MEDSURGE FINAL
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
1 Your 72 year-old patient returns from a cardiac catheterization. Upon assessment, vitals are:
BP is 62/40
HR 120, RR 24
CVP 16
CI 1.0
CO 1.8
You auscultate rales in his lungs bilaterally, note JVD, and 2+ edema in the LE. His skin is cool
and clammy, he is SOB, and pulse ox 88%.
What kind of shock state do you suspect?
A. Cardiogenic
B. Obstructive
C. Distributive
D. Hypovolemic
A. Cardiogenic
The patient has been admitted to the critical care unit with a diagnosis of sepsis. He is s/p liver
transplant, taking cyclosporine. His leukocyte (WBC) and neutrophil counts are low, but his
temperature is 103°F orally. The patient states that he has been feeling fine but woke up this
morning feeling feverish and having chills. The nurse realizes that this patient is probably
A. suffering from hemolytic anemia.
B. immunocompromised.
C. in sickle cell anemia crisis.
D showing signs of thrombocytopenia.
B. immunocompromised.
which of the following situations is not a contraindication for a patient to receive a liver
transplant
a. current lung cancer, receiving chemotherapy
b. chronic UTI, resistant to antibiotic treatment, history of splenectomy
c. previous medical history of alcoholism, currently without ETOH for 5 years
d. paranoia behaviors, currently exacerbated by the death of family members
c. previous medical history of alcoholism, currently without ETOH for 5 years
Which of the following is NOT recommended for preventing ventilator associated pneumonia?
a. Head of bed at 30 degrees
b. Stress ulcer prophylaxis
c. Oral care with chlorhexidine
d. Use PPN for nutrition***
d. Use PPN for nutrition***
A 30-year-old patient is brought to an emergency trauma center with a hand injury from a
nail gun sustained while remodeling an old barn. His BP is 90/50, HR 120, RR 16, and he is
alert and oriented x 3; there is a strong odor of alcohol and the patient admits to having three
beers in 3 hours. Which assessment finding is most important for the nurse to evaluate first?
A Current blood alcohol level
B Blood type
C DNR status
D Date of last flu vaccine
B. Blood Type
Your patient is being discharged home with a diagnosis of CVA. You would expect all of the
following to be on his discharge home med list EXCEPT :
A ASA
B Lipitor
C tPA
D Plavix
C. tPA
A client with type 1 diabetes is admitted for treatment of influenza. The client is hypotensive
and very weak. Which serum glucose level would suggest that this client is in diabetic
ketoacidosis?
A. 75
B. 300
C. 55
D. 100
B. 300
Which statement reflects the relationship between serum lactate levels and degree of
hypoperfusion?
A There is no correlation between serum lactate levels and degree of hypoperfusion.
B The lower the lactate level, the more significant the hypoperfusion.
C The higher the lactate level, the more significant the hypoperfusion.
C The higher the lactate level, the more significant the hypoperfusion.
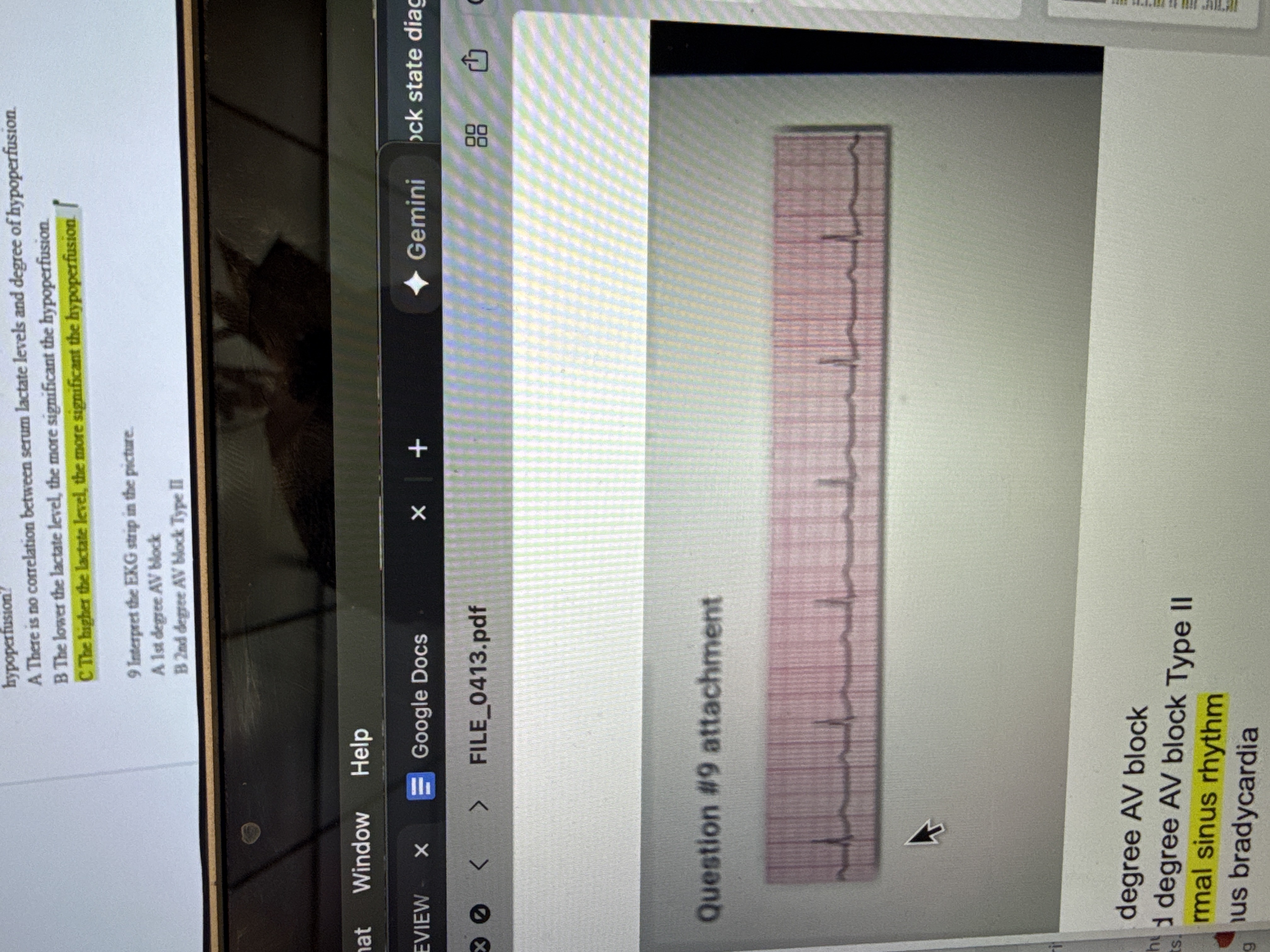
Interpret the EKG strip in the picture.
A 1st degree AV block
B 2nd degree AV block Type II
C Normal sinus rhythm
D Sinus bradycardia
C Normal sinus rhythm
The most common causes of ARDS is
Answers: A - D
A blood transfusion
B trauma
C sepsis
D burns
C sepsis
Which of the following is the highest priority for the nurse caring for a patient with burn
injuries during the resuscitative phase?
A Adequate IV fluid administration
B Refer to support groups
C Increase range of motion to prevent contractures
D Prevent compartment syndrome
A Adequate IV fluid administration
The nurse would be concerned about kidney damage if a client's serum report revealed which value?
Answers: A - D
A Sodium 140 mg/dL
B Hgb 12.4
C Creatinine 4.3 mg/dL
D Potassium 4.5 mEq/L
C Creatinine 4.3 mg/dL
Your patient Mr. F . arrives in the ED via an ambulance. He is pale, diaphoretic and reports
crushing chest pain. His VS are HR 112, RR 24, BP 172/114, SPO2 93% on 2L NC. He has a
history of angina and takes propranolol daily and nitroglycerin sublingual as needed. You
suspect he is having an acute MI.
What would be priority assessments for Mr. F . at this time? (select all that apply)
Answers: A - D
A Heart sounds, rhythm, pulses, capillary refill
B Ask him about his Advanced Directive
C SPO2, lung sounds, RR
D 12 Lead EKG
A Heart sounds, rhythm, pulses, capillary refill
C SPO2, lung sounds, RR
D 12 Lead EKG
What abnormal lab values are you monitoring for if you suspect your patient has DIC?
Answers: A - D
A Decreased platelets, decreased INR, increased fibrinogen
B Increased fibrinogen, increased INR, increased RBC
C Increased WBC, decreased RBC, increased neutrophils
D Increased PTT , decreased platelets, decreased fibrinogen
D Increased PTT , decreased platelets, decreased fibrinogen
A client with type 2 diabetes is admitted to the ED after becoming unconscious at home. The
client's plasma glucose is 910 mg/dL, arterial pH 7.30, and serum osmolality is 310 mOsm/kg.
Which information suggests that this client has hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS) rather
than diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Answers: A - D
A Glucose
В pH
C Obesity
D Periperal vascular disease
A Glucose
Mr. E is post-op day 1 of a 4 vessel CABG surgery. The nurse obtains Mr. E's Central
Venous Pressure (CVP) and it is 4. What does this measurement indicate?
Answers: A - D
A Left heart preload status
B Right heart preload status
C Vein patency
D Increased pulmonary vascular resistance
B Right heart preload status
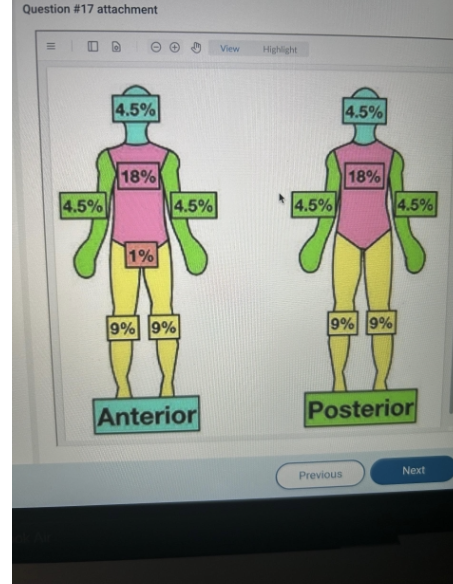
A nurse uses the rule of nines to assess a patient with full thickness burn injuries to the
entire right arm, front of the head, and entire right leg. How should the nurse document the percentage of the patient's body that sustained burns?
31.5

You work in the ED and have a patient that came in c/o chest pain. She states that her chest
began hurting after dinner last night and she just wants to make sure it's not a heart attack. On
the monitor, this rhythm appears. How do you interpret this?
A This is pulseless electrical activity, begin CPR.
B You can't read EKGs, you're just a nurse. Go ask the doctor!
C This is ventricular tachycardia with a pulse, prepare to cardiovert.
D This is pulseless ventricular tachycardia, prepare to defibrillate.
C This is ventricular tachycardia with a pulse, prepare to cardiovert.
You admit a 37 yo male to the ICU following a biking accident, and suspect that he is experiencing hypovolemic shock. Which of the following clinical indicators would support this?
A. HR = 60
B. BP = 110/78
C. Bounding pulses
D. Confusion
D. Confusion
What are major concerns associated with the administration of cyclosporine?
It may be administered orally.
The patient cannot drive while taking this medicine.
It is the cause of most graft vs. host disease.
It is highly incompatible with other medications.
It is highly incompatible with other medications.
Prozac is a
antidepressant
Norepinephrine is a
vasoconstrictant
Lovenonx
antithromboic
Methyleprednisolone
antiinflammatory
Albuterol
Bronchodilator
Pantoprazole
Stress Ulcer Prevention
Chlorhexidine
Pneumonia Prevention
Fentanyl
Pain control/comfort
Which is the best intervention for a patient experiencing intrapulmonary shunting?
A. Improve ventilation, open alveoli
B. Give 02
C. Increase cardiac output
D. Give blood products
A. Improve ventilation, open alveoli
The etiology of pulmonary edema in acute respiratory distress syndrom (ARDS) is related to:
A. Decreased cardiac output
B. volutrauma and hypoxemia
C. tension pneumothorax
D. Damage to the alveolar-capillary membrane
D. Damage to the alveolar-capillary membrane
Which statement best describe nutritional support for the trauma client?
A. It should be instituted as soon as the client is removed from mechanical ventilation
B. It should be instituted as early as possible
C. Best practice is that the client remain NPO for 7 days before initiating nutrition support
D. TPN is always indicated for trauma patients
B. It should be instituted as early as possible
A nurse is developing educational materials on burn prevention. The nurse would discuss
which reasons that older adults are prone to burn injury? (Select all that apply)
A. As people age, their reaction times slow.
B. Older adults often have impaired senses.
C. Aging increases people's tendency toward risk taking behaviors.
D. Older adults spend the majority of their time alone.
A. As people age, their reaction times slow.
B. Older adults often have impaired senses.
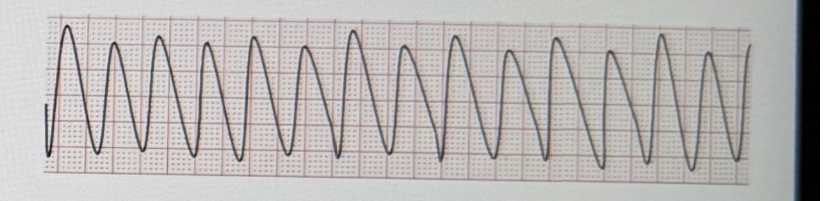
Mr. T . arrives at the ED via an ambulance. He is pale, diaphoretic and reports crushing chest pain. His VS are HR 112, RR 24, BP 172/114, SPO2 93% on 2L NC. He has a history of angina and takes propranolol daily and nitroglycerin sublingual as needed. You suspect he is having an acute MI.
You notice that his rhythm, which was initially sinus tachycardia, is now this:
What is your initial action in this situation?
A. Check for a pulse
B. Defibrillate
C. Give 2 breaths
D. Call a code
A. Check for a pulse
Which of the following is NOT in the 1-hour bundle for sepsis protocol?
A. Administer antihypertensives
B. Obtain blood cultures
C. Measure serum lactate levels
D. Fluid resuscitation
A. Administer antihypertensives
Which nursing intervention is appropriate for managing hepatic encephalopathy in a patient with liver failure?
A. Administering lactulose as prescribed
B. Initiating hemodialysis to remove ammonia
C. Restricting protein in the diet
D. Providing high-carbohydrate nutritional supplements
A. Administering lactulose as prescribed
MELD scoring is used to prioritize patients for transplants, based on mortality, risks, and urgency.
A. Kidney
B. Lung
C. Liver
D. Heart
C. Liver
Example ABG :
pH 7.28
PaCO₂ 60 mmHg
HCO₃⁻ 24 mEq/L
Respiratory Acidosis
A mean arterial pressure (MAP) below 65 mmHg may result in which condition?
A. Inadequate renal perfusion pressure
B. Increased GFR
C. Release of substances that produce local vasodilation
D. Renal artery obstruction
A. Inadequate renal perfusion pressure
Potential pathological mechanisms of hyperglycemia in the non-diabetic hospitalized patient include:
A. An increase in stress hormones
B. A decrease in glycogen production
C. A decrease in ketones
D. An absolute insulin deficiency
A. An increase in stress hormones
This type of spinal cord injury is characterized by loss of position, touch, and vibration sensations.
A. Brown Sequard syndrome
B. Anterior cord syndrome
C. Posterior cord syndrome
D. Central cord syndrome
C. Posterior cord syndrome
Conditions that produce acute kidney injury by directly acting on functioning kidney tissue are classified as intrarenal. What is the most common intrarenal condition that produces such a kidney injury?
A. Prolonged hypotension
B. Urethral strictures
C. Bladder stones
D. Acute tubular necrosis
D. Acute tubular necrosis
The Monroe-Kellie Hypothesis asserts that the skull is a rigid box filled to capacity with three elements. They are:
A. Brain tissue, cerebrospinal fluid, blood
B. Brain tissue, cerebellum, brain stem
C. Brain tissue, cerebrospinal fluid, ventricles
D. Brain tissue, blood, amygdala
A. Brain tissue, cerebrospinal fluid, blood
A patient brought into the emergency department after a motor vehicle crash involving a chest injury has decreased lung sounds on the left with a tracheal shift.
Which intervention would the nurse prepare the patient for?
A. Chest tube placement
B. CPR
C. Pericardiocentesis
D. Fibrinolytics
A. Chest tube placement
Poikilothermia in the spinal cord injury patient refers to which of the following?
A Inability to respond to changes in position when bladder is distended
B sensory/motor dysfunction on one side of the body
C Inability to regulate body temperature due to loss of sympathetic outflow
D Inability of the body to respond to electrolyte disturbances
C Inability to regulate body temperature due to loss of sympathetic outflow
Your patient in the ICU has a long recovery expected. Which enteral feeding tube would be most appropriate?
A ET tube
B OG tube
C PEG tube
D NG tube
C PEG tube
Which of the following are criteria for discontinuing ventilator weaning attempt?
A SpO2 = 85%
B RR = 18|
C Patient is calm
D The patient's family comes in to visit
A SpO2 = 85%
Autonomic Dysreflexia
Life threatening
Occur after SCI
Extreme Hypertension, headache, blurred vision
Loosen restrictive clothing
Cause: distended bladder, fecal impaction
Tx: antihypertensive
Your patient is undergoing consideration for organ donation by the Gift-of-Life. Donor-recipient compatibility testing consists of which of the following? (Select all that apply)
A Type of family the patient was raised in
B ABO blood typing
C Histocompatibility through tissue typing
D Enneagram number
B ABO blood typing
C Histocompatibility through tissue typing
Which of the following are important for the nurse to consider when caring for the patient with a ventriculostomy?
A Keep at the level of the phlebostatic axis
B ICP should increase with time
C Keep drain open at all times
D Monitor for neuro changes
D Monitor for neuro changes
A patient is admitted with superficial partial burns on the face, neck anterior chest, and hands.
The nurse's priority action would be:
A Assess for dyspnea and stridor
B Cover the burned area with a sterile dressing
C Initiate IV fluid administration
D Administer pain medication as ordered
A Assess for dyspnea and stridor
You are administering rPA to your neuro ICU patient. You would immediately discontinue the
infusion if your patient manifested which of the following assessment findings?
A Glucose Level 165
B Abdominal discomfort
C Depressed mood
D Blood pressure 180/100
D Blood pressure 180/100
What is a common cause of acute adrenal crisis?
A Acute kidney injury
B High doses of corticosteroids
C Sudden deficiency of corticosteroids
D Addison's disease
C Sudden deficiency of corticosteroids
The proper placement of a nasogastric tube in an unconscious patient can be accurately assessed by...
A obtaining an x-ray to verify placement
B palpating the abdomen to feel the tube
C watching for gastric air bubbles in the tube
D instilling 30cc of normal saline through the tube
A obtaining an x-ray to verify placement
A potential transplant recipient can become sensitized to foreign HLA antigens in which of the following ways?
A Blood donation
B Prior organ transplantation
C Prior psychological problems
D History of medication use
B Prior organ transplantation
Return of spontaneous circulation, following CPR, can be detected early by measuring -
A End tidal CO2
B T emperature
C Respirations
D Capillary refill
A End tidal CO2
3a | eGFR: 45–59 | Moderate CKD | Fatigue, mild anemia, early bone/mineral changes |
3b | 30–44 | Moderate CKD | Same as 3a, higher risk of complication |
Nursing Tips:
Monitor labs: creatinine, eGFR, electrolytes, hemoglobin
Control BP and prevent progression
Educate on diet, hydration, and avoiding nephrotoxic drugs
STAGE 3
Signs and symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis include:
A Hyperactivity, diaphoresis
B Fruity breath, deep/rapid breathing
C Shallow breathing, flushed skin
D Dilated pupils, HA
B Fruity breath, deep/rapid breathing
Treatment of the patient with SIADH may include which of the following interventions? (Select all that apply)
A Daily electrolyte monitoring
B Fluid restriction
C Bedrest
D Regular fluid boluses
A Daily electrolyte monitoring
B Fluid restriction
The patient is admitted with a platelet count of 15,000/microliter. The nurse is aware that the patient...
A is at risk for spontaneous bleeding.
B has a normal platelet count.
C is facing certain death.
D has hyperactive bone marrow.
A is at risk for spontaneous bleeding.
Your adult male patient was admitted post fall from scaffolding and sustained a T4 vertebral burst fracture with cord impingement and edema. He also had multiple lower limb fractures. The patient is developing neurogenic shock. Which of the following vital signs would you NOT expect to see related to this spinal cord injury?
A BP 80/40
B Resp 20
C T emp 36.6
D HR 120
D HR 120
The nurse should monitor the EKG for which of the following changes if the patient is hypokalemic?
A Peaked T waves
B Flattened T waves
C Asystole
D Extreme bradycardia
B Flattened T waves
The nurse is aware that the patient receiving chemotherapy is at risk for Tumor Lysis Syndrome and will monitor the patient closely for which abnormalities associated with this oncologic emergency?
Answers: A - C
A Low Uric Acid ,Low Calcium, high Sodium
B Low Potassium, Low Sodium, High Calcium
C High Potassium, High Uric Acid, High Phosphorus
C High Potassium, High Uric Acid, High Phosphorus
A client with Type I diabetes is admitted after developing an infection. Her temperature is 37.8 C. She responds to verbal stimuli but then immediately closes her eyes and begins groaning.
What laboratory result would support a diagnosis of diabetic ketoacidosis in the client?
A PaCO2 28 mmHg
B pH 7.36
C Hgb 15
D Anion gap 18 mEq/L
D Anion gap 18 mEq/L
All of the following are interventions that help control active hemorrhage, EXCEPT :
A Order a CT scan
B Administer blood products
C Apply direct pressure on wound •
D Give tranexamic acid
A Order a CT scan
Your patient in the ED has presented with hematemesis. Which intervention could you anticipate for this patient?
A Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) for banding of varices
B Initiate TPN
C Cardioversion with sedation
D Chest tube insertion
A Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) for banding of varices
You are caring for a 70 yo female patient admitted to the CICU with chest pain. You measure her CVP at 15. Which of the following clinical manifestations would you expect to assess in this patient?
A JVD
B Pink, frothy sputum
C Absent bowel sounds
D Cyanosis
A JVD
Your 50 yo client in septic shock has been prescribed a vasopressor medication. Which assessment finding would the nurse evaluate as indicating the need to question this order?
A Mentation has not improved
B Urine output: 10 cc in the last hour
C HR = 50
D Breath sounds: crackles
C HR = 50
Your patient has a BP of 140/71. The MAP is…
A 78
B 130
C 3425
D 94
D 94
CPP is the difference between the_
and the_
A PaOP , ICP
B MAP , СО
C MAP , ICP
D SVR, MAP
C MAP , ICP
Which type of shock occurs when a patient who cut their head in a car accident loses a great deal of blood and becomes confused and combative?
A Obstructive
B Cardiogenic
C Hypovolemic
D Distributive
C Hypovolemic
After receiving the hand-off report from the day shift charge nurse, which patient should the evening charge nurse assess first?
A A mechanically ventilated patient with a GCS of 6
B A patient with an intracranial pressure ICP of 20 mm Hg and an oral temperature of
104° F
C A patient with DKA who has visitors today
D A patient with bacterial meningitis on droplet precautions
B A patient with an intracranial pressure ICP of 20 mm Hg and an oral temperature of
104° F
One way to prevent dumping syndrome in a patient with an OG tube is to...
A. Maintain hyperglycemia
B. Ensure a slow rate of infusion
C. Keep visitors to a minimum
D. Place the patient in a prone position
B. Ensure a slow rate of infusion
In the patient experiencing hemorrhage, medications that are used to decrease bleeding.
A. Vasoconstrict
B. Vasovagal
C. Vasodilate
D. Valsalva
A. Vasoconstrict
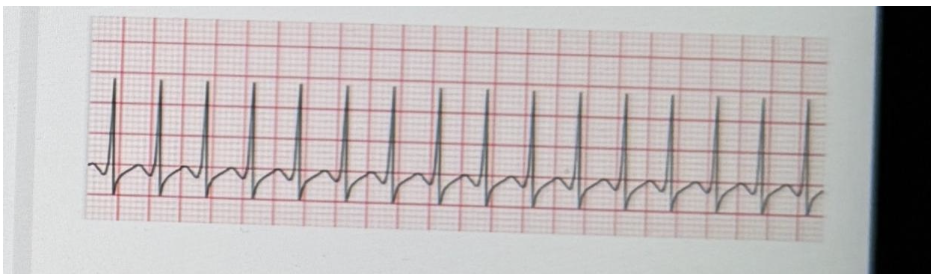
Your patient has presented to the ED c/o chest tightness, anxiety, and heart pounding. She is diaphoretic and distressed. The EKG shows this rhythm. You identify the rhythm to be…
A.Ventricular fibrillation
B. Supraventricular T achycardia
C. Ventricular tachycardia
D. Atrial flutter
B. Supraventricular T achycardia
A client sustained an injury to the right side of the neck 5 years ago that resulted in
Brown-Sequard syndrome. The nurse who is admitting this patient to the hospital for an elective procedure would expect which assessment findings? (Select all that apply)
A. Loss of temperature sensation on the left
B.Loss of sensation on the right
C. Loss of voluntary motor movement on the right
D. Inability to feel pain on both sides
A. Loss of temperature sensation on the left
C. Loss of voluntary motor movement on the right
PEEP is helpful for patients in ARDS because it...
A. Improves lung's functional residual capacity and prevents alveolar collapse.
B. Is controlled by the respiratory therapist.
C. Decreases ETCO2.
D. Improves discharge rates.
A. Improves lung's functional residual capacity and prevents alveolar collapse.
A patient is being ventilated and has been started on enteral feedings with a nasogastric
small-bore feeding tube. What is the primary reason the nurse must frequently assess tube
placement?
A. T o maintain the patency of the feeding tube
B. To prevent aspiration of the feedings
C. T o assess for paralytic ileus
D. T o monitor for skin breakdown on the nose
B. To prevent aspiration of the feedings
A transplant candidate undergoes basic psychological testing for which reason?
A. There is a risk of post-transplant psychosis.
B. Depression is a major contraindication for transplantation.
C. A higher mortality is associated with pre-transplant bipolar disorder.
D. Certain psychological profiles increase risk of post-transplant non-adherence to the
drug regimen.
D. Certain psychological profiles increase risk of post-transplant non-adherence to the
drug regimen.
The patient has low blood pressure, JVD, and muffled heart sounds. These findings are associated with acute cardiac
A. tamponade
B. instability
C. myopathy
D. arrhythmia
A. tamponade
An INR >1.5 indicates disfunction with which organ?
A. Spleen
B. Brain
C. Duodenum
D. Liver
D. Liver
Shockable Rhythms for defib
V fib
Pulseless Vtach
Rhythms for cardioversion
Unstable
Afib
A flutter
SVT
Vtach w/pulse
Pacing Rhythms
Symptomatic Bradycardia
Second Degree TYPE 2
Third Degree
What will ETCO2 show in ROSC
greater than or equal to 40mmhg
tx for inhalation injury
100% humidifed o2
How long is the resuscitative phase of burns and the goal
0-48hrs
Goal: prevent burn shock
Warm patient = prevents vasoconstriction
Fill patient = massive LR resuscitation
Watch pee = best indicator of perfusion
Spinal vs Neurogenic Shock
Spinal:
Acute SCI injury
Below level of injury
Decrease reflexes, loss of sensation, transient (not permaent)
Physical
Neurogenic:
Hemodynamic shock
Loss of vasomotor tone
Hypotension, Bradycardia, Pikothermia
Fluids, atropine, vassopressors
Types of shock
Hypovolemic
Distributive
Obstructive
Hypovolemic - Lack of fluids
Distributive - Loss of muscle tone (Tubes are vasoconstriction preventing blood flow)
Obstructive - Mechanical blockage (blood clot)
Cardiogenic - Pump malfunction (failure of cardiac contractility)
Normal lactate
Sepsis lvl lactate
Normal: 0.5-1
Sepsis: 4 and up
What is Phlebostatic axis?
Level at the rigth atrium
used to properly level a arterial line or CVP
DKA VS HHS
DKA:
Hyperglycemia
Ketone production
Metabolic acidosis
Abrupt onset, dry mucucous membranes
fruity breath, kussmaul respirations
HHS:
No jetones
Hyperosmolarity - thick sticky blood
HIGHER BG >600