1.5 NUCLEIC ACIDS + FUNCTIONS
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
What are nucleic acids?
Polymers made up of monomer sub-units called nucleotides. (DNA+RNA)
What functions are nucleic acids essential for ?
Inheritance , Metabolism
Give 3 examples of nucleic acids?
DNA, RNA, ATP
What is a nucleotide?
The basic building blocks of nucleic acids
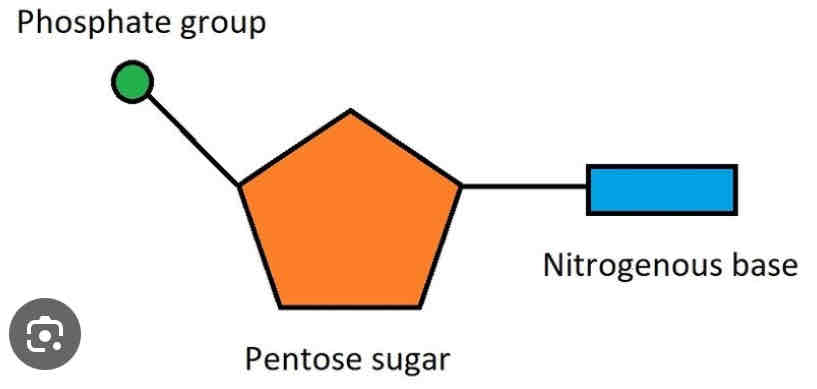
What is the structure of a Nucleotide ?
MADE UP OF 3 COMPONENTS:
A Phosphate groups
. A Pentose sugar
.An Organic/Nitrogenous base
What is a phosphate group?
H3PO4 - has the same structure in all nucleotides. May be more than 1
What is the pentose sugar?
The pentose is:
Ribose in RNA
Deoxyribose in DNA
What is an organic organic base also known as?
A Nitrogenous base
Draw and label a diagram of a nucleotide
LABELLED IMAGE
What 2 different groups can the organic base belong to
. Pyrimidine group
.Purine group
What are the bases of the PYRIMIDINE group
T-Thymine , C-Cytosine , U-Uracil ( all single ringed structures)
What are the bases of the PURINE gorup
A-Adenine , G-Guanine ( both double ranged structures)
What are the pairs for bases
A-T , C-G (In RNA A-U)
How many hydrogen bonds in the different base pairs ?
A-T = 2 hydrogen bonds
F-C = 3 hydrogen bonds
Where do Heterotrophic organisms (animals) get their chemical energy from?
Food
Where do Autotrophic organisms (green plants) get their chemical energy from?
Light energy which they convert to chemical energy during photosynthesis
What is ATP?
Adenosine Triphosphate . ATP is a nucleotide
What are ATP molecules useful in
. Makes energy available when needed
. ATP molecules are a reservoir of potential chemical energy
. Is a common intermediate in metabolism - linking energy and energy yielding reactions
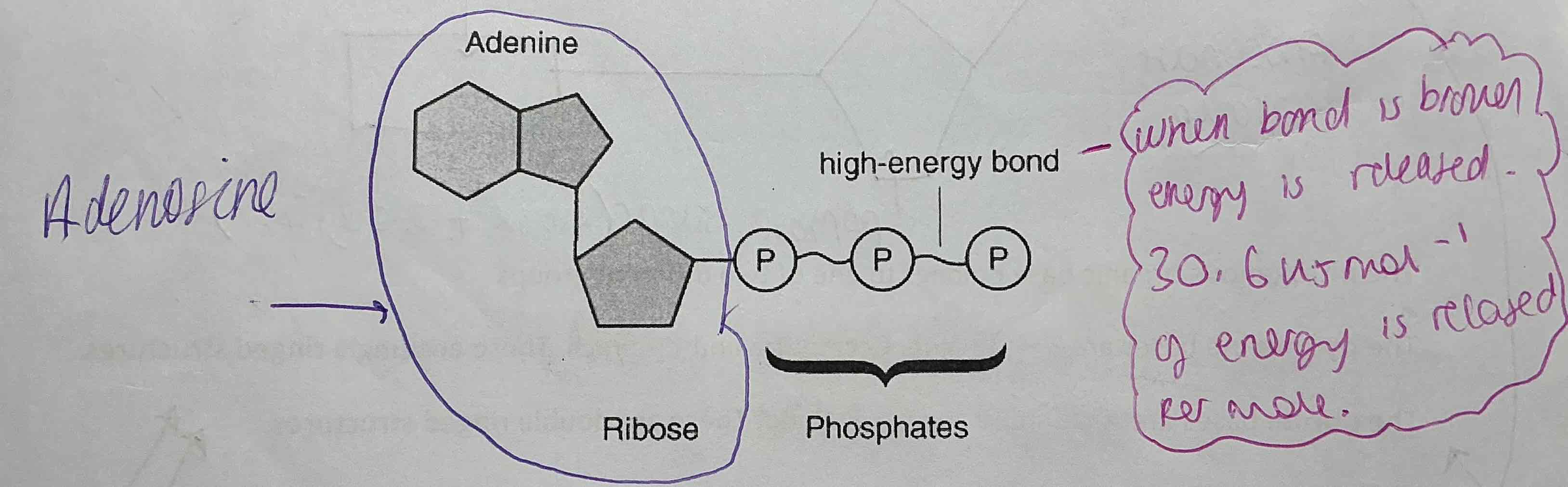
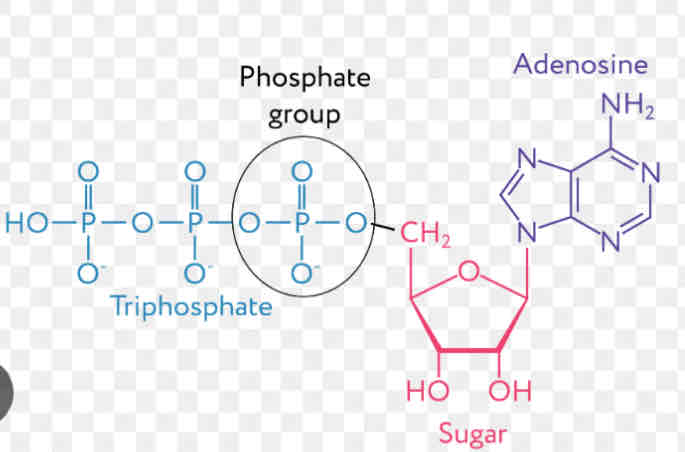
What is the structure of ATP
Made up of 3 parts- ATP is a nucleotide so contains :
. An ORGANIC/NITROGENOUS BASE -Adenine
. A FIVE CARBON (Pentose sugar)- Ribose
.THREE PHOSPHATE GROUPS LINKED TOGETHER - 3 phosphates in ATP
Draw and label ATP
Draw and label structural formula of ATP
Why is ATP sometimes called “universal energy currency”
It provided the energy for all reaction in all cells and in all organisms
How does using ATP work?
ATP is synthesised when energy is made available in the cytoplasm ,mitochondria and chloroplasts, and it is broken down when energy is needed , such as on muscle contraction or nerve impulse transmittion.
What happens during the ATP cycle ?
ADP—> ATP
.For immediate energy ADP ( containing 2 phosphate groups ) coverts into ATP (containing 3 phosphate groups)
.Condensation/ phosphorylation reaction
.Uses a inorganic phosphate ion
.Produces ATP and water
. +30.6 (KJmol-1 ) energy required
.Endergonic reaction
.ATP synthetase catalyses formation of ATP
ATP—>ADP
.Hydrolysis reaction
.Uses water
.Produces ADP and a inorganic phosphate ion
. -30.6m (KJmol-1) energy released
.Exergonic reaction
.ATPase catalyses formation of ADP
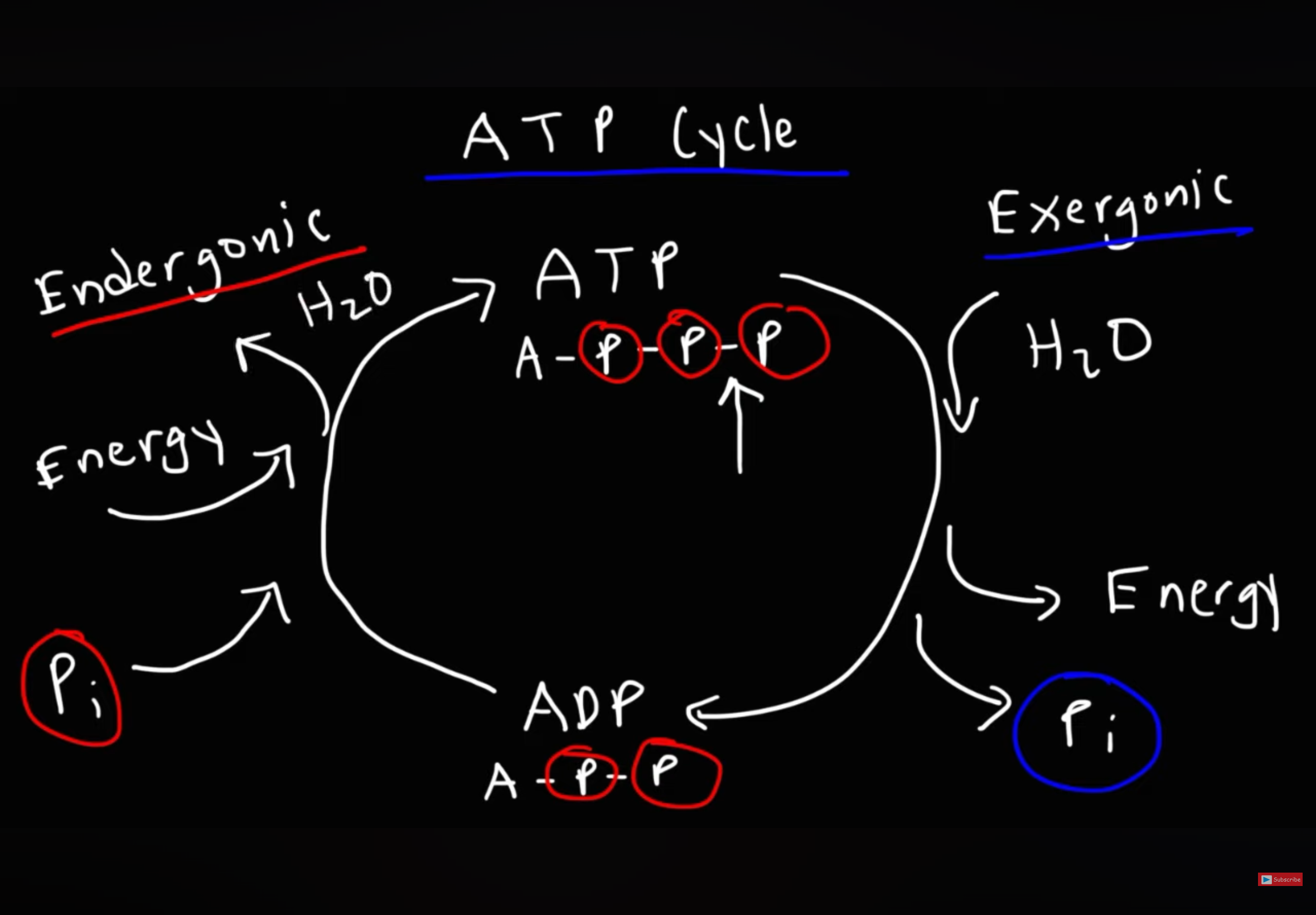
Write out the 2 reactions for the ATP cycle

Why is energy transfer inefficient ?
.ATP transfers FREE ENERGY from energy-rich compounds - Glucose to cellular reactions where it is needed.
.Energy transfers - inefficient as some energy is always LOST AS HEAT
.The UNCONTROLLED RELEASE of energy from glucose - produce a temp increase that would destroy cells
What do organisms do instead of the uncontrollable release of energy from glucose ?
.Living organisms release energy gradually, in a series of small steps called RESPIRATION
.When a phosphate group id transferred from ATP to another molecule it makes it more reactive which LOWERS THE ACTIVATION ENERGY of a reaction involving that molecule.
What is activation energy ?
The minimum energy required for a reaction to occur
What are the advantages of ATP?
.A single reaction
.One ezyme
.Small amounts of energy released (avoids energy being lost as heat)
.Soluble and easily transported
How does the cell use ATP?
.Protein synthesis
.Active transport
.Cell division
.Endo/exocytosis
What does DNA stand for ?
Deoxyribonucleic acid
What is DNA?
.DNA contains the information about an organism , in the form of a genetic code
.Only found / contained in the nucleus of the cells
.Determines its inherited characteristics
What is the structure of DNA?
DNA is made up of two polynucleotide strands wound around each other in a double helix
EACH DNA NUCLEOTIDE IS MADE UP OF :
A phosphate group (H3PO4
A Pentose sugar which is always DEOXYRIBOSE (C5H1004)
One of the four organic/nitrogenous bases
A-adenine , G-Guanine (Purine bases)
C-cytosine , T-thymine (Pyrimidine bases)
A-T , C-G
How are the three parts joined ?
.CONDENSATION reaction - form nucleotide
.Millions of nucleotide linked together to form - POLYNUCLEOTIDE strand.
.DNA molecule made of- 2 VERY LONG POLYNUCLEOTIDE STRANDS - held by HYDROGEN BONDS between pairs of the organic bases
What are the organic base pairs?
CYTOSINE pairs with GUANINE (C-G)
ADENINE pairs with THYMINE (A-T)
This is the complementary base pairing rule
How is the shape of the helix maintained ?
.HYDROGEN BONDS between bases - maintain shape of the double helix
.The DEOXYRIBOSE and PHOSPHATE - on outside of the DNA molecule + form the BACKBONE .
.The TWO POLYNUCLEOTIDE STRANDS - twisted to from a spiral or a DOUBLE HELIX
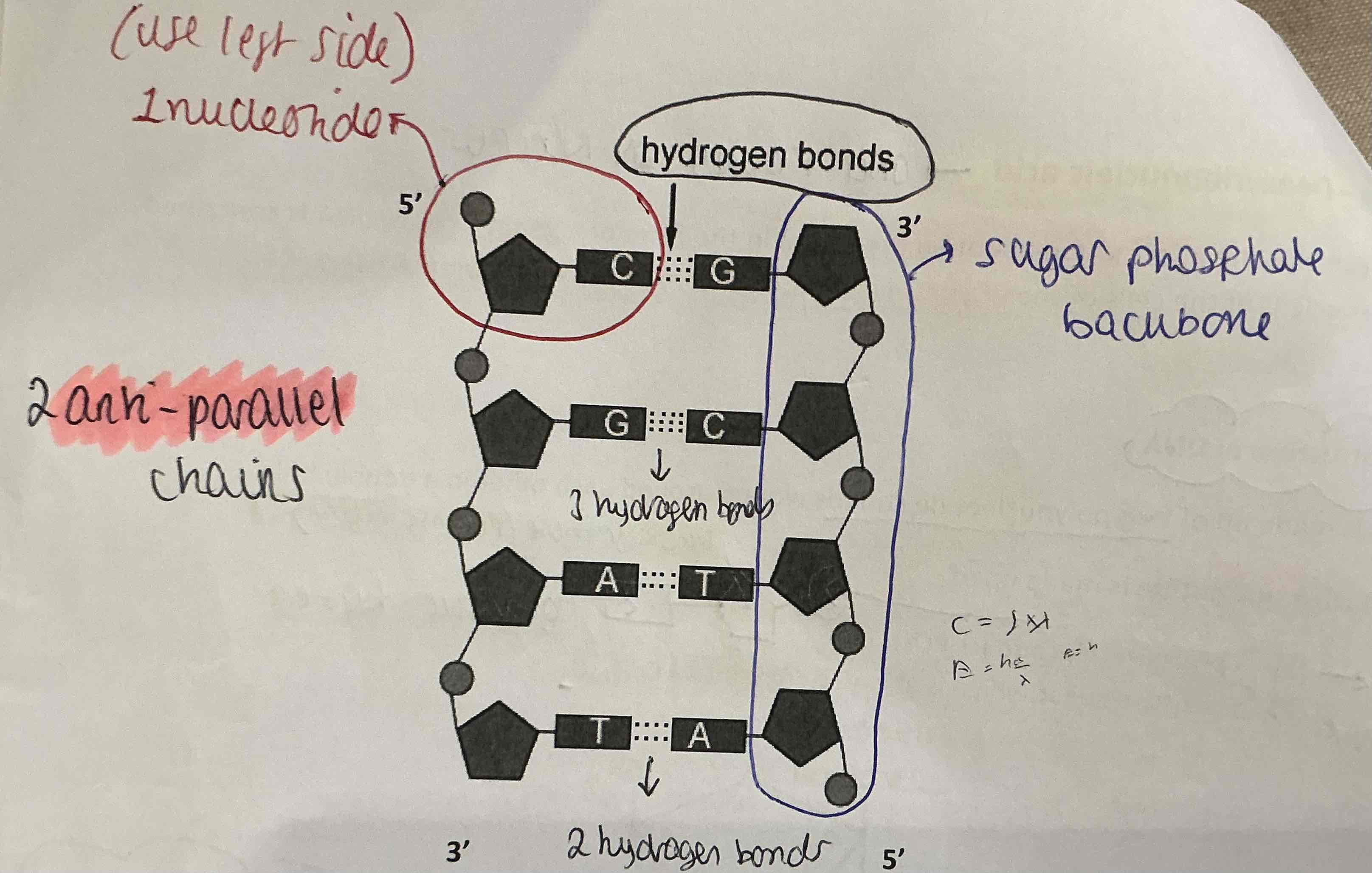
Draw and label a DNA molecule
. The nucleotides in one strand are arranged in the opposite direction from those in the complementary strand
.The two polynucleotide strands are arranged ANTIPARALLEL to each other.
.A DNA molecule is very long and thin and is tightly coiled within a chromosome
.The double helix is 2nm in diameter
What does RNA stand for
Ribonucleic acid
What is the structure of RNA
RNA is a single stranded polynucleotide . Each RNA nucleotide consists of:
A Phosphate groupv(H3PO4)
A pentose sugar which is always ribose (C5H1005)
One of the four organic/nitrogenous bases
A-Adenine , G-Guanine , C-cytosine , U-uracil (replaces a thymine)
A-U , C,G
What are the 3 types of RNA which all have a role in protein synthesis
.Messenger RNA ( mRNA) = synthesised in the nucleus but carries out function on ribosomes
.Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) ( constituent of ribosomes )= synthesised in the nucleolus but carries out function in ribosomes
.Transfer RNA (tRNA) = synthesised in the nucleus but carries out function in cytoplasm and ribosomes
What is mRNA (Messenger RNA)
mRNA is a long, single stranded molecule wound into a helix
Where is mRNA made?
In the NUCLEUS during the process of TRANSCRIPTION
What does mRNA carry?
.mRNA carries the genetic code for one gene from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm
.Each gene codes for a particular polypeptide
.Different mRNA molecules have different lengths
Where is rRNA (ribosomal RNA) found?
In the cytoplasm and is a component of ribosomes
What is the other component of rRNA?
Protein. Ribosomes are synthesised in the nucleolus and leave the nucleus via nuclear pores
What is rRNA?
.A large , complex molecule made up of both double and single helices
.Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis by a process called TRANSLATION
What is tRNA?
.A small single stranded molecule which folds so that in places there are base sequences forming complimentary pairs.
.acts as a carrier, bringing the correct amino acid to the ribosome based on the codon (sequence of three nucleotides) on the mRNA
Describe the structure of tRNA?
.One end of the chain,the 3 end , has the base sequence CCA at which point the specific amino acid that is carries attaches itself.
.At the opposite end is a sequence of three bases called the anticodon.
.tRNA molecules transport specific amino acids to the ribosome so that proteins can be synthesised
What are the differences between RNA and DNA ?
. RNA is single stranded whereas DNA is double stranded
.RNA has the base uracil whereas DNS has the base thymine
.RNA has ribose sugar groups whereas DNA has deoxyribose sugar groups
What are the 2 main functions of DNA?
.Replication in dividing cells
.Protein synthesis
How does replication in dividing cells work ?
.DNA is made up of two complementary strands
.The base sequence of one determines the base sequence of the other
.If the two strands of a double helix are separated , each parent strand acts as a template for the synthesis of a new COMPLEMENTARY STRAND
.So that two identical double helices can be formed
How does protein synthesis work ?
.The sequence of bases represents the genetic code
.Whereby the sequence of bases on the DNA determines the sequence of AMINO ACIDS in proteins
What is conservative replication
Conservative replication, where the parental double helix remains intact, ( is conserved ) and a whole new double helix is made.
What is semi conservative DNA replication ?
.Each original strand of DNA used as a template to make a new DNA strand
Each New DNA (mols) made of an old/original strand linked to a new strand; (not: if ref. to new DNA strand)
What is dispersive replication ?
. The 2 new double helices contain fragments from both strands of the parental double helix s=
. So you would see the hybrid strand only (light + heavy)
Where and when does replication occur ?
.Replication occurs in the NUCLEUS before a cell divides either by mitosis or meiosis.
.During a stage called INTERPHASE
What are the steps in DNA replication ?
1.DNA HELICASE unwinds and unzips helix -by breaking the Hydrogen bonds between the complementary base pairs of the two strands of the DNA molecule - exposes the unpaired bases of DNA on the template strand .
2.As DNA strands separate - enzyme DNA polymerase catalyses the addition of free DNA nucleotides to the exposed bases- each chain acts as a template so that free nucleotides can be joined to their complimentary bases.
3. This process results in the formation of two identical DNA molecules; each made up of one newly synthesised chain and one chain from the original molecule.
What did Meselson and Stahl do ?
They provided the evidence for semi conservative replication of DNA. This is that Each new
strand of DNA formed is composed of an original strand and a newly synthesised
strand
How did Meselson and Stahl provide evidence for SCR?
.Meselson and Stahl cultured the bacterium Escherichia coli, for several generations on a
medium containing amino acids made with the heavy isotope 15N.
. The bacteria incorporated the 15N into their nucleotides
.nucleotides contain an organic base which contains nitrogen (nitrogenous base)
. After several generations all the DNA contained 15N.
Explain what they did
The scientists extracted the bacterial DNA and centrifuged it.
1. The DNA settled at a low point in the tube because it contained the heavy 15N
isotope (a).
2. The bacteria were washed, then transferred to a medium containing the normal
lighter isotope 14N and were allowed to replicate once.
3. When extracts of DNA from the first generation culture were centrifuged it was
shown to have a mid-point density (positioned in the middle of the tube); half the
strand was made up of 15N DNA and the other half was made up of new 14N DNA (b).
4. When extracts of DNA were taken from the second generation grown in a 14N
medium the DNA settled at mid-points and high-points in the tube after
centrifugation (c).
5. This provided evidence which supported the semi-conservative hypothesis.
What is the second function of DNA?
Acts as a store of genetic information that can be used to make proteins
How is this genetic information coded?
In the sequence of bases in the DNA in thousands of sections along its length , called genes
What is the genetic code ?
The length of DNA making up a gene which carries the information to make a particular polypeptide
What does the sequence of bases in the DNA determine?
The sequence that the amino acids join together ( primary structure of protein )
What is a triplet code/codon ?
3 bases code for a single amino acid; this is called the triplet code or a codon.
What are the 4 bases in DNA?
A-adenine , G-Guanine , C-cytosine , T-thiamine
PAIRS + A-T , C-G
How many commonly occurring amino acids do we have ?
20
What are 3 main characteristics of the genetic code?
.Its triplet - three base pairs or a codon code for one amino acid
.Its degenerate - most amino acids have more than one code
.Its linear - each triplet is read separately
What are the 2 stages in protein synthesis ?
.Transcription
.Translation
What is transcription ? - the process of making an RNA copy of a gene's DNA sequence
DNA does not leave the nucleus; it acts as a template for the production of mRNA (messenger RNA). The mRNA is copied from a specific region of DNA called the cistron. The cistron is equivalent to a gene and codes for a specific polypeptide.
1.DNA helices unwinds and unzips 1 gene or 1 cistron by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the complementary base pairs , exposing the DNA bases
2. One strand acts as a template
3. Free RNA nucleotides complementary base pair with the bases on the template strand A with U , C with G
4. RNA polymerase joints the bases together by catalysing the formation of the sugar-phosphate backbone by condensation reaction , forming the phosphodiester bonds
What is POST TRANSCRIPTIONAL MODICFICATION ?
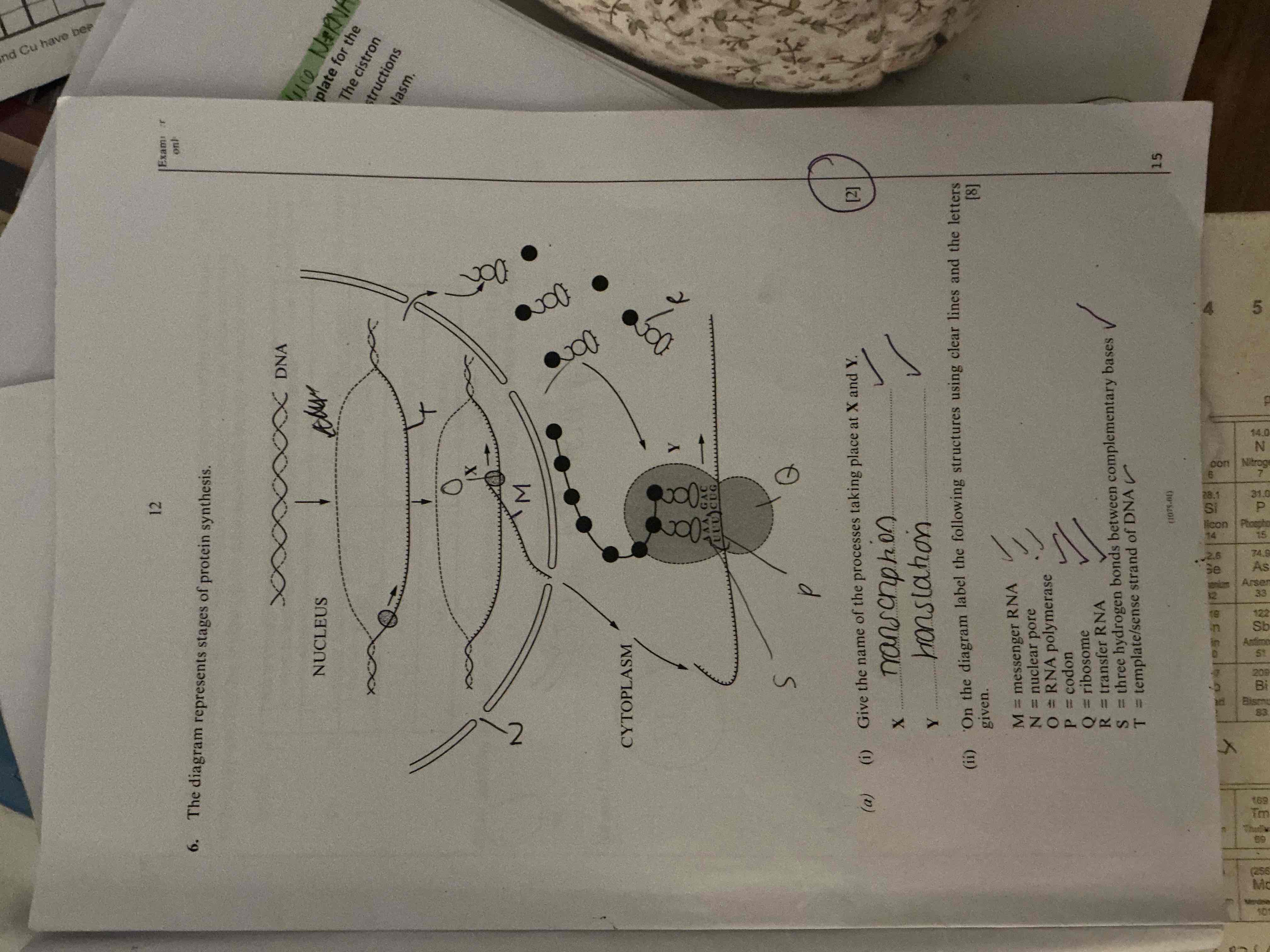
What is translation ? - nucleotide sequence of mRNA is used to determine the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide
The mRNA binds to the ribosome
The ribosome reads the first codon on the mRNA
A tRNA with the complementary anticodon enters the ribosome and binds to the first tRNA binding site. The tRNA transports a specific amino acid into position.
The anticodon complementary base pairs with the codon of the mRNA A-U, C-G forming a codon-anticodon complex
The ribosome read the second codon on the mRNA and a second tRNA molecules enters the ribosome and attaches to the second tRNA binding site
The ribosome moves one position to the right and continues to read the codons until it reaches a stop codon
The ribosome releases the primary structure of the protein to the RER and Golgi apparatus for post translational modification
What is the triplet code hypothesis
.64 possible codons: With four nucleotide bases (A, U, C, G)
.there are 43 = 64 possible codons, which is more than enough to code for the 20 standard amino acids and stop signals.
