AQA A level Biology - Respiration
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What is the equation for aerobic respiration?
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + 38ATP
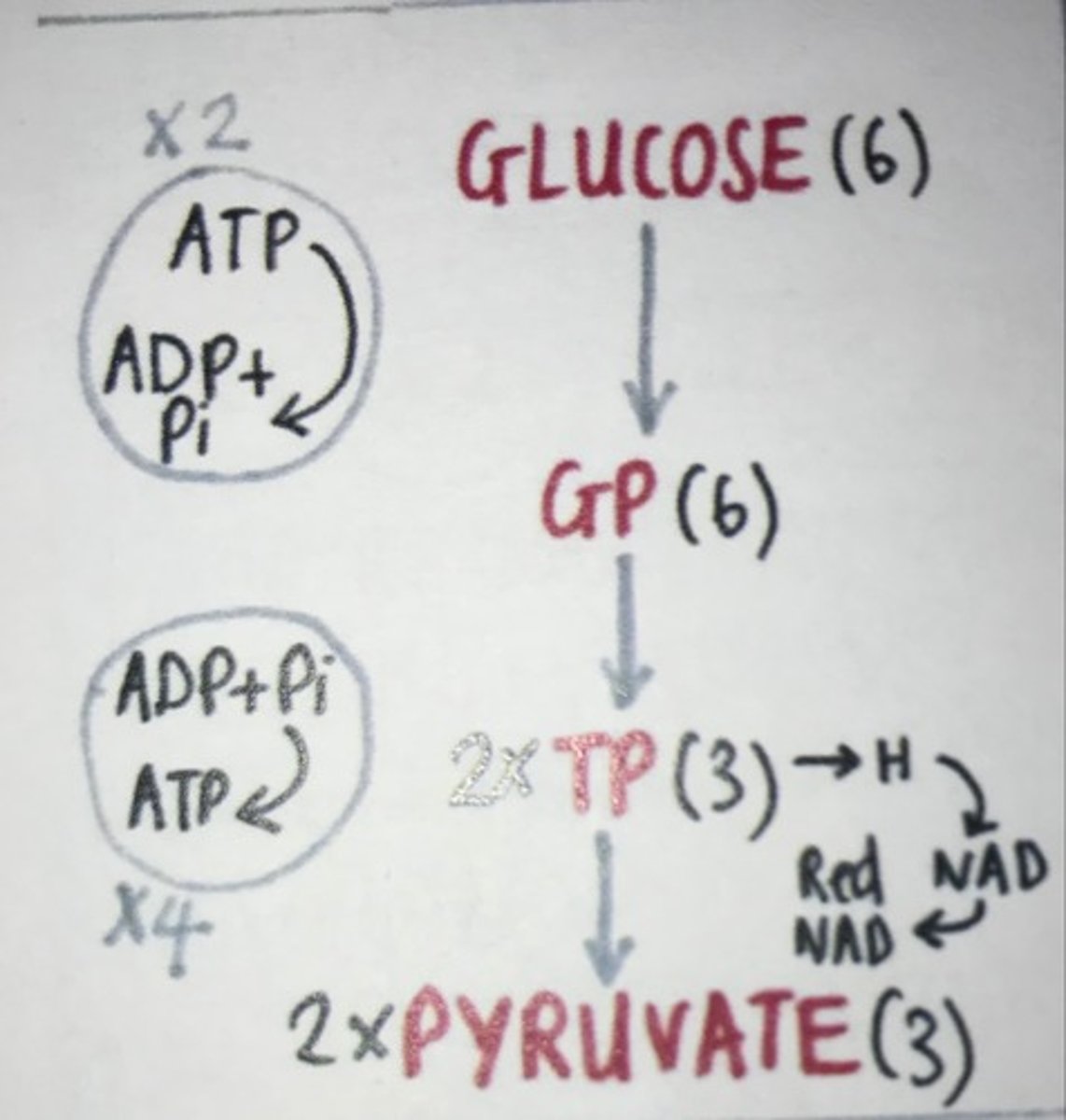
Draw and describe the order of events in glycolysis
Happens in cytoplasm
Phosphorylation of glucose - Two ATP molecules donate phosphate groups to glucose, forming hexose bisphosphate.
Lysis - The hexose bisphosphate molecule is split into two molecules of triose phosphate (TP).
Phosphorylation of TP - A second phosphate group is added to each TP molecule, converting them into two molecules of triose bisphosphate.
Dehydrogenation - A hydrogen is removed from each triose bisphosphate molecule (they are oxidised) and used to form two molecules of reduced NAD, two molecules of pyruvate, and four molecules of ATP through substrate-level phosphorylation.
Draw and describe the order of events in link reactions
Happens in the matrix
Pyruvate release carbon dioxide and hydrogen to form acetate (decarboxylase)
Hydrogen the reduces NAD (dehydrogenase)
Coenzyme A combines to acetate to form acetylCo enzyme A

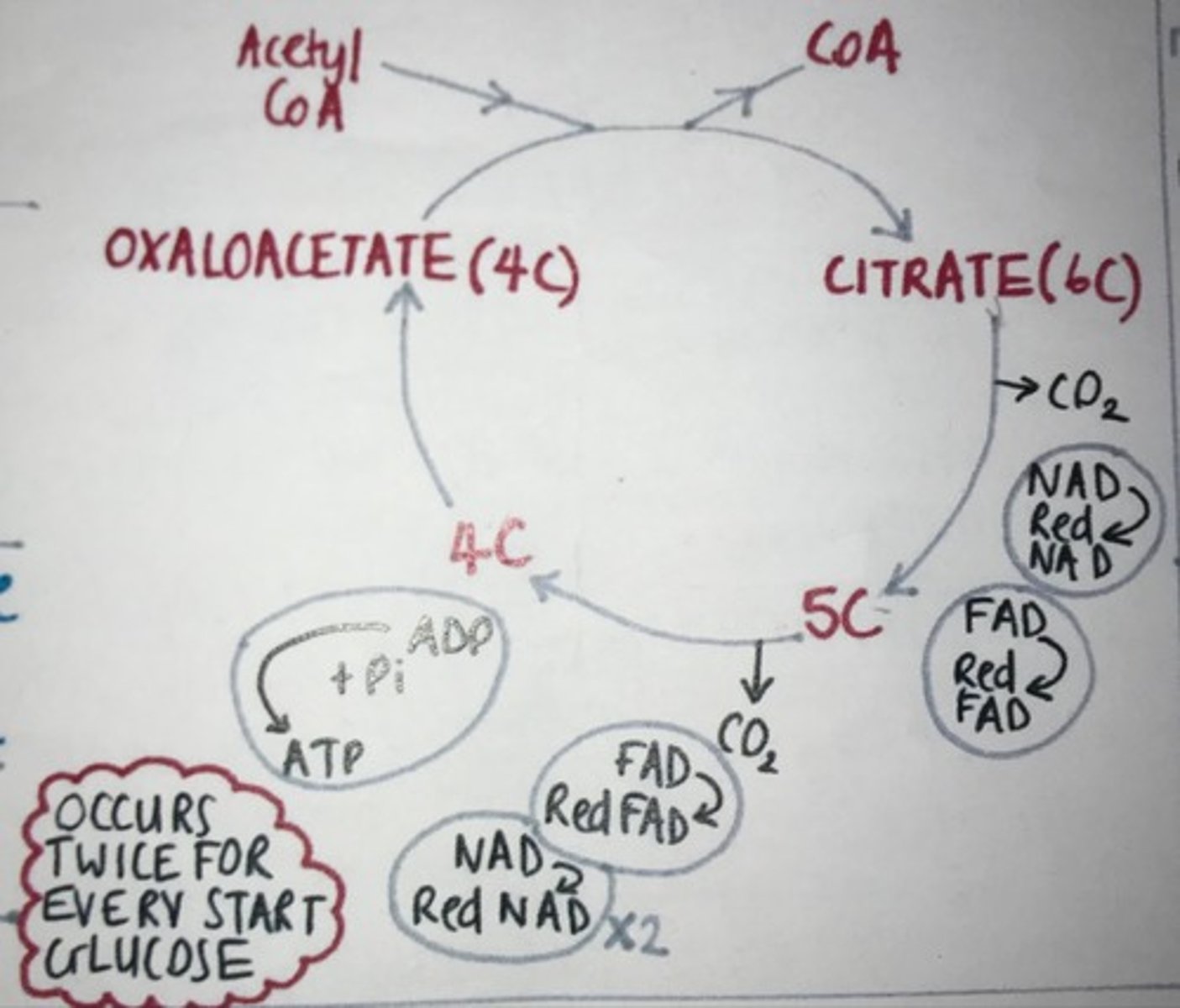
Draw and describe the order of events in Krebs cycle
The two-carbon (2C) acetyl CoA merges with a 4C molecule to create a 6C molecule.
The 6C molecule is decarboxylated, releasing two molecules of carbon dioxide.
The 6C molecule is also dehydrogenated (oxidised), releasing hydrogens that reduce NAD and FAD.
For each acetyl CoA that enters the cycle, one ATP (or GTP in some organisms) is synthesised directly via substrate-level phosphorylation.
The 4C molecule is regenerated for the next turn of the cycle.
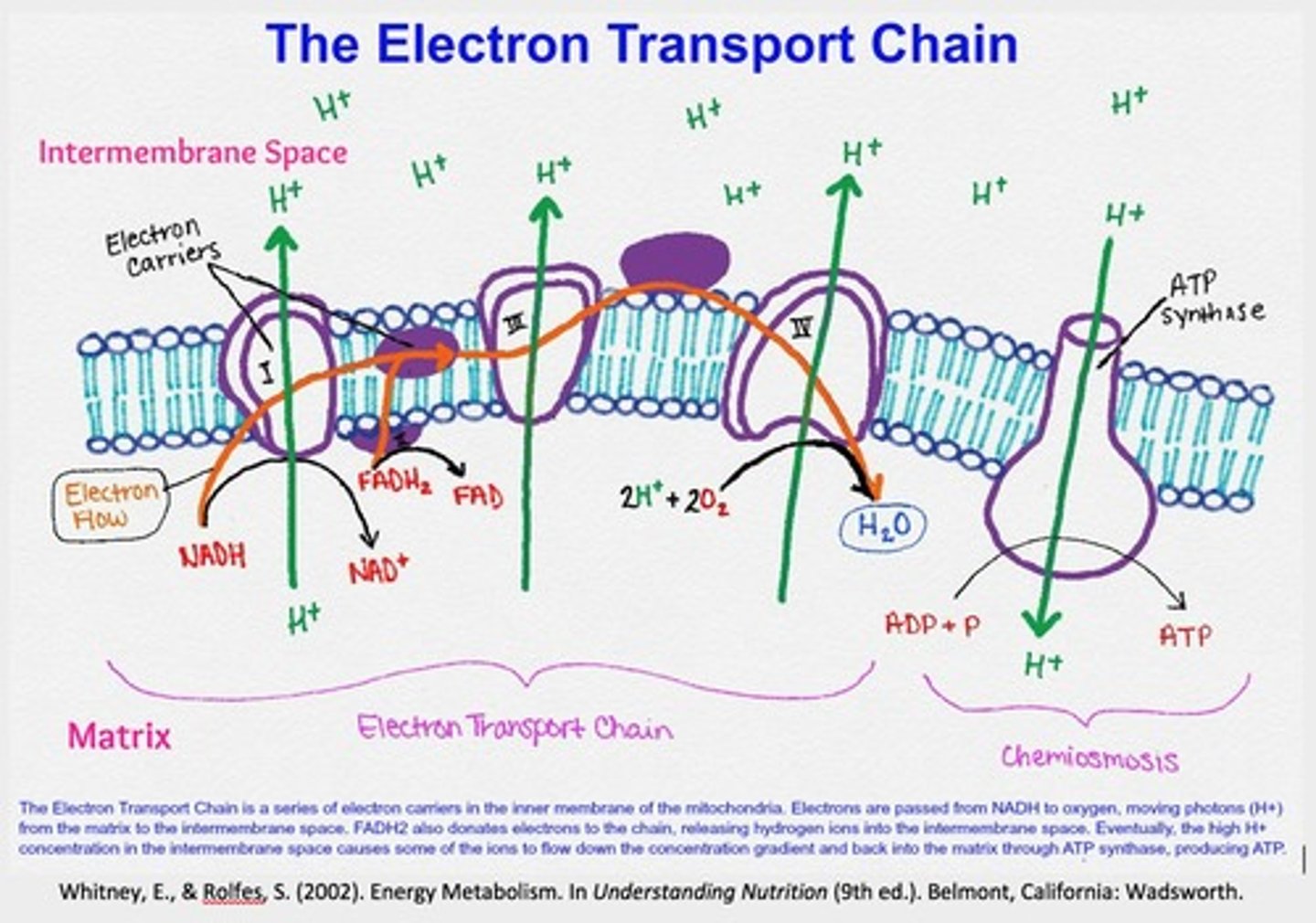
Draw and describe the order of events in oxidative phosphorylation
1.The reduced coenzymes (NAD/ FAD) release hydrogens which are photo ionised into protons and electrons
2.The electrons are transferred along the ETC in a series of redox reactions and the energy released is used to pump protons across the cristae into the the interemembrane space
3.This creates an electrochemical gradient so protons diffuse out through ATP synthase and activate it
4.ATP synthase phosphorylates many ADP into ATP
5.At the end oxygen acts as the final acceptor and is reduced by the protons and electrons to produce water
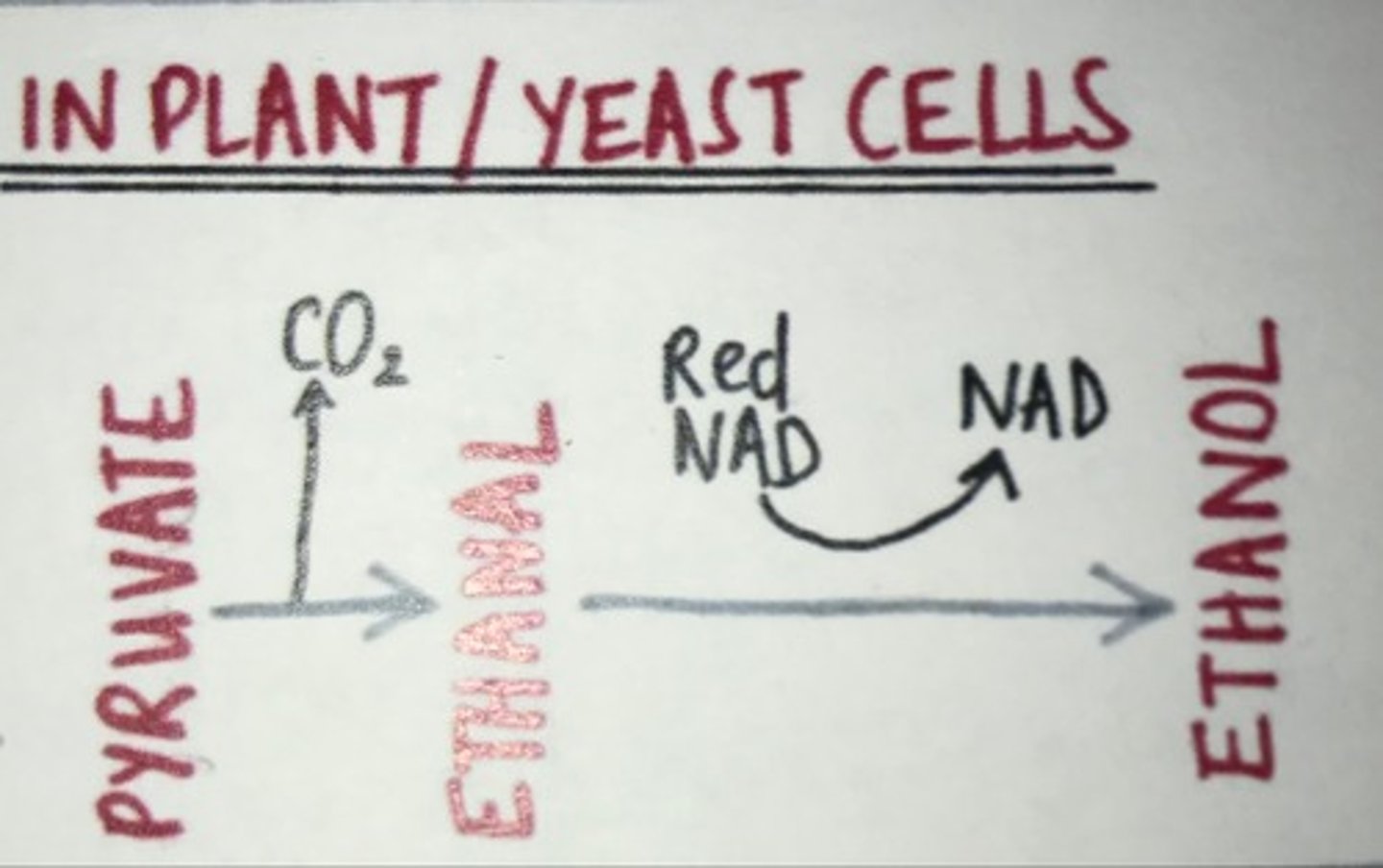
What is the equation for anaerobic respiration in plants?
glucose --> ethanol + carbon dioxide + energy
Where does anaerobic glycolysis occur?
cytoplasm
What is the equation for anaerobic respiration in animals?
Glucose -------> Lactic acid + (releases some energy)

What are the steps on anaerobic respiration?
glycolysis steps to produce pyruvate
In plants carbon dioxide is released to produce ethanal and then reduced NAD is oxidised and ethanal is reduced into ethanol
In animals pyruvate is reduces by the hydrogen released from reduced NAD.
Why is anaerobic respiration fast?
This is because it is only one step of glycolysis and is cyclic as the reduced NAD is used and reconverted continually
What are respiratory substrates?
Carbohydrates, all forms of carbohydrates (starch/glycogen/lactose/sucrose) are turned into glucose
Proteins, excess amino acids are converted into keto acid
[keto acid turned into pyruvate and intermediates of krebs cycle]
Lipids, provided fatty acids and glycerol
[fatty acids become acetylcoenzyme A, glycerol becomes triose phosphate]