NPTE Integumentary System
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
Skin is the largest body organ
15-20% of body weight
Skin: Primary functions
Protection, insulation, holding organs together, sensory, fluid balance, temperature control absorbing UV radiation, metabolizing vitamin D, and synthesizing epidermal lipids
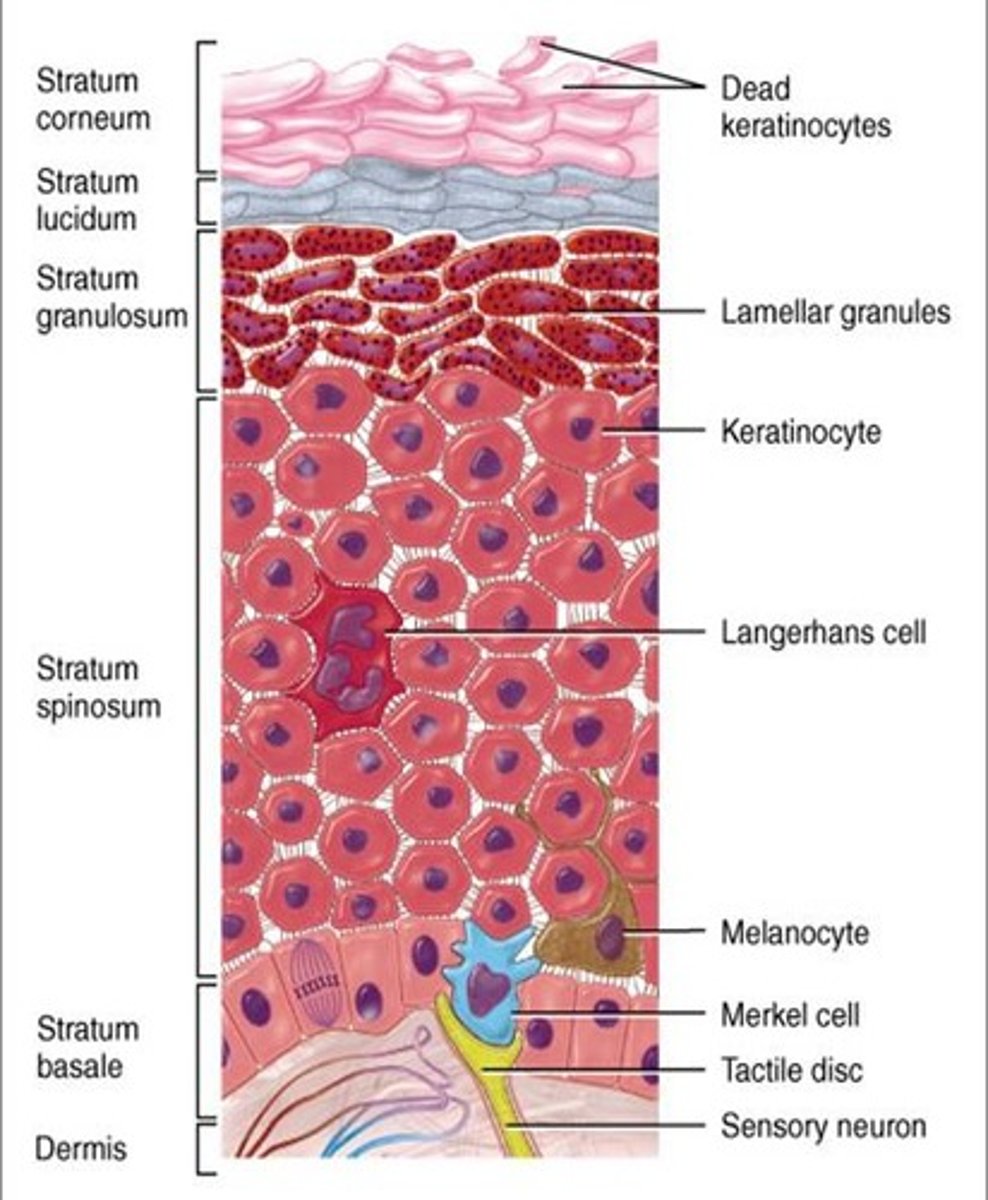
Epidermis
Keratinocytes, Melanocytes, Langerhans Cells (immune cells), Basal Cells
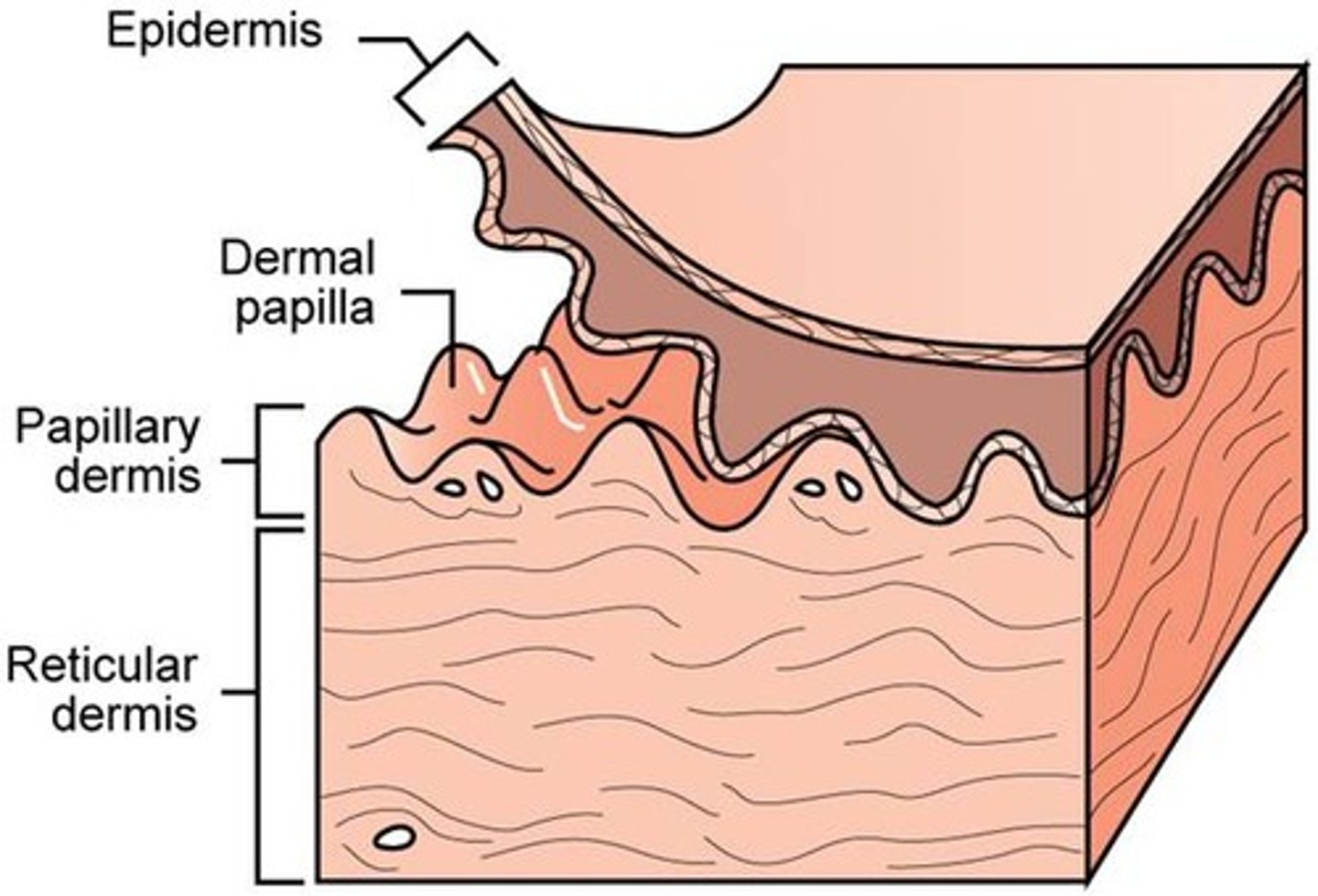
Dermis
Has the most important structures, they are protected. Collagen, Reticulum, Fibroblasts, Macrophages, Lymphatic Glands, Blood Vessels, Nerve Fibers
Meissner's Corpuscles
Detect light touch and texture
** Meissner's and Merkel = both have an M : pain/touch
Meissner: Mice(MEISsner) DISCRIMINATIVE TOUCH all your food in the kitchen at night to find a snack.
Merkel Disks
Detect light touch, texture and pressure
** Meissner's and Merkel = both have an M : pain/touch
Merkels discs - in hairless smooth (glabrous) skin - with a high density in the fingertips
Pacinian Corpuscles
Detect deep pressure and vibration
** Pacinian has a P for Pressure
Pacinian: PACinian --> Think of being under PRESSURE when playing the game PACman
Ruffini Endings
Detect warmth, stretch, deformation within joints
Ruffini: A Dog goes Ruff Ruff → RuffRuffRuffini = Dogs breath is HOT and WARM
Ruffini and Pacinian have "IN" spelled in the words, so they are DEEP in the skin --> located in dermis
Free Nerve Endings
Detect pain, temperature, touch, pressure, tickle and itch
Krause End Bulbs
Detect cold temperature
** Think like SANTA KRAUSE - He comes in the winters so COLD sensation.
Golgi Tendon Organs
Sensitive to muscle contraction force.
Golgi Tendon Organ: TENDON- TENSION in the muscles
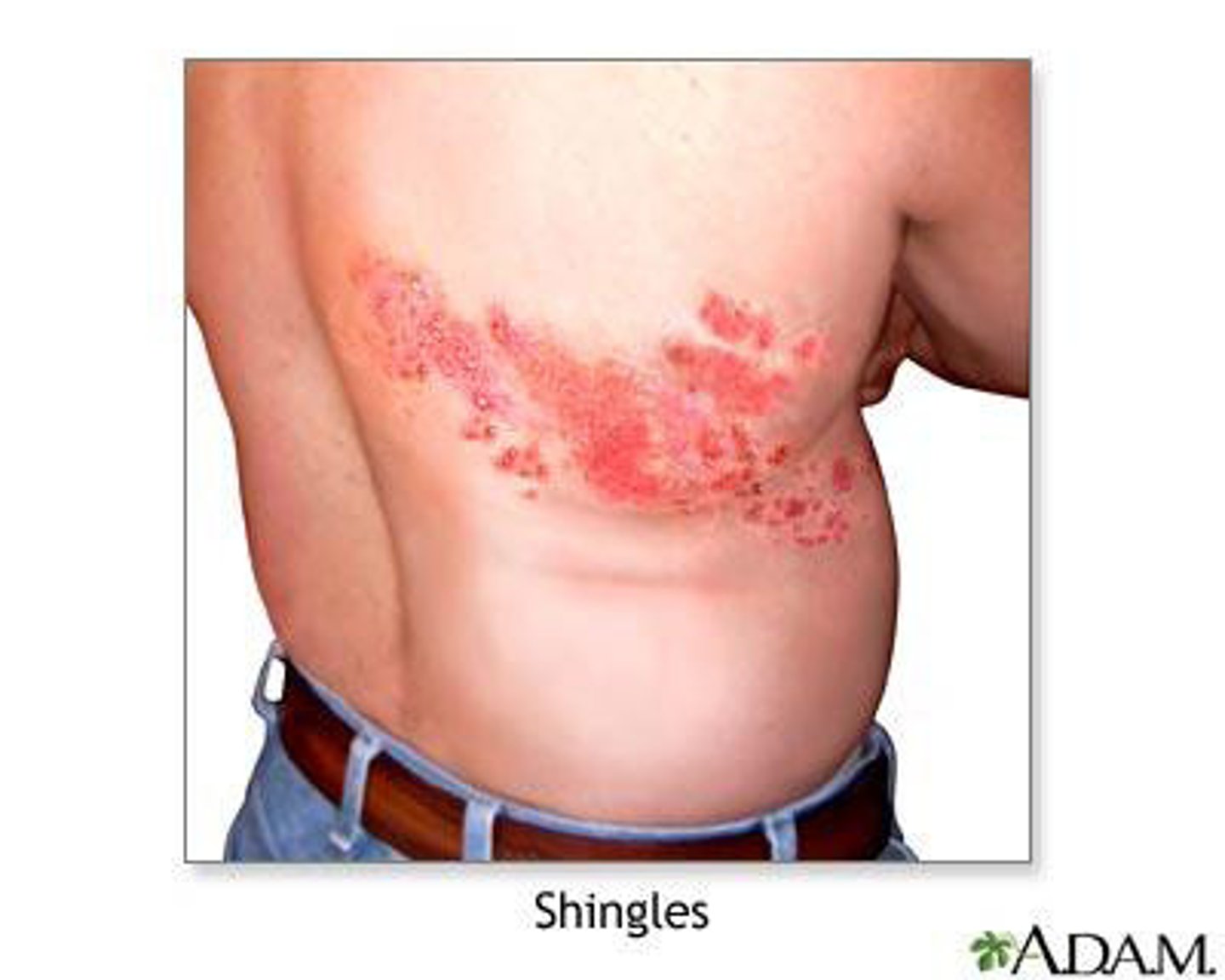
Herpes Zoster (shingles)
Dermatomes: Herpes zoster has initial symptoms of pain and paresthesia located to the affected dermatome (unilateral)
- If we apply TENS the pads have to follow the dermatome level.
Integumentary:
-- Present as painful rash with clusters of fluid filled vesicles
-- Mostly unilateral
-- Raised to palpation (<2 mm height)
-- Pink with silvery white appearance
Which CN can be affected?
CN 5, 3, 7, 9, 10
Precautions:
Airborne and contact so you need the mask and gloves.
What CN are affected with Herpes Zoster?
3, 5, 7, 9, 10
Precautions for Herpes Zoster?
Airborne and contact so we need mask and globes
Herpes Symplex HSV-1
Herpes labialis "fever blister")
Found on the lip or skin near the mouth. Generally only infects areas ABOVE the waistline and occurs when oral secretions or mucous membranes infected with HSV come in contact with a break in the skin.
Contact precautions
Herpes Symplex HSV - 2
Also known as genital herpes.
Can cause cold sores but usually does not
Contact precautions
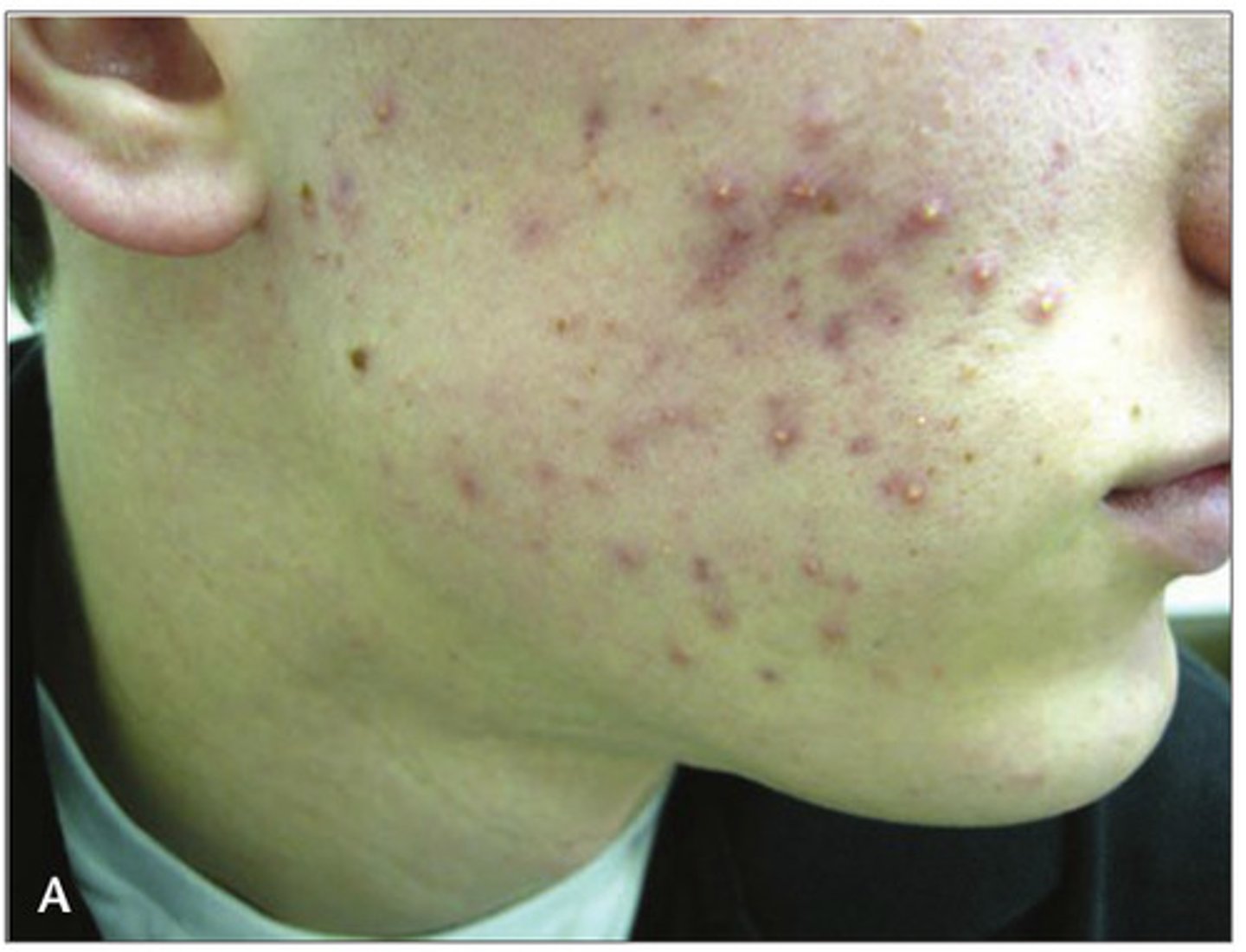
Acne Vulgaris
Formation of comedones, papules, pustules, nodules and/or cysts as a result of obstruction and inflammation of pilosebaceous units (hair follicles and their sebaceous gland).
Acne develops on the face and upper trunk, usually in adolescents.
Scleroderma
Scleroderma is an autoimmune condition characterized by inflammation and fibrosis of many parts of the body, including the skin, blood vessels, synovium, skeletal muscle, and certain internal organs such as the kidneys, lungs, heart and GI tract.
- Rare condition that can impact adults and children, with more incidences in Caucasian women.
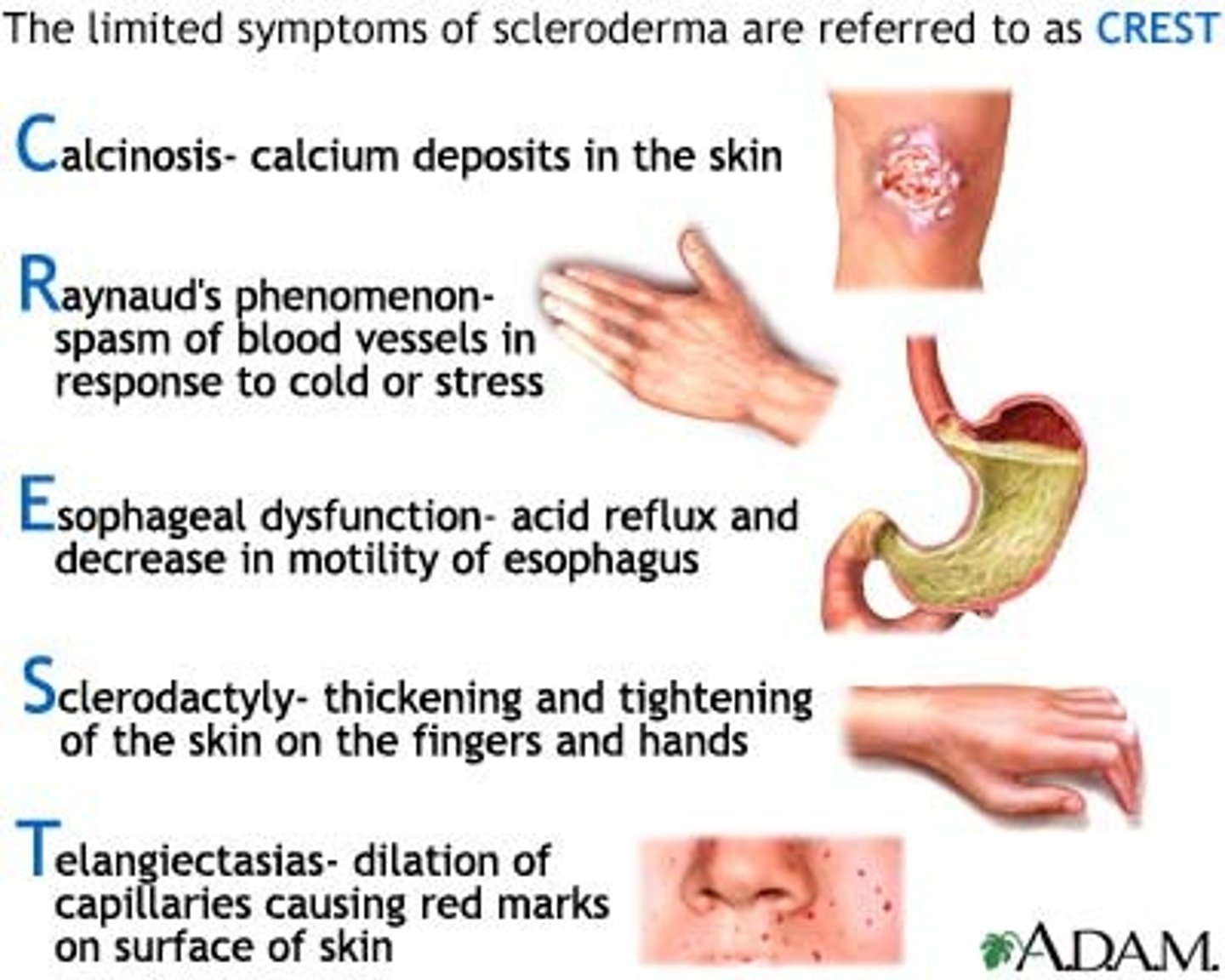
CREST
Calcinosis: calcium deposits in the skin
Raynaud's phenomenon: spasm of blood vessels in response to cold or stress
Esophageal dysfunction: acid reflux and decrease in motility of esophagus
Sclerodactyly: thickening and tightening of the skin on the fingers and hands
Telangiectasias: dilation of capillaries causing red marks on surface of the skin
CREST
Calcinosis: calcium deposits in the skin
Raynaud's phenomenon: spasm of blood vessels in response to cold or stress
Esophageal dysfunction: acid reflux and decrease in motility of esophagus
Sclerodactyly: thickening and tightening of the skin on the fingers and hands
Telangiectasias: dilation of capillaries causing red marks on surface of the skin
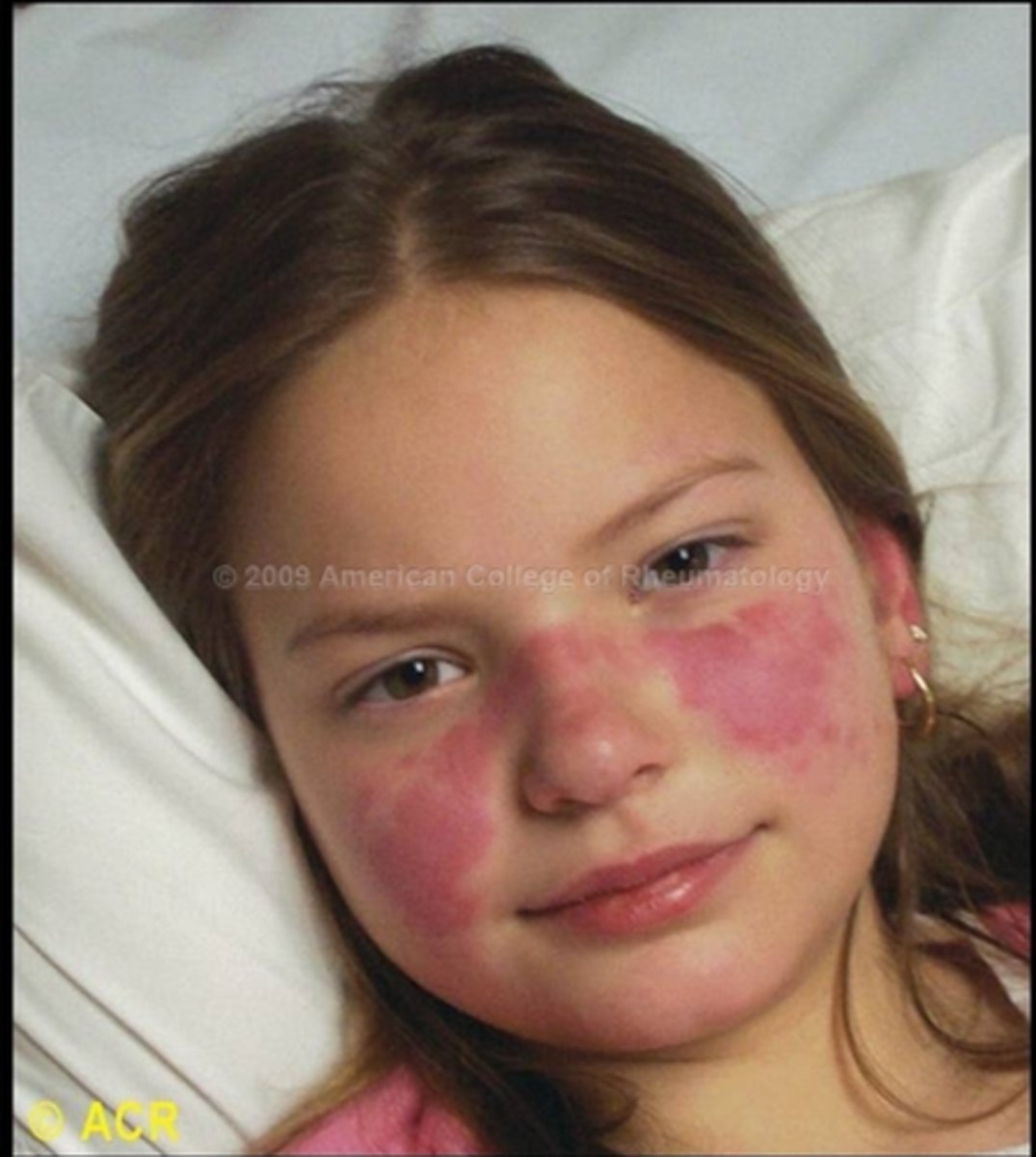
Systemic Lupus Erythematous (SLE)
Autoimmune disease and is an example of a type III hypersensitivity resulting in a chronic condition.
- SLE is the most common form of lupus
Hallmark presentation is malar rash that looks like a red butterfly across the cheeks and nose
- Skin rash can also appear over the extensor surfaces of the arms, forearms, and hands/fingers
- Arthralgia, arthritis, fever, malaise, photosensitivity, dyspnea, cough and peripheral neuropathy.
Epidemiology:
More common in African-American, African-Caribbean, Hispanic-American, American-Indian, and Asian persons > Caucasians
- Women > Men
- 15-40 years old
Fungal Infection: Ringworm
"Tinea Corporis" is marked by the formation of ring-shaped pigmented patches covered with vesicles or scales that often become itchy
- Transmission includes: person to person, animal to person, or from an inanimate object. It will spread without treatment.
Treatment:
Maintaining clean, dry skin
Applying anti fungal powder or topicals as prescribed
- Griseofulvin - may take weeks to months to complete and should be continued throughout the prescribed dosage. Has many side effects including liver.
Fungal Infections: Athlete's foot
Tinea Pedis causes erythema, skin peeling, and pruritus between the toes that may spread
Treatment:
Maintaining clean, dry skin
Applying anti-fungal powder or topicals as prescribed; if needed, intestinal yeast may be required
Clean, dry socks and adequate footwear
Treatments helps to prevent cellulitis (bacterial infection in the leg - red sores, redness, warmth, flaky skin)
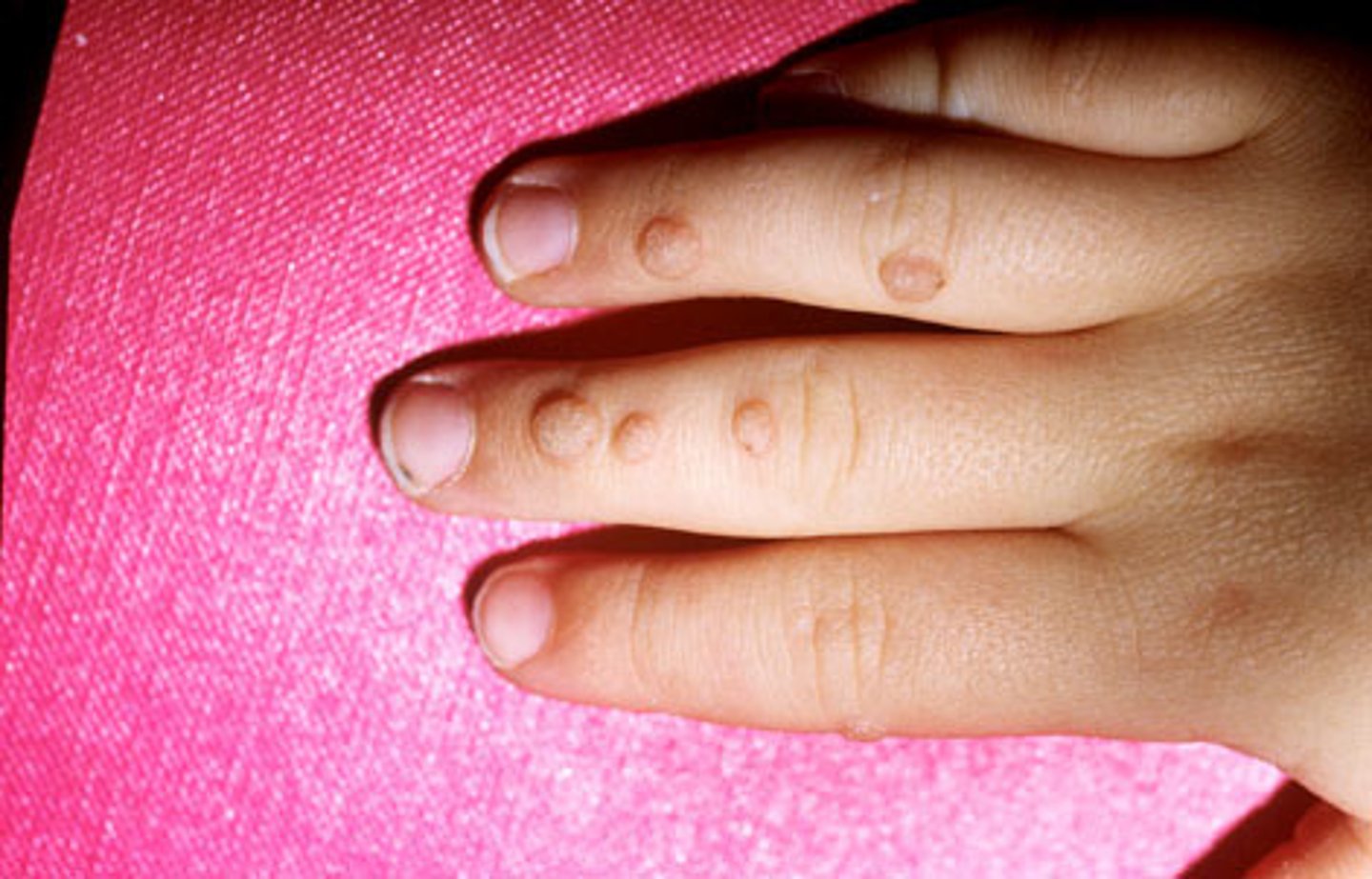
Warts
Benign infection caused by human papilloma virus (HPV) seen on the skin especially hands, fingers, pressure points of feet
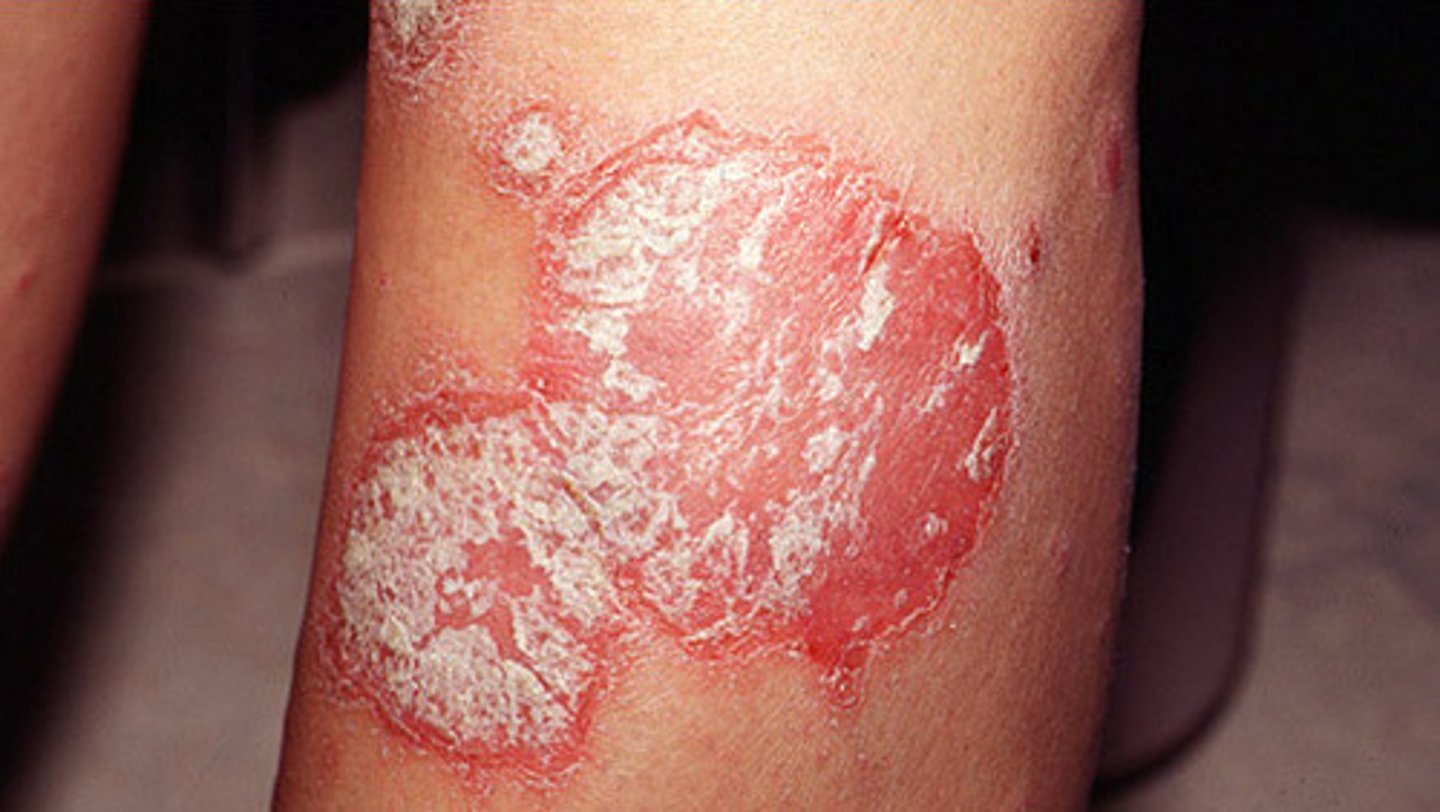
Psoriasis general
Silvery, scaly patches on the skin. Common in those who have psoriatic arthritis.
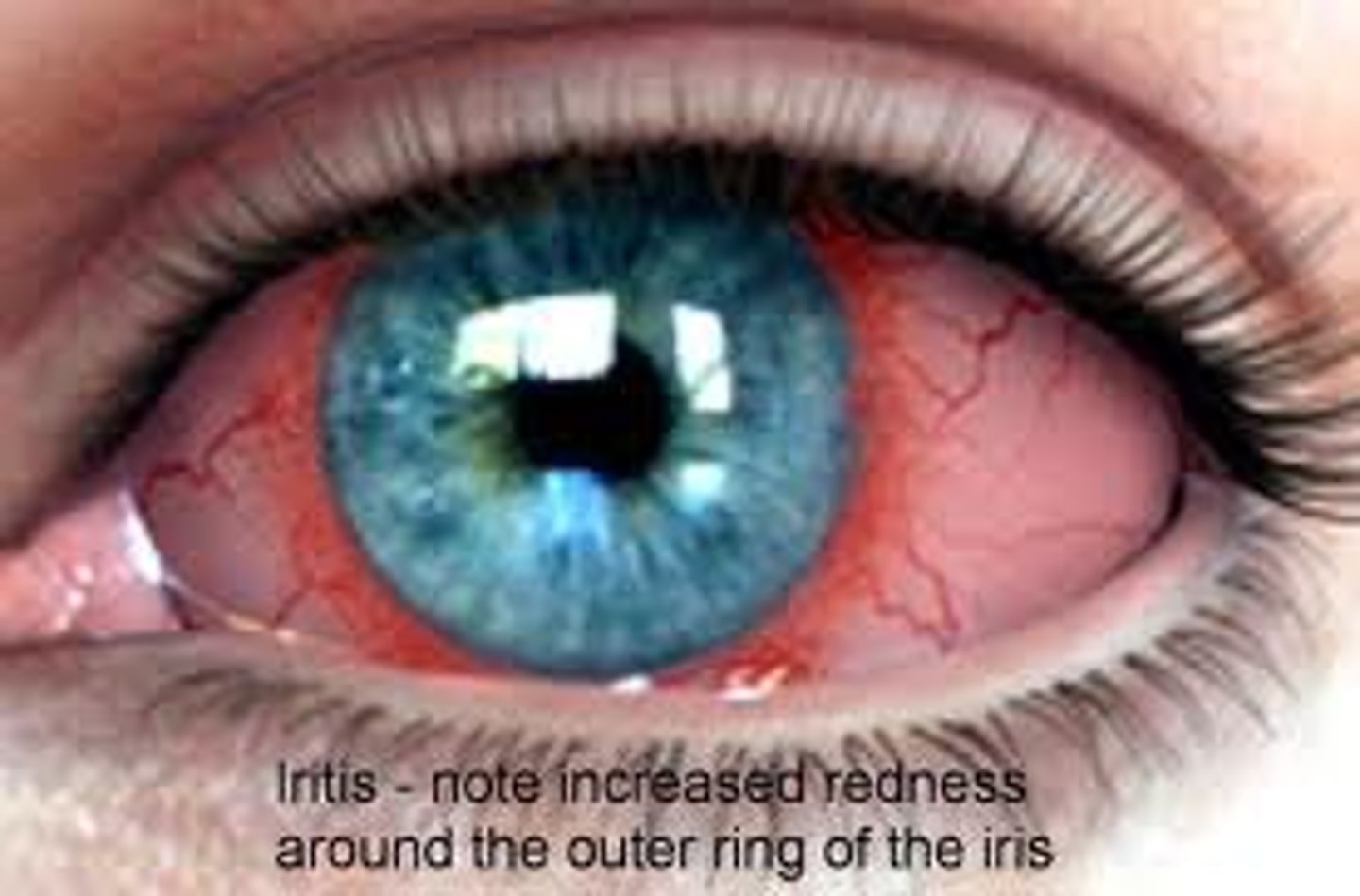
Uveitis
commonly found in patients with ankylosing spondylitis
Urethritis
Commonly found in patients who have Reiter syndrome. Occurs after an infection.
Yeast infections
Usually appear as a bright red rash with tiny macules and papules, can also appear scaly
Pediculosis
Lice. Found on the head, body and genital area
Stages of Lipedema
Stage I: skin surface is smooth, subcutaneous fat thickened, fat structure fine-knotted
Stage II: skin surface uneven, fat structure coarsely knotted
Stage III: Tissue additionally coarser and harder, large-lobed deforming fat lobes
Stage IV: Additional severe lipolymphedema
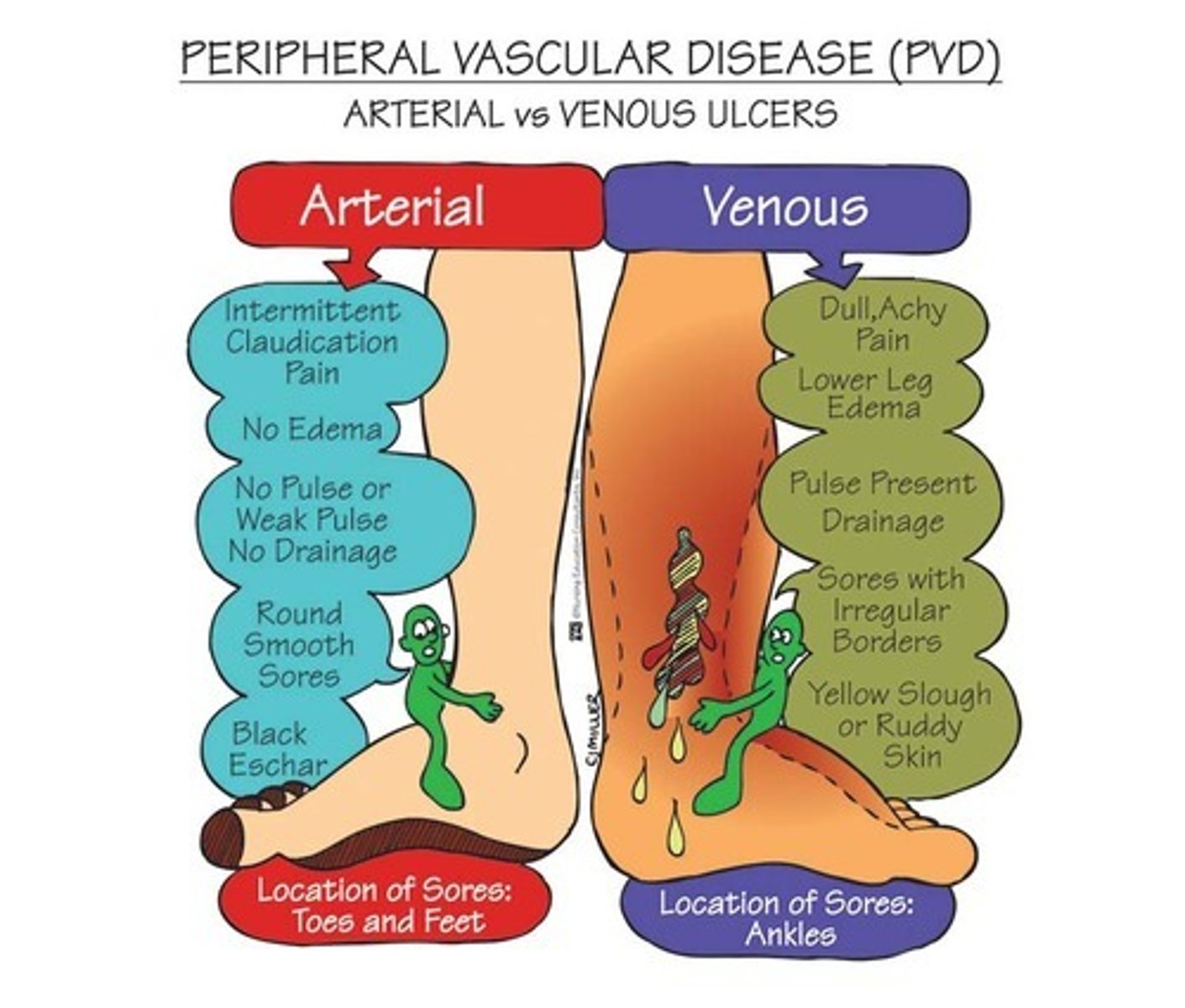
Venous insufficiency
Refers to inadequate drainage of venous blood from a body part, usually resulting in edema and/or skin abnormalities and ulcerations.
- Carry blood to the heart
- Affect blood going to the heart = blood accumulates in the leg = swelling/edema and wet skin
- ELEVATION HELPS SYMPTOMS
Arterial insufficiency
Refers to a lack of adequate blood flow to a region of the body
- Arteries supply blood to the extremities
- Affect blood supply to the limb = less blood to the limbs = pale/dry skin
- ELEVATION WORSENS SYMPTOMS
Intermittent claudication is typically related to arterial insufficiency - specifically peripheral artery disease. Occurs when blocked arteries reduce blood flow to the muscles during activity and cause pain or cramping in the legs. Subsides with rest
Venous insufficiency: clinical presentation
- Proximal to the medial malleolus VENMO Venous = medial malleolus.
- Irregular, shallow appearance
- Flaking, brownish discoloration - hemosiderin staining
- Wet wound
- Mild to moderate pain
- Elevation decrease pain
- Can be bilateral or unilateral. Bilateral cases often due to systemic issues like chronic venous insufficiency, unilateral cases usually due to DVT or trauma.
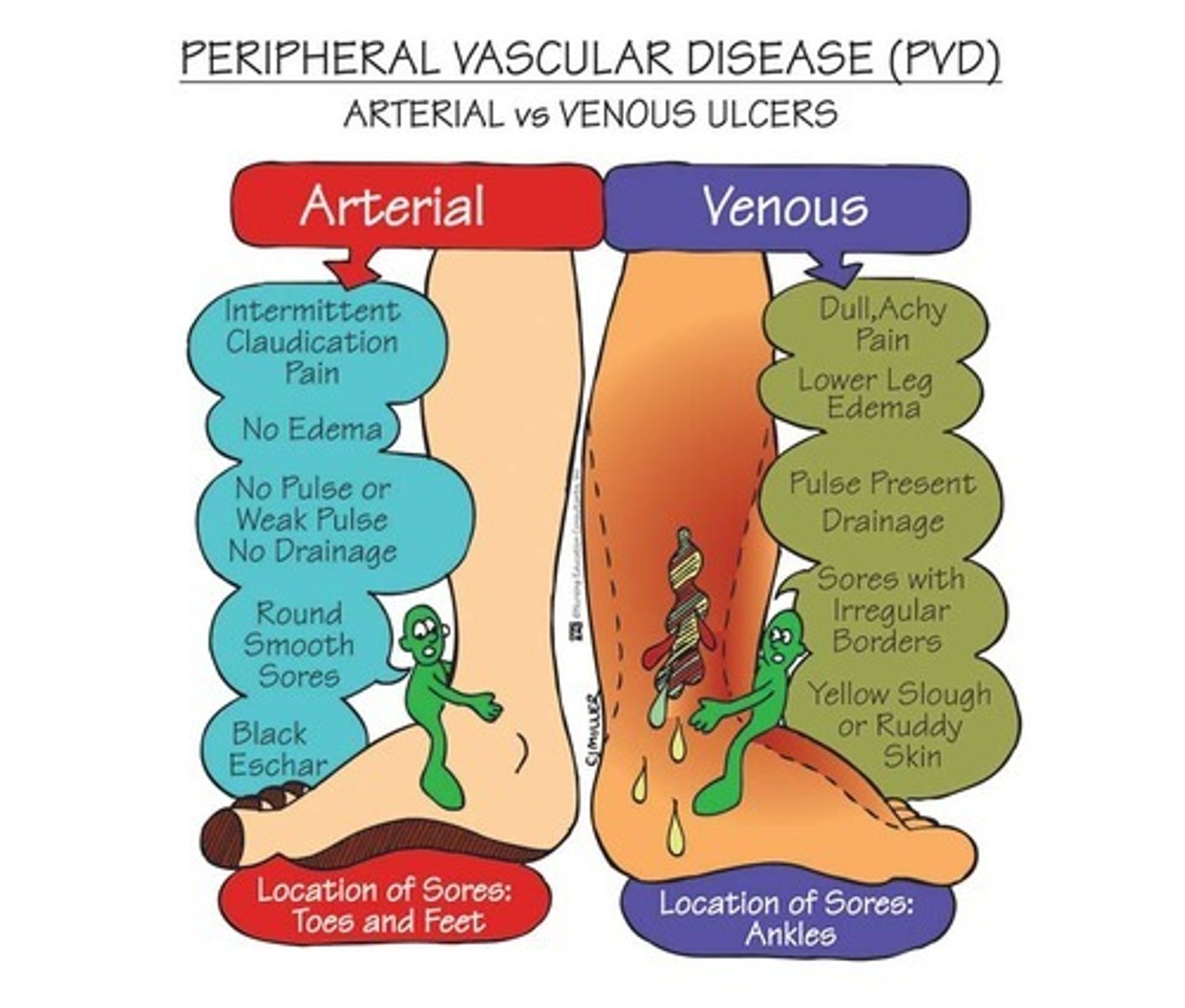
Arterial insufficiency: clinical presentation
- Lower 1/3 of leg, toe, dorsum of foot, lateral malleolus ALMA = Arterial Lateral Malleolus
- Smooth edges, well defined, tend to be deep
- Thin and shiny, hair loss, yellow nails, dry skin
Severe pain
- Intermittent claudication
- Elevation increases pain
Intermittent Claudication Scale
Grade I: definite discomfort or pain, but only at initial or modest levels
Grade II: moderate discomfort or pain from which the patient's attention can be diverted
Grade III: Intense pain from which the patient's attention cannot be diverted
Grade IV: Excruciating and unbearable pain
* when making an intermittent walking program they will walk and rest. Pain will increase with walking because there isn't enough blood going into the legs.
Ankle Brachial Index (Ankle SBP/Arm SBP)
Measured using three arteries: Brachial artery for upper extremity and either the dorsalis pedis or posterior tibial artery for the ankle.
> 1.2 = falsely elevated, arterial disease, diabetes
1.19-0.95 = normal
0.94-0.75 = mild arterial disease & intermittent claudication
0.74-0.50 = moderate arterial disease and rest pain
< 0.50 = severe arterial disease
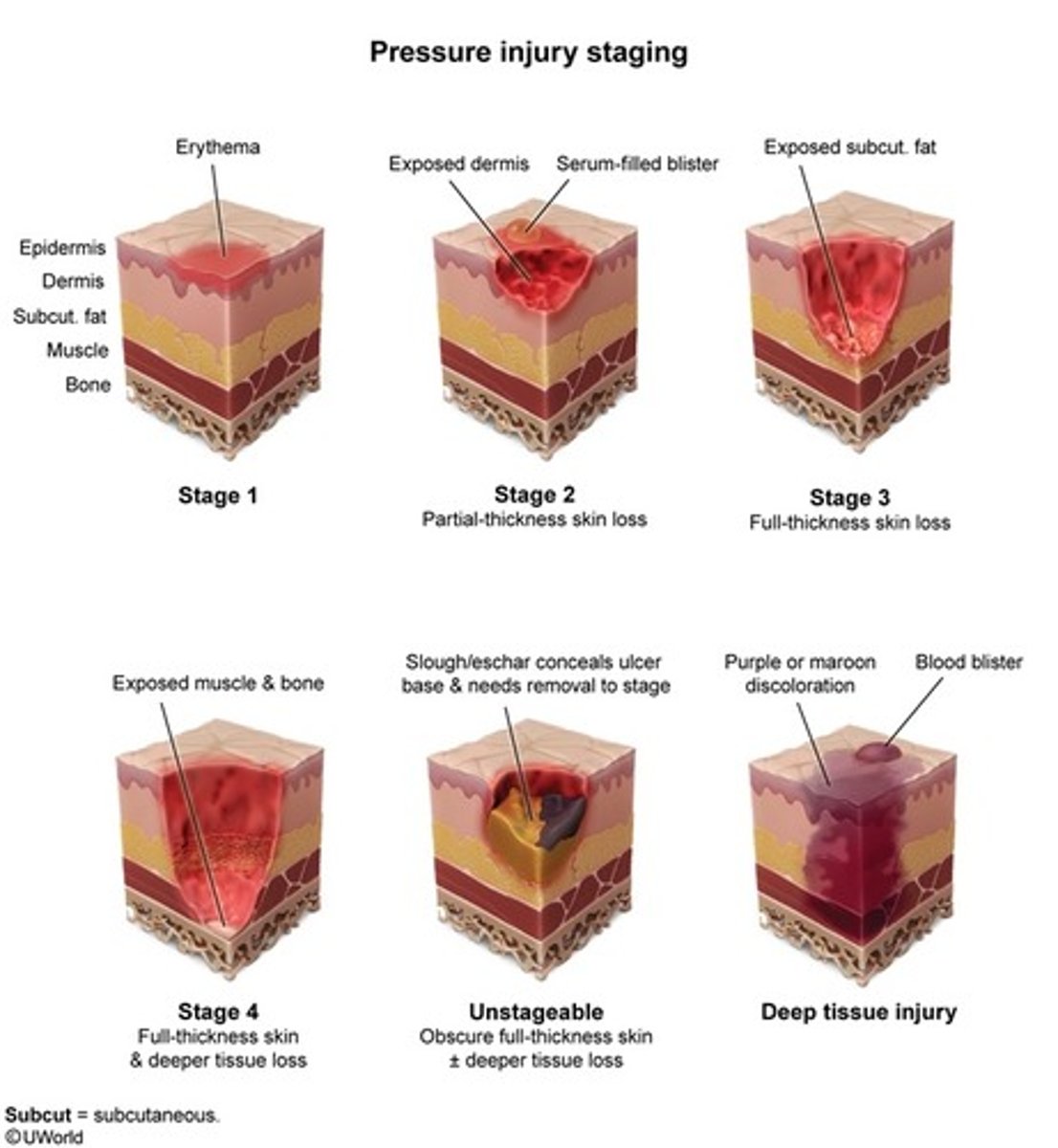
Pressure Ulcers stages
Stage 1: intact skin with non-blanchable redness
Stage 2: Partial thickness wound. Superficial in nature with pink/red wound bed (shallow crater)
Stage 3: full thickness wound. Subcutaneous fat tissue visible but no bone, tendon and muscle exposed (deep crater). Slough/eschar present. Undermining and tunneling may occur. FAT three letters, stage 3
Stage 4: Full thickness with exposed bone, tendon or muscle. Slough/eschar present. Undermining and tunneling often occur.
Unstageable: wound bed covered with slough/eschar (unable to identify the depth)
Deep tissue injury: intact skin purple maroon appearance. Something was injured but the skin was intact, like a bruise.
Stage 1: reddened area that doesn't go away
Stage 2: First 2 layers of skin. Superficial in nature
Stage 3: Fat. Down to fascia
Stage 4: bone
Undermining and Tunneling
Undermining: not as deep as tunneling, can be wider and under the wound bed
Tunneling: deeper and with an exit point.
*Once it gets to a stage it's always that stage, it can improve but the classification remains the same. Can only change the name if it gets worse.
Key points to remember: diabetic ulcers, venous insufficiency ulcers, arterial ulcers and pressure ulcers
Diabetic ulcers: generally located on the weight bearing surface of the foot
Venous insufficiency ulcers: frequently are proximal to the medial malleolus. They are edematous.
Arterial ulcers: generally located on the lateral malleolus, distal toes or areas of trauma
Pressure ulcers: the result of unrelieved external pressure on an area
Wound location and size
Measure: length x width x depth using a disposable ruler
A disposable cotton swab can be used to assess the depth
Wound characteristics
Granulation tissue - viable
Necrotic tissue - non viable
Wound edges
thin or thick (indurated), rolled (epibole)
Periwound
the surrounding of the wound; can be infected
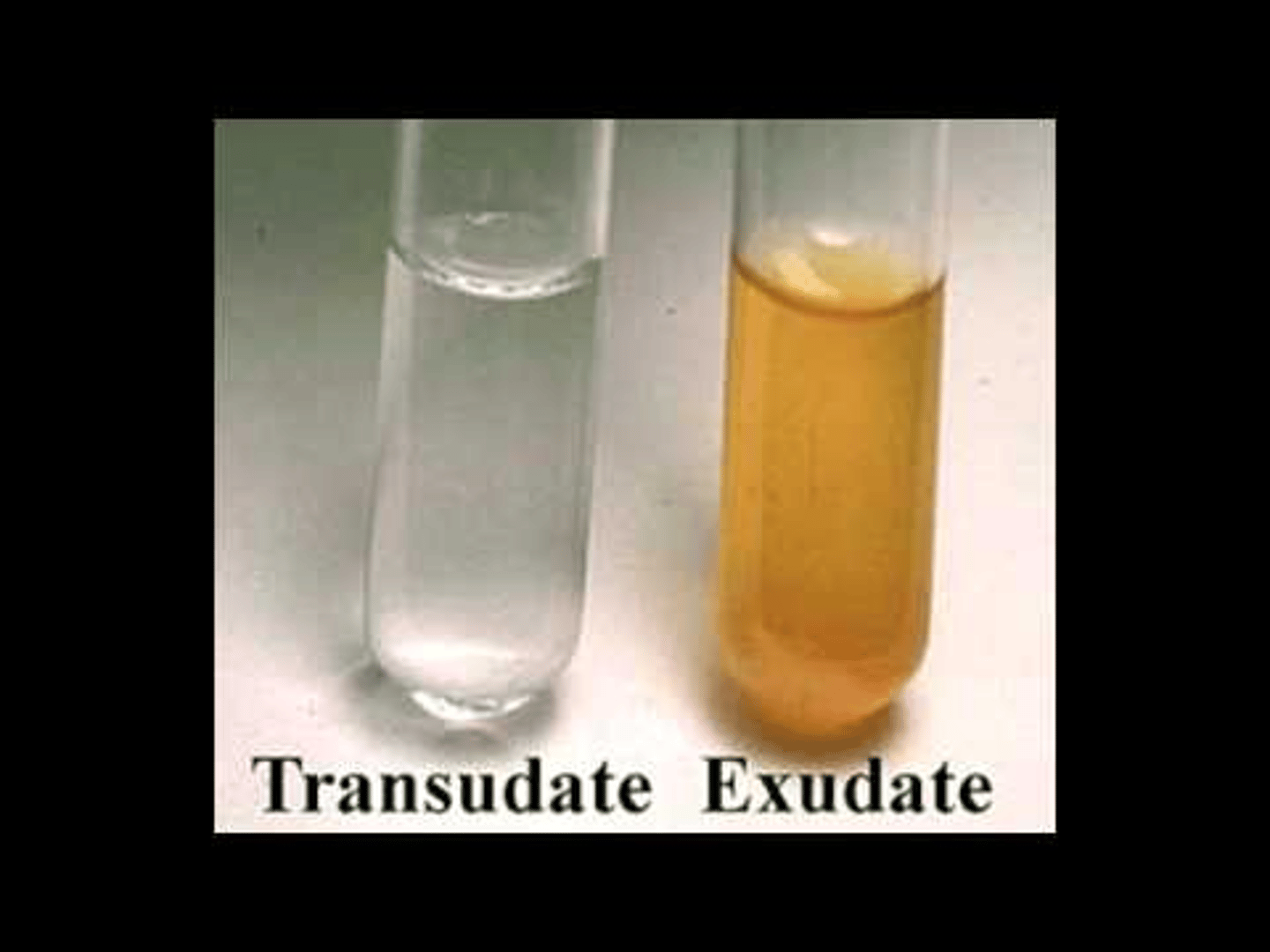
There are 6 drainage types
Transudate: clear, thin and watery
Serosanguineous: Clear tinge of red/brown - thin and watery, normal and indicates the wound is healing
Serous: clear/amber, thin and watery
Sanguineous: bloody, right red fluid - indicates inflamed wound
Pus: yellow/brown - moderate to very thick
Infected pus: hues of yellow, blue, green - thick usually indicating infection (may be normal as WBC, macrophage necrotic cells turn them into slough); drainage can be foul and yet the wound may not be infected.
Transudate
clear, thin and watery
Serosanguineous
Clear tinge of red/brown - thin and watery, normal and indicates the wound is healing
Serous
clear/amber, thin and watery
Sanguineous
bloody, right red fluid - indicates inflamed wound
Pus
yellow/brown - moderate to very thick
Infected pus
hues of yellow, blue, green - thick usually indicating infection (may be normal as WBC, macrophage necrotic cells turn them into slough); drainage can be foul and yet the wound may not be infected.
Delayed wound healing: Maceration
If a wound is too moist, the edges and periwound will become macerated
It is identified as white, friable (refers to tissue that is easily irritated - making it more prone to bleeding or tearing), overhydrated, and sometimes wrinkled skin
Cause: inappropriate wound care, uncontrolled wound drainage, perspiration or incontinence
Delayed wound healing: Dessication
If a wound lacks moisture, the wound and periwound will become dessicated
It is identified as cracked, with dry or flaky edges, and the tissue within the wound bed may be hard or crusty
Cause: inappropriate wound care, inadequate moisture, infection, dehydration
Wound care
Wound cleaning : we clean the wound with a cleaning material
Wound debridement : get rid of what we don't need
Wound dressing : cover them so they heal faster
Selective debridement
Removal of only nonviable tissues from a wound "SEA" (sharp, enzymatic, autolytic)
If 50% or more isn't infected then there is hope to save it.
- Sharp debridement: use of scalpel, scissors, forceps
buse of a topical application of enzymes
- Enzymatic debridement: use of a topical application of enzymes
- Autolytic debridement: use of the body's own mechanism to remove nonviable tissue
Nonselective debridement
Removal of both nonviable and viable tissues from a wound, when infected area is > 50% (can use brief intense TENS for pain relief)
- Wet to dry dressings: application of a moistened gauze over area of necrotic tissue to be completely dried and removed
- Wound irrigation: moves necrotic tissue from wound bed using pressurized fluid
- Hydrotherapy: using a whirlpool with agitation directed towards a wound requiring debridement.
Very mild exudate
Transparent films
Minimal Exudate
Hydrogel dressing (infected), hydrocolloid (non infected)
*hydros for minimal
Moderate exudate
foams
Heavy exudate
calcium alginates, hydrofiber (max capacity)
* calcium and fiber are hard/heavy
Heavy exudate usually indicated infection.
Infected wounds
"HAG" hydrofiber, hydrogels, calcium alginates and gauze
Red
Cover the wound, keep it moist and clean, protect it from trauma
Use a transparent dressing (such as Tagadem or OpSite) over a gauze dressing moistened with normal saline solution, or use a hydrogel, foam or hydrocolloid dressing to insulate and protect the wound.
Yellow
Clean the wound and remove the yellow layer
Cover the wound with a moisture-retentive dressing, such as hydrogel or foam dressing or a moist gauze with or without a debriding enzyme
Consider hydrotherapy with whirlpool or pulsatile lavage
Black
Debride the wound as ordered. Use an enzyme product (such as Accuzyme or Panafil), conservative sharp debridement, or hydrotherapy with whirlpool or pulsatile lavage
For wounds with inadequate blood supply and non-infected heel ulcers, don't debride. Keep them clean and dry
Superficial burn
epidermis; dry/red skin without open areas; heals in 5 days without scarring
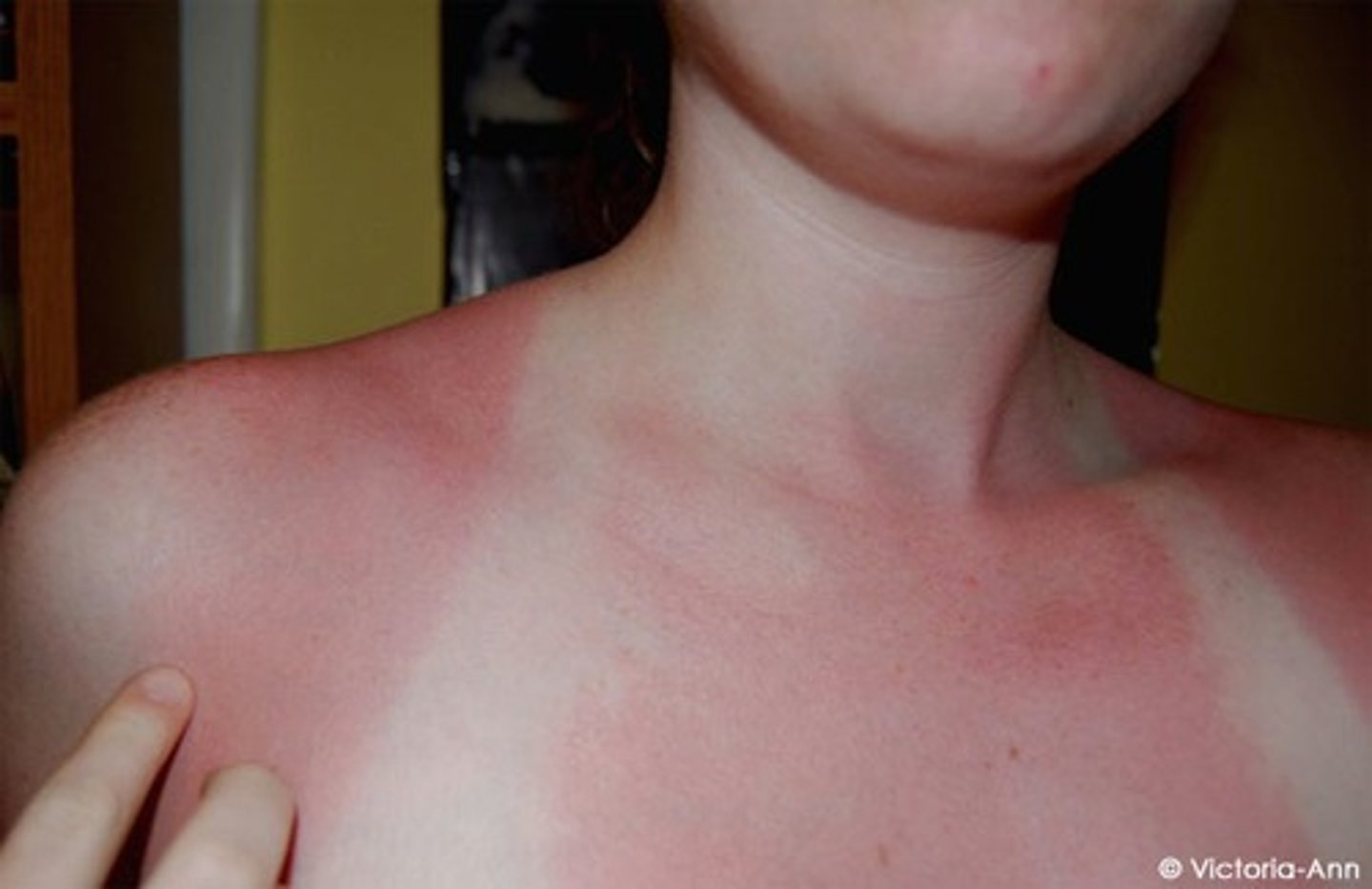
Superficial partial thickness burn
epidermis/some dermis; mottled red, intact weeping blisters, blanches to pressure with quick capillary refill, extremely painful; heals in 10-14 days with minimal scarring
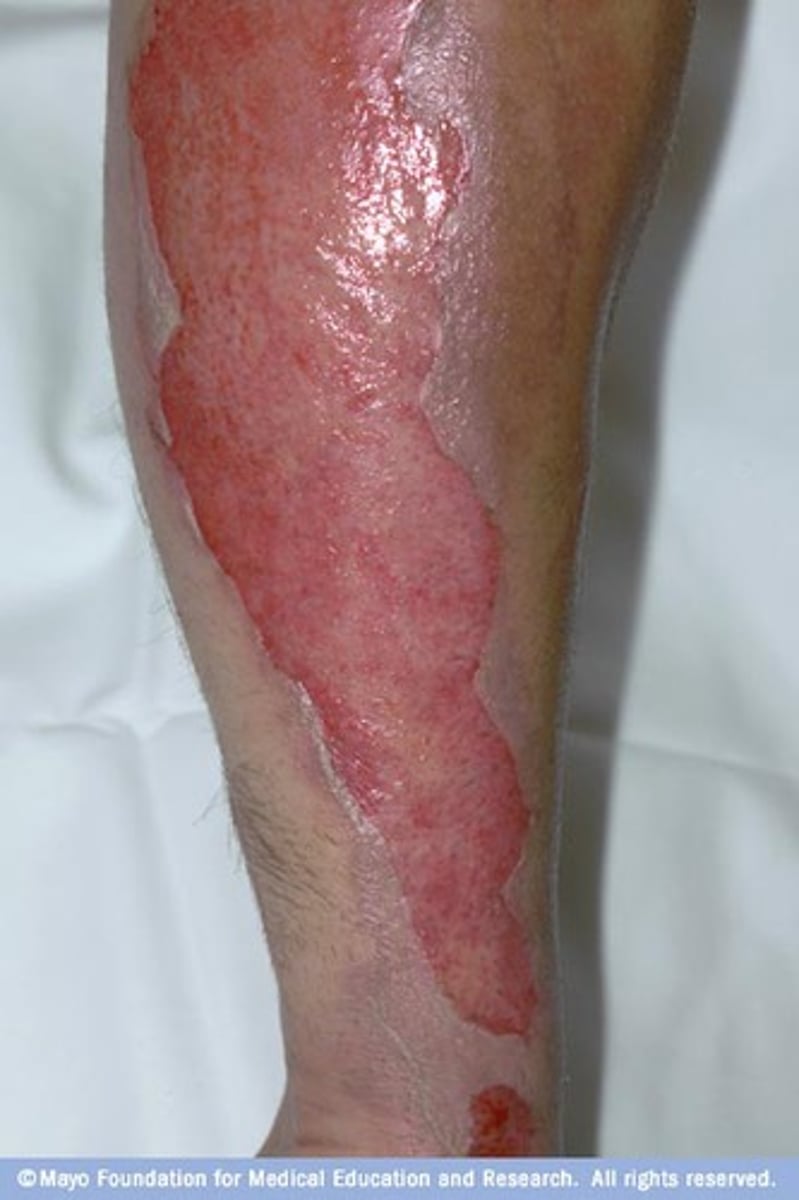
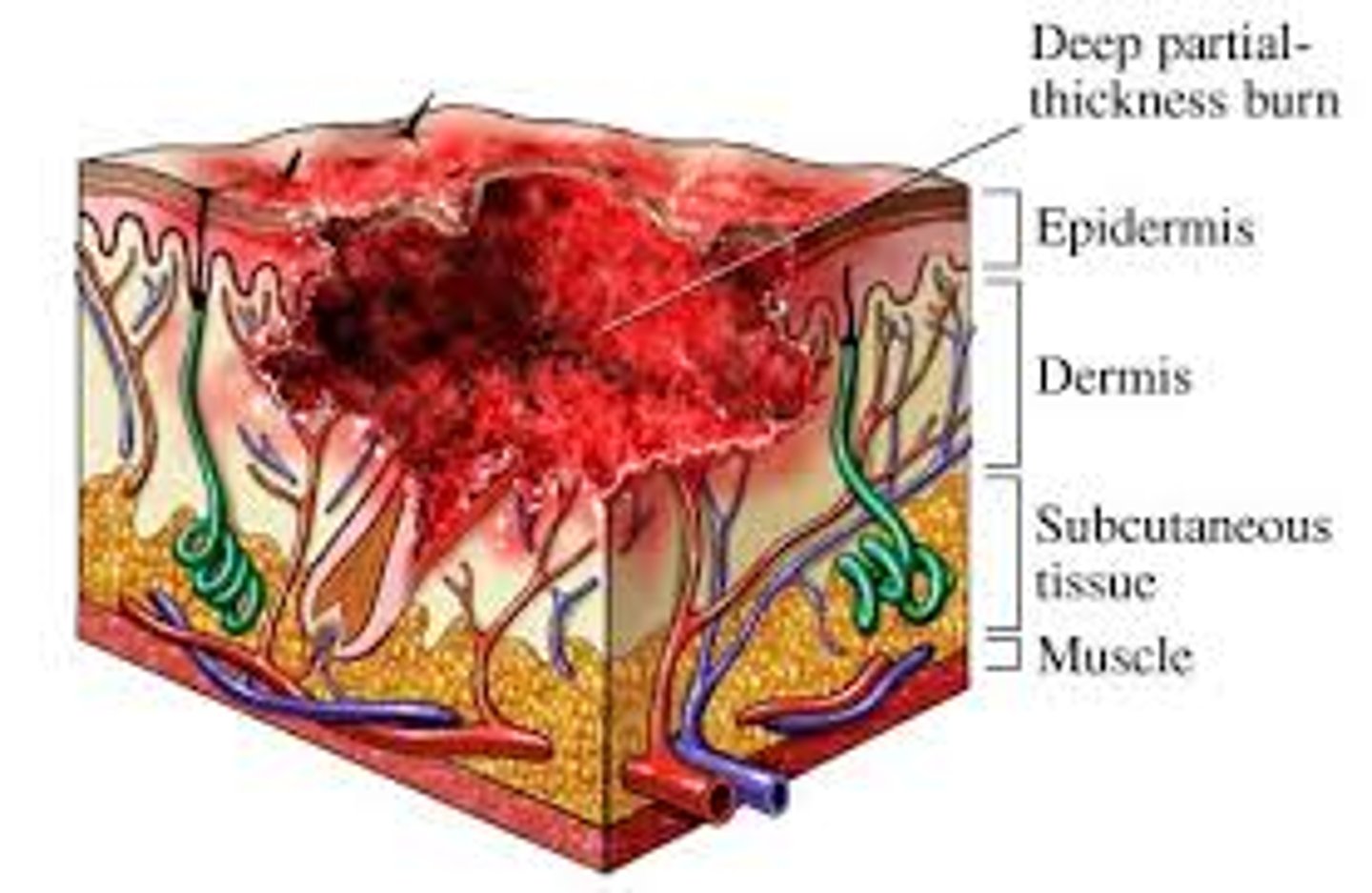
Deep partial thickness burn
epidermis/dermis; mixed red and waxy white areas, blanches to pressure with slow capillary refill, decreased pinprick sensation, pain on deep pressure; can take up to 3 weeks to heal, large wounds can be managed surgically. Development of hypertrophic and keloid scars is common.
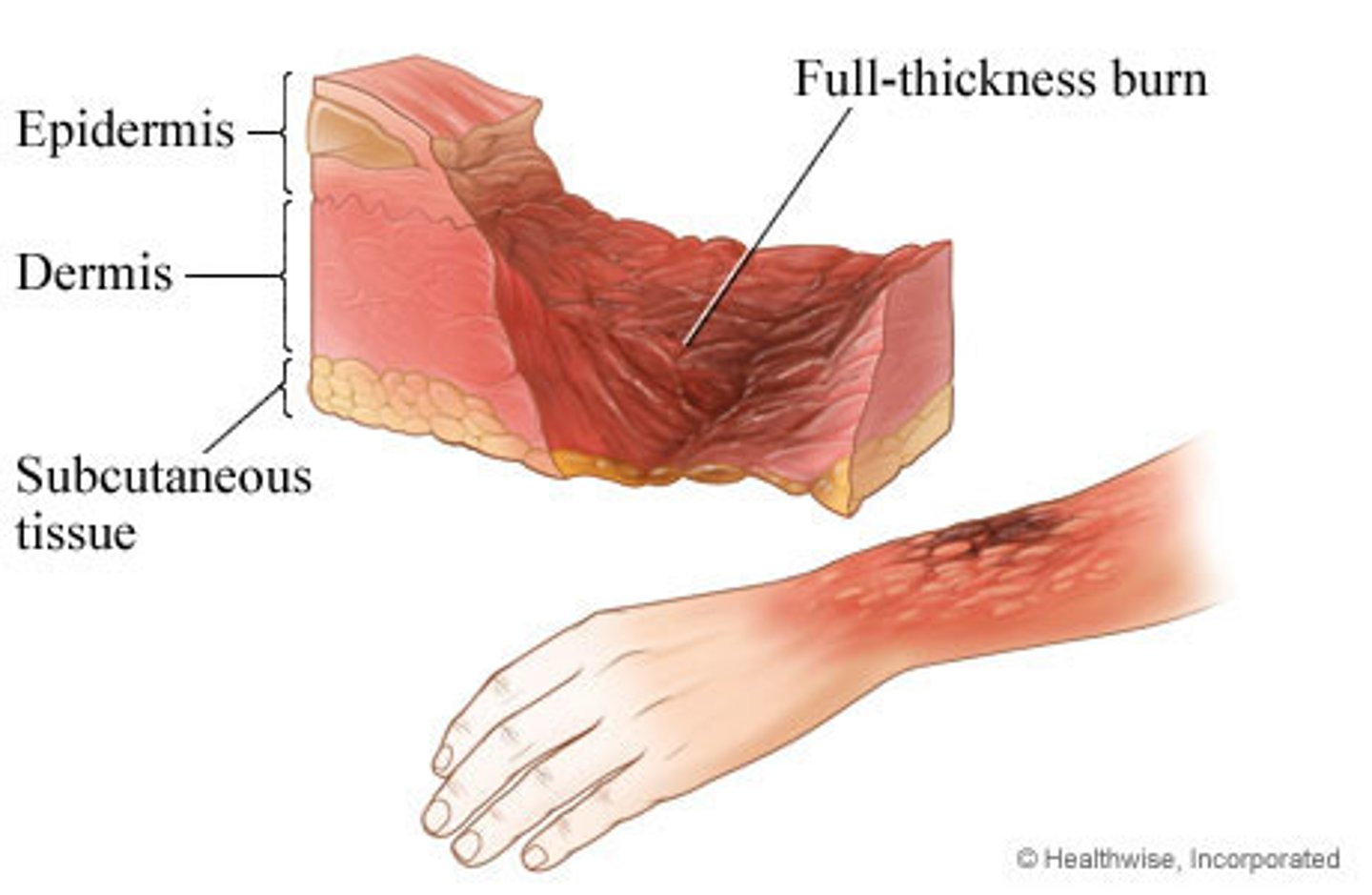
Full thickness burn
epidermis/dermis/some subcutaneous tissue; dry, rigid and leathery eschar, lack of pain, pressure and temperature sensation; requires more than 3 weeks and will requires surgical closure, may have contractures
Subdermal burn
epidermis/dermis/subcutaneous tissue; charred, dry and exposed deep tissue; requires surgical interventions and amputation/paralysis is possible.
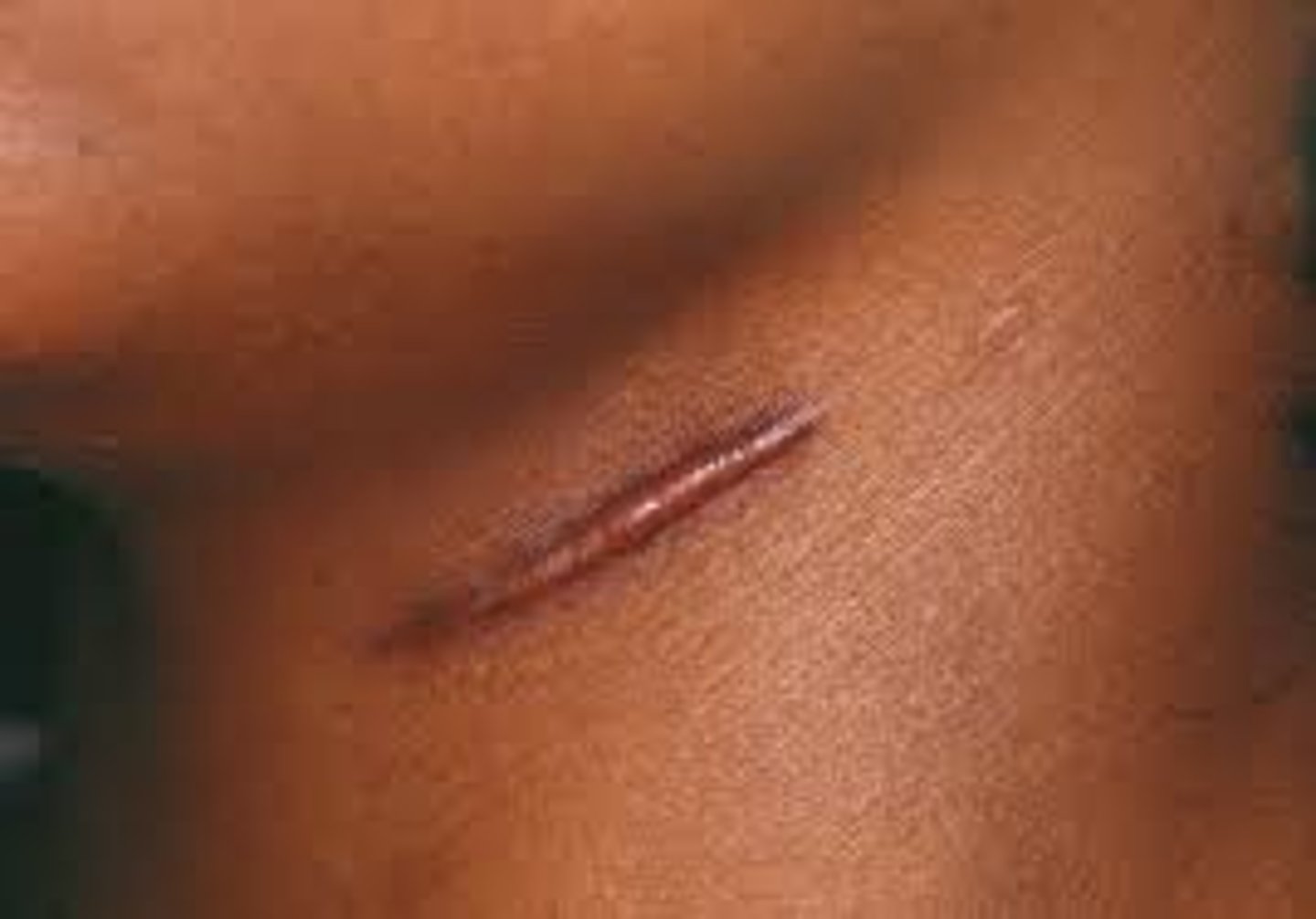
Normal scars
flat and similar to skin color
Hypotrophic scars
sunken and often hyperpigmented appearance due to loss of collagen (rare)
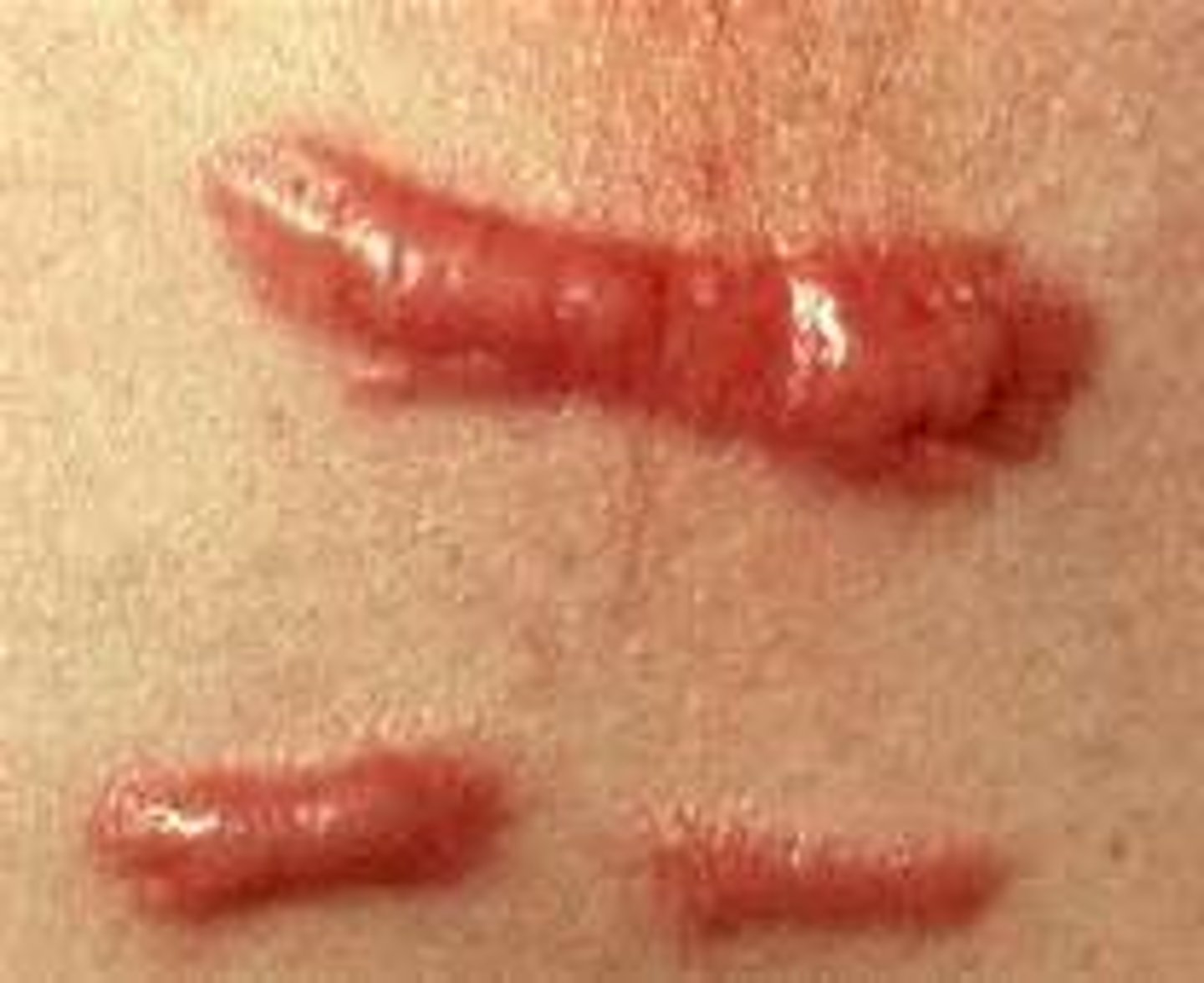
Hypertrophic scar
a healed wound with thick fibrous tissue that remains within the original wound border
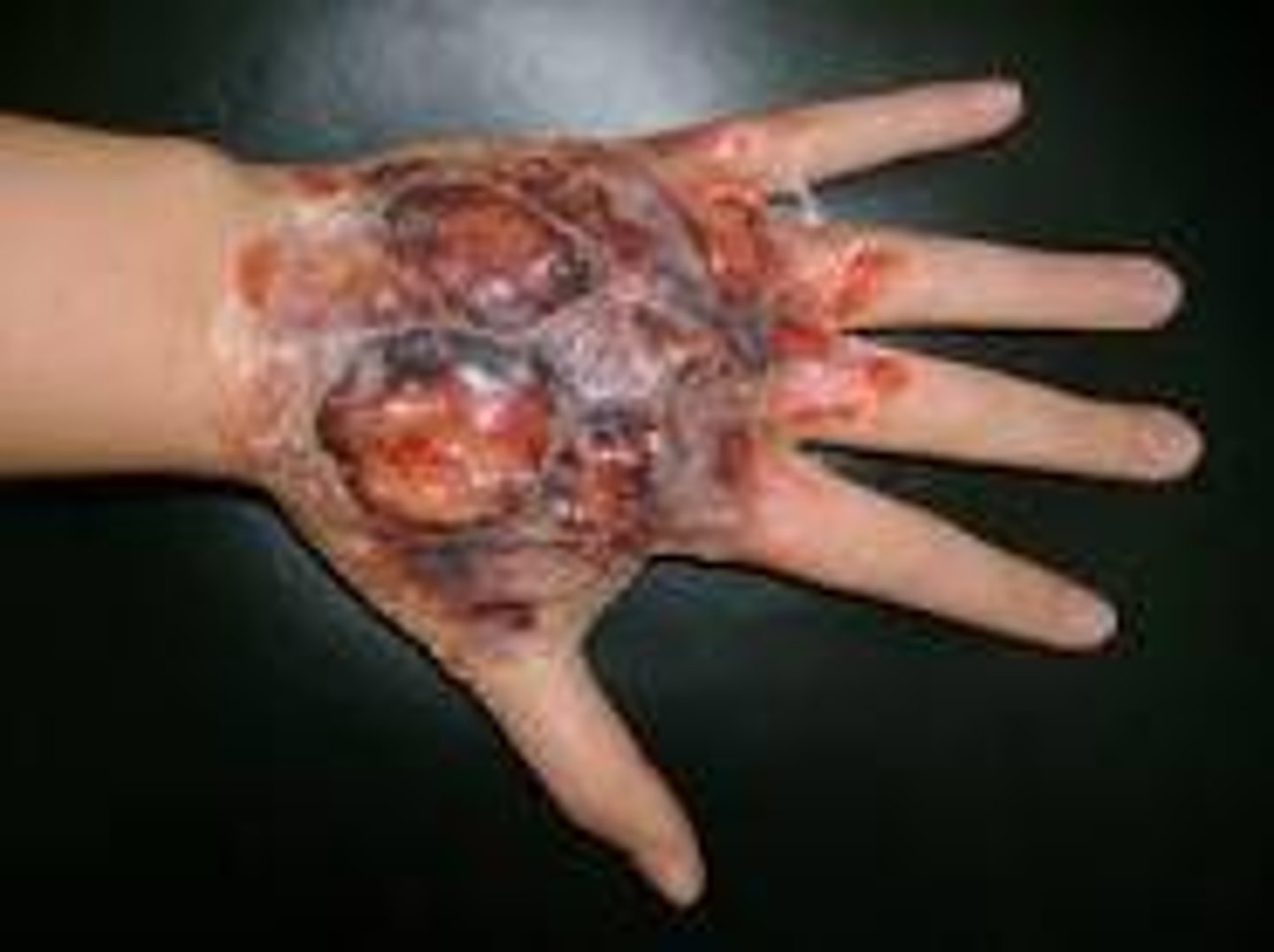
Keloid
excessive scar tissue grows outside of the original margins of the wound. Hypertrophy but spread out.
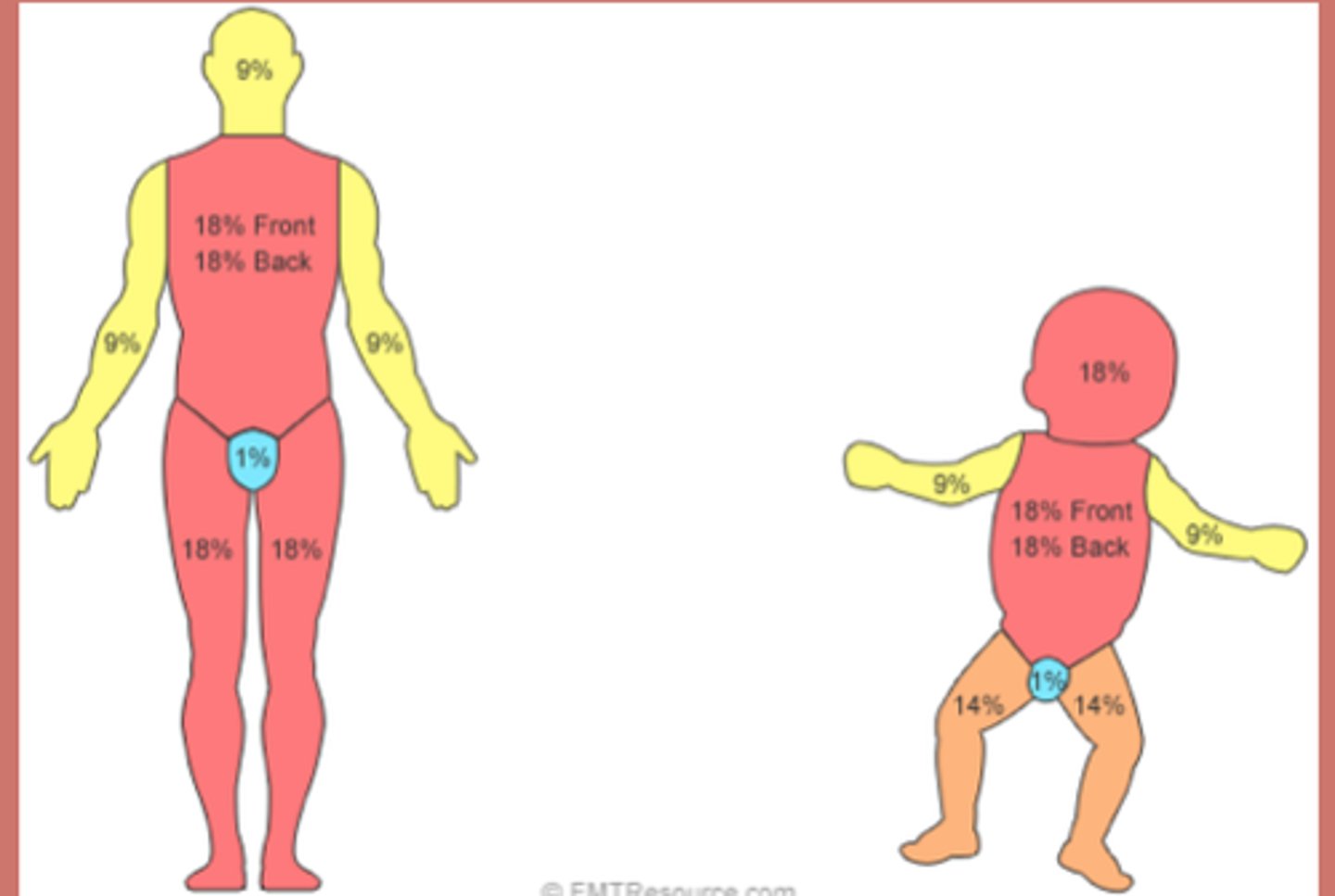
Rule of 9's
Head and neck = 9%
Upper Ex = 9% each
Lower Ex = 9% each
Front trunk = 18%
Back trunk = 18%
Child head = 8.5% (front and back)
Child arm = 4.5% (front and back)
Child thorax = 18% (front and back)
Child legs = 6.5% (front and back)
The trunk is the only one where we can divide it into upper and lower.
If they ask about the glutes remember it's with the trunk and not the legs.
Diabetic Foot Care
- Inspect the skin
Look at the foot everyday to check between the toes and bottoms of the feet
Look for blisters, sores, corns, calluses, red spots, swelling, pain, drainage from sores, broken toenails, cracked skin and odor
- Take care of the skin
Wash the feet gently everyday using lukewarm water (85F) and mild soap. Test the temperature with the hand before washing the feet
Dry the feet well, especially between the toes: can use powder
Do NOT walk barefoot: they could get cuts and wounds
- Check the shoes
Alternate the shoes everyday to allow them to dry and check for small things inside the shoe
Shop for shoes in the afternoon when the feet are the largest
See your healthcare provider
- Have regular appointments
Call your healthcare provider immediately if there is a wound on the foot
Dermatitis
Acute- red open sores
Subacute - scales/scabies.
Chronic - pigmentation.
Irritation of the skin, super common. Can be from allergies. Redness, skin irritation, pururitis.
Allergies is because of any
contact with latex, k tape, poison ivy, chemicals like harsh soaps, anything.
Actinic dermatitis: because of photosensitivity, the sun.
Atopic dermatitis: unknown, could be hereditary, allergic, psychologic disorders, stress/anxiety
Precaution: caution - we need to wear gloves!!
Statis Dermatitis
Blood is accumulated in the lower extremity because of venous pooling/insufficiency
Redness of the skin
Especially in lower extremity due to chronic venous insufficiency
Eczema
Dry skin that needs to be kept moist
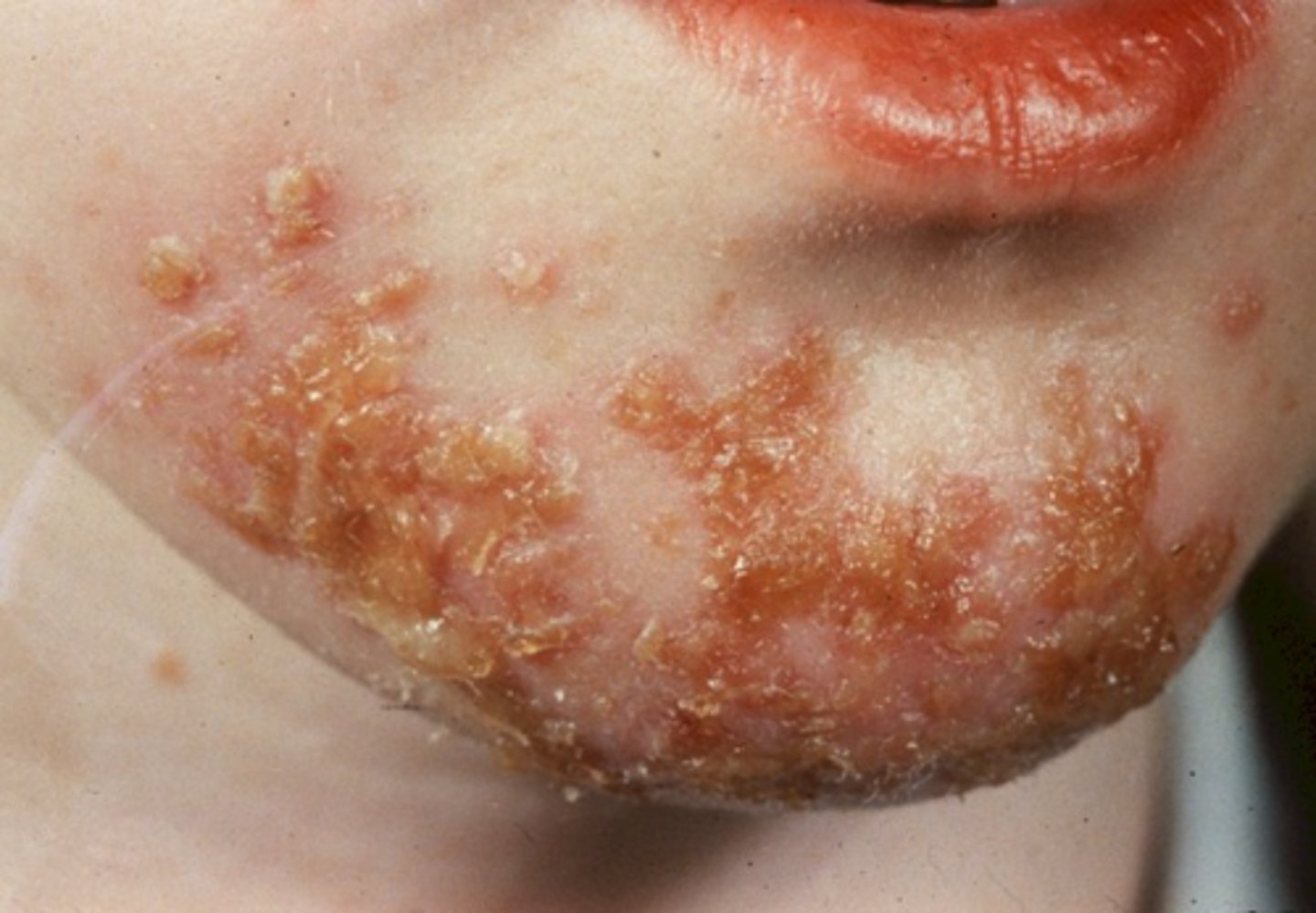
Impetigo
Superficial bacterial skin infection (staff aurus)
- Small, yellow, pus filled vesicles
- Honey crust appearance
Especially seen around the mouth in children and elderly
CONTACT precautions - we have to wear gloves!
** we remember this with small yellow pus filled vesicles. Like honey.
Initially starts as small vesicles that are filled with pus, once it dries out it looks like a honey crust appearance.
- Usually seen with children and elderly population because they are immunocompromised and can get a bacterial infection easier.
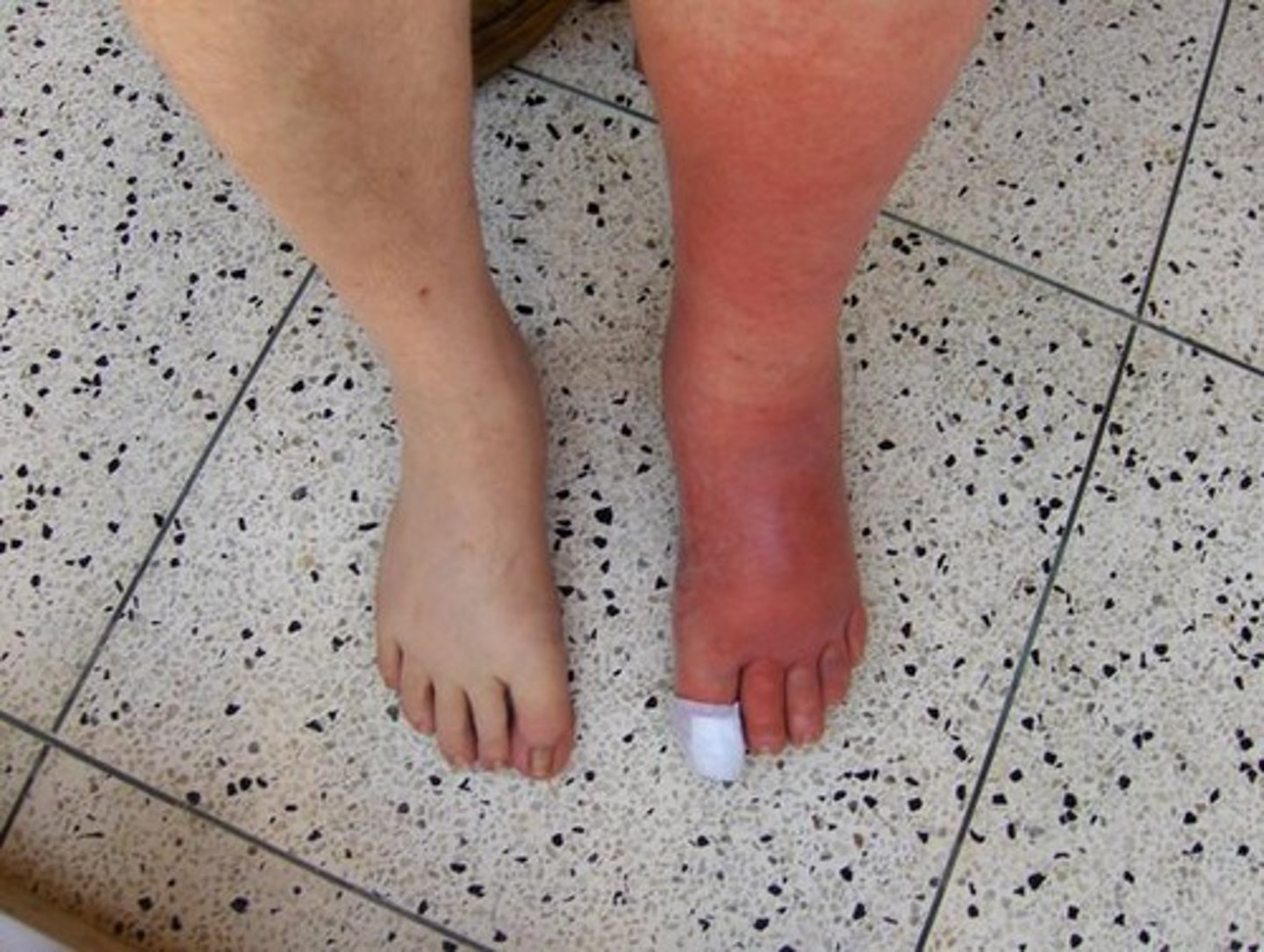
Cellulitis
Bacterial skin infection but now it's deep
- Staff/strep aurus has gone deep inside the connective tissue.
- HOT RED EDEMATOUS !!
- Can lead to sepsis. First thing is antibiotics and getting rid of the infection. - Can cause lymphangitis, gangrene etc. Advanced lymphedema + bacteria can cause this. Can have a fever as well because it's an infection. Fever/chills
- Can be unilateral or bilateral
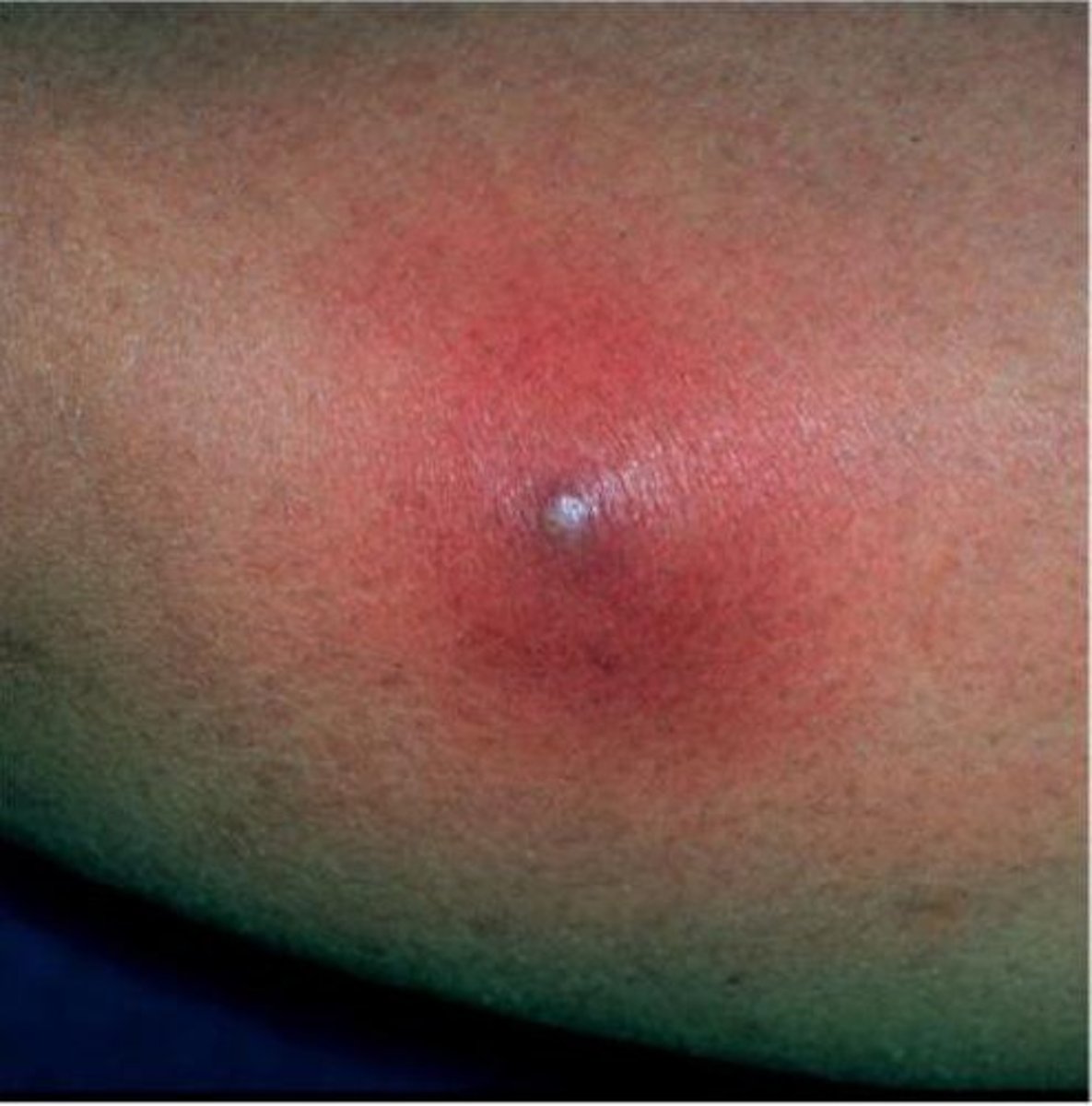
Abcess
Cavity filled with pus
Local bacterial infection
Pull of hair
Antibiotics and needs to be drained.
Very painful
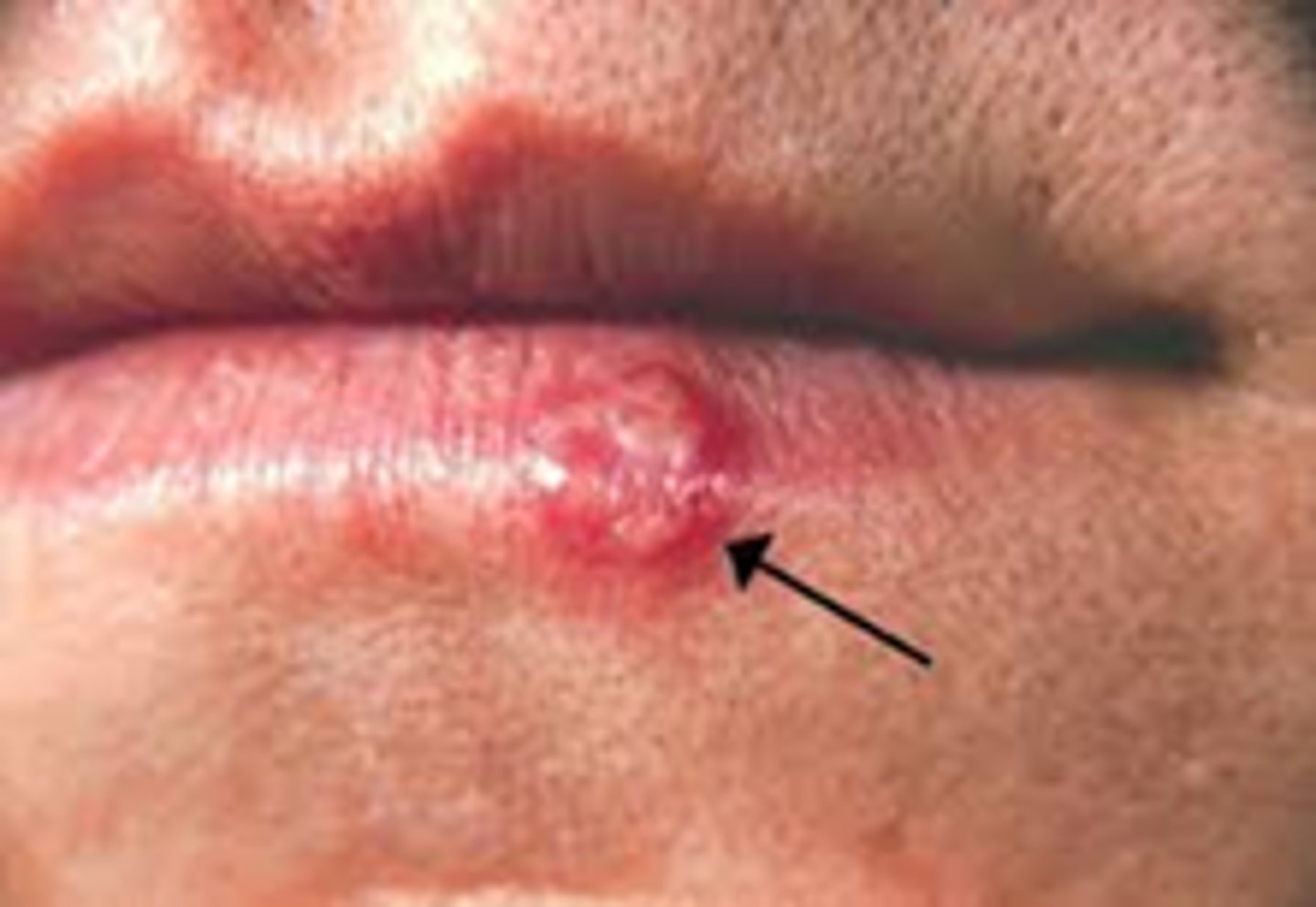
Herpes Simplex HSV 1
Cold sores
Occurs on the face and around the mouth
Sore and itchy
CONTACT precaution
** we have to remember the three types of herpes
Vesicular eruptions. Small vesicles erupt around the mouth. "Fever blister" Very sore and itchy. Spreads through contact so we use gloves. These same vesicular eruptions happen in HSV 2 but these mainly happen in the genital area/below the waist.
Herpes simplex HSV 2
Occurs below waist - over genitals
CONTACT precaution / Sexually transmitted
Can happen in newborns and can cause meningoencephalitis which can be fatal
Herpes zoster
The virus is varicella
- Same virus that causes shingles/chicken pox.
- Dorsal root ganglion - it's dormant and then it gets reactivated
- Follows dermatomal pattern
- Spinal nerves and cranial nerves can be affected / dermatomal pattern.
- Unilateral - over trunk/thoracic region
- Very painful
- Airborne and CONTACT precaution
Can affect CN 3: ocular complications. And CN 5: trigeminal neuralgia, sharp shooting pains.
- Postherpetic neuralgia = after the virus has attacked we still have nerve pain that's constant. This can stay for weeks, months or even years after the herpes is done.
Shingles vaccine is recommended in 50+.
When we treat these patients and they have a lot of pain over these regions. Don't give heat to pacify the pain, no hot packs, no diathermy. We can give cryotherapy or TENS conventional mode.
Antiviral medications sometimes corticosteroids.
Which organisms require water to wash off?
C diff and bascilis anthrax - they cannot be killed with sanitizer.
Otherwise only use soap and water if hands are visibly soiled
Wart
Benign infection HPV on the hands, fingers, plantar warts on feet.
- Contact precautions
- We can use ice. Over the counter medications.
What causes fungal infections?
Poor hygiene, sweating, moisture, direct contact
Tinea corpis/ring worm
Little vesicles or scales that form in a ring like pattern. The cure is antifungal creams, making sure there isn't too much moisture or sweat around that area. Exposure to sunlight is good.
CONTACT precautions
Tinea pedis/athletes foot
Fungal infections between the toes. Redness, swelling, erythmea. Exposure to sunlight is good. Keep it dry. Use antifungal creams and ointments
Candidiasis - yeast infection
Can be in the tongue/oral
Foul breath, pain
Genital area
Treat with antifungal creams and ointments
Parasite infections
They require a host body to survive
Pediculosis: head lice
Scabies
Lymes disease
Deer tick
Stage 1: localized stage, early. Redness, fever, chills, headache 5-7 days after the tick bite. Headache, lethargy, myalgias, arthralgias.
Stage 2: Months after the infection infection is disseminated. It's spreading so we have small rashes in the skin. Bulls eye rash/erythema migrans. Now it's not only limited to the muscle ache. Now we can have neurological complications - meningitis, stiff neck, nerve issues, bells palsy. CN issues. Radiculopathies. Can affect the heart - lymes carditis. It is spreading everywhere.
Stage 3: years after the infection. Late persistent. Even though years have passed we still may have joint swelling, achiness, myalgias, arthralgias
Psoriasis (LSP)
Autoimmune
Silvery scales
CONTACT precaution
Common areas to see the scales:
- Elbow
- Knee
- Foldable joints
- SCALP is very common
- Behind the ears
- Even in the genital region
Most patients can get affected with psoriatic arthritis. Usually in the small joints (DIP, PIP, nail changes - yellow nails).
May affect unilaterally, can progress bilaterally. Can have exacerbations and remissions
Cold weather, anxiety, smoking, stress can trigger it
Only management for all autoimmune conditions is corticosteroid medications and stress reduction.
Discoid Lupus Erythematous DLE
Umbrella term
Discoid only affects the skin and it can get worse with sun exposures. Can cause scars. It's not systemic. Just a condition affecting the skin. May have flareups due to sun. Can leave hypo or hyper pigmentation marks. Just know it if it's in an option
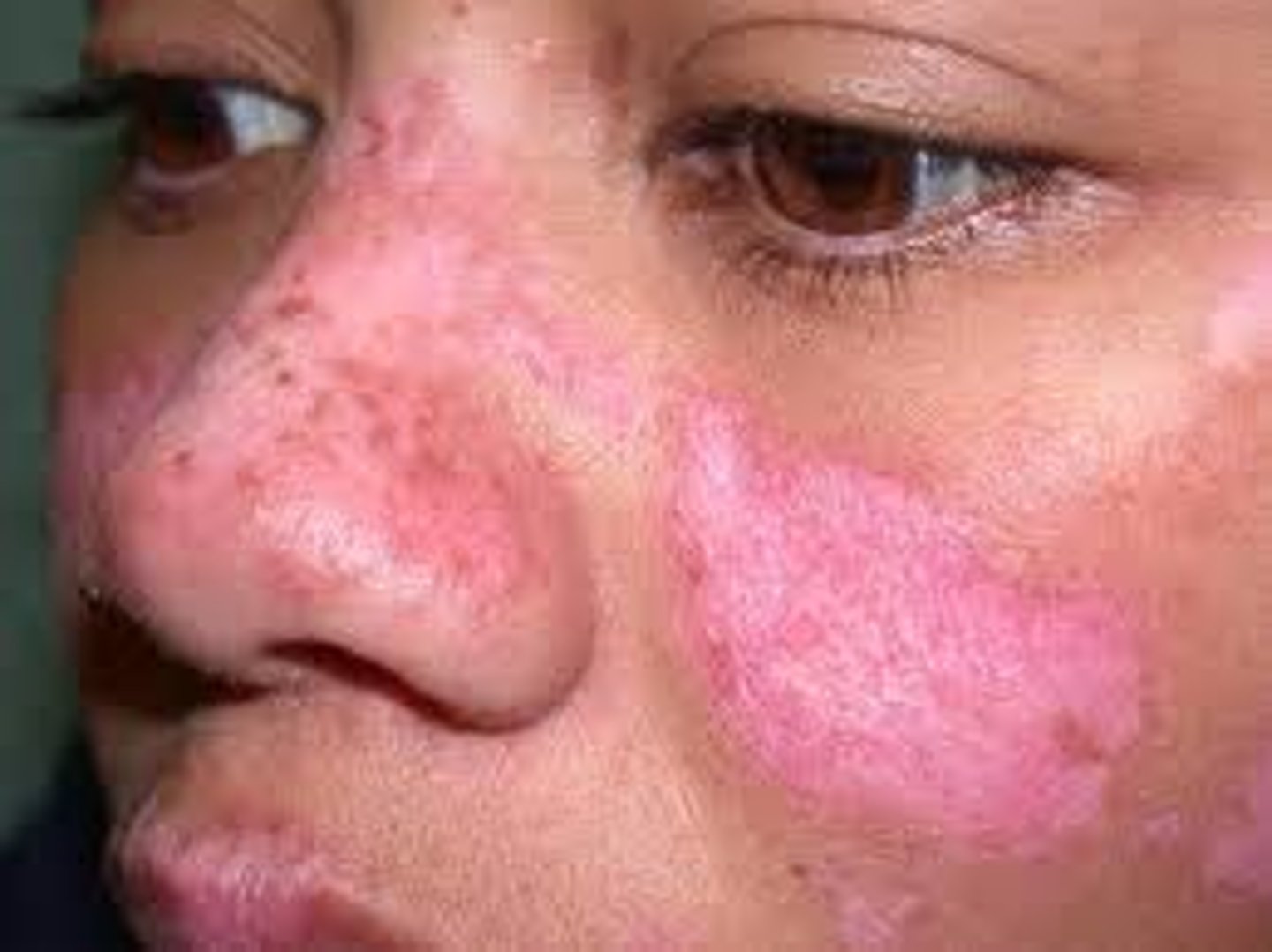
Systemic Lupus Erythematous SLE
Characteristic butterfly rash/malar
Chronic autoimmune condition that affects the skin/ can affect all the organs because it's inflammatory. Kidneys, heart, nervous system, GI system etc. can affect anywhere can have myalgia, arthralgia, joint pain. And RAYNAUDS PHENOMENON. They can also have photosensitivity - this will get worse when exposed to sunlight.
Medical management = corticosteroids (always!)
More present under the age of 50 for all of these conditions.
If we are seeing a patient with this condition, in a flare up phase and on long term corticosteroids we need to make sure were aware of osteoporosis. Ask about fractures. Cushing like features. 3-6 months is considered long term steroid use.
Scleroderma: FIBROSIS of the skin
CONTACT precaution
CREST syndrome
- Calcinosis: calcific depositions
- Raynaud's phenomenon: spasms of the small capillaries because of exposure to cold, stress, caffeine
- Esophageal dysmotility: poor mobility of esophagus = leads to GERD
- Sclerodactyly: stiffening and thickening, tightening of skin in fingers and hands. Skin will be very taut and firm. Firmly adhered to the subcutaneous tissue. You can't lift it up. Affects more distally.
- Telangiectasis: spider veins, dilated blood vessels that look like spider veins.
Hands are stiff so we are going to be SLOW prolonged stretching. Functional mobility. We don't want to do aggressive stretching. Splinting is okay. It is symmetrical distal involvement. Low load stretching, functional activities, holding things, combing hair, eating, etc. Work on improving the hand mobility.
Polymyositis
Multiple muscles are inflamed
P for poly P for proximal
The proximal muscles are getting inflamed. This is symmetrical. ((scleroderma was DISTAL and symmetrical))
- All autoimmune conditions have flareups and remissions
- They will have issues with any activity with overhead activities, ADLS because of inflammation and degeneration of the muscles. Swallowing, speaking will be difficult. Can affect respiratory muscles.
If muscles are already inflamed and degenerated we don't want to work them out a lot. Light mobility exercises, no aggressive stretching or strengthening. Lots of interval training and breaks. Muscle fibers are already damaged. Don't make it work more. Interval training, no resistance, no stretching, no strengthening. Autoimmune.
** We don't know how severe it can be due to the flareups.
A patient has this and starts getting skin inflammation over the knuckles and the skin. This is called DERMATOMYOSITIS
Muscle inflammation + skin issue "dermato"
If we exercise them at heavy intensity: rhabdomyolysis can happen. Muscle breakdown. This is a 911 situation
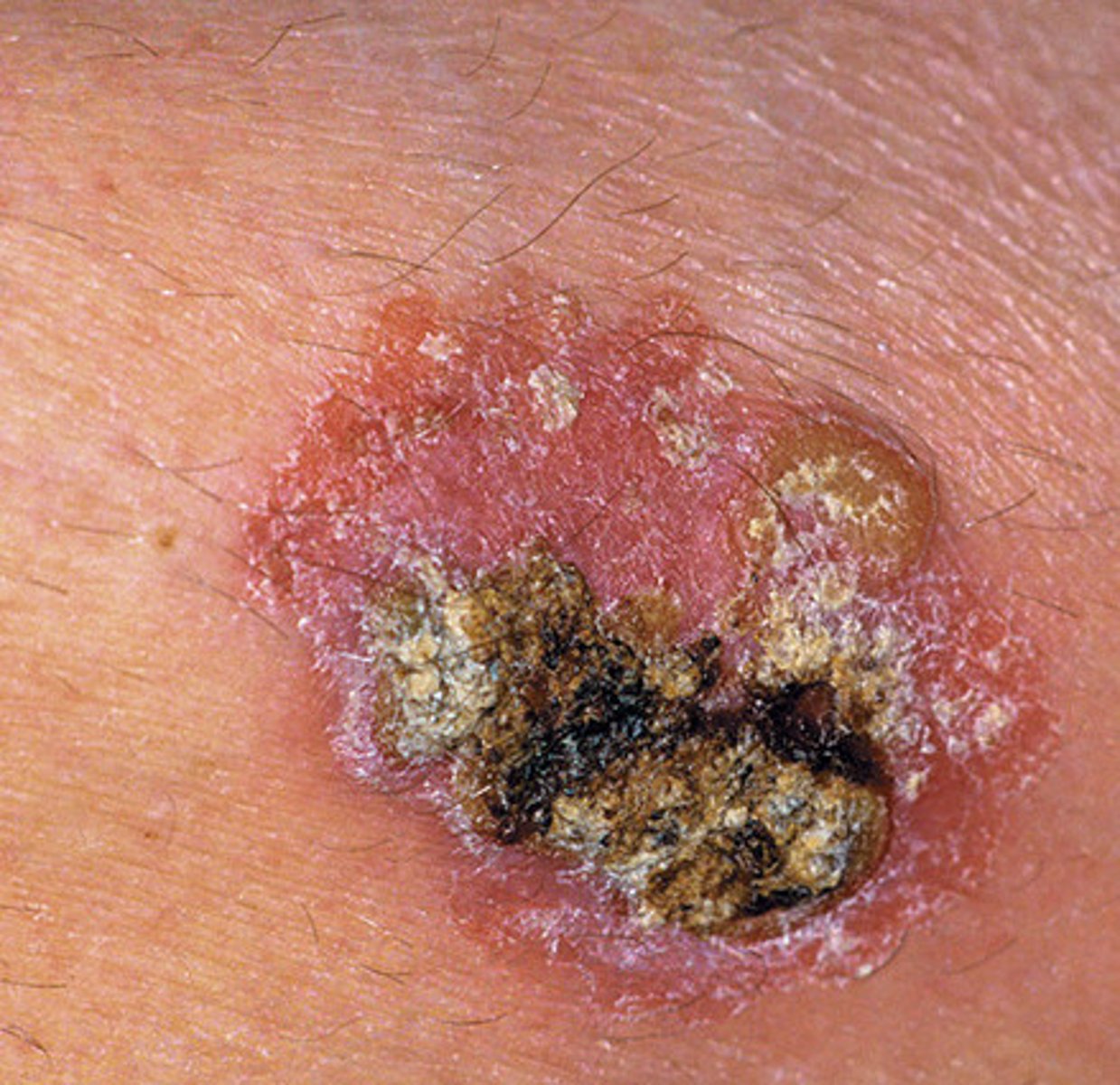
Squamous cell carcinoma
Fast growing
Flat
Metastases fast. This is the problematic one. Can spread to the surrounding tissues, mucosa.
Skin cancers.
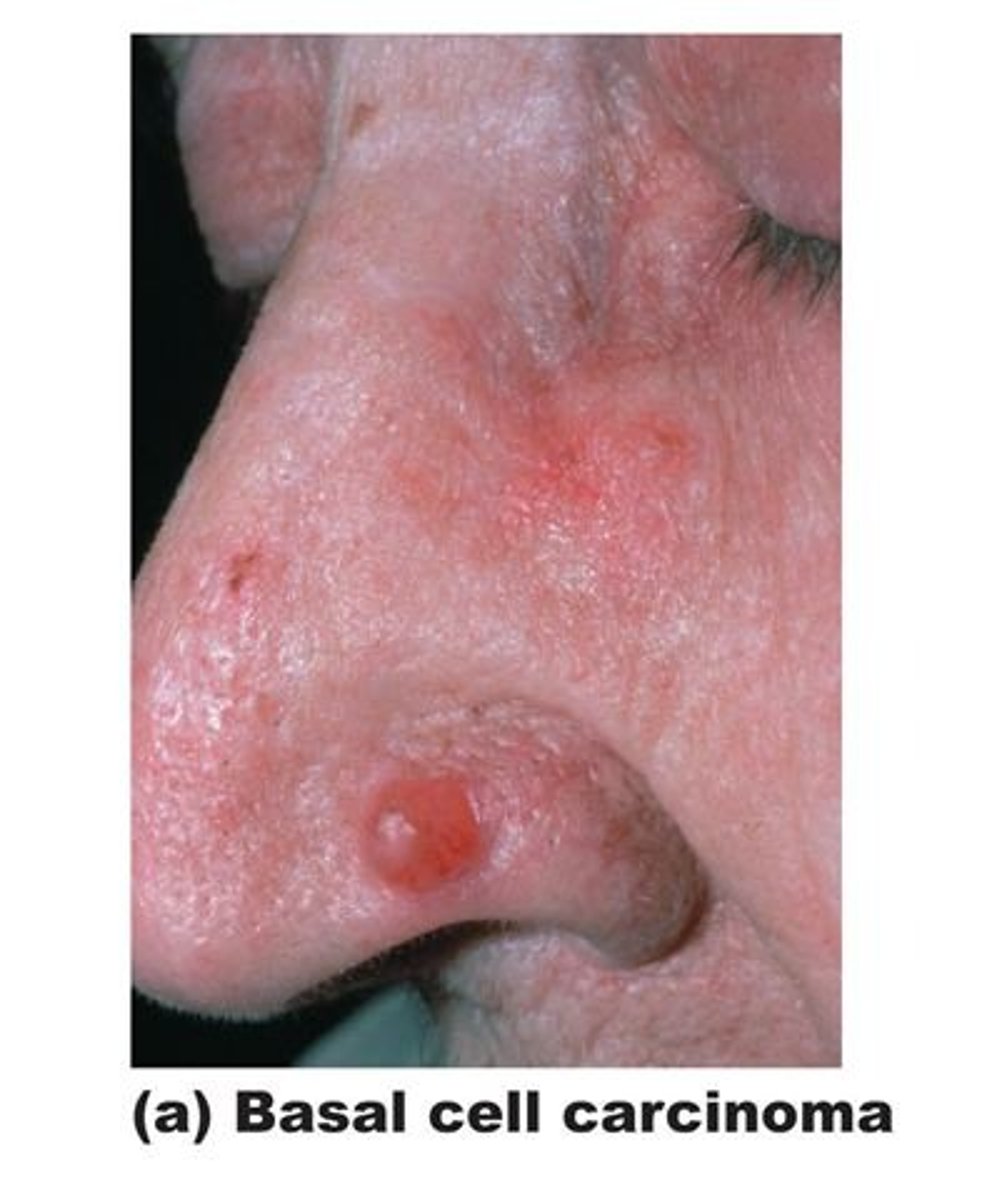
Basal cell carcinoma
Slow growing
Raised
Metastases rarely. If it's not immediately diagnosed it's okay
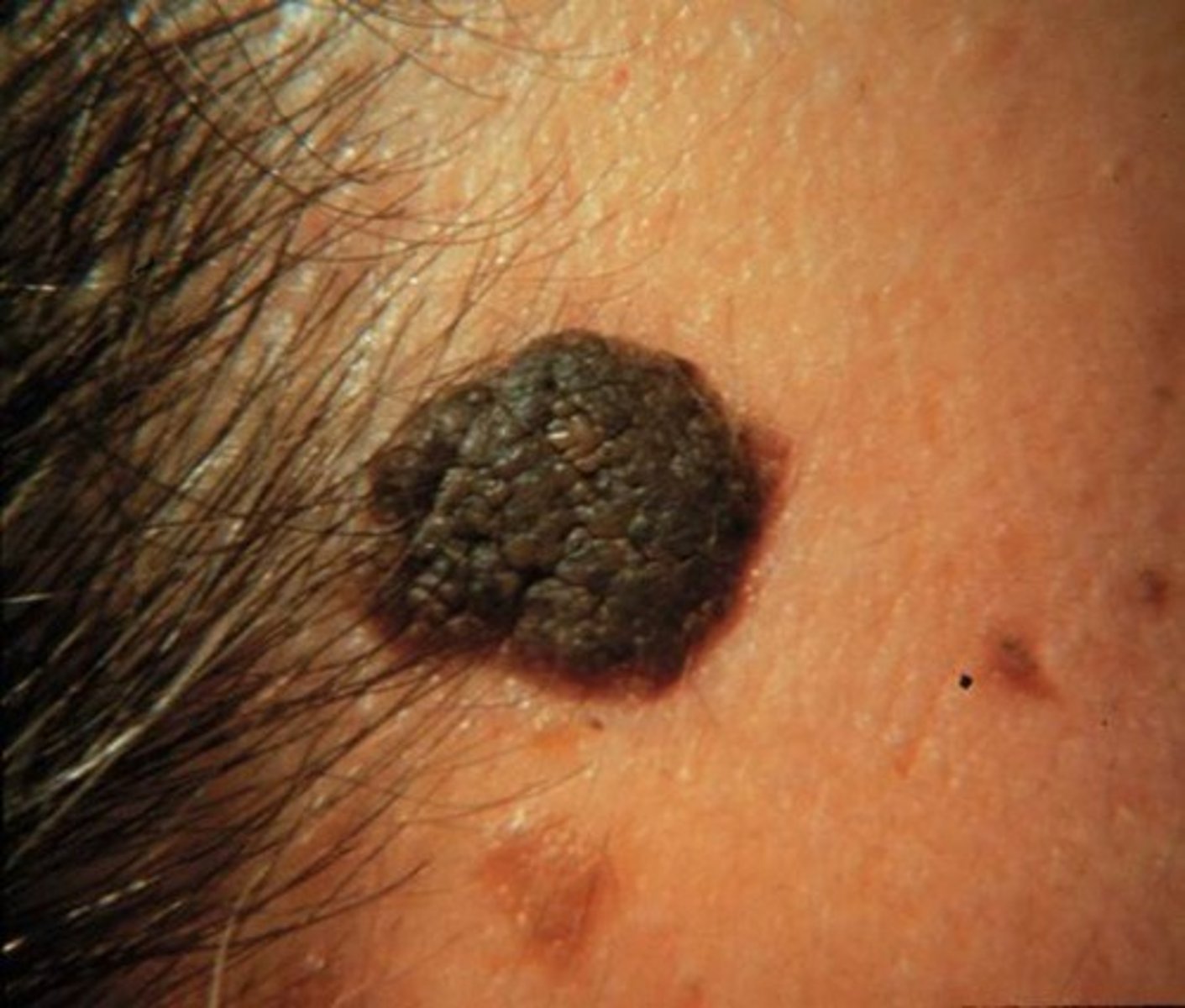
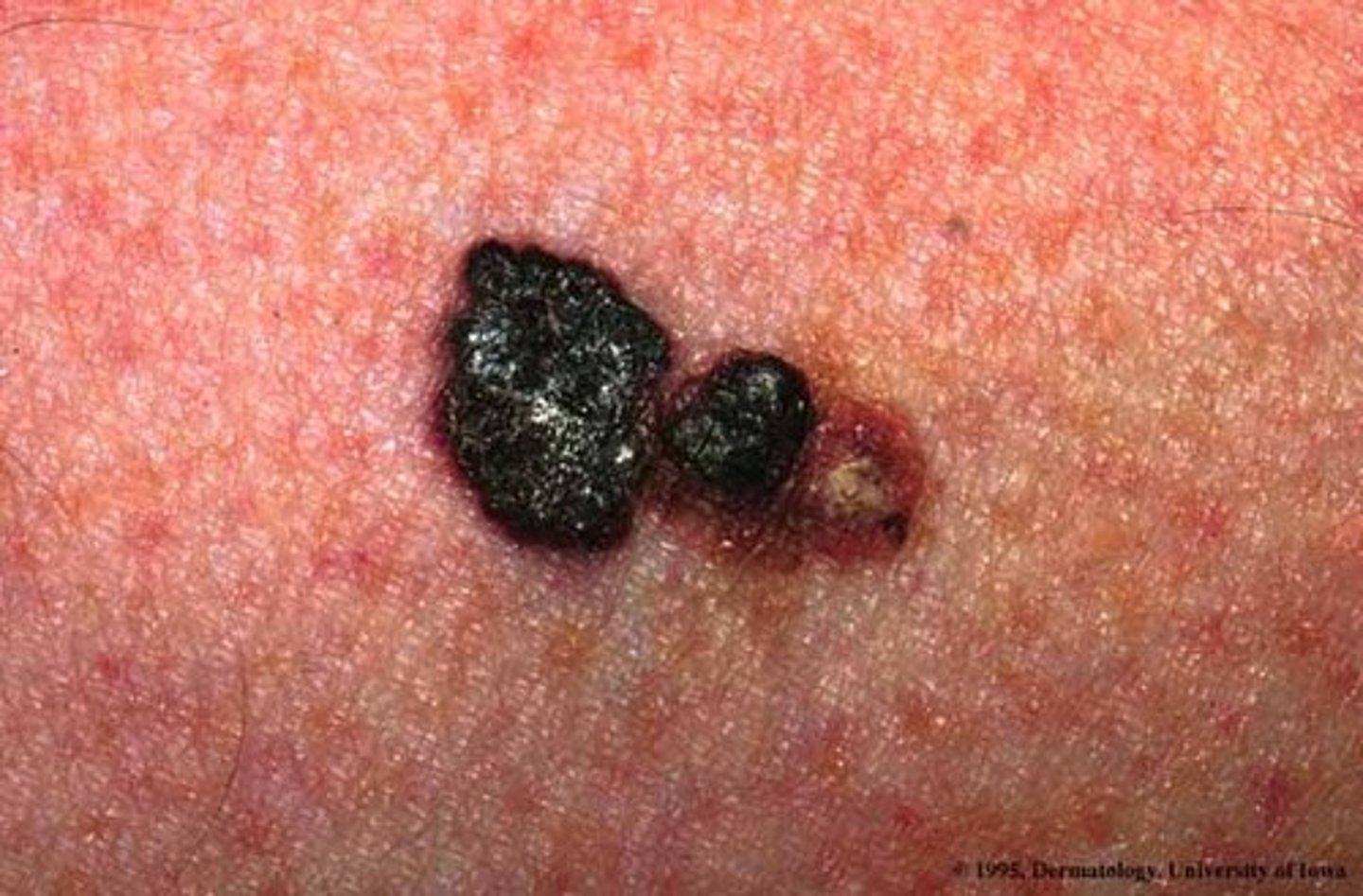
Malignant melanoma
VERY IMPORTANT for exam.
Nevus - a term to describe a mole.
Nevi - many small moles
If someone comes to us with a nevus that's benign, we don't do anything. Just assess it. Make sure that it hasn't undergone changes. If it has then it's a malignant melanoma.
ABCDE
- Asymmetry: it's not symmetrical, can have raised areas and flat areas
- Border irregularity : borders aren't round. They are irregular.
- Color : Color may be black, blue or red. not like a nice brown
- Diameter : greater than 6mm
- Evolution : flat moles will change in color, elevation, etc. have increased in size.
Initially they may look like harmless moles. It takes skill to assess these lesions.
We need to refer them out. Finish the eval and then tell them to make an appt with their dermatologist.
Kaposi's sarcoma
AIDS
Kaposi's sarcoma is caused by the human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8), also known as Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus (KSHV).
Most people with HHV-8 don't develop Kaposi's sarcoma.
Kaposi's sarcoma is more likely to develop in people with weakened immune systems (AIDS)
Painful
Seborrheic keratosis
Proliferation of basal cell
Raised lesion
Irritation
Pain
Don't really need to know. But a raised lesion. Not cancerous.
Exposure to the sun