reactions of alkenes
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
hydrogenation
—> with H2 with metal catalyst (Pd/C or Pt/C) syn addition
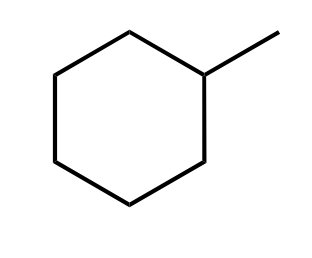
Hydration
Oxymercuration-Reduction
1)Hg(OAc)2/THF/H2O
2)NaBH4
or H3O+/H2O
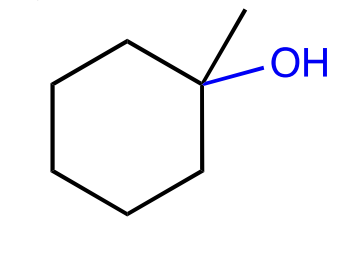
alcohol addition
alkoxymercuration-reduction
1) Hg(OAc)2 in alcohol solvent
2) NaBH4 to make OR on more substituted carbon, no carbocation rearrangement, anti addition
acid catalyzed add. of an alcohol
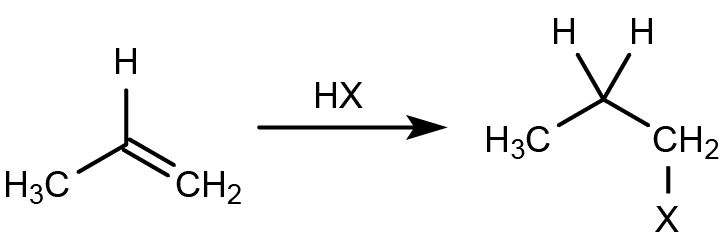
hydrohalogenation
electrophilic addition of HCl/HBr,
markovnikov’s rulehalogen goes on more substituted carbon
alkene protonated + C=C broken
Halide ion attacks Markovnikov carbon
carbocation rearrangement possible if more stable c-c can be formed through alkyl/halide shift
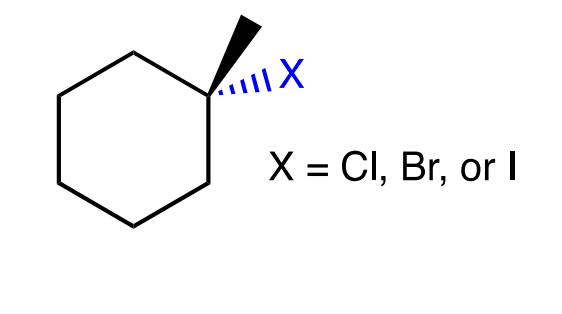
it will follow Markovnikov's rule except in certain cases like HgOAc
if there is a carbocation intermediate
anti markovnikov
if you do a hydrohalogenation in extreme light or heat the product will be
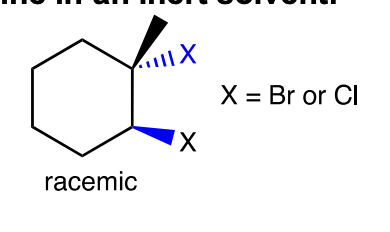
halogenation in inert solvents
anti addition of halogens
( like CHCl2 or CCl4 )
halohydrin reaction
addition of molecular Br/Cl in water
—>X2/H2O
addition of halogen on least sub. carbon,
addition of hydroxy group on more sub. carbon;
anti+Markovnikov
—>same mechanism with alcohol solvent
acid catalyzed hydration
—>H3O+/H2O
adding OH Markovnikov, hydride shift can occur
oxymercuration
1) Hg(OAc)2 in water solvent,
2) NaBH4 to make OH on more substituted carbon.
No carbocation rearrangement, anti addition, markovnikov
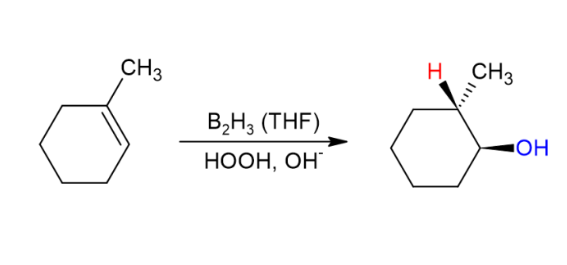
hydroboration oxidation
anti Markovnikov regiochem, syn stereochem addition of an alcohol,
1) BH3, THF (syn addition of BH3)
2) H2O2, NaOH, H2O
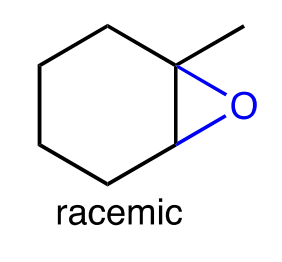
epoxidation
peracids like RCO3H and mCPBA
that adds an O attached to both carbons, stereochemistry is preserved
how would you make a product with two OH groups on different sides?
epoxidation and acid catalyzed hydration
how do you make a product with two OH groups on the same side?
1) OsO4 2) KMnO4 or Na2SO3/H2O
ozonolysis with reduction
cleaves pi bond to make two oxygen double bonds; makes ketone; O3 with solvent that does (CH3)2S
ozonolysis with oxidation
cleaves pi bond to make 2 oxygen double bonds; makes carboxylic acid, O3 with solvent that does contain oxygen (H2O2)
cyclopropanation
1) CH2I2/Zn(Cu) or CH2N2, which would create a carbon propane ring
cyclopropanation with chlorine
make carbon propane ring with halogens attached. if you see 3 halogen -> add 2. syn addition
full reduction of an alkyne
H2/metal catalyst will add H completely 2x
how to make a cis alkene from an alkyne?
H2/Lindlar's catalyst
how to make a trans alkene from an alkyne?
Na/NH3
hydration of an alkyne
1) HgSO4, 2)H2S04, H2O; gives us an enol where alcohol Markovnikov, which tautomerizes into a ketone
hydroboration oxidation of an alkyne
1) R2BH, THF 2) H2O2, NaOH, H2O; alcohol anti-Markovnikov, tautomerizes into an aldehyde
hydrohalogenation of an alkyne
X halogen adds to more sub carbon and same carbon if in excess addition
halogenation of an alkyne
X2, 4 halogens added
ozonolysis with terminal alkyne
add double bonded O groups and OH, becomes a carboxylic acid
ozonolysis with internal alkyne
H end will decompose into CO2
permanganate oxidation neutral with alkyne
1) KMnO4/H2O neutral results in 2 OH groups on each carbon, which tautomerizes into double bond C-Os. 2 C-Os made
permanganate oxidation with hot and basicity with alkyne
1) KMnO4/H2O makes O group and oxygen nucleophile
NaNH2/NH3
makes acetalide ion, which is a very good carbon nucleophile
epoxide formation and basic alcoholysis
1) RCO3H, 2) ROH/NAOR; OH on more substituted while OR on less
epoxide formation and acidic alcoholysis
1) RCO3H, 2) ROH/H+; OR to more sub carbon and OH to less sub carbon
mark rule
regioselectivity of addition to unsymmetrical alkenes
carbocation intermediate
favors more stable carbocation on MORE substituted carbon
ex: acid catalyzed hydration + hydrohalogenation of alkenes= alkyl halides and alcohols
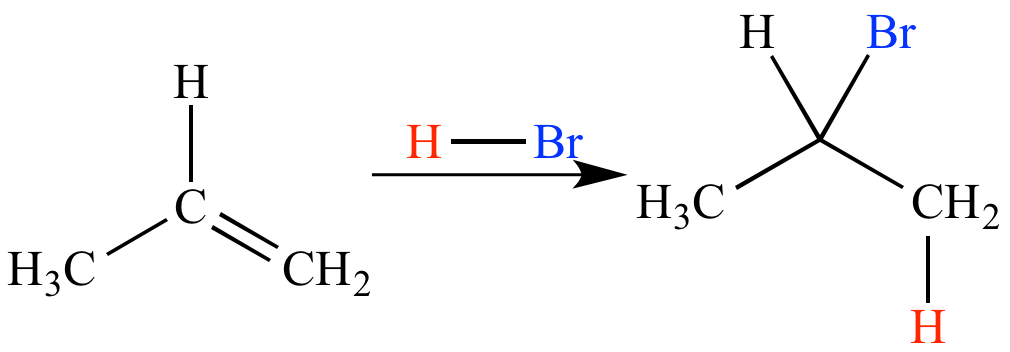
anti mark rule
regioselectivity of addition to unsymmetrical alkenes
hydrogen atom adds to the less substituted carbon of an unsymmetrical alkene
other part of the reagent adds to the more substituted carbon
ex: free radical halogenation + hydrboration oxidation