological functions of PGI2
Decrease platelet aggregation and vasodilation
Biological function of TXA2
Increased platelet aggregation, vasoconstriction, decrease T cell activity
Biological functions of LTC/D4
Bronchoconstriction, vascular leakage, neutrophil extravasation
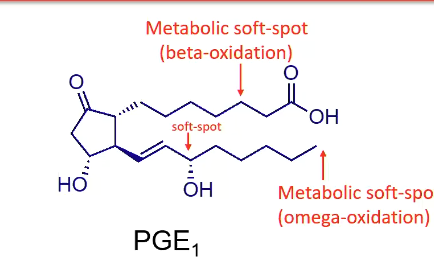
How many double bonds does PGE1 have? What is it used to treat? What is its metabolism?
one double bond
infants with ductal dependent congenital heart disease
80% is metabolized in one pass through beta/omega oxidation
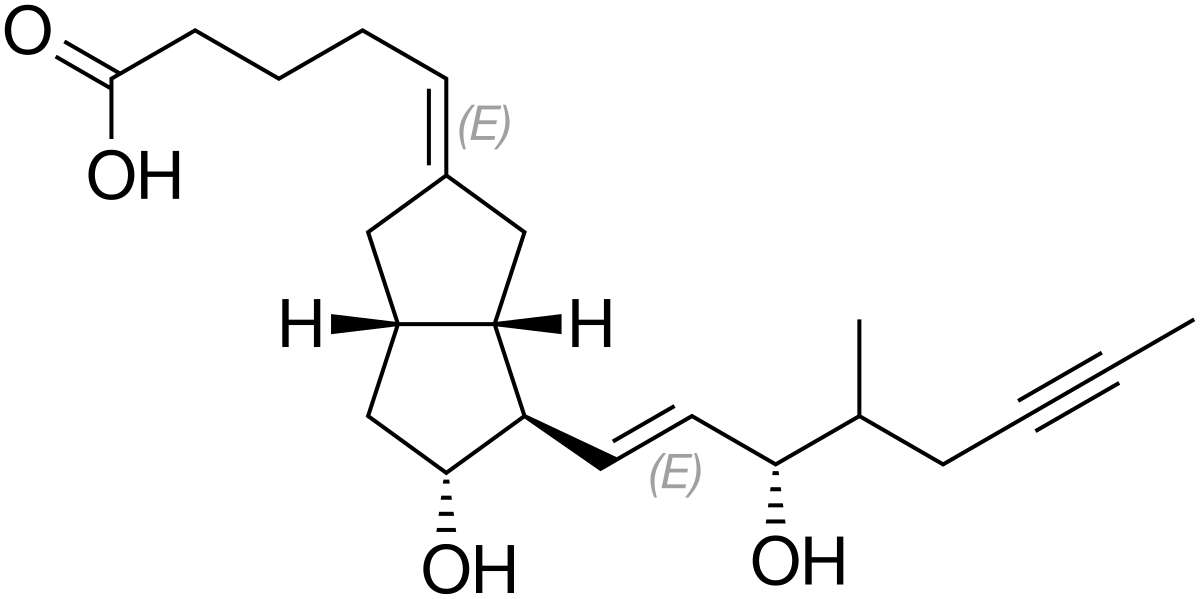
Where is the soft spot of iloprost?
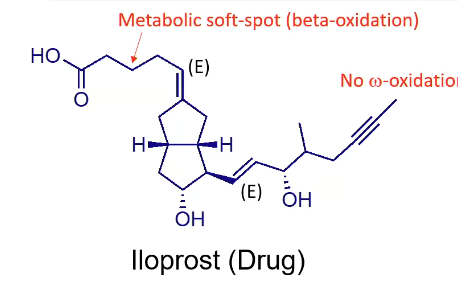
How does iloprost compare to prostacyclin PGI2
iloprost = primarily beta oxidation (has acetylene), E vs Z
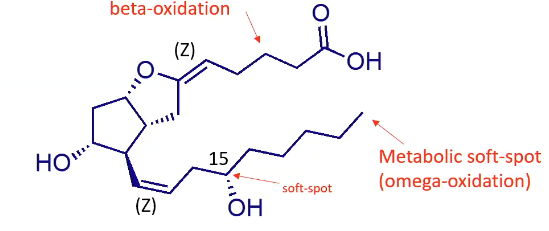
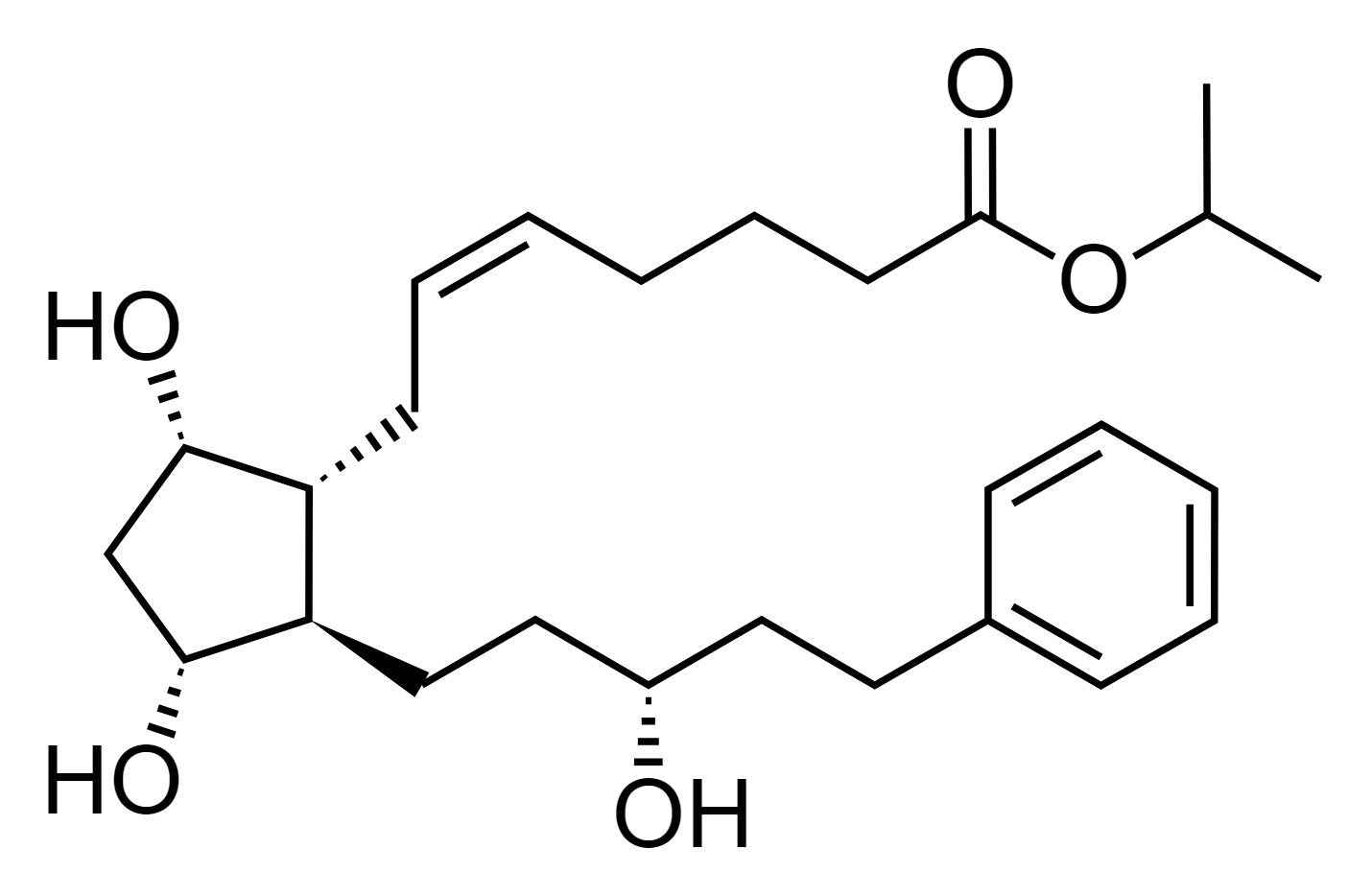
Soft spots of latanoprost?
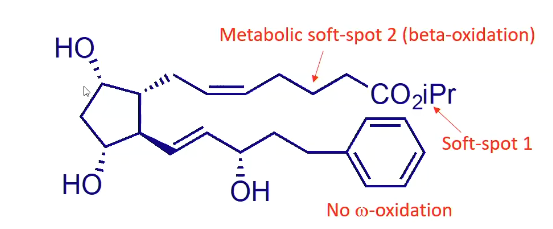
Is latanoprost a prodrug, what is the primary metabolism?
Yes, it is a prodrug
Hydrolyzed by esterases
Primarily metabolized via fatty acid beta oxidation
FP receptor
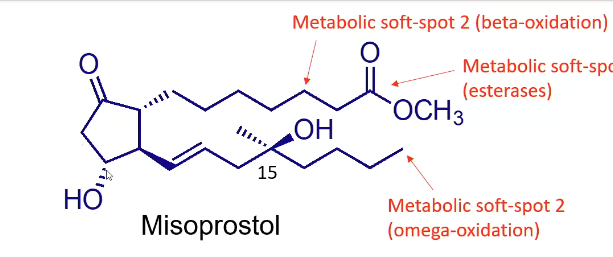
Misoprostol soft spots?
has 1 double bond
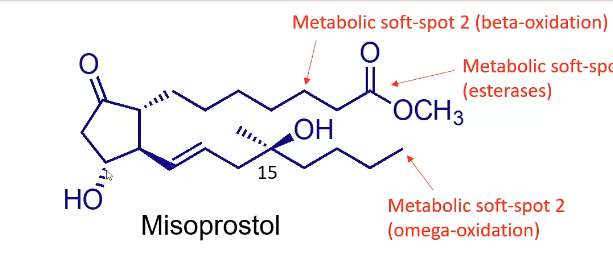
How quickly is misoprostol absorbed? Which metabolism is blocked?
Rapidly absorbed, peak 30 mins (pro drug)
Metabolism of 15-hydroxy blocked by 15-methyl group
What is the Singulair / LTD4 pharmacophore? Metabolism?
Hydrophobe, Acid, Hydrophilic
CYP2C8 - heavy metabolism
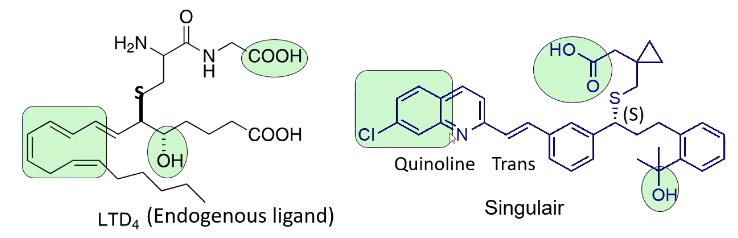
What heterocycle is in singulair?
Quinoline