LE Muscle Length Testing
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
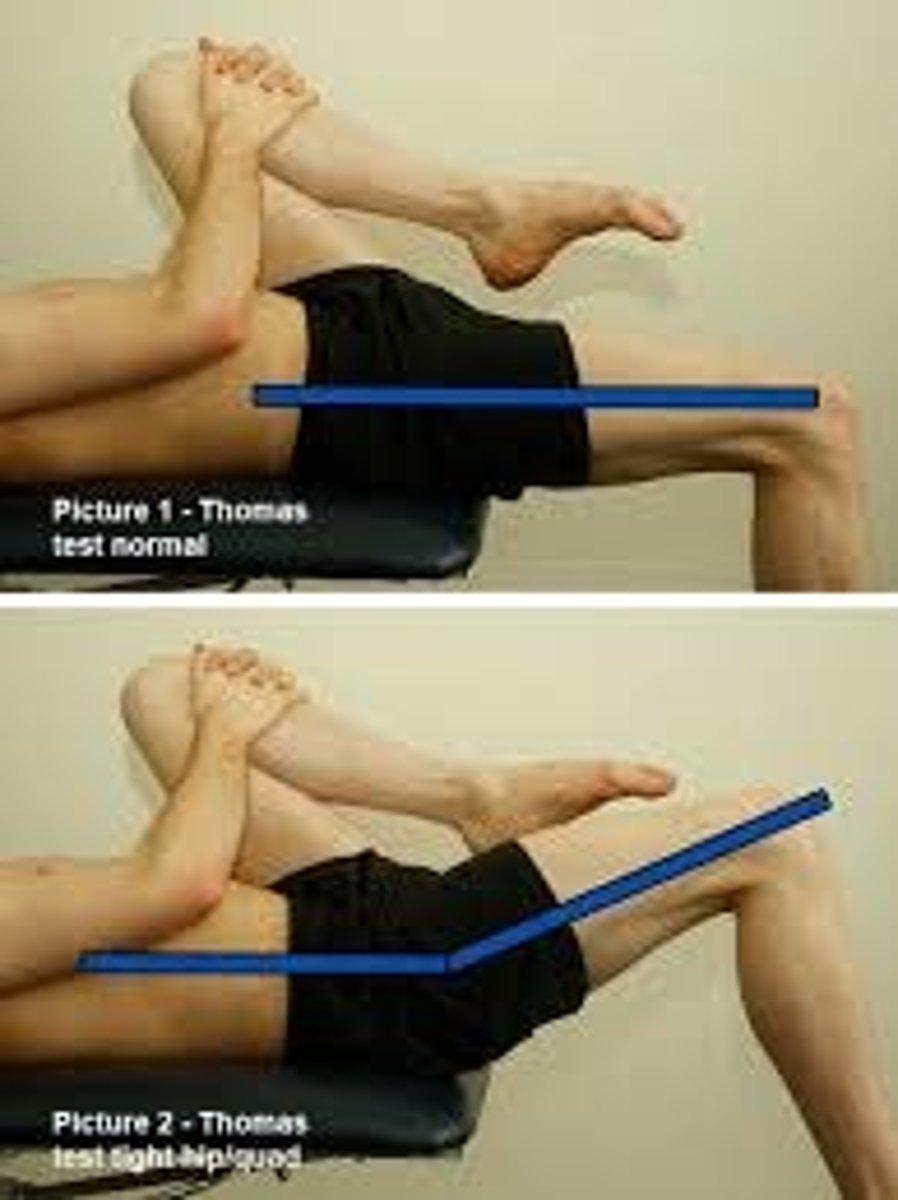
Thomas Test
•The Thomas test evaluates the length of the one and two joint muscles that flex the hip
•Testing Position: Supine with knees to chest at end of table
•Stabilization: Knee to chest stabilizes spine
•Testing motion: Lower one leg while stabilizing spine with other knee to chest (compare each side)
•End feel: firm
•Interpretation: If the testing leg's thigh lies flat on the table, and the knee remains in at least 80 degrees of flexion, the iliopsoas and rectus femoris muscles are of normal length
+ if straight leg rises off table
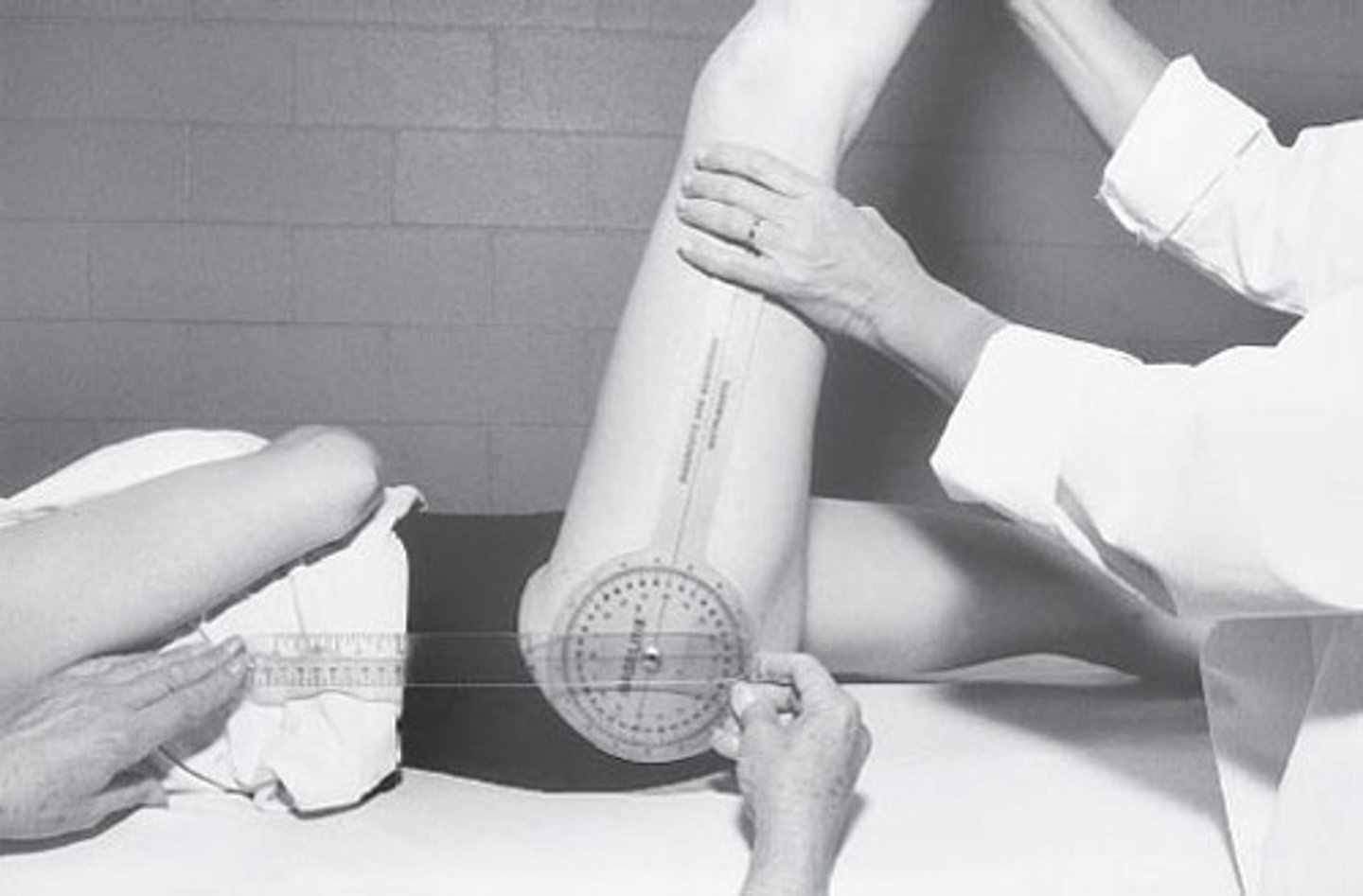
•Measure to document progress - goniometer alignment as with hip flex
•Positive finding: Iliopsoas vs Rectus femoris tightness
•If positive findings, extend knee, if no change in thigh position=Iliopsoas tightness and/or joint structures such as the anterior joint capsule, iliofemoral ligament, & ischiofemoral ligament
•If thigh returns to table with knee ext=rectus femoris tightness
SLR Muscle Length Test
•The straight leg raise test evaluates the length of the hamstring muscles
•Testing position: Supine
•Stabilization: Stabilize anterior distal femur and posterior distal tibia to maintain knee extension
•Testing motion: Hip is passively flexed with knee in extension, pelvis in neutral (compare each side)
•End feel: firm
•Interpretation: If hip flexion measurements are between 68°-80°, SLR is considered (-) or normal
•The end of the testing motion occurs when resistance is felt from tension in the posterior thigh and further flexion of the hip causes knee flexion, posterior pelvic tilt, or lumbar flexion
•Differential diagnosis: If hip flx increases with knee flx=hamstrings; If there is no change in ROM= glut max or other inert joint structures
•Measure to document progress - goniometer alignment as with hip flex

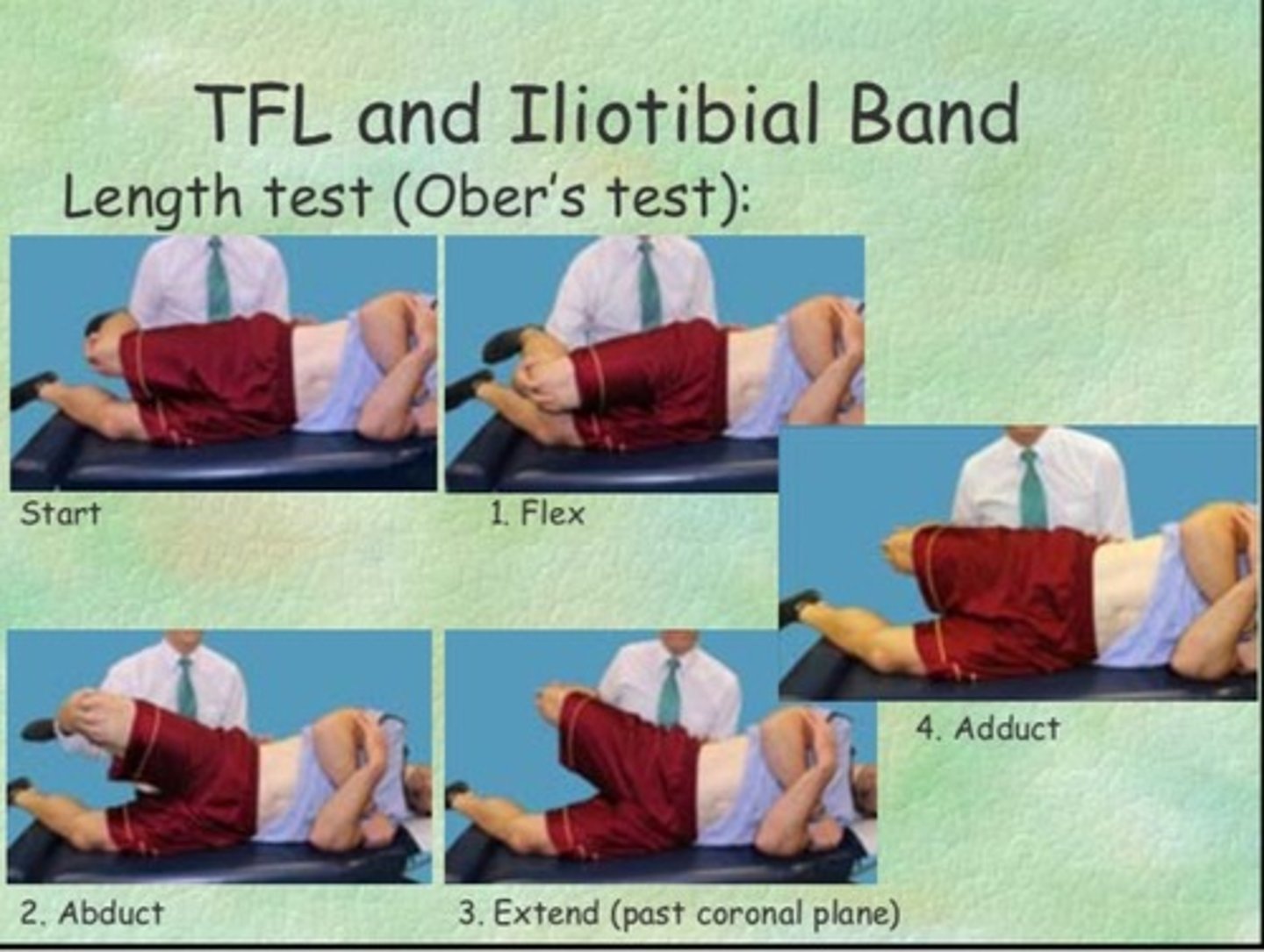
Ober Test - TFL Length
•The Ober test examines the length of the tensor fascia lata and the iliotibial band that act to abduct the hip
•Testing Position: Sidelying with inferior hip and knee flexed
•Stabilization: Iliac crest (limit pelvis rolling forward or back)
•Testing motion: With the knee flexed to 90 degrees, the superior hip is passively ABD and EXT to position ITB posterior to greater trochanter, then lowered into aduction; Modified Ober with knee straight
•End Feel: firm
•Interpretation: If the thigh drops below horizontal (10 degrees of adduction), the test is (-) and the TFL and IT band are of normal length
•If the thigh remains abducted above horizontal= (+) test; the TFL, IT band, glut med/min, and/or hip joint structures might be short
•Measure to document progress - goniometer alignment as with hip Abd
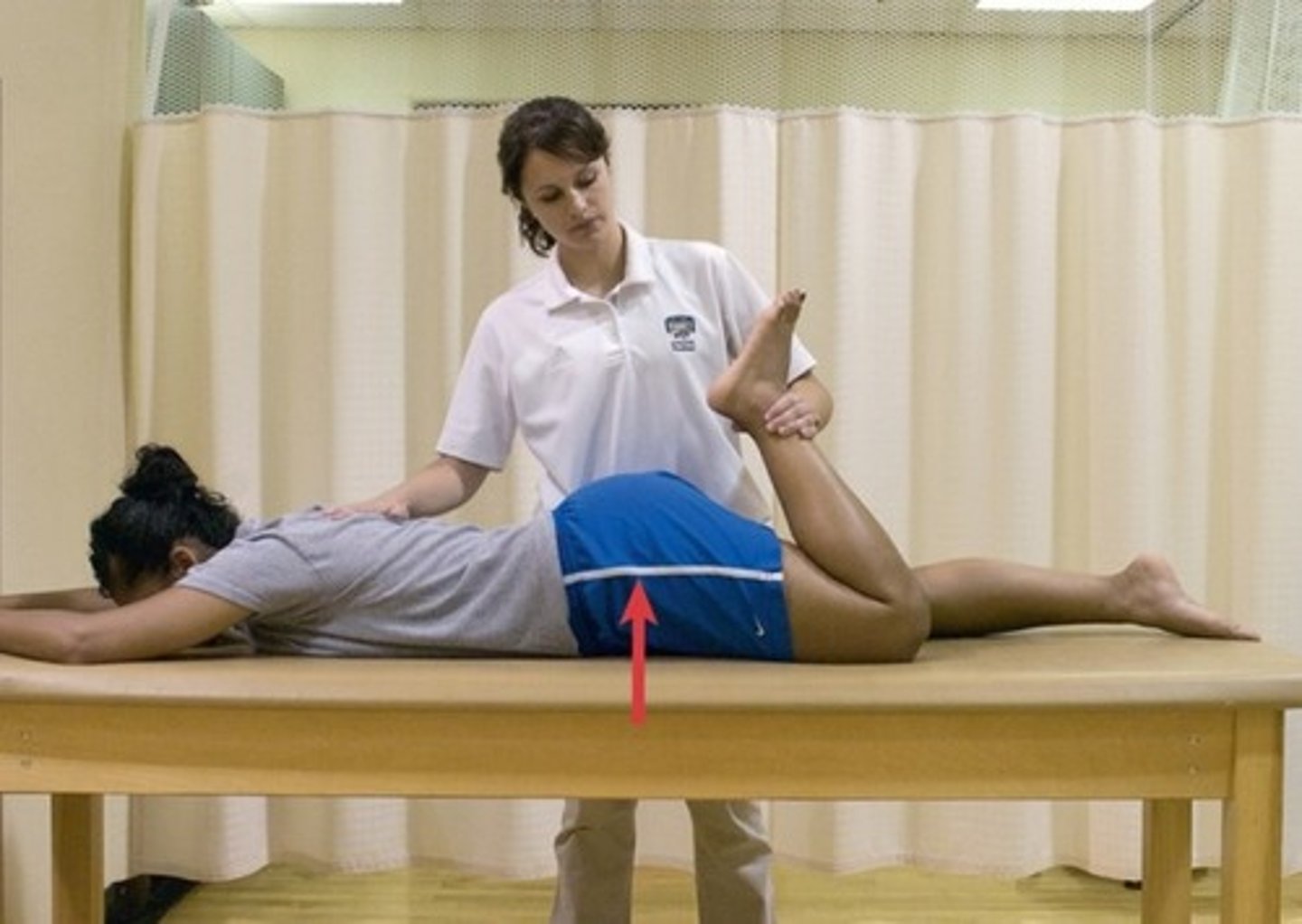
Ely's Test - RF Length
•The Ely test is used to evaluate the length of the rectus femoris muscle by positioning the hip in 0 degrees of flexion and then flexing the knee
•Testing position: prone with both feet off of the exam table
•Stabilization: Hip (do not allow hip to flex)
•Testing motion: Flex the knee by lifting the lower leg off table. Testing is terminated when resistance is felt from tension in the anterior thigh and further knee flexion causes the hip to flex
•End feel: firm
•Interpretation: If the knee can be flexed to 90 degrees with the hip in neutral, the length of the rectus femoris is considered normal, the test is considered (-)
•Measure to document progress - goniometer alignment as with knee flex
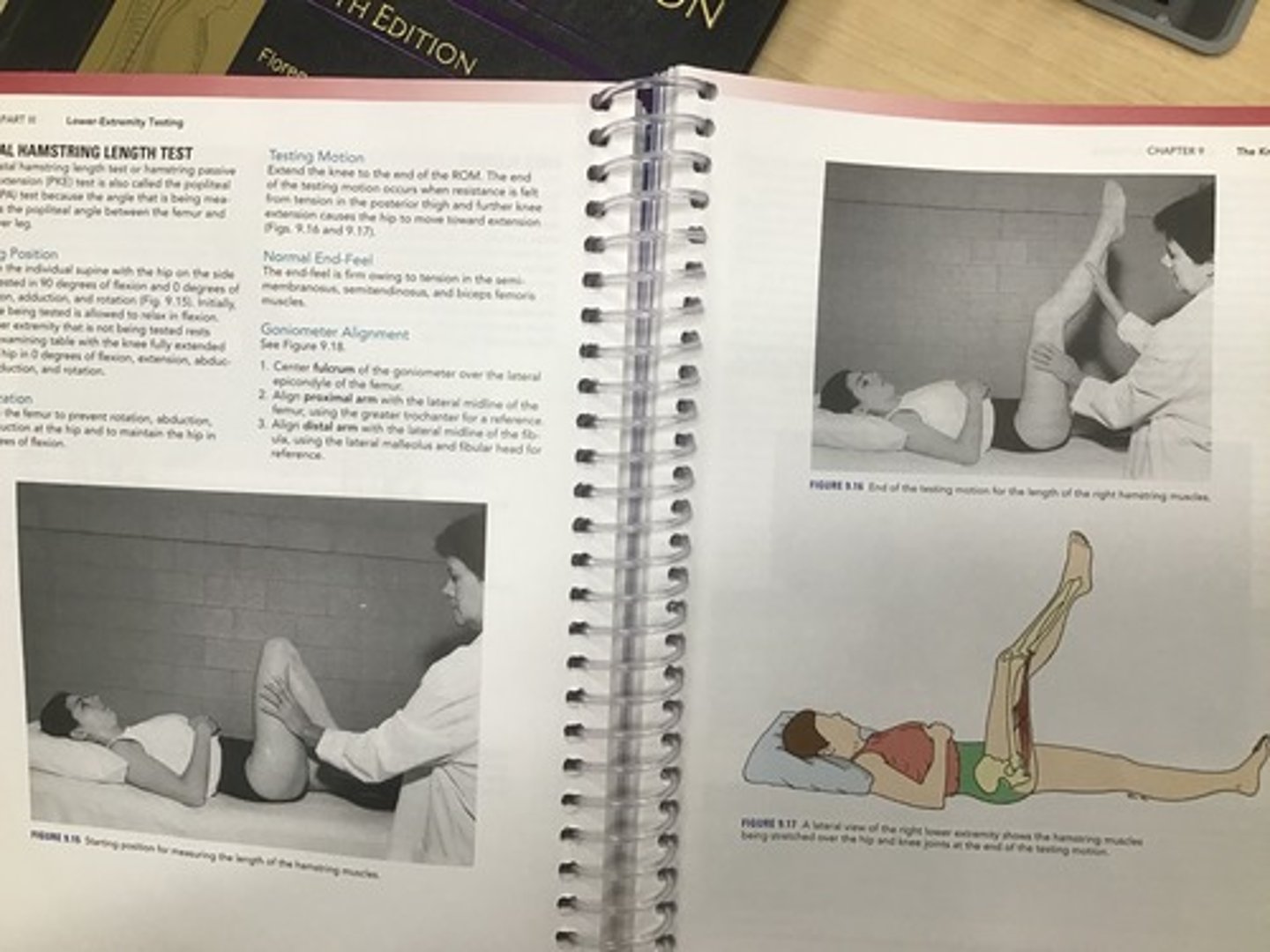
Distal Hamstring Length
•The distal hamstring length test or hamstring passive knee extension (PKE) test is also called the popliteal angle (PA) test
•Testing position: Supine, hip flx to 90 degrees, knee flexed at rest
•Stabilization: femur; prevent rotation, ABD/ADD
•Testing motion: Extend the knee to the end of the ROM. The end of the testing motion occurs when resistance is felt from tension in the posterior thigh and further knee extension causes the hip to move into extension
•End feel: firm
•Interpretation: Mean ROM 31 degrees
•The end of the testing motion occurs when resistance is felt from tension in the posterior thigh and further flexion of the hip causes knee flexion, posterior pelvic tilt, or lumbar flexion
•Measure to document progress - goniometer alignment as with knee extension
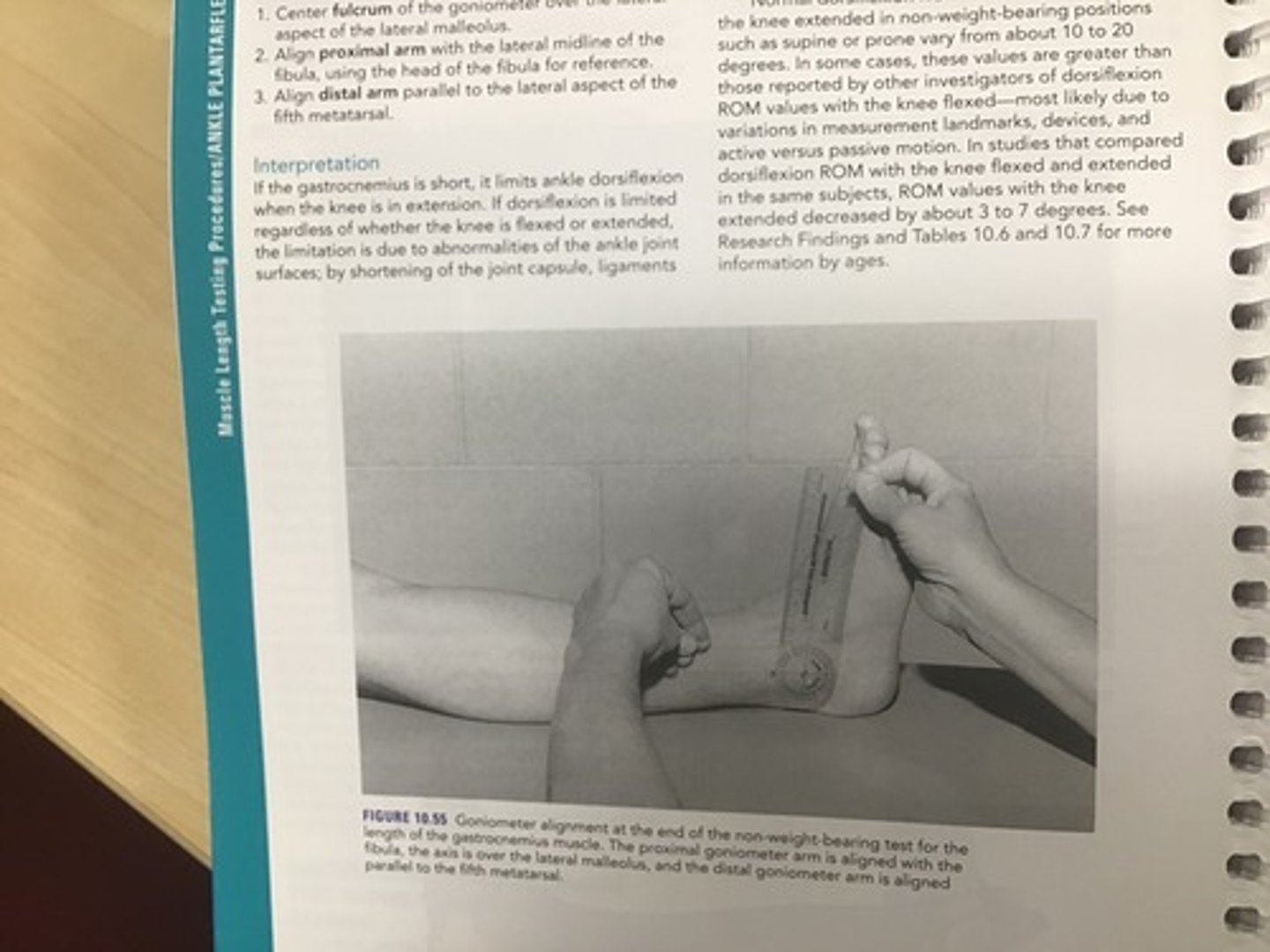
Gastroc Muscle Length: Supine non-weight bearing
•Testing position: supine, knee extended
•Stabilization: Tibia to maintain knee extension
•Testing motion: Ankle is passively Dorsiflexed, with pressure at the metatarsal heads
•End feel: firm
•Measure to document progress - goniometer alignment as with ankle DF
•Interpretation: If the gastroc is short, it only limits DF when the knee is in extension. If DF is limited regardless if the knee if flexed or extended, the limitation is within the ankle joint
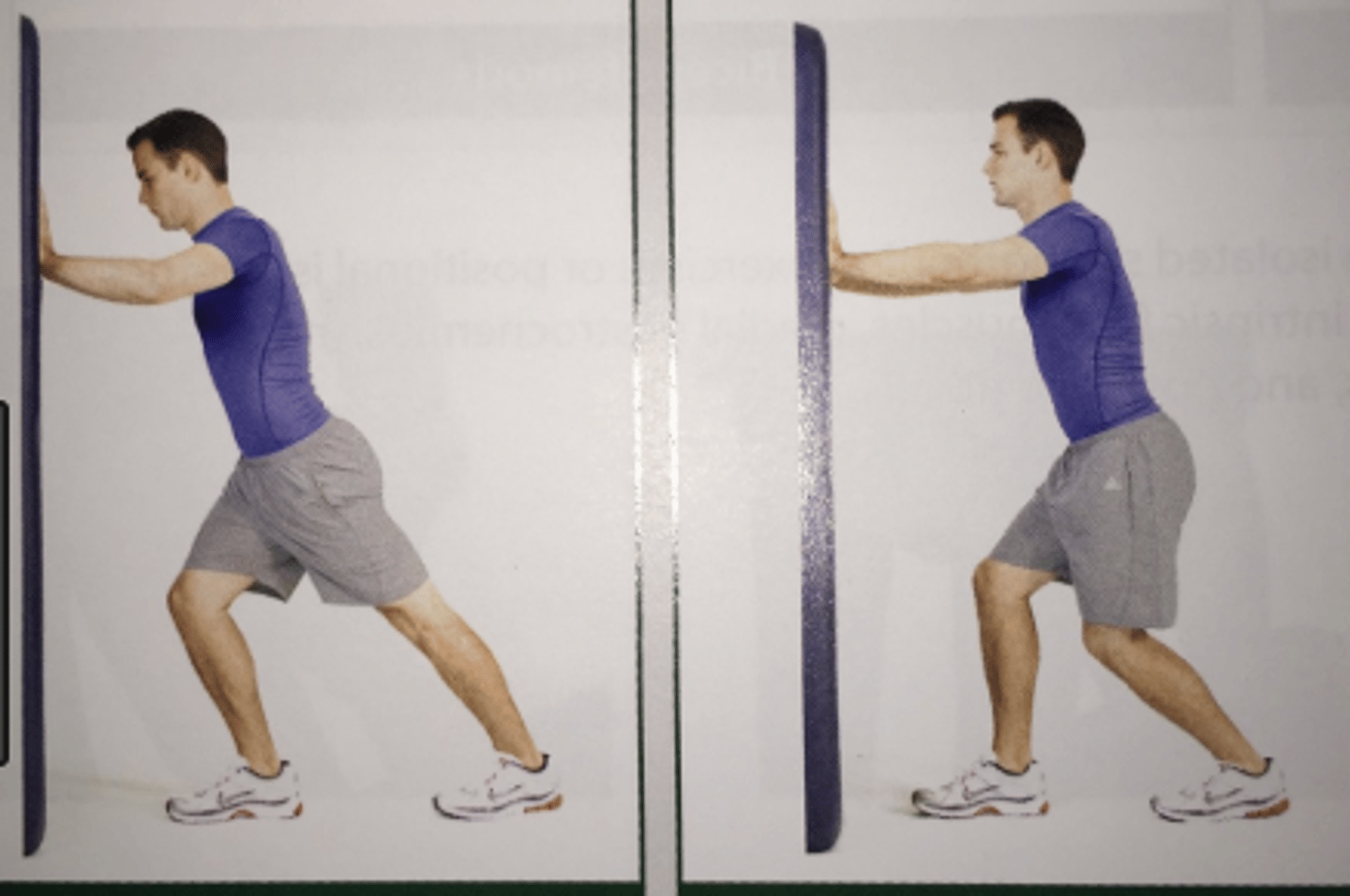
Gastroc Muscle Length: Standing-weight bearing
•Testing position: standing, knee extended, and foot in line with the lower leg and knee
•Stabilization: maintain heel in contact with the floor
•Testing motion: individual dorsiflexes the ankle by leaning forward. The end of testing motion occurs when the individual feels tension in the posterior calf and knee, and further ankle DF causes the knee to flex or the heel to lift off the floor
•Measure to document progress - goniometer alignment as with ankle DF
•Interpretation: If the gastroc is short, it only limits DF when the knee is in extension. If DF is limited regardless if the knee if flexed or extended, the limitation is within the ankle joint
•Normal DF ROM: 22-25 degrees
