Speciation
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
What is speciation?
When two different species mate to produce infertile offspring
When a single species becomes two different species over a long period of time
When two different species develop a similar phenotype over time
B
Complete the following statement.
For speciation to take place, there must first be………….isolation.
Where parts of the orgional ……….. reproduce in ……….. groups a a result of factors such as ………… separation or variation caused by ………… mutations
reproductive
species
separate
geographical
random
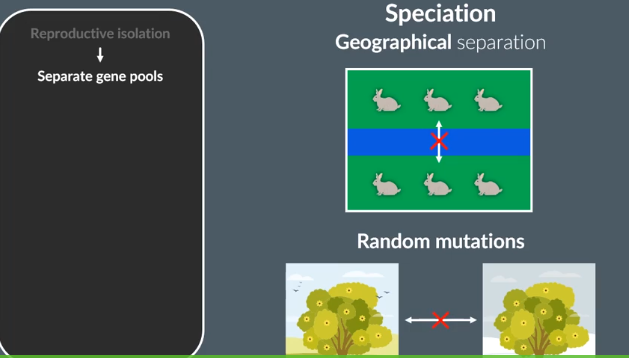
Which two factors can lead to reproductive isolation?
1………….. separation
2. Variation caused by random………… such as differences in flowering season or………….behaviour.
As a results, the 2 seprated populations have separate …. …….
geographical
mutations
courtship
gene pools
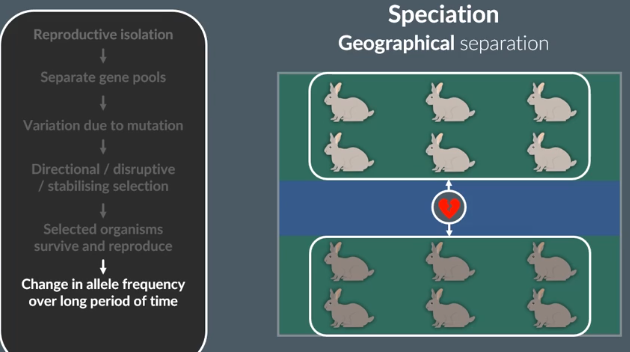
Explain how reproductive isolation can lead to speciation.
First, reproductive isolation causes two populations of a species to have separate ….. ………
Next, within each new population, there is genetic variation caused by………. ……….
As a result of natural selection within each population, different alleles are selected for and passed on.
Over a long period of time, this changes the………. …………in each population.
Eventually, the two new populations become so different that they cannot …………to produce …….. offspring. In other words, they become different………...
gene pools
random mutation
allelle frequencies
interbreed
fertile
species
Complete the following statements.
Speciation that arises as a result of variation in fertilisation or courtship behaviour is called………….speciation.
Speciation that arises as a result of geographical separation is called…………speciation since teh new species are located in ………….. habitats
sympatric
allopatric
different
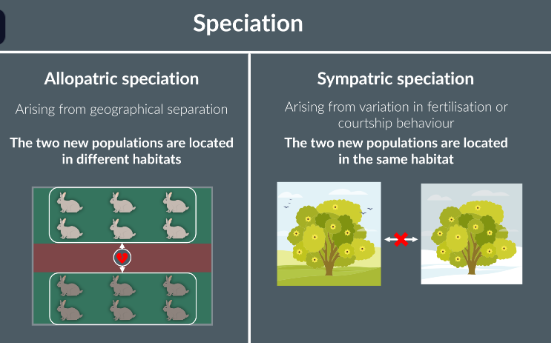
Allopatric speciation leads to two new species located in…
the same habitat.
different habitats.
Sympatric speciation leads to two new species located in…
the same habitat.
different habitats.
B
A