ANTH 121 Lecture 7: Kinship ***
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to kinship, descent, marriage, family, and household structures as discussed in the lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Kinship
A system of relationships between individuals related by blood or marriage.
Consanguineal relatives
Relatives with a genetic relationship.
Affinal relatives
Relatives related by marriage.
Nominal kin
Relatives we know about but have little or no contact with.
Effective kin
Kin we meet regularly, such as at family functions.
Intimate or core kin
Family members we maintain close relationships with.
Industrial societies
Societies where nuclear families (parents and children) are most common.
Modified extended family
A family that maintains emotional ties and support networks without residential proximity.
Fictive kin
Close friends who play an important role in the family and may be adopted into the kinship network.
Matrilineal descent
Descent traced through the female line only.
Patrilineal descent
Descent traced through the male line only.
Unilineal descent
Descent traced through either the male or female line only.
Bilateral descent
Descent reckoned through both parents equally.
Double descent
A rare descent system that is both matrilineal and patrilineal.
Ambilineal descent
Descent where individuals can choose to trace their lineage matrilineally or patrilineally.
Lineage
A unilineal group tracing descent from a common ancestor.
Clan
A descent group that assumes descent from a real or fictitious ancestor.
Phratry
A group composed of two or more clans sharing a supposed common ancestor.
Moiety
Two major descent groups in a culture that share a common ancestor.
Kinship notation
Standard abbreviations and symbols used to represent kinship relationships.
Ego
The individual from whom kinship is reckoned.
Kinship symbols
Abbreviations like M (mother), F (father), B (brother), D (daughter) used in kinship diagrams.
Sexual access
The rights to engage in sexual relations, often established through marriage.
Incest taboo
A social rule prohibiting sexual relations between closely related individuals.
Endogamy
Marriage within a particular social group.
Exogamy
Marriage outside of a social group.
Nuclear family
A family unit consisting of two parents and their children.
Extended family
A family unit that includes beyond the nuclear family to other relatives.
Polygyny
A marriage pattern in which one man is married to multiple women.
Polyandry
A marriage pattern in which one woman is married to multiple men.
Group marriage
A marriage pattern where more than one man and one woman are married to each other.
Levirate
A practice where a man marries the widow of his deceased brother.
Sororate
A practice where a man marries the sister of his deceased wife.
Serial monogamy
A practice where an individual has a series of spouses, one after the other.
Arranged marriages
Marriages that are arranged by families rather than chosen by the individuals.
Cousin marriage
Marriage between cousins; preferred or proscribed depending on culture.
Bride price
A payment made by the groom or his family to the bride's family as part of the marriage.
Dowry
Wealth that a woman brings to her marriage, typically under the control of her husband.
Bride service
The work that a husband performs for his wife's family before or after marriage.
Divorce
The legal dissolution of a marriage.
Enculturation
The process through which culture is passed down from one generation to the next.
Economic cooperation
Shared economic responsibilities and labor roles within a family unit.
Patrilocal residence
A residence pattern where the wife moves to live with her husband's family.
Matrilocal residence
A residence pattern where the husband moves to live with his wife's family.
Ambilocal residence
A choice between living with the wife’s or husband's family.
Neolocal residence
A residence pattern where a couple establishes their own home separate from both families.
Avunculocal residence
A residence pattern where a couple lives with the husband's mother's brother.
Problems in families
Diverse challenges that different family types and structures face.
Polygamous family issues
Challenges arising from jealousy and relationships in polygynous or polyandrous families.
Single-parent families
Families where children live with only one parent, often after a divorce.
Kinship systems
Different frameworks through which cultures understand and organize relationships.
Hopi kinship
A form of matrilineal descent where lineage and kinship are defined by maternal lines.
Yanomamo kinship
A kinship system where lineage and family decisions are rooted in matrilineal descent.
Mundrucu kinship
A cultural example of strict gender segregation in living arrangements and kinship.
Ju/'hoansi marriage practices
Cultural nuances in marriage, emphasizing mobility and flexibility in family arrangements.
Chinese Canadian kinship
Adapting traditional kinship structures in a new cultural context post-immigration.
cross cousins
children of mother’s brothers or father’s sisters (children of siblings of the opposite sex)
parallel cousins
children of mother’s sisters or father’s brothers are parallel cousins (children of siblings of the same sex)
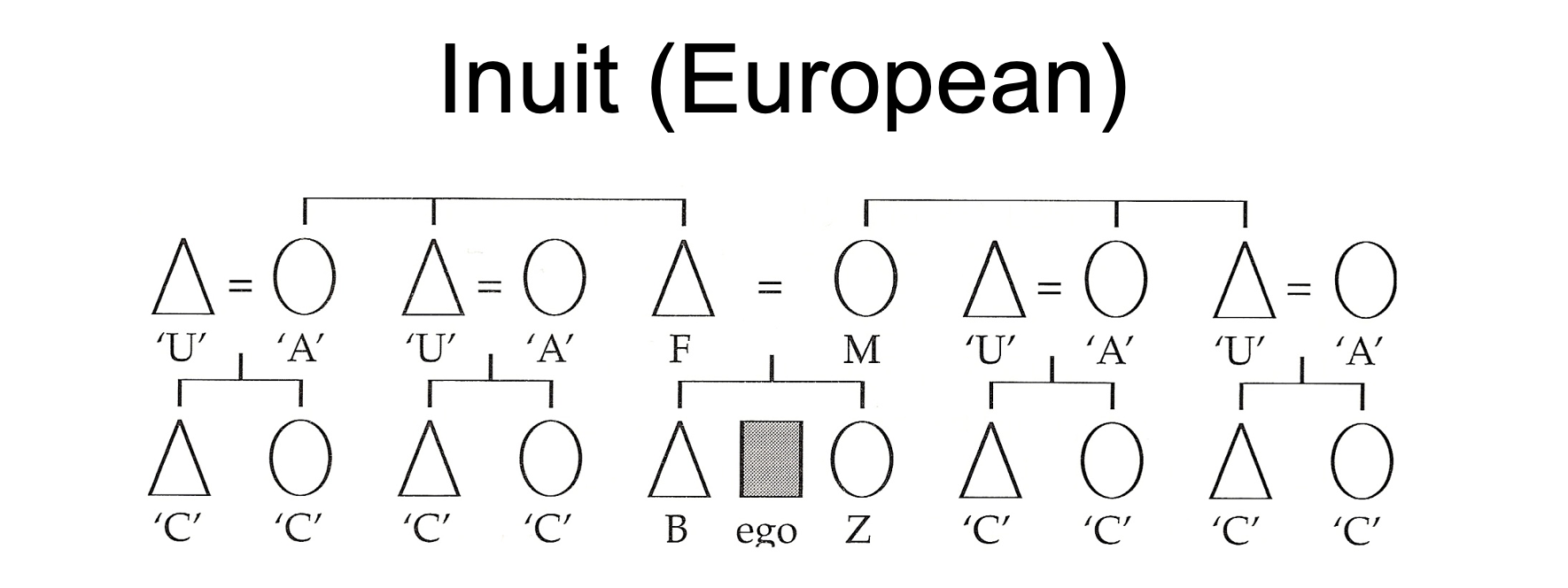
Inuit kinship system
•Similar to what is found in most European cultures
•Does not differentiate between paternal or maternal ‘aunts’ and ‘uncles’ or affinal or consanguineal ‘aunts’ and ‘uncles’
•All cousins are given the same title regardless of sex or parentage
•Associated with bilateral descent
Hawaiin kinship system (generational)
•All relatives in the father’s and mother’s generation and of the same sex are referred to by the same term
•Does not differentiate between affinal and consanguineal relations
•In Ego’s generation, male and female are given different terms which are also used for cousins
•Tends to be found in cultures with ambilineal descent

Iroquois Kinship System
•Father and father’s brother(s) use the same term as do mother and mother’s sister(s)
•Parallel cousins are called ‘brother’ and ‘sister’
•Cross cousins have different terms based on their sex but not on whether the relationship is through the male or female line
•Father sister(s) and mother’s brother(s) have a different term than their siblings
•Cross-cousins are preferred as spouses
•Tends to be found in matrilineal cultures, but is also seen in patrilineal societies practicing clan exogamy

Sudanese Kinship System
•Everyone is given a distinctive term (Descriptive)
•Occurs where differentiating between elder and younger siblings in the parent’s generation is important
•Cross and parallel cousins are given different terms based on whether they are in the male or female lines
•Tends to be found in cultures with bilateral descent
