EXAM #3 RAD31
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Engisch
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
What is Source to Skin distance requirment?
federal requirement
SSD stationary unit
not less than 38 cm (15 inches)
SSD mobile unit
not less than 12in (30cm)
Filtration
functions to abdorb low energy photons (soft x-ray)
Total filtration
must be at least 2.5mm Al equivalent
What does filtration do?
reduces patient dose
What are x-rays make it through filtration?
high energy (hard x-rays)
Collimation
beam restricting device
How should the boarders be for collimation?
unexposed boarder must be visible at 35cm above tabletop with collimator fully open
Exposure Switch
Dead man type - terminated exposure when pressure is released
How long should the exposure switch be?
cord must be at least 6 feet long
Bucky Slot Cover during fluoro exam
Tray must be moved to the end of the table
What is the minimum lead for Bucky Slot Cover
should be 0.25 mm of lead
Lead Apparel
Should be worn during all fluoro procedures
Protective Curtain should be positioned where?
Should be positioned between the fluoroscopist and patient
Minimum lead for Protective Curtain
should be at least 0.25 mm of lead
Primary purpose for Protective Curtain
reduces scatter from patient
When should the protective curtain be removed?
during a sterile procedure
Cumulative Timer produces?
Produces an audible signal when fluoro time exceeds 5 min
Leakage Radiation
Emitted from tube housing isotropically
What is the limit for leakage radiation?
not to exceed 100mR/hr at 1 meter
who is the main source of Scatter Radiation ?
patient is main source of occupation exposure during fluoroscopy
How is scatter radiation produced?
primarily by compton interaction
What helps to minimize radiation exposure
under table tubes
What are increasing factors that affect scatter?
high kVp
large field size
thick body part
Primary Barriers
a barrier to attenuate the useful beam
What is most often used with Primary Barriers?
Lead bonded to sheet rock or wood paneling most often used
Primary Barrier: what can be used as alternate to lead
Concrete or steel can be used as alternatives to lead for primary barriers.
height required for primary barrier
must be at least 7 feet tall; rule of thumb - 4in of masonry = 1/16in of lead
Secondary Barrier
A barrier to attenuate leakage and scatter radiation
How much less is Secondary than Primary Barrier?
less thick than primary barriers (1/32in)
What is not required in Secondary barrier?
Lead not required, usually gypsum board, glass or lead acrylic is used
What does Protective Barrier Thickness depend on
Depends on distance (distance adjacent to occupied area, not inside of walls of x-ray room)
Areas in department
Controlled Area
Uncontrolled Area
Controlled Area
Occupied by x-ray personnel and patients
What are controlled areas limits based on?
based on proportionate weekly exposure (radiology personnel and patient
What is the exposure rate for controlled area?
exposed rate must be less than 100mrem (1sV/wk)
Uncontrolled Area
Can be occupied by anyone
What are uncontrolled areas limits based on?
can be occupied by anyone (hallway, hospital staff other than radiology)
What is the exposure rate for uncontrolled area?
Exposure rate must be less than 2mrem/wk
What is Workload?
greater number of exams done each week = the thicker the shielding required
use factor (u) = ?
percentage of the x-ray beam is on and directed toward a particular wall
kVp (penetrability) depends on
kVp used in exam room
NCRP recommends Use Factor
¼ use factor - wall
1 use factor - floor
Personnel monitoring devices
Thermoluminescence dosimetry monitor radiation exposure
What is dosimeter made of?
crystals are made up of lithium fluoride
What is the process of personnel monitoring dosimeter?
Once exposed to ionizing radiation and then heated, these crystals give off light depending on amount of radiation received.
NCRP #1 16 recommends (re:dose)
a max annual effective dose limit of 50 mSv recommended to provide for annual exposure
What does OSL stand for?
Optically Stimulated Luminescence dosimetry
Steps for OSL
Exposed to ionizing radiation
laser illumination
measurement of the intensity of the stimulated light emission
What does OSL use?
Uses aluminum oxide as the radiation detector material
What is a pocket dosimeter aka
Pocket ionization chamber
Describe what a pocket dosimeter
Small pocket sized instrument thst discharged a capacitor by ionization of air with in the presence of ionizing radiation.
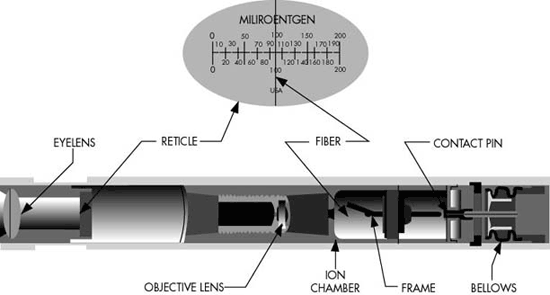
When is pocket dosimeter used?
used primarily when working with large amounts of radiation; gives a daily reading of ionizing radiation exposure.
What is pulsed fluoroscopy?
Uses short pulses of x-ray (5 msec or less) instead of constant output
T/F does Pulsed Fluoroscopy reduce patient dose?
TRUE; Reduces patient dose and occupational exposure
General Fluoro
30 pulse/sec
Pulsed Fluoro
15 pulses/sec
What is the max table top dose for High-level fluoro?
Max tabletop dose rate is 20 mrads/min unless recording devices are used
Cardinal Principles of Radiation Protection
Time, Distance, Shielding - collectively known as ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable).
What is patient dose directly related to?
duration of exposure
Operators exposure to scatter is directly related to
patient exposure
What should be kept to a minimum to reduce pt and personnel exposure?
Time of exposure
What is the reset time
5 min
As distance from the source of exposure increase
the radiation exposure decreases
What does ALARA include?
Both occupational dose as well as pt dose
What three recommendations associated with ALARA
Radiation exposure must have benefit
all exposures must be ALARA
individual dose levels must remain below the max allowed
Whole-body dose includes? **
Refers to the cumulative radiation exposure to head, trunk (including gonads and internal organs), arms above the elbow, and legs above the knee.
4 Way(s) to reducing Radiation Dose in Fluoroscopy
Methods include:
higher kVp values,
more x-ray tube filtration,
reducing fluoroscopy times,
keeping the image intensifier close to the patient.
What are 3 Radiologic Devices?
A Radiation Exposure Device (RED)
A Radiologic Dispersal Device (RDD)
An Improvised Nuclear Device (IND)
Radiation Exposure Device (RED)
A sealed source of radioactive material that directly exposes individuals.
EX: a source of radiation sitting in one spot radiating radioactive material
Radiologic Dispersal Device (RDD)
A bomb that disperses radioactive contamination over a wide area when exploded.
NOT usually life threatening
Improvised Nuclear Device (IND)
Contains nuclear material capable of producing a nuclear explosion.
What is IND considered?
A nuclear weapon
The dose limits established by the NCRP are derived from
biological effects of ionizing radiation and neural stem cell reports
Dose limitse are based on ______ dose-responce relationship to radiation
linear, non-threshold
Patient dose is __________ to the duration of an exposure
directly related
When is it necessary to shield a patient
whenever feasible
What is involved in a whole-body dose?
head, trunk, arms above elbows, legs above the knees
What is ESE stand for?
Entrance Skin Exposure
What is ESE?
The dose of radiation to which the surface of the body is exposed during a radiographic procedure.
AKA for ESE
Patient Dose
How is ESE estimated?
can be estimated by using a nomogram
How is ESE measured?
Can be measured by Thermoluminescence dosimeters (TLD) and optically stimulated luminescence dosimeters (OSLD)
What is BMD stand for?
Bone Marrow Dose
Why is BMD important?
Why is bone marrow dose important?it is believed to be responsible for radiation induced, lympoma and myeloma (stocastic)
What is BMD also expressed as?
MMD - Mean Marrow Dose
What is the dose of BMD linked to?
The stocastic responses are linked to dose to the stem cells fo the bone marrow
T/F can BMD be measured?
FALSE; can only be estimated
What does GSE stand for?
Genetically Significant Dose
What is GSE?
An estimate fo the genetic significance of gonad radiation dose
is GSE difficult to estimate?
no
What does DRT stand for?
Digital Radiographic Tomosynthesis
What may DRT replace?
may replace a number of CT exams
What is DRT approved for?
Mammography
How does DRT work?
takes 6 to 10 x-ray exposures made at various angled to the IR using a total patient radiation dose approx equal to single DR
Fluoroscopic Patient Radiation Dose
ESE in Fluoro is must more difficult to estimate than in radiography because x-ray fields move and varies in size
it is difficult to estimate how much each organ is affected