Aice International History
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Causes for scramble of Africa
-commerce and trade
-strategic
-political
-medical
-transport
exploration
-moral

Strategic
-trade routes (suez canal in Egypt)
-acquisition of naval bases (protection of trade routes/defense of communication lines)
Political
-no possibility of expansion in Europe
-needed to look overseas in order to prosper
-trying to maintain dominance
Medical
-effective for malaria yellow fever (quinine) allowed travel into the interior of Africa
Transport
-creation of infrastructure within the continent
-development of railways and steamboats
commerce and trade
-raw materials
-new markets
-greater investment oppurtunities
exploration
-opening up the african continent
-merchants pressured by wealthy businessmen to find new resources
moral
-social darwinism (strong shall survive)
-white man's burden
-the three C's (Commere, Christianity, and Civilization)
aims of berlin conference
-to establish rules
-to ensure possessions are respected
-to ensure that vital transport routes (such as the Congo and Niger rivers) remained open to all.
-abolish slavery
Fashoda incident
- rivalry between Britain and France over Sudan.
-proved that neither Britain or France were prepared To war over African territory
-safety no risk of war
Benefits to africa
-efficient government and administration
-education
-transport and communication
-health (water and sanitation)
-farming methods
Disadvantages to Africa
-ruled by Europeans
-loss of traditional culture
-exploitation of resources
-prevented from developing own industries
-new boundaries
-taking no account of local and tribal groupings
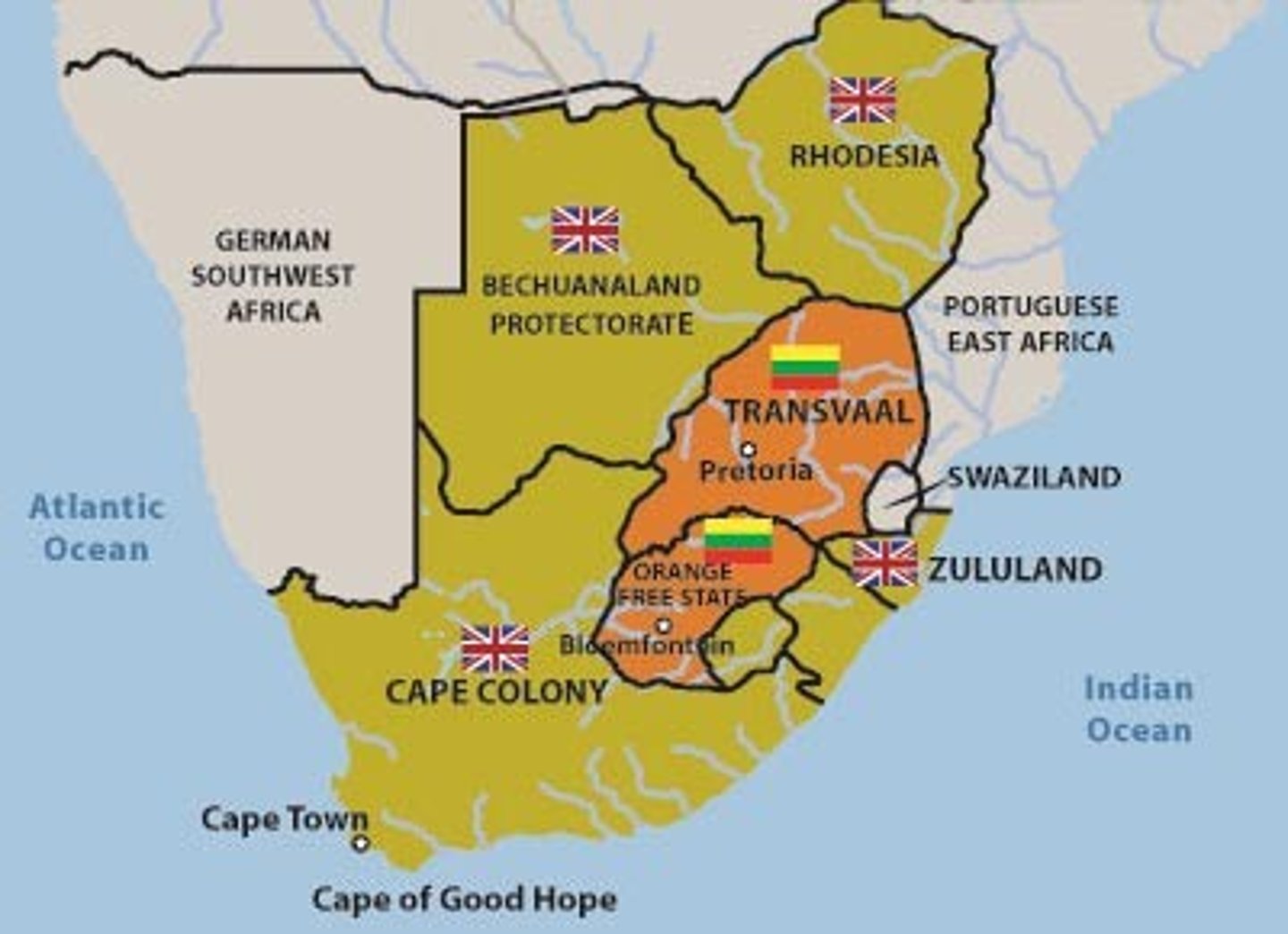
Boer Wars
-disputed over ownership of the Transvaal and orange free state, problems faced by Britain in defeating boers
-isolated (ended isolation)
-damaged Anglo-German relations
Conflicts of scramble
-treaty of Berlin
-fashions incident
-Boer Wars
-increased tension between European rivals
3 conspiracies involved in USS Maine
-Cuba: wanted US Involvement in the war with Spain
-Spain: didn't like our battleship so close to their colony
-US movement: needed a reason to convince the American people to support war
Three territories US gained as a result of war
-Philippians
-Guam
-Puerto RICO
-Cuba
-(Platt Amendment)
Expansionist/imperialist
Early 1900s opposite of isolationist
Protectionism
Policy of placing high tariffs on imports in order to protect domestic industries from foreign completion
Two reasons why the USA abandoned the isolationist position
-economic downturn of 1893
-sinking of the USS Maine
Issue usa was dealing with in 1800s that led to isolationist foreign policy
-westward expansion (manifest desfinany)
-American civil war
President candidates in 1900 electoon
-William mckinley: imperialist (wonJ
-William Jennings Bryant: anti-imperialist
Why was it important for the USA to develop a strong navy and acquire over seas based in the late 1800s and early 1900s
To protect us interest and merchant ships
American revolution 1775-1783
History of not wanting to interfere in others affairs, nor be interfered with ours
Civil war 1861-1865
Preoccupied with internal matters
Manifest destiny
Westward expansion justifiable and inevitable
Isolationism
The policy of isolating ones country from the affairs of other nations by avoiding and international commitment
Why was the Monroe doctrine formed
Fear over European countries trying to win back colonies that had gained independence in the Americas led to new legislation
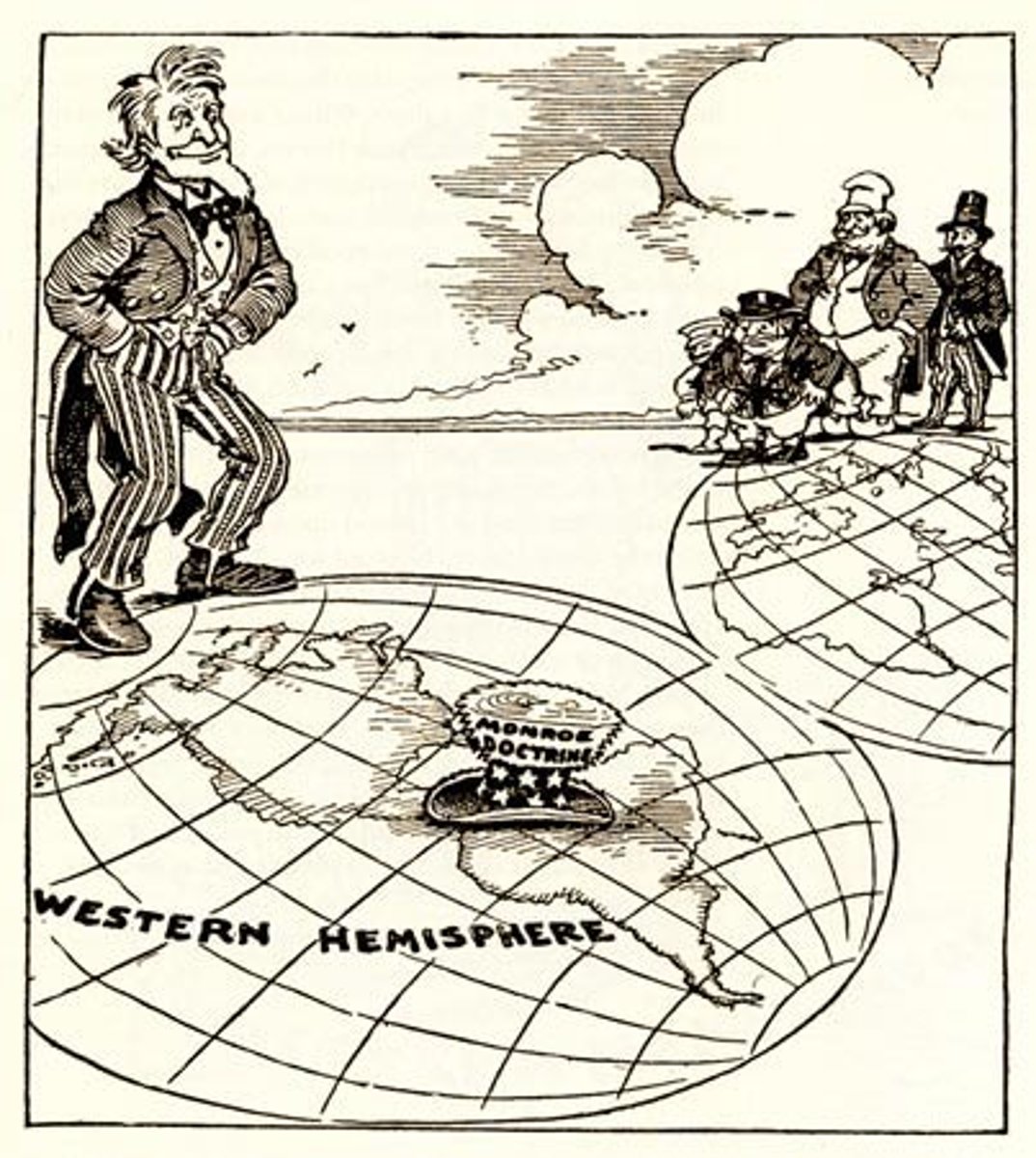
Monroe doctrine
States that the USA would not interfere in European affairs and that any attempt by european affairs to interfere in the American would be seen as an act of aggressive and dealt with accordingly

Economic growth
USA experienced enormous industrial growth in the late 1800s
Reasons USA was industrial in the late 1800s
-rich supplies of raw materials
-expansion of railways
-large scale immigration (provided labor and market)
-protectionism policies (import tariffs proffered us industry from foreign competition)
Why was there an economic downturn in 1893 in USA
Over reliance on domestic markets
How was economic downturn tried to be fixed / what did they need to do
-Sell more goods abroad
-European nations practiced protectionism
-need for overseas bases and strong navy
-needed access to Chinese Marks's
Cause of Spanish American war
-yellow journalism
-sinking of the Maine
-economic pressures
-American public opinion
Effect of Spanish American war
-USA gains former Spanish territories (Treaty of Paris 1898)
-effective control of Cuba (platt amendment)
-Philippines, Puerto Rico, Guam
Roosevelt corolladg
Extension of Monroe doctrine specific to the Caribbean
Platt amendment
Gave effective control of Cuba to the US
Panama control
Directly responsible for construction and the US control
Attempt to gain trading rights in China challenges
-less successful on the pacific region
-unable to gain trading rights in China
-stern opposition from established powers in Europe and Japan
Great white fleet
Roosevelts insistence on developing a strong navy
Views of William Kennings Bryant
-traditional (always been isolationist)
-historical (American revolution fought to gain independence from foreign rule)
-values ( imperialism goes against the ideology of democracy)
Views of William McKinley
-social Darwinism (the USA needed to expand in order to avoid decline)
-racial inequality (it was the USA's duty to expand in order to bring civilization to others)
-economic arguments (the downturn of 1893 led many industrialists to argue that foreign markets were essential)
Japan prior to 1871
-underdeveloped (backward in terms of agricultures, industry)
-under threat from the USA and European nations (threat posed by foreigners wanting to exploit Japan's resources and market)
Japan after 1871
-rapid industrialization and modernization (development of education, transport,industry, mines)
-military development (increasing prosperity used to find military strength;conscription;naval development)
Proof of Japanese expansionism
-war with China 1894 (victory leading to treat of shimonoseki)
-triple intervention (Japanese gains cut back by Russia, France, and Germany)
-Anglo-Japanese alliance 1902 (japans reasons for wanting the alliance)
-Russo-Japanese war(cause and reasons for Japan's victory)
How was Japan from 1600-1853? (Policy)
-isolated
-built a highly ethnocentric society
-not allowed to travel outside of the nation
-foreigners were not allowed inside the nation
-effectively resisted pressure to open ports in the 1800s to Russia,Britain, and the USA
Japan government 1600-1853
-rigid class system
-feudal society was ruled by shoguns (medieval social structure)
-farming, transport, industry had changed little for centuries
Why did the us want to open trade
-new markets
-refueling station in far pacific
Why were the Japanese willing to listen to Matthew Perry
-modern navy
-threat of force
What was Japan scared of?
-fearful of the Chinese fate (opium wars)
-European merchants seizing control imposing own laws and destroying local culture
Why did Japan want to modernize?
-foreign imperialistic threat
-complete with Europe
-people's demand for better way of life
Japanese reform
-new constitution giving citizens rights
-installing the emperor as the central government figure replacing the military shogun
-modernizing the military inspired by their European counterparts
How did Japan develop their military
-increased prosperity assisted the development of Japan's military
-1/3 of the national budget was spent on the army and navy
-Japan developed from a country threatened by the imperialistic ambitions of other nations, to own capable of its own
War with China (1894)
-dispute over who should control Korea
-china surrendered and under the terms of the shimonoseki treaty (1895) Japan gained Formosa and Port Author
Triple intervention:France, Russia, and germsny
-Russian main instigator of agreement (wanted port author)
-France supported in hopes of maintaining alliance with Russia
-Germany involved in exchange for Russian support for their own colonial ambitions
Anglo-Japanese alliance (1902)
-who: Britain and Japan
-what: both countries would be neutral if the other involved in a war with only one country (come to aid if attacked)
-why: after 1895 victory over china, Japan had been forced to give back territorial gains;they are looking for a powerful alliance
-Britain wanted to end splendid isolation
-concerned about German naval development
-negative European reaction to the Boer war
Causes of the Russo-Japanese war
-Japan's resentment for triple intervention to give Port Author to Russia
-refusal to negotiate with Korea (not a threat)
-Russia's invasion of Japanese-controlled Korea
-Japan's new found confidence due to the Anglo-Japanese alliance
Reasons Japan won
-Japan modern warships outdated Russia's slow moving vessels
-Britain refusing access to Suez Canal (Russia fired on British fishing ship/ Britain's alliance with Japan)
-home field advantage (easier to resupply war effort)
- Russian internal issues distracting the tsar (population dissatisfaction with his rule)
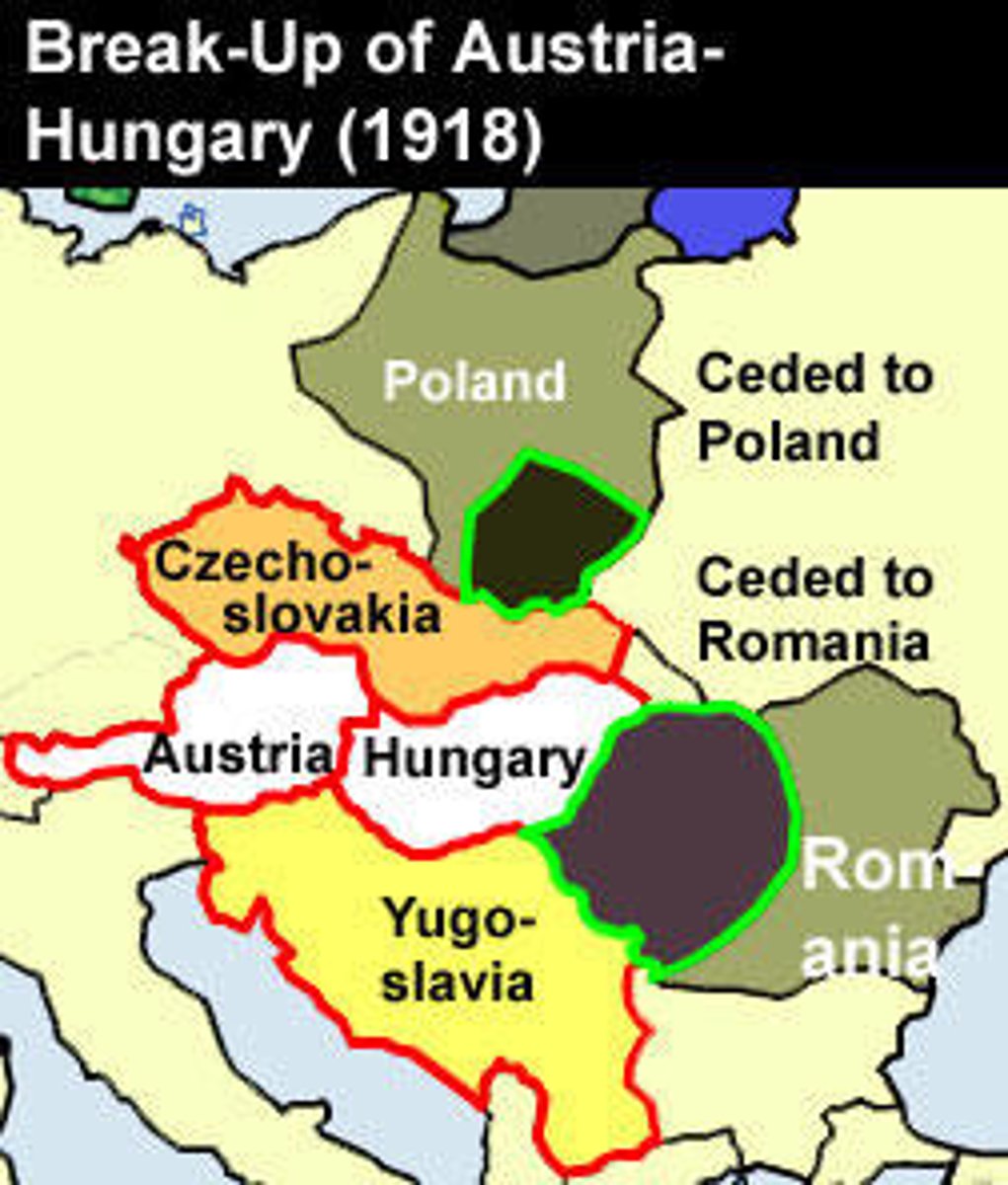
Unification of Germany
-Franco Prussian war (creation of German empire in 1871: vulnerable location)
-Bismarck foreign policy
Aims of Britain's foreign policy
-ensure security of the newly united Germany
-isolate potential enemies (France)
-kept Germany out of scramble to avoid conflict with potential rivals
Drekaisarbund (1873)
-Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Russia
-weak due to disputes between Austria-Hungary and Russia (Balkans)
-isolate France
-tried but failed to reduce balkans tension
-1873-1889
Dual alliance (1879)
-Germany and Austria Hungary
-come to aid if Russia attacked (neutral with France)
-protect/isolate
-ongoing tensions with Russia
-1879-1882
Triple alliance (1882)
-Germany Austria-Hungary, and Italy
-come to aid if attacked by France
-Italy mad at France when annexed funks wanted own empire in Africa
-isolate/protect
-tension with Russia over balkans
-1882-1914
Kaiser Wilhelm II
-takes control of foreign policy
-adaption of a more aggressive foreign policy
-imperial expansion (actively seeking overseas possessions)
-naval development (rapid naval expansion lead to a naval arms race with Britain)
-Kruger telegram (furthered distance between Germany/Britain)
-lack of effort with reinsurance treaty
Reinsurance treaty (1887)
-wanted to maintain friendly relations with Russia
- secret which caused alarm between countries such as Britain and France
-neutral if involved in war
-three emperors league fell apart causing tension
-1887-1890(not renewed)
What were the main aims of Kaiser Wilhelm II's German foreign policy?
-grow the German navy
-acquire colonial territory
-cut ties/obligations made by Bismarck (reinsurance treaty)
-less diplomatic (Kruger telegram)
-to increase the power and prestige of Germany
How did German foreign policy make war more likely?
-increased tension with aggressive foreign policy in Europe
-Britain(Kruger telegram, development of navy, and lapse of reinsurance treaty)
-Europe (participation in scramble for Africa/build up of navy leads to arms race)
Franco-Russian alliance (1884)
-France and Russia
-defensive alliance against triple alliance
-France threatened by Germany, France had given several large loans to Russian and both wanted to offset Germany's military threat
-1894- as long as triple alliance existed
Entente Cordiale (1904)
-Britain and France
Settled colonial disputes (Africa) and feared isolation and support for third county
Concerned about growing power and protection
-1904-1928
Anglo-Russian entente (1907)
-Britain saw Germans as threat to interests in the Far East
-Russia feared triple alliance (concerned Austria/Germany wanted to the Balkans (major trade route for Russia)
- Britain no longer afraid of Russia due to Japanese defeat
-1907-1918
Schlieffen plan (1904)
-offensive plan in case of war
-attack France first (surprise attack through neutral Belgium)
-concentrate full effort on Russians (take longer to defeat)
-aggressive foreign policy (invading France through Belgium)
Italy motivation for alliances
-preserve own national security
-France
Balkans
-preserve own national security
Nationalists
-preserve own national security
Austria-Hungary empire
-mixture of many different nationalities
Serbian nationalists
-believed that the parts of Habsburg lands were predominantly Serb pupopulation s should become part of greater Serb
-believed domino effect
-solved by going to war

USA enters WWI
-U Boat campaign (sinking of Lusitania)
-Zimmerman telegram (Germany to Mexico)
-Woodrow Wilson supported allied cause
Japan enters WW1
-Anglo-Japanese alliance
-opportunity to gain territory in Asia with Europe was preoccupied
Britain motivation for alliances
-fearing German naval development
-isolation
-boer Wars
Germany motivation for alliances
-geographically vulnerable
-isolate France
-avoid war on two fronts
France motivation for alliances
-angered by defeat of Franco-Prussian war
-feared German growing power and triple alliance
-wanted to avoid isolation
Italy motivation for alliances
-preserve national security
-angry at France for seizing Tunishia
Russia motivation for alliances
-fear triple alliance
-wanted to avoid alliance
-Japan war highlighted weaknesses
Causes of WWI
-Bismarc's alliance
-arms race
-schlieffen plan
-commercial/imperial rivalries (self interest/scramble)
-Wilhelm's aggressive foreign policy
-nationalism
-Austria vs Russia
-Germany vs France (franco Prussian war)
Aims of Mussolini foreign policy
-to restore Italian pride (Paris peace settlement)
-to make Italy great respected and feared (mare nostrum)
Early aggression Mussolini
-Fiume 1923 free city used by Italy and Yugoslavia;Italy takes control
-Corfu 1923 boarder dispute between Greece and Albania compensation from Greece
Reasons for Mussolini cautious approach
-fear of isolation (only facist country)
-could not challenge Britain's supremacy
-Ensure Italian security
Locarno treaties
: developed effective relations with Britain, France, Germany and Belgium; played a key role in securing agreements.
Secured Italy's strategic position in Adriatic Sea
developed good relations with Greece, Hungary and Albania.
Invasion of Abbysinia 1935
for a propaganda boost; earlier Italian attempt to take Abyssinia (1896) had failed; argued that imperial expansion would provide Italy with raw materials and market; weak reaction of League of Nations.