AAPC CPB Chapter 11 Review
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
A Medicare patient presents with an injury sustained at his part-time job. His injury status is verified by his company. After services are rendered, in what order are the claims submitted?
a. The worker's compensation is primary, and Medicare is secondary
b. Either may be filed first, whichever pays better
c. Medicare is primary, and Worker's compensation is secondary
d. The patient must pay for services and files claims himself
a. The worker's compensation is primary, and Medicare is secondary
Rationale: If an individual is entitled to Medicare and is covered under Workers' Compensation because of a job-related illness or injury, Workers' Compensation is the primary for healthcare items or services re-lated to job-related illness or injury claims.
Which coverage under TRICARE is a Medicare wrap around plan?
a. TRICARE for Life
b. TRICARE Reserve Select
c. TRICARE Prime
d. CHAMPVA
a. TRICARE for Life
TRICARE for Life is a Medicare-wrap around coverage for TRICARE eligible beneficiaries who have Medicare Part A and B. Enrollment is automatic if the member has Medicare Part A and B, but you must pay Medicare Part B premiums. TRICARE for Life pays after Medicare in the U.S. and U.S. Territories but is the first payer in all other overseas areas.
A 21 year-old patient presents for fillings for two if his teeth. Are these services covered under EPSDT?
a. No, because these types of services are not covered.
b. Yes, if the patient lives in a state that covers dental services.
c. No, because the patient is not under the age of 21.
d. Yes, all services are covered under Medicaid.
c. No, because the patient is not under the age of 21.
The EPSDT benefit provides comprehensive and preventive healthcare services for enrolled children under the age of 21.
A patient has Medicare and a Medigap policy. Box 13, signature on file, is checked off on the electronic claim submission. An EOMB is received with remittance notice MA19. What does the office need to do?
a. Nothing. This means the claim has been crossed over to the Medigap plan.
b. The biller must file the secondary insurance as the cross-over claim is not going to be sent due to missing information.
c. The biller must check the claim filed for missing information, add the missing information, and send back to Medicare for processing.
d. Nothing. The notice means that the patient is responsible for the bill.
b. The biller must file the secondary insurance as the cross-over claim is not going to be sent due to missing information.
When information is missing or incorrect in block 9, MACs do not forward a transaction record to the Medigap carrier and the following remittance notice is sent on the EOMB: MA19—Information was not sent to the Medigap insurer due to incorrect/invalid information you submitted concerning the insurer. Please verify your information and submit your secondary claim directly to that insurer.
What is true regarding Medigap policies?
a. They cover everything that Medicare does not.
b. They cover deductibles, copayments, and coinsurances usually.
c. All Medigap policies are the same and offer the same coverage.
d. Medigap policies must cover patients if they injured outside the United States.
b. They cover deductibles, copayments, and coinsurances usually.
Medigap refers to a Medicare supplemental policy that is sold by private insurance companies to help cover some of the costs that original Medicare does not cover, like deductibles, copayments, and coinsurances.
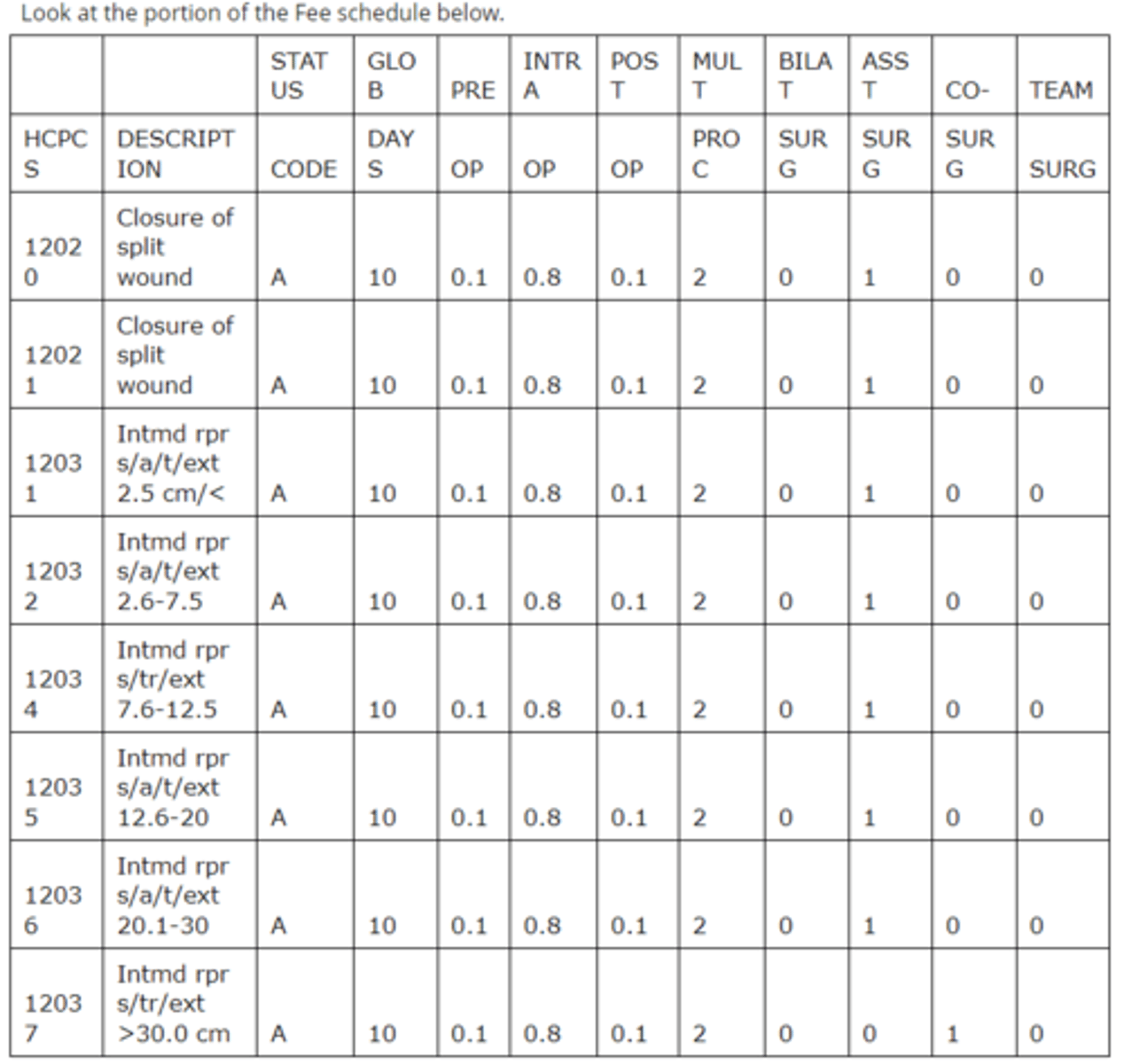
Using the portion of the schedule above, what is true about the codes?
a. Code 12032 has restricted coverage.
b. Code 12035 may be billed with modifier 50.
c. Code 12034 may not be billed with modifier 62.
d. Code 12037 can never be billed as a co-surgery under any circumstances.
c. Code 12034 may not be billed with modifier 62.
Modifier 62 is the modifier to indicate two surgeons shared a surgery. The co-surgery status code for 12034 is a 0, indicating that co-surgery is not permitted. Code 12032 has a status code of A, indicating it is an active code that is payable under the fee schedule. Code 12035 has a status code for bilateral procedures of 0, indicating that bilateral billing of this code is inappropriate. Code 12037 has a status code for co-surgery of 1, indicating that a co-surgery may be paid with supporting documentation that supports medical necessity.
A Medicare patient receives services from a participating provider on January 6, 2016, but the charges are missed and don't get entered in to the computer. How long does the office have to bill Medicare for the services?
a. 3 months
b. 12 months
c. 6 months
d. 1 month
b. 12 months
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) amended the time period for filing Medicare fee-for service claims. Claims must be filed within one calendar year, 12 months, after the date of service.
A Medicare patient has prescription drug coverage, but does not have Medicare Advantage. What Medicare coverage does the patient have for his medications?
a. Part A
b. Part B
c. Part C
d. Part D
d. Part D
Medicare Part A is hospital insurance, Part B is medical insurance, Part C is Medicare Advantage, and Part D is the prescription drug plan.
A Medicare patient is seen by her physician. The physician has opted out of the Medicare program. The patient and physician have a private contract. The charges for the services rendered are $300.00. Medicare's approved amount would be $200.00. What can the office charge this patient?
a. $160.00 (80 percent of the approved amount)
b. $218.50 (115 percent of the approved amount for non-Par providers)
c. $300.00
d. $250.00
c. $300.00
Providers that have opted-out of the Medicare cannot bill Medicare and may charge whatever they desire to patients as they are not subject to Medicare's fee schedule or limiting charge. The condition of the contract between the provider and the patient is that the patient is liable for all provider charges without any Medicare balance billing limits.
A Medicare patient presents for her pelvic, pap, and breast examination (PPB). The patient is not sure when she had her last PPB. As she is checking out, the front desk rep has her sign an ABN. The service is billed and denied for frequency. Can the patient be balance billed? Why?
a. Yes. It does not matter when you get an ABN signed.
b. No. The ABN must be signed before the service is performed.
c. Yes, as long as the patient has met her deductible.
d. No. An ABN is not required, but the patient is required to pay at time of service or the bill has to be written off.
b. No. The ABN must be signed before the service is performed.
The ABN must be reviewed with the patient and signed by the patient before the item or service is rendered to be valid. If it is not, the patient cannot be billed for the service if Medicare does not approve it.
After review of the information provided, are there any errors on the claim form? If so, which elements are incorrect?
I. The provider must accept assignment
II. Provider name conflict
III. Medicare ID number is missing information
IV. Medicaid ID number is missing information
V. Medicare ID number in the wrong field
VI. Medicaid ID number in the wrong field
VII. Ordering provider name and NPI
VIII. Place of service code
IX. Diagnosis code(s)
X. Diagnosis pointer(s)
a. I, V, VI, and X
b. I, VI, IX, and X
c. III, IV, VIII, and IX
d. There are no errors on this claim.
b. I, VI, IX, and X
When providers provide physician services to individuals dully entitled to Medicare and Medicaid, they are required to accept assignment. The patient's Medicaid number should be listed in item 10d. For Medicare, only one diagnosis pointer is entered per line item. Apnea NOS is not mentioned in the medical record and documentation supports ICD-10-CM code I21.9 Acute Myocardial Infarction, unspecified, rather than I21.3.
What should be done to correct this claim?
I. Correct assignment on the claim.
II. Correct primary insurance information on the claim.
III. Correct secondary insurance information on the claim.
IV. Correct the provider information on the claim.
V. Correct the diagnosis on the claim.
VI. Correct the diagnosis pointer(s) on the claim.
a. III and IV
b. I, III, V, and VI
c. I - VI
d. None of the above.
b. I, III, V, and VI
When providers provide physician services to individuals dully entitled to Medicare and Medicaid, they are required to accept assignment. Item 27 should be marked yes. The patient's Medicaid number should be listed in item 10d. For Medicare, only one diagnosis pointer should be entered per line item. On this claim, three are entered. Apnea NOS (R06.81) is not mentioned in the medical record documentation that supports ICD-10-CM code I21.9 Acute Myocardial Infarction, unspecified, rather than I21.3.
After review of the information provided, are there any errors on the claim form? If so, which elements are incorrect?
I. Patient name
II. Primary insurance ID number
III. Authorization number
IV. Place of service
V. Site of service
VI. Provider NPI number
VII. CPT® code
VIII. Modifier
IX. Diagnosis conflict
X. Units of service
a. I, III, V, VII, and IX
b. I and VII
c. I, II, and VII
d. None of the above.
b. I and VII
The patient's name on the claim form must be identical to the name on the patient's Medicare card. The patient is an established patient but a new patient visit is reported.
What should be done to correct this claim?
I. Correct the patient's name on the claim.
II. Review the medical record to verify the diagnosis code.
III. Add the correct modifier.
IV. Add the authorization number.
V. Correct the CPT® code.
a. III and IV
b. I and V
c. I and II
d. None of the above.
b. I and V
The name on the claim form should be changed to BROWN DONNY JOE. The CPT code for a level IV established patient office visit is 99214.
After review of the information provided, are there any errors on the claim form? If so, which elements are incorrect?
I. The provider must accept assignment
II. Provider name conflict
III. Medicare ID number is missing information
IV. Medicaid ID number is missing information
V. Medicare ID number in the wrong field
VI. Medicaid ID number in the wrong field
VII. Units are missing
VIII. CPT® codes are incorrect
IX. Modifier use
X. Diagnosis pointer
a. IV only
b. I, IV, VI, VII, and IX
c. II, III, V, VIII, and X
d. None of the above.
a. IV only
The Medicaid number is missing in Item 10d.
According to the LCD, what diagnosis pointer should be listed in Item E of the CMS-1500 claim form corresponding to CPT® code 93010?
a. A
b. B
c. A or B
d. None of the given diagnoses are covered according to this LCD.
a. A
According to the LCD, Acute myocardial infarction, unspecified (I21.9) is covered diagnoses for 93010.
After review of the information provided, are there any errors on the claim form? If so, which elements are incorrect?
I. The provider must accept assignment
II. Provider name conflict
III. Medicare ID number is missing information
IV. Medicaid ID number is missing information
V. Medicare ID number in the wrong field
VI. Medicaid ID number in the wrong field
VII. Ordering provider name and NPI
VIII. Place of service code
IX. Diagnosis code(s)
X. Diagnosis pointer(s)
a. VIII and IX
b. I, VI, VIII, IX, and X
c. III, IV, and IX
d. There are no errors on this claim.
a. VIII and IX
Place of service 11 is for an office visit. This visit was to the emergency department which is reported with place of service 23. An acute myocardial infarction is reported with ICD-10-CM I21.9. R06.02 shortness of breath is a sign or symptom of an acute myocardial infarction, therefore should not be reported. Refer to ICD-10-CM guidelines I.B.4 & I.B.18.
Dr. Gregory performs the pre-op and surgery for code 12034, but not the post-op care. The approved amount for the entire service is $200. Using the table above, what will Dr. Gregory's reimbursement be for his portion of the service?
a. $150
b. $160
c. $180
d. $200
c. $180
Rationale: Looking at the table the pre-op portion is 10%, the intra-op portion is 80%, and the post-op portion is 10%. Dr. Gregory performed the pre-op and intra-op portions, which would equate to 90% of the approved amount. The approved amount is $200 and 90% is $180.
MAC is the acronym for:
a. Medicare Administrative Contractor
b. Medicare Administrative Contact
c. Medical Access Center
d. Medicare Advantage Contractor
a. Medicare Administrative Contractor
Rationale: Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC) administers and processes claims for Medicare Part A and Part B services organized in multi-state regions.
The total RVU is composed of which of the following components:
a. Sustainable growth rate (SGR), conversion factor (CF), and malpractice insurance (MP)
b. Sustainable growth rate (SGR), practice expense (PE), and physician work
c. Physician work, practice expense (PE), and malpractice insurance (MP)
d. Conversion factor (CF), practice expense (PE), and malpractice insurance (MP)
c. Physician work, practice expense (PE), and malpractice insurance (MP)
Rationale: Total RVU is based on three components of physician services: physician work, practice expense (PE) and malpractice insurance (MP).
Beth has purchased a Medigap policy to supplement her Medicare coverage. She has authorized Medicare to send payments directly to the physician, and Medicare has transferred their claims information to the Medigap insurance company. This transfer of information is known as:
a. Cross-under
b. Shared billing
c. Cross-over
d. Data sharing
c. Cross-over
Rationale: The transfer of claims information from Medicare to Medigap is called cross-over.
Barbara's late husband, Joe, was a lieutenant in the Navy. He served for 30 years, retiring 10 years prior to his death. His Death was due to a service connected disability. Barbara will still have healthcare coverage as Joe's widow under which of the following healthcare programs?
a. CHAMPVA
b. Medicare
c. CHAMPUS
d. TRICARE
a. CHAMPVA
Rationale: The Civilian Health and Medical Program of the Department of Veterans Affairs (CHAMPVA) is the healthcare program in which the Department of Veterans Affairs covers spouses, widows and widowers, and the children of a veteran who is rated permanently and totally disabled due to a service connected disability, died of a service-connected disability, or died on active service and the dependents are not eligible for TRICARE.
TRICARE is the healthcare program for which department of the US government?
a. Department of Military Service
b. Department of Finance
c. Department of Defense
d. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services
c. Department of Defense
Rationale: TRICARE, formerly known as CHAMPUS, is the Department of Defense healthcare program for military families and retirees.
When processing Medigap claims, Item 9a of the CMS-1500 claim form must have the policy and/or group number of the Medigap insured preceded by:
a. MEDIGAP
b. MG
c. MGAP
d. Any of the above
d. Any of the above
Rationale: MEDIGAP, MG, or MGAP must precede the policy or group number in Item 9a of the CMS-1500 claim form to allow for proper processing of Medigap claims.
The Clinical Prior Authorization (PA) Program assists in the monitoring of:
a. Medicaid eligibility requirements.
b. procedures that need prior authorization.
c. drug interactions.
d. drugs not on Medicaid's formulary.
d. drugs not on Medicaid's formulary.
Rationale: Clinical Prior Authorization (PA) Program was implemented to manage drug classes not listed on Medicaid's formulary as well as drugs that require additional monitoring, ensuring drugs are being prescribed for the right patients and the appropriate reasons, as well as monitoring drug expenditures.
Medicare's payment amount for services are determined by which of the following formulas?
a. Total Practice Expense (PE) X Conversion factor(CF) = Medicare payment
b. Total Malpractice insurance (MP) X Conversion factor (CF) = Medicare payment
c. Total RVU X Conversion factor(CF) = Medicare payment
d. Sustainable growth rate (SGR) X Geographic Practice Cost Index (GPCI) = Medicare payment
c. Total RVU X Conversion factor(CF) = Medicare payment
Rationale: Medicare payments are determined based on the Total RVU X Conversion Factor. The complete formula includes [(Work RVU X Work GPCI) + (RVUPE X PE GPCI) + (MP RVU X MP GPCI)] = Total RVU X Conversion Factor = Medicare payment
Medicaid claims must be filed:
a. based on the individual state's timely filing requirement.
b. within 180 days.
c. within 95 days.
d. within 365 days.
a. based on the individual state's timely filing requirement.
Rationale: Medicaid timely filing requirements will vary from state to state. Billers need to be aware of the filing limits within the individual state.
Which TRICARE option allows enrollees the most choices by utilizing the fee-for-service model?
a. TRICARE for Life
b. TRICARE Select
c. TRICARE Prime
d. Both a and b
b. TRICARE Select
Rationale: TRICARE Select is a fee-for-service option that allows the enrollees the most choices.
Andrew has selected TRICARE Prime as his health plan. Who will be responsible for coordinating his health care, maintaining his medical records, and referrals to specialists when needed?
a. PCM - Primary Care Manager
b. PCP - Primary Care Provider
c. PCN - Primary Care Networker
d. PCC - Primary Care Coordinator
a. PCM - Primary Care Manager
Rationale: TRICARE Prime is a managed care model in which the insured will select their primary care manager who will be responsible for coordination of care, medical record maintenance, and referrals.
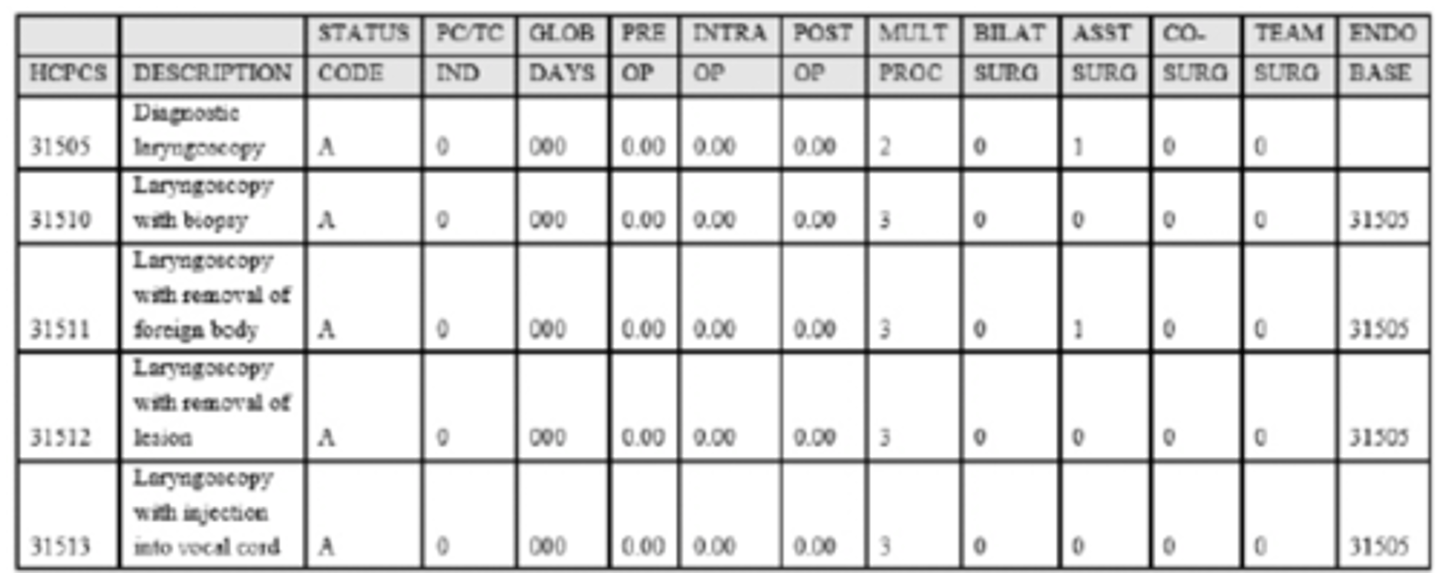
A physician performs a diagnostic laryngoscopy with biopsy and removal of a separate laryngeal lesion. The patient has Medicare which will pay 80% of the approved amount after deductible for these procedures. The patient has met his deductible. The approved amounts are as follows:
31505 - $75.00
31510 - $150.00
31512 - $200.00
What reimbursement should the physician receive from the health plan?
a. $250.00
b. $280.00
c. $220.00
d. $340.00
c. $220.00
Rationale: The RBRVS table shows that the multiple procedure indicator for 31510 and 31512 is 3, which means that the special endoscopic rules apply. The table also shows the base endoscopic code is 31505. No payment is made for the base code (31505) as it is bundled into the surgical codes. The highest paid code is 31512 at $200, so that is paid at 80% ($160). The second procedure is paid after the cost of the base procedure is subtracted. Code 31510 is $150, so $75 is subtracted and the remainder is $75; paid at 80% ($60). Total payment for all procedures would be $220.00.$160 + ((150.00- 75.00)*80%) = $220.00
Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnostic, and Treatment (EPSDT) is a program associated with:
a. All insurance carriers
b. Medicaid
c. Medicare
d. Commercial insurance carriers
b. Medicaid
Rationale: EPSDT is a benefit of Medicaid that provides comprehensive and preventive healthcare services for enrolled children under the age of 21.
Medicare statutorily excluded services are:
a. Non-covered items and services.
b. Not reimbursed by Medicare.
c. Reimbursed on a case-by-case basis
d. Both a & b
d. Both a & b
Rationale: Non-covered items and services are statutorily excluded and are not reimbursed by Medicare. Examples of statutorily excluded services are routine foot care, cosmetic surgery, and acupuncture.
Medigap policies must conform to minimum standards identified by federal and state laws and clearly be identified as:
a. Medicare Secondary Insurance
b. Medicare Subsequent Insurance
c. Medicare Supplement Insurance
d. Medicare Selective Insurance
c. Medicare Supplement Insurance
Rationale: The Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1990 requires all Medigap insurance policies to conform to minimum standards including standardized benefits and consumer protection requirements. Every Medigap policy must follow federal and state laws and be clearly identified as Medicare Supplement Insurance.
Dr. Allen who is a non-PAR provider performs an appendectomy on a 67-year-old Medicare patient. The physician's UCR for the surgery is $1500. Medicare's approved fee for this procedure is $1100. What is the limiting charge that this non-PAR provider can charge to this Medicare patient?
a. $1500
b. $1100
c. $1201.75
d. $1265
c. $1201.75
Rationale: A non-PAR provider's fee schedule is 95% of Medicare approved amounts for PAR providers, which sets the fee at $1045 ($1100 X .95). The provider's limiting charge would be 115% of the Medicare approved amount for non-PAR ($1045 X 115% = $1201.75)
The term for a supplemental policy for Medicare is:
a. Medicare Plus
b. Medigap
c. Medicare Secondary
d. Medifill
b. Medigap
Rationale: Medigap is a Medicare supplemental policy to help cover costs that are not covered by Medicare.
Medicaid agencies are required to report EPSDT performance information
a. annually
b. monthly
c. weekly
d. quarterly
a. annually
Rationale: State Medicaid agencies must inform all Medicaid-eligible individuals under the age of 21 that EPSDT services are available, provide or arrange for the provision of screening services for all children, arrange for corrective treatment as determined by the health screenings, and report the performance information on an annual basis.
The conversion factor is updated by CMS:
a. Annually
b. Semi-annually
c. Quarterly
d. Monthly
a. Annually
Rationale: The conversion factor is updated annually and has increased by 0.5% from 2016 to 2019 according to the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015 (MACRA).
A 45-year-old patient is diagnosed with N18.6. Based on this diagnosis, would this patient be eligible for Medicare coverage?
a. Yes, because he has ESRD which is a condition that qualifies for Medicare benefits.
b. No, because he is not 65 years old.
c. No, because Medicare only covers patients with chronic renal failure.
d. Yes, because he has acute renal failure which is a condition that qualifies for Medicare benefits.
a. Yes, because he has ESRD which is a condition that qualifies for Medicare benefits.
Rationale: Medicare is a health insurance program for people age 65 and older, people under 65 with certain disabilities, and people of any age with end stage renal disease.
To determine the Medicare coverage and payment policy for a service or procedure, which of the following resources will indicate if a service or procedure is payable, noncovered, or bundled into another service?
a. PC/TC indicator
b. Global surgery indicators
c. Status codes
d. Both a & b
c. Status codes
Rationale: Status codes should be reviewed to determine the status of a code, i.e. A= Active code, B=Bundled code, D=Deleted, etc.
Which of the following are mandatory benefits that must be provided by Medicaid programs in order to receive matching federal funding.
I. Outpatient hospital services
II. Podiatry services
III. Home health services
IV. Federally Qualified Health Centers services
V. Inpatient hospital services
VI. Chiropractic services
VII. Occupational therapy
a. II, III, VII
b. I, III, IV, V
c. I, III, IV, VI, VII
d. IV, V, VI, VII
b. I, III, IV, V
Rationale: Outpatient hospital services, home health services, Federally Qualified Health Centers services, and inpatient hospital services are among some of the mandatory services required to secure matching federal funding. A complete listing of mandatory and optional benefits can be accessed at the following website.
Medicare Supplement Insurance policies or Medigap is sold by:
a. Healthcare providers
b. Medicaid
c. Private insurance companies
d. Medicare
c. Private insurance companies
Rationale: Medigap refers to a Medicare supplemental policy that is sold by private insurance companies to help cover some of the costs that original Medicare does not cover.
A Medicare patient receiving inpatient care in a critical access hospital would be covered under
a. Part D
b. Part B
c. Part A
d. Part C
c. Part A
Rationale: Part A helps cover inpatient care in hospitals, including critical access hospitals, and skilled nursing facilities for Medicare patients.