HK 302 Exam 2 pathology
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
clavicle fractures mechanism
- direct blow
- FOOSH (fall on outstretched arm)
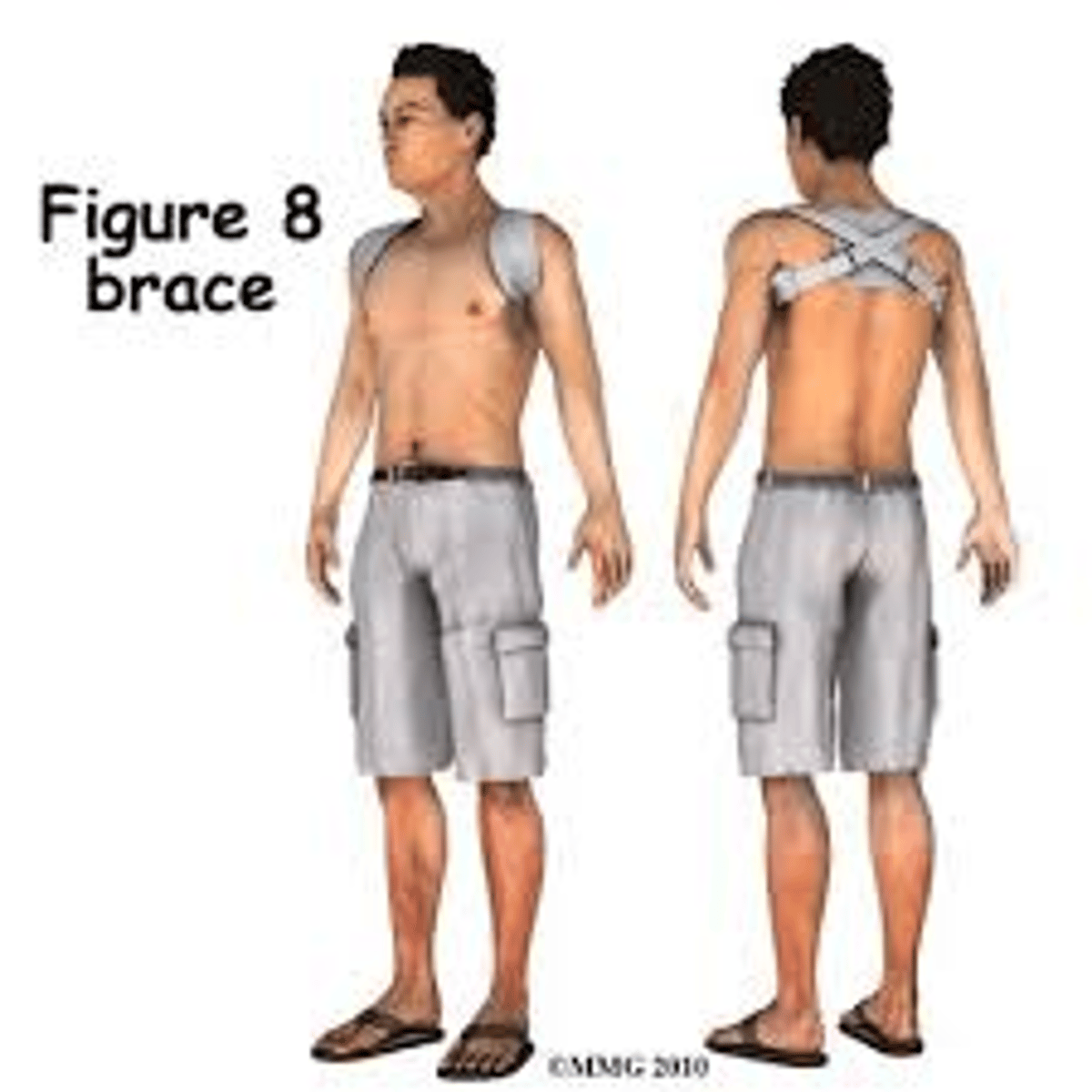
clavicle fracture damage and management
- 80% of clavicle fractures occur in middle
- figure 8 brace vs surgery
humerus fracture mechanism
fall or direct blow
humerus fracture structures damages
surgical neck is the most common site for proximal humerus fracture
humerus fracture management
- immobilize in sling and swathe
- immediate referral to ER/doctor
swathe
a sling that keep the arm in place around the body
glenohumeral joint dislocation (shoulder)
- 90% of shoulder dislocations are anterior and/or inferior
- humeral head is often sitting in axilla anteriorly
with any dislocation
there could be associated fractures or nerve damage
shoulder dislocation looks like
- concave deltoid
- leaning forward because head of humerus in armpit
reduction of shoulder
team doctor
- longer out - harder to put back in
- 1 attempt to reduce
acromioclavicular joint sprain called
"separated shoulder"
AC joint sprain mechanism
- direct blow to the shoulder
- fall on the point of the shoulder
structures damaged in AC joint sprain
- coracoclavicular ligaments (conoid, trapezoid)
- acromioclavicular igaments
- deltoid and trapezius muscles
with most injuries including shoulder sprain
bone AND muscle injured. muscles need rehab
impingement can occur at the acromion
when arms go up the head needs to slide inferiorly
- irritated bursa
- bone spurs
what muscle will be sore from carrying a backpack
levator scapulae
winging of scapula
- caused by weakness in serratus anterior or entrapment of long thoracic nerve
- disrupts the scapular force couple
test winged scapula
5-10 push-ups will make it pop up
rotator cuff tear/ strain mechanisms
- chronic micro trauma over time (overuse)
- acute trauma
- FOOSH
- arm yanked or pulled while muscle contracted
why is rotator cuff a critical zone for injury
the supraspinatus tendon does not get good blood flow
structures damaged in rotator cuff tear or strain chronic
supraspinatus is primarily involved with chronic degenerative tears
structures damaged in rotator cuff tear or strain acute
surpraspinatus/infraspinatus involved in acute episodes
when supraspinatus is hurt
deltoid can't abduct because supraspinatus initiates abduction
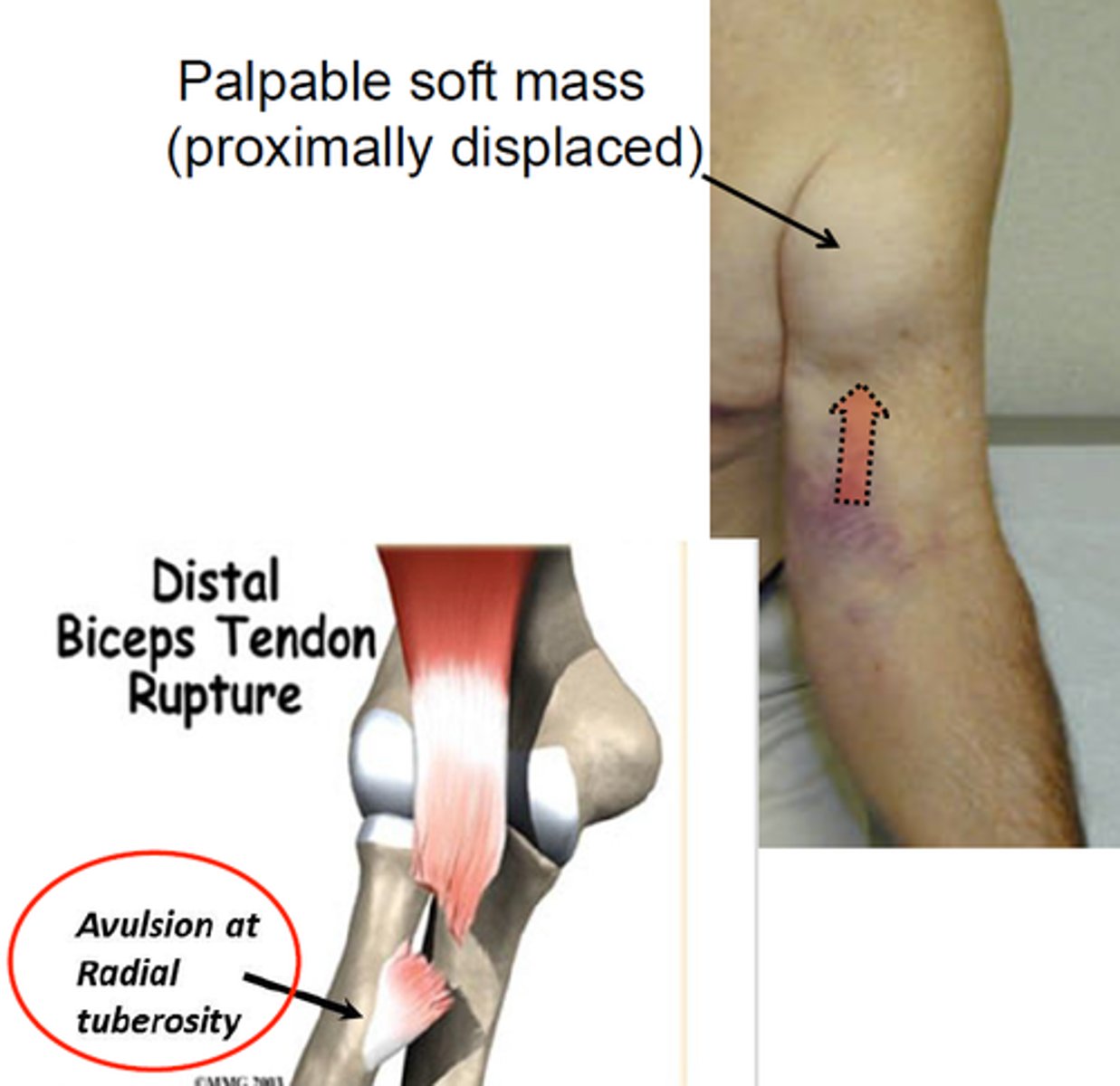
biceps tendon rupture mechanism
- prolonged tendinitis
- degenerative - tendon weak
- traumatic - distal rupture
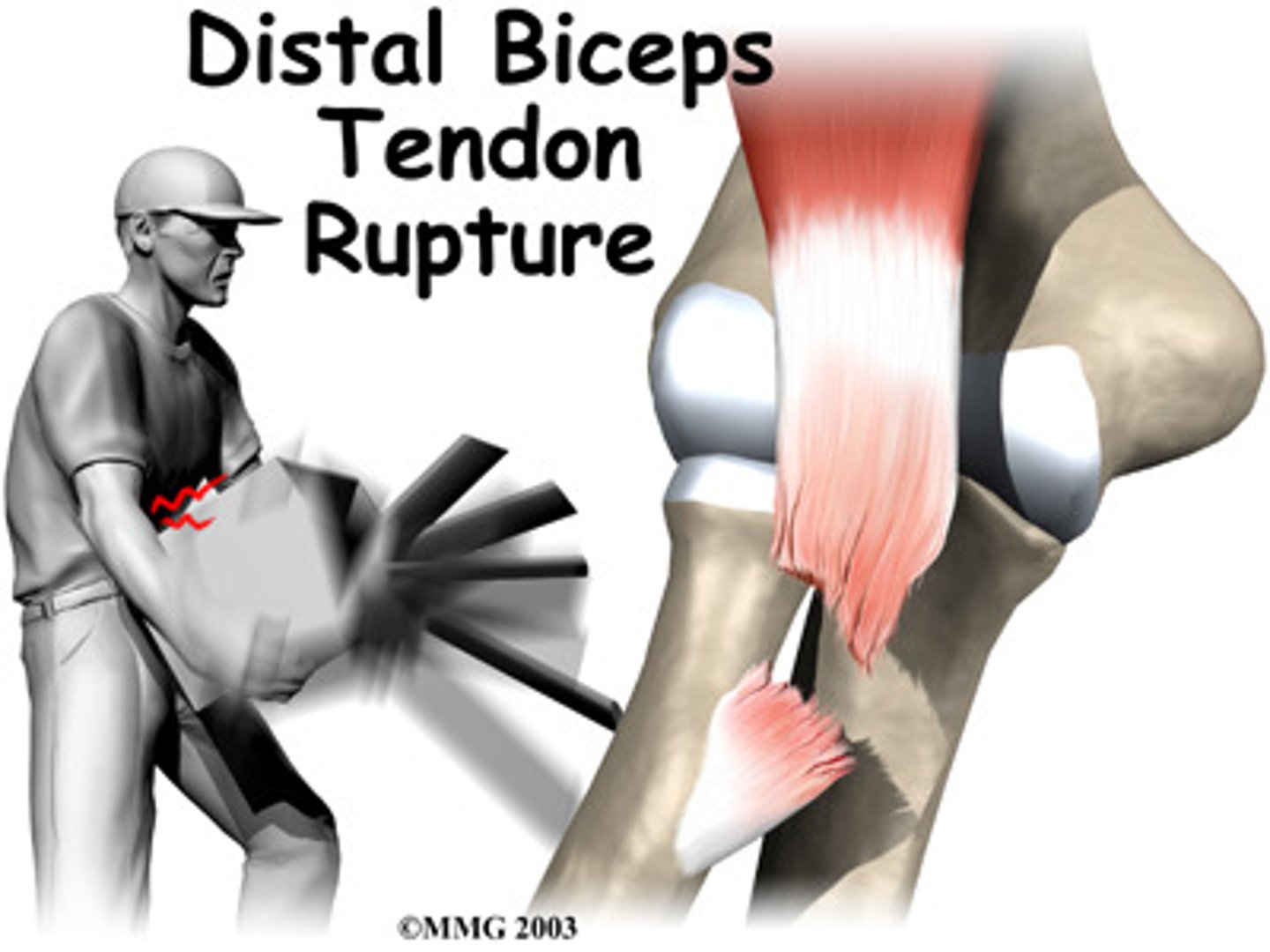
biceps tendon rupture
biceps tendon - proximal or distal
"Popeye" contract in a ball
Tommy John surgery problem
the ligament that connects two arm bones at your elbow gets torn, usually from overuse
Tommy John surgery fix
a surgeon removes the torn ligament, drills tunnels in the two bones, threads the tendon from forearm or leg through tunnels and secures ends together
Tommy John athlete
first successful player to return to play the same success after surgery
"nurse maid's elbow"
annular ligament loose in children and can be pulled out of place from swinging a child by arms
olecranon bursitis
acute or chronic injury - can be septic (infected)
- olecranon area fills with thick fluid
- baseball slide
- check for fracture underneath
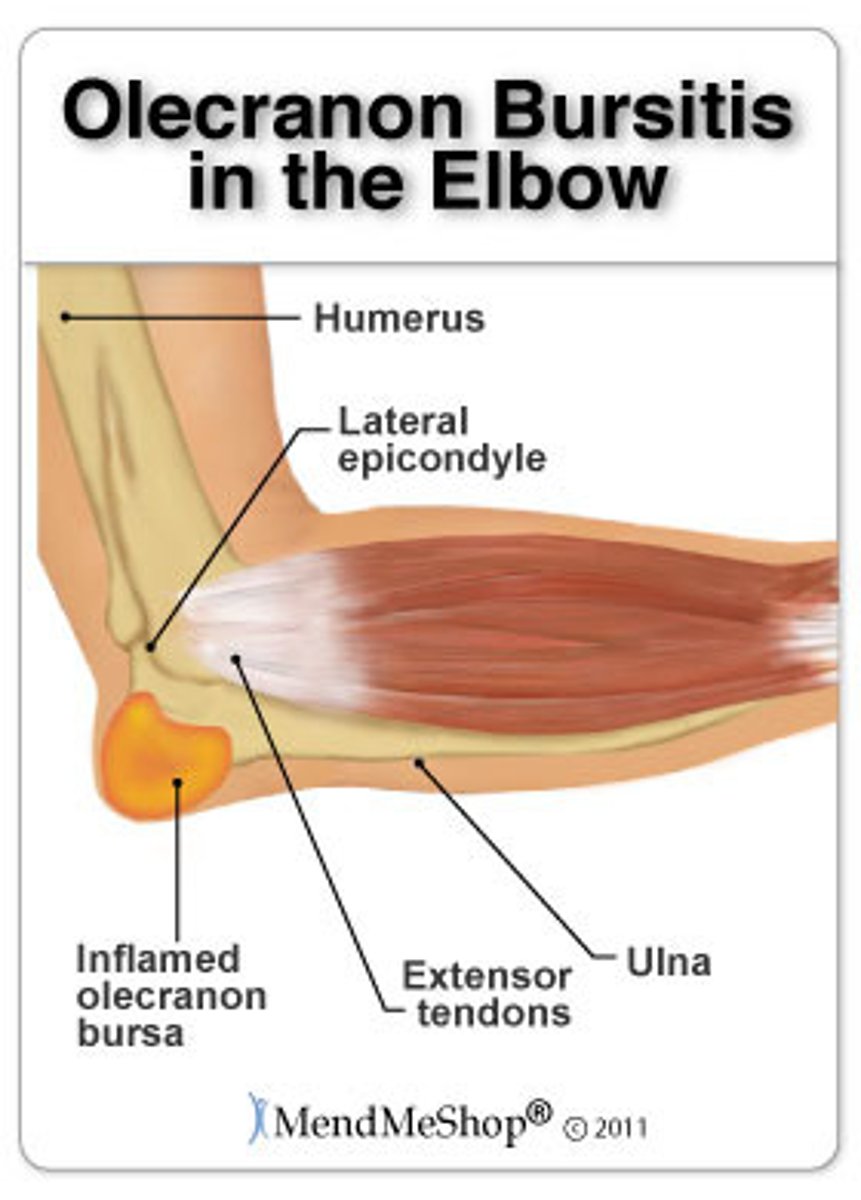
bursa
- fibrous sac filled with synovial fluid
- located between adjacent muscles, between bones and skin where a tendon passes over bone
- cushion muscles, help tendons slide more easily over joints
olecranon is covered by
thick bursa
superficial location of bursa
predisposes it to injury
elbow dislocations mechanism
- hyperextension
- FOOSH
- extreme valgus force
elbow dislocations have high percentage of
associated fractures
- most frequent is radial head which hits as it goes with ulna
- or coronoid process which gets broken off on way out or way back in
elbow dislocation management
- immobilize and call 911
- reduce under anesthesia
- may need surgery if there is a fracture
elbow dislocation happens in what joint
humeroulnar joint
colles fracture
- fracture of the distal radius and ulna
- commonly FOOSH
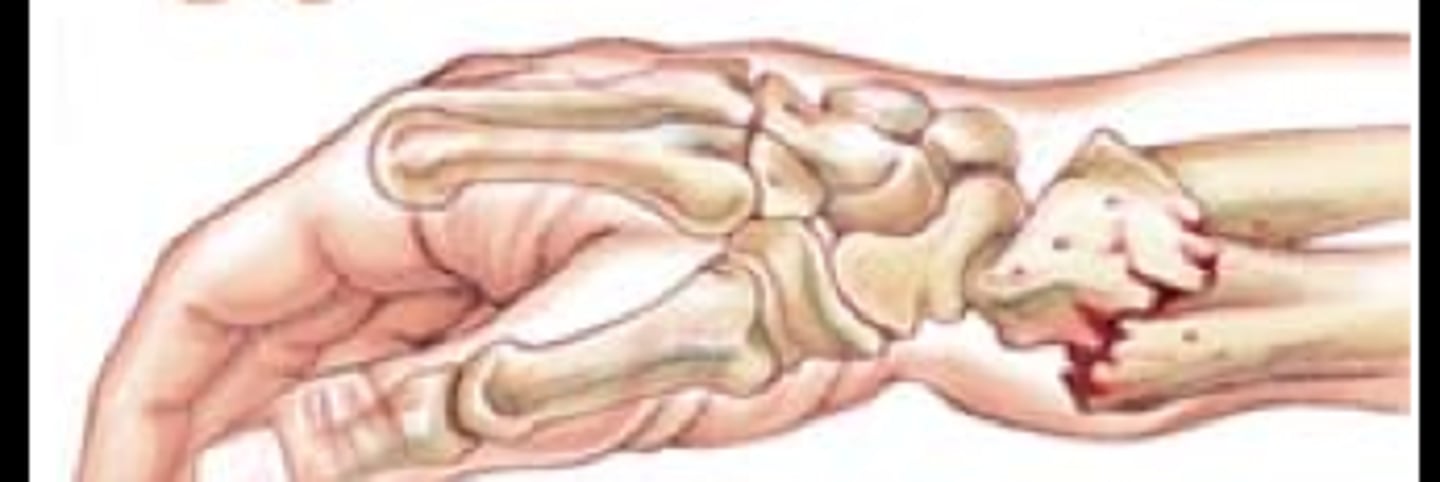
colles fracture management
- immobilization
- doctor referral
- urgent if near growth plate
- bind them where you find them - joint above and below
scaphoid fracture
- most common wrist bone fracture and carpal injury
- difficult to diagnose on x-ray
signs and symptoms of scaphoid fracture
- history of FOOSH
- pain with palpation of anatomical snuff box
management of scaphoid fracture
RICE, application of splint, doctor referral
- surgery for quicker fix for athlete
- scaphoid has bad blood supply- heal slow
triangular fibro cartilage complex - TFCC
if injured can't put weight down on it
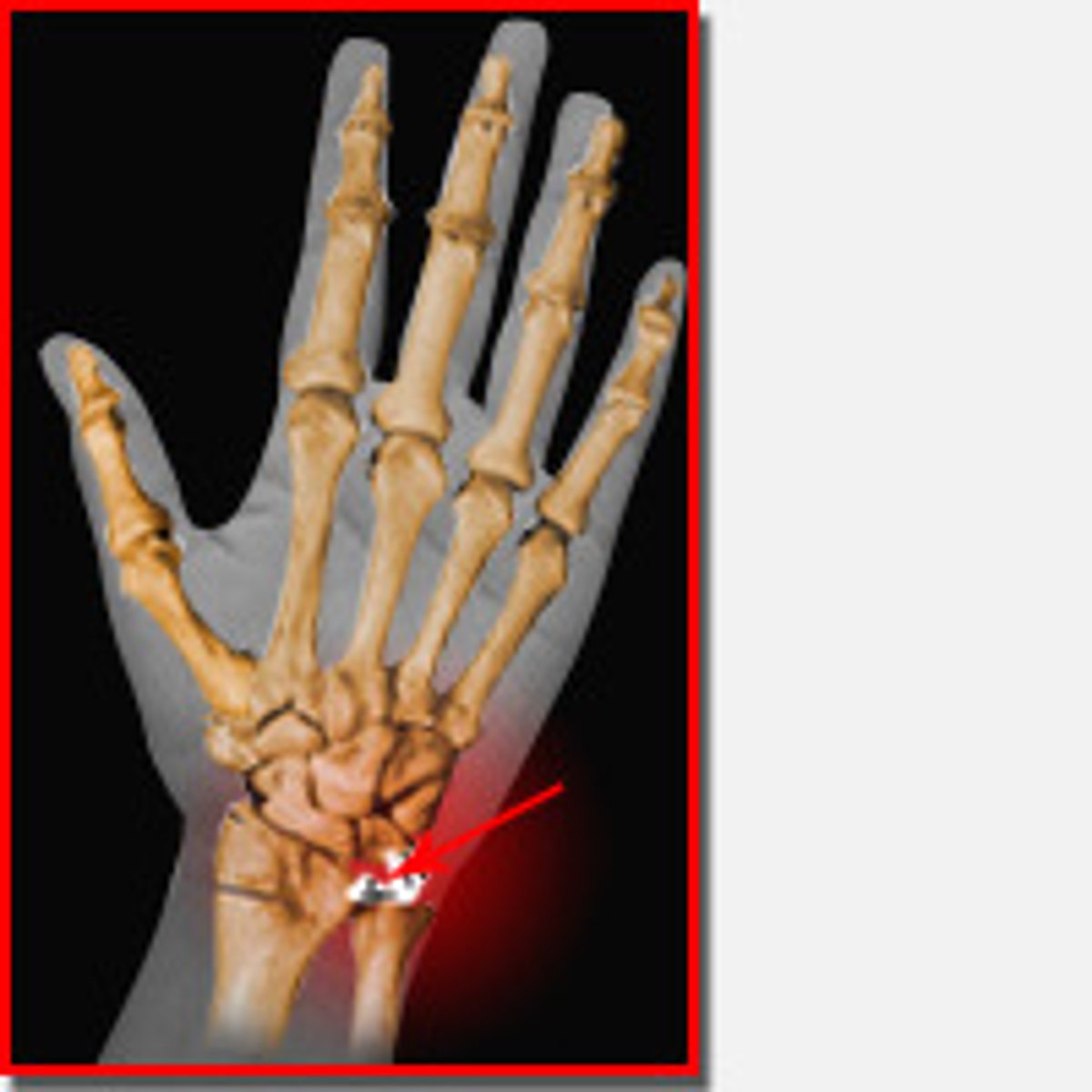
if the transverse carpal ligament is too tight
median nerve tingle and wrist problems (carpal tunnel)
carpal tunnel syndrome is the most common
compression syndrome of the wrist and hand
- typically in dominant hand
- transverse carpal ligament too tight
carpal tunnel syndrome signs and symptoms
- pain
- numbness
- tingling
- burning
felt in fingertips or thumb - middle finger
carpal tunnel syndrome management
- ice and NSAIDs
- injection vs surgical release if symptoms don't resolve
syndrome
A group of symptoms typical of a particular disease or condition
NSAIDs
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
surgical release for carpal tunnel
small cut of retinaculum to relieve pressure
boxer's fracture
fracture of the distal end of fourth or fifth metacarpal
- phalanges won't be parallel
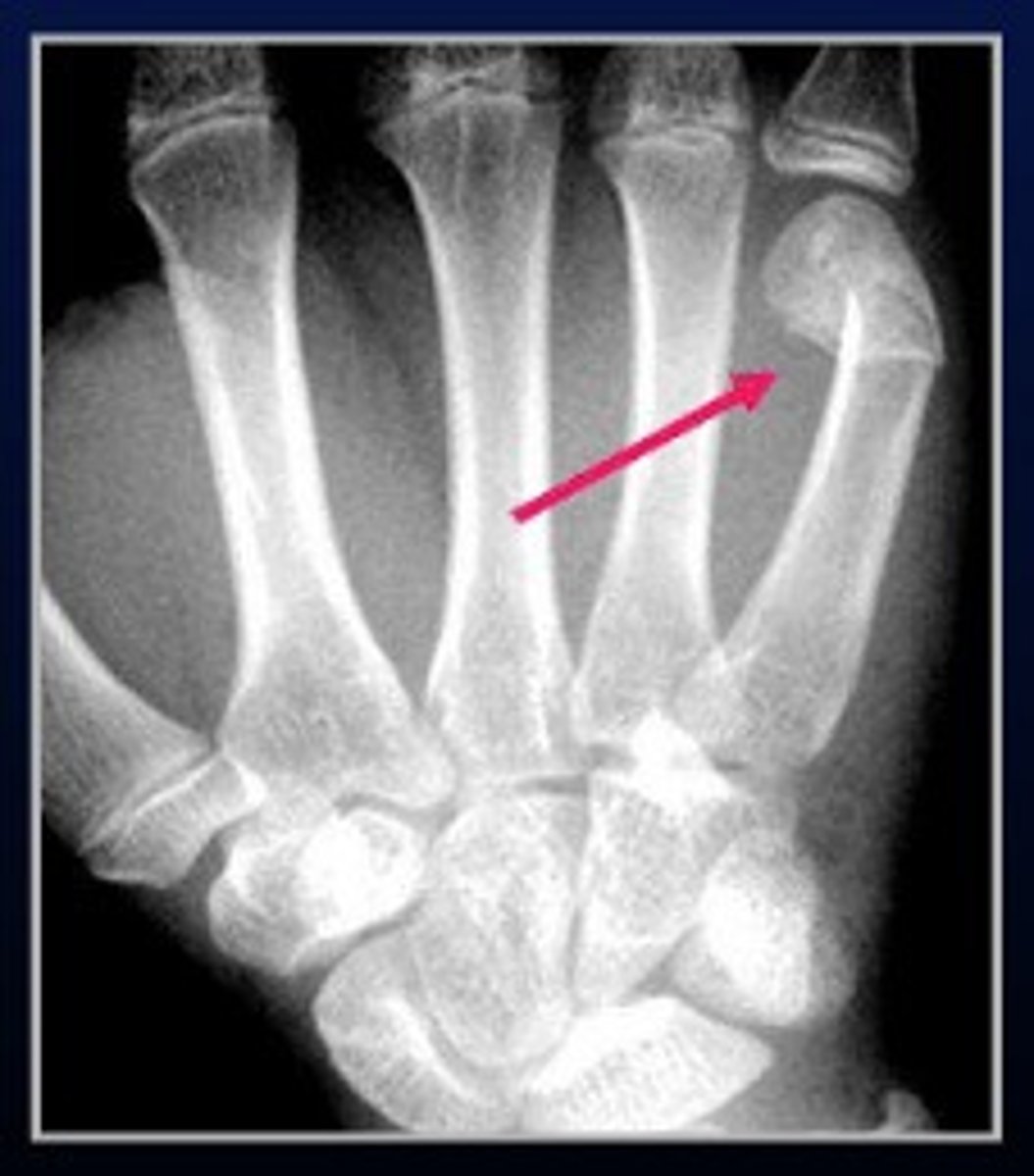
phalanx dislocation
- MCP joints rare but significant
- PIP joint most common dislocation in body
mechanism of phalanx dislocation
hyperextension with axial compression usually
- often open dislocation because there isn't extra skin there for space
palmaris longus is often
the tendon harvested for surgeries
lateral epicondylitis caused
by eccentric loading of the extensor muscles:
- ex. backhand in tennis
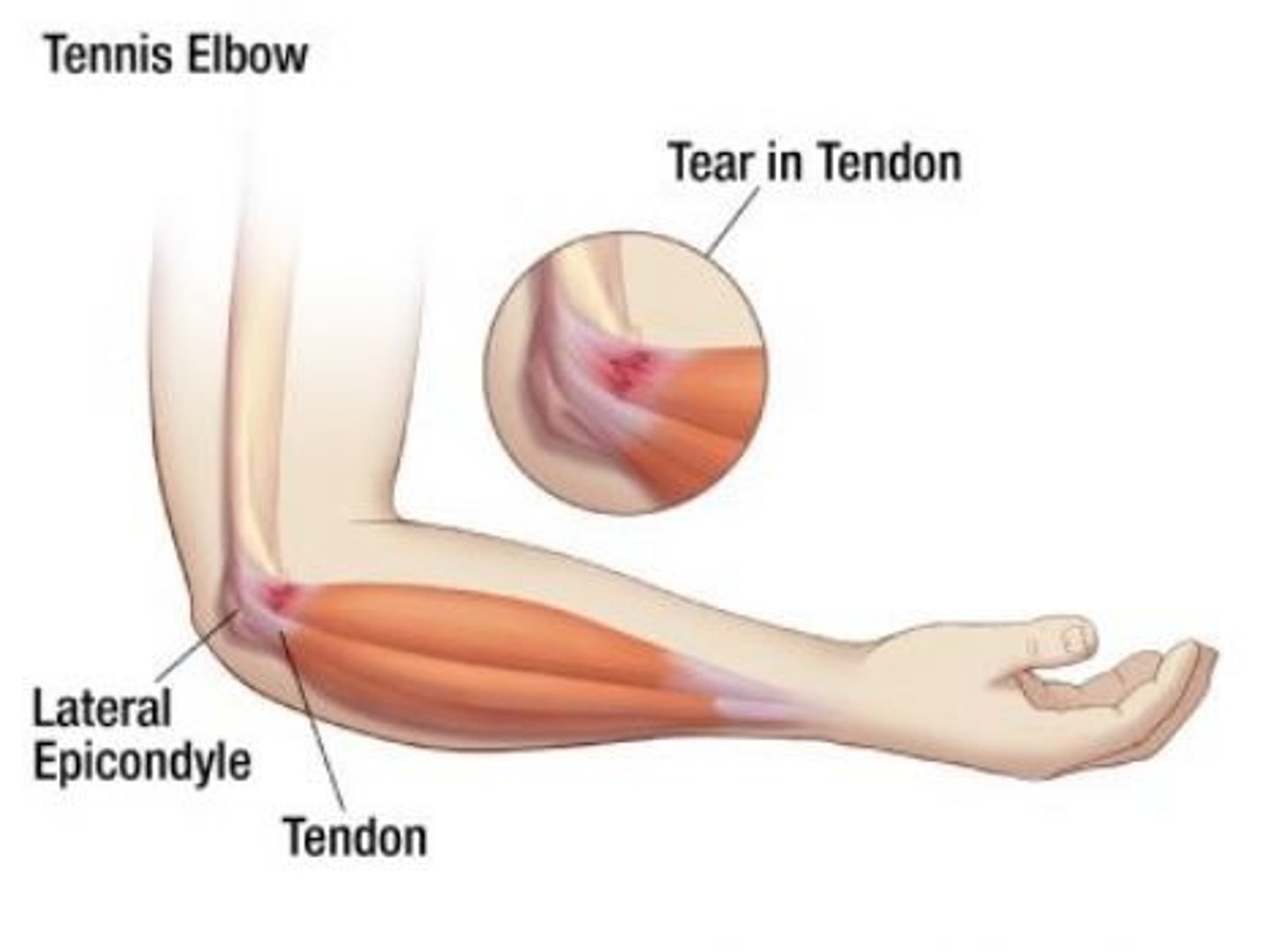
signs and symptoms of lateral epicondylitis
- pain over/around lateral epicondyle
- pain with resisted movement - picking up cup/soda can
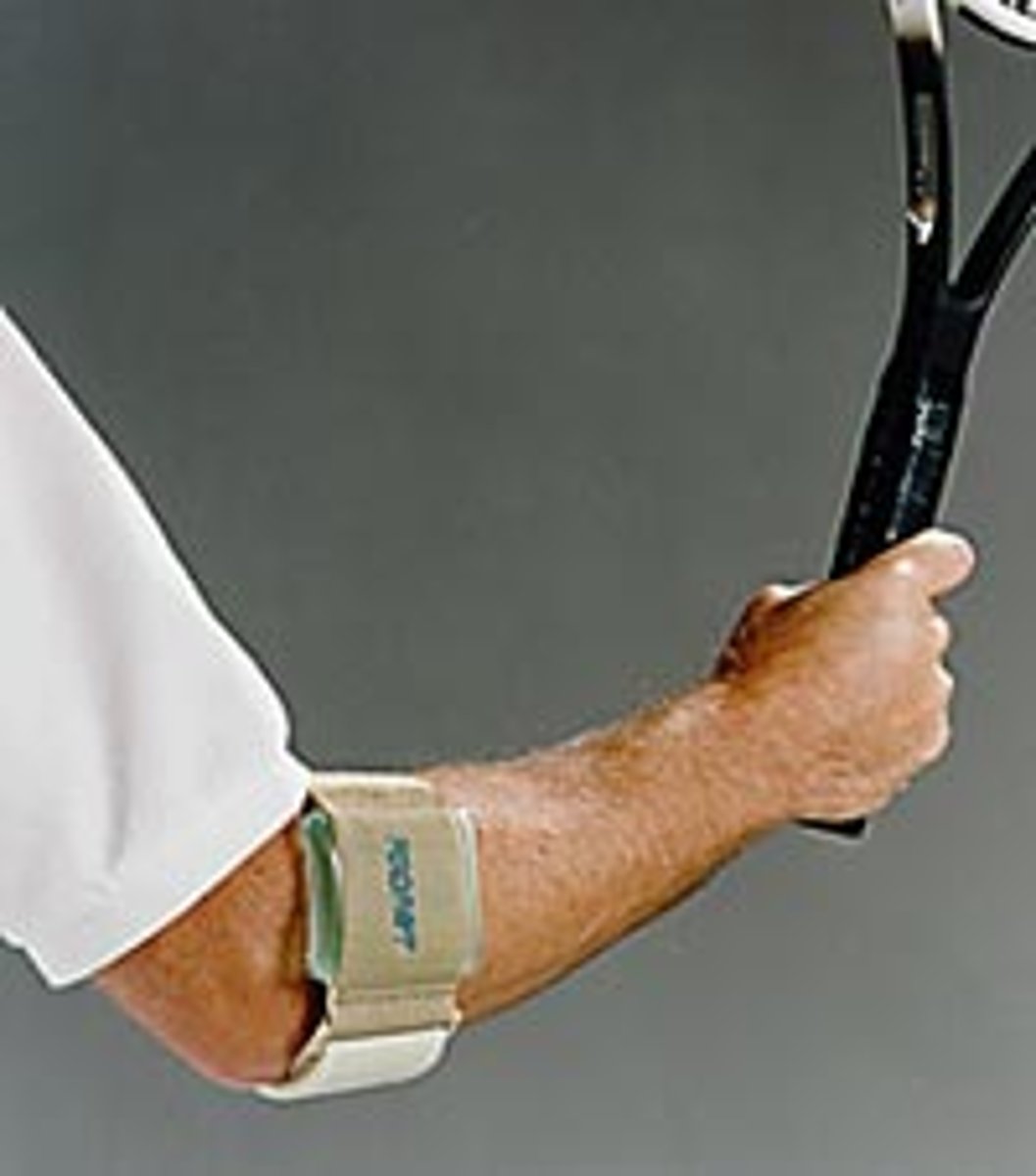
lateral epicondylitis treatment
can use a counter force brace below the extensor muscle to disperse stress on extensor tendon

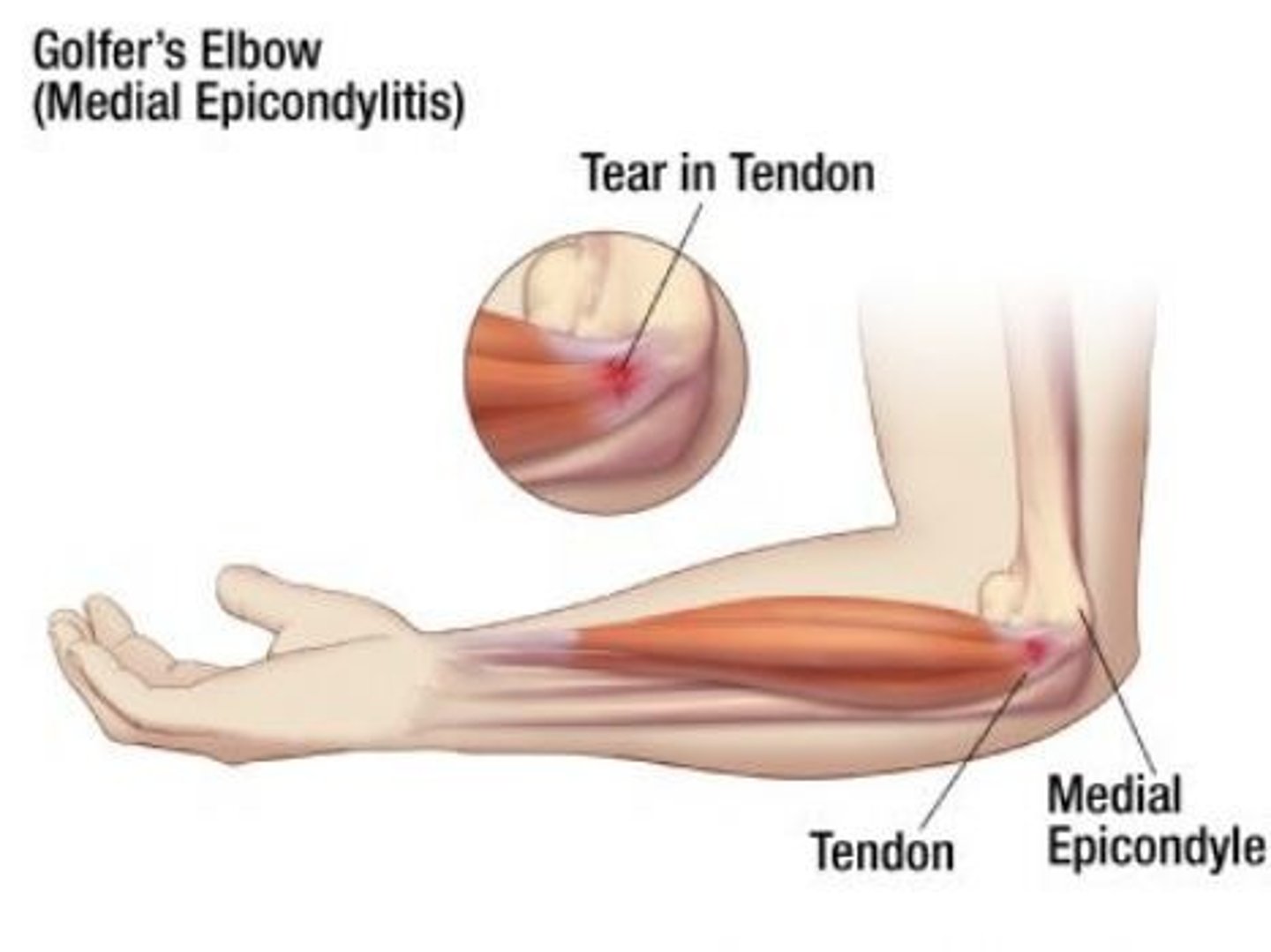
medial epicondylitis can be caused by
pitching
finger tendon injuries
- jersey finger
- mallet finger
- boutonniere deformity
- swan neck deformity
- trigger finger
jersey finger
- rupture and avulsion of flexor digitorum profundus
- from grabbing a jersey twisting and turning to get away
- can't flex DIP can flex PIP
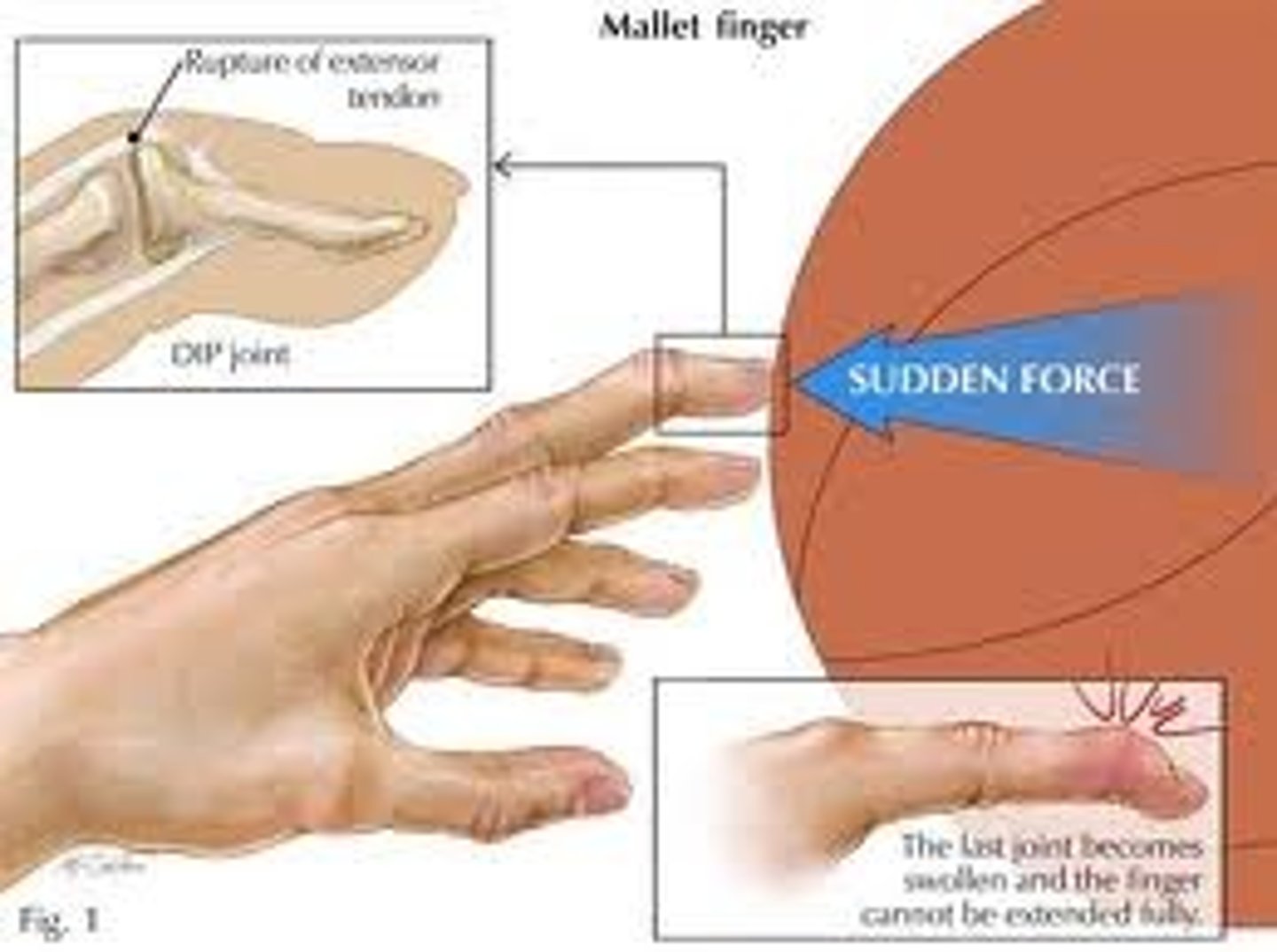
mallet finger
- rupture and avulsion of the extensor tendon at distal phalanx
- tendon can't retract
- immobilize in hyperextension for 8 weeks
- DIP can't extend
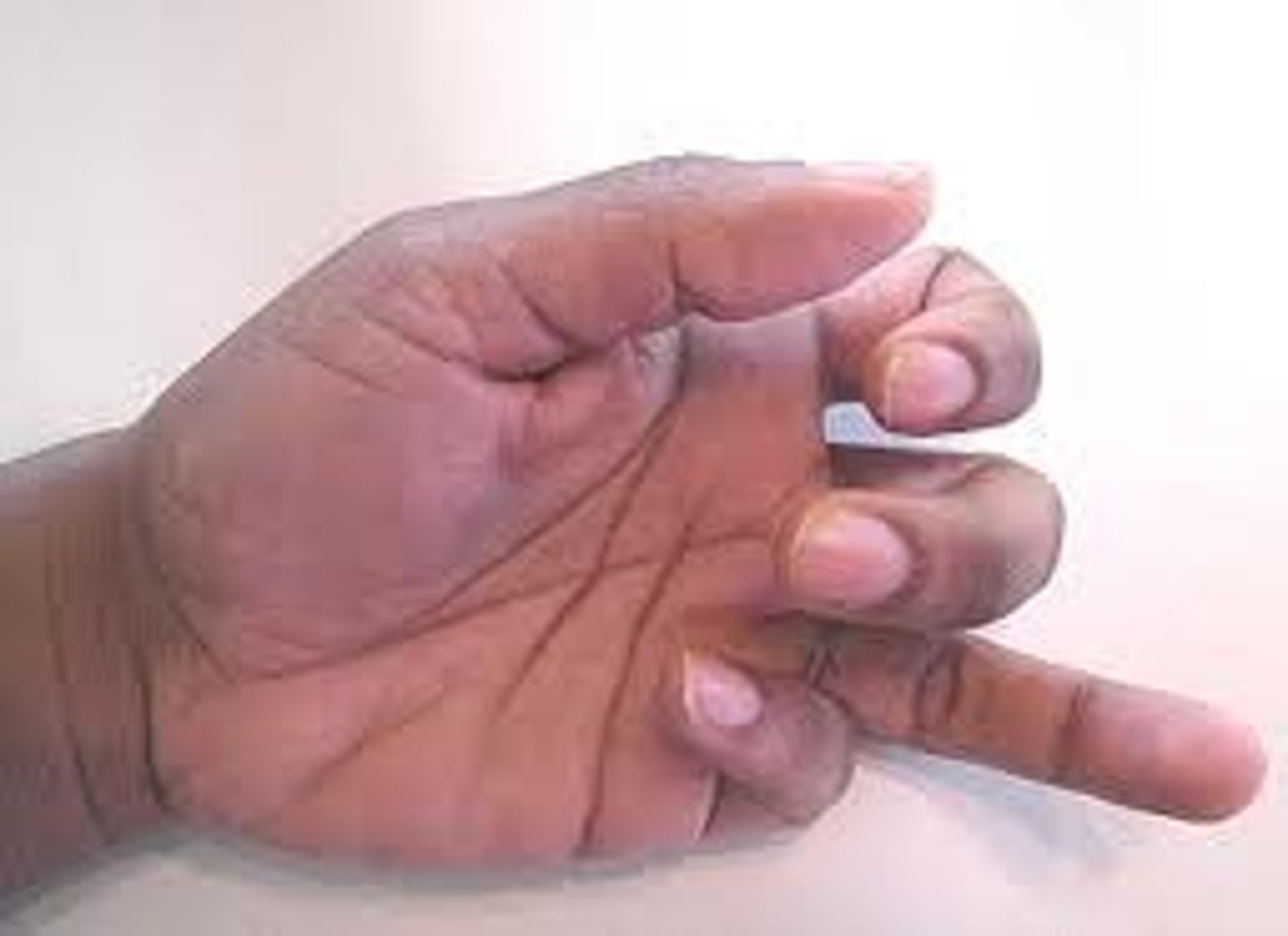
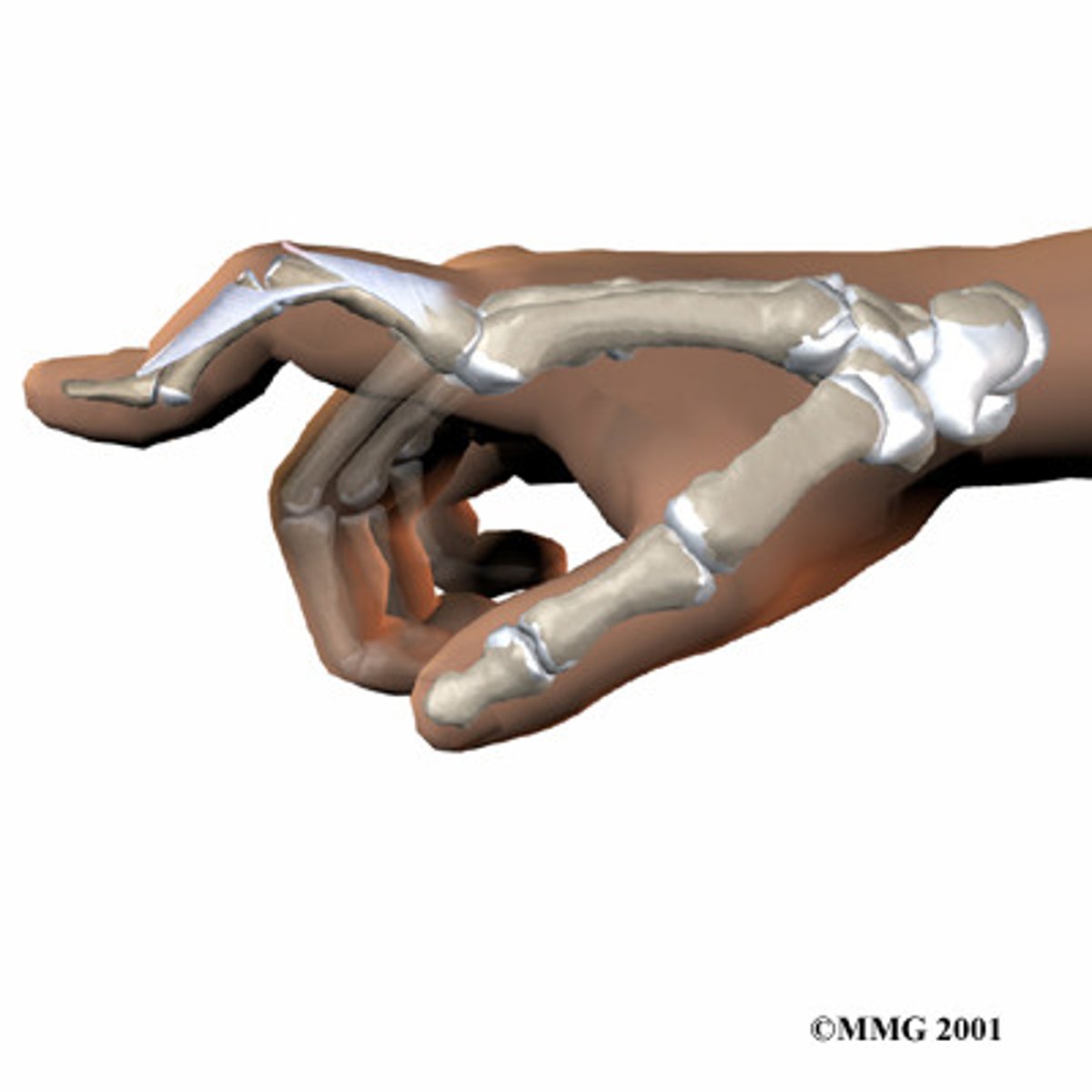
boutonniere deformity
- rupture of central slip of extensor tendon at middle phalanx
- flexion of PIP and extension of DIP
- looks like holding a pin hard

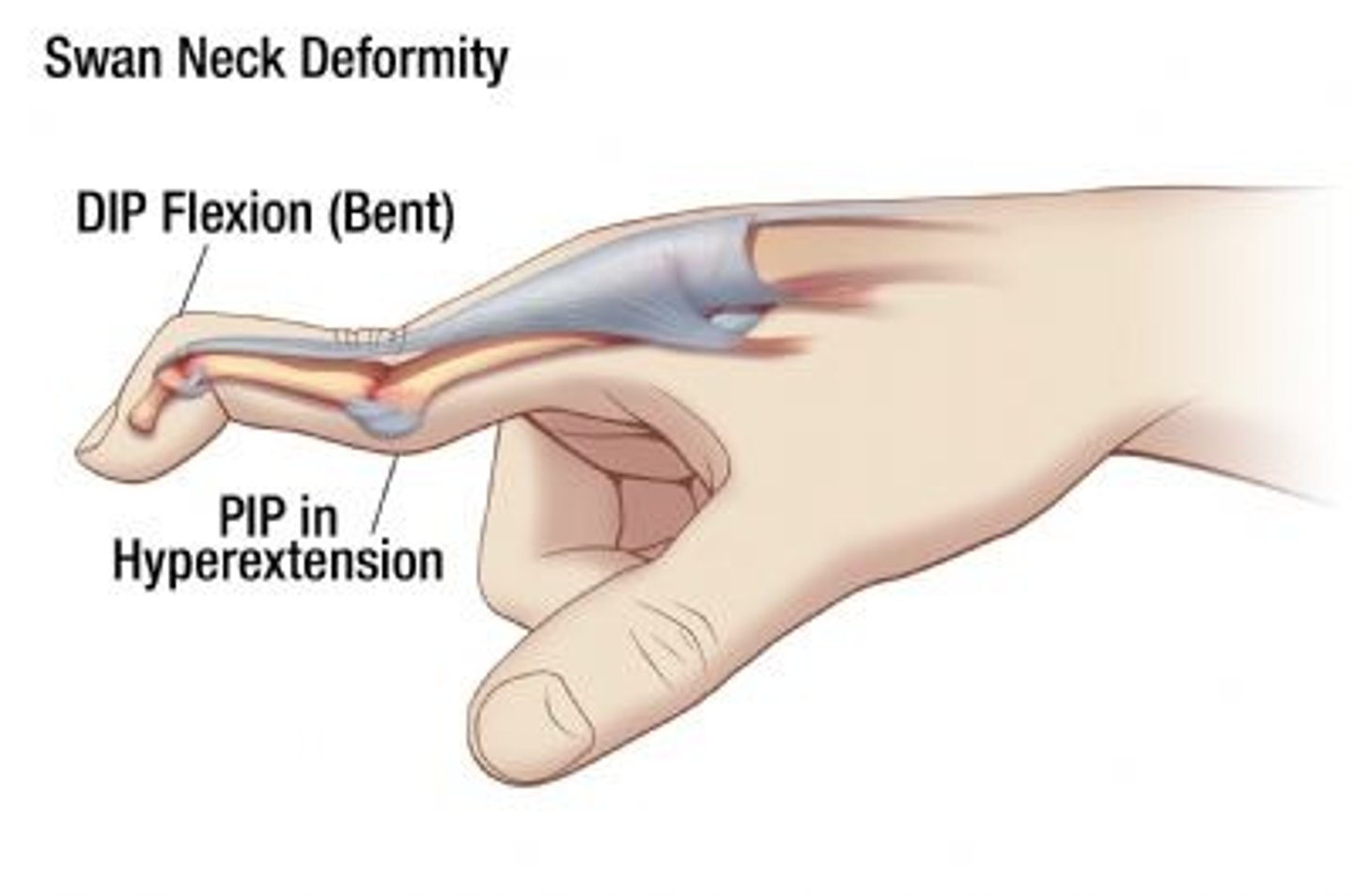
swan neck deformity
- hyperextended PIP joint and flexed DIP joint
- caused by loose solar plate at PIP
- rheumatoid arthritis or joint dislocation
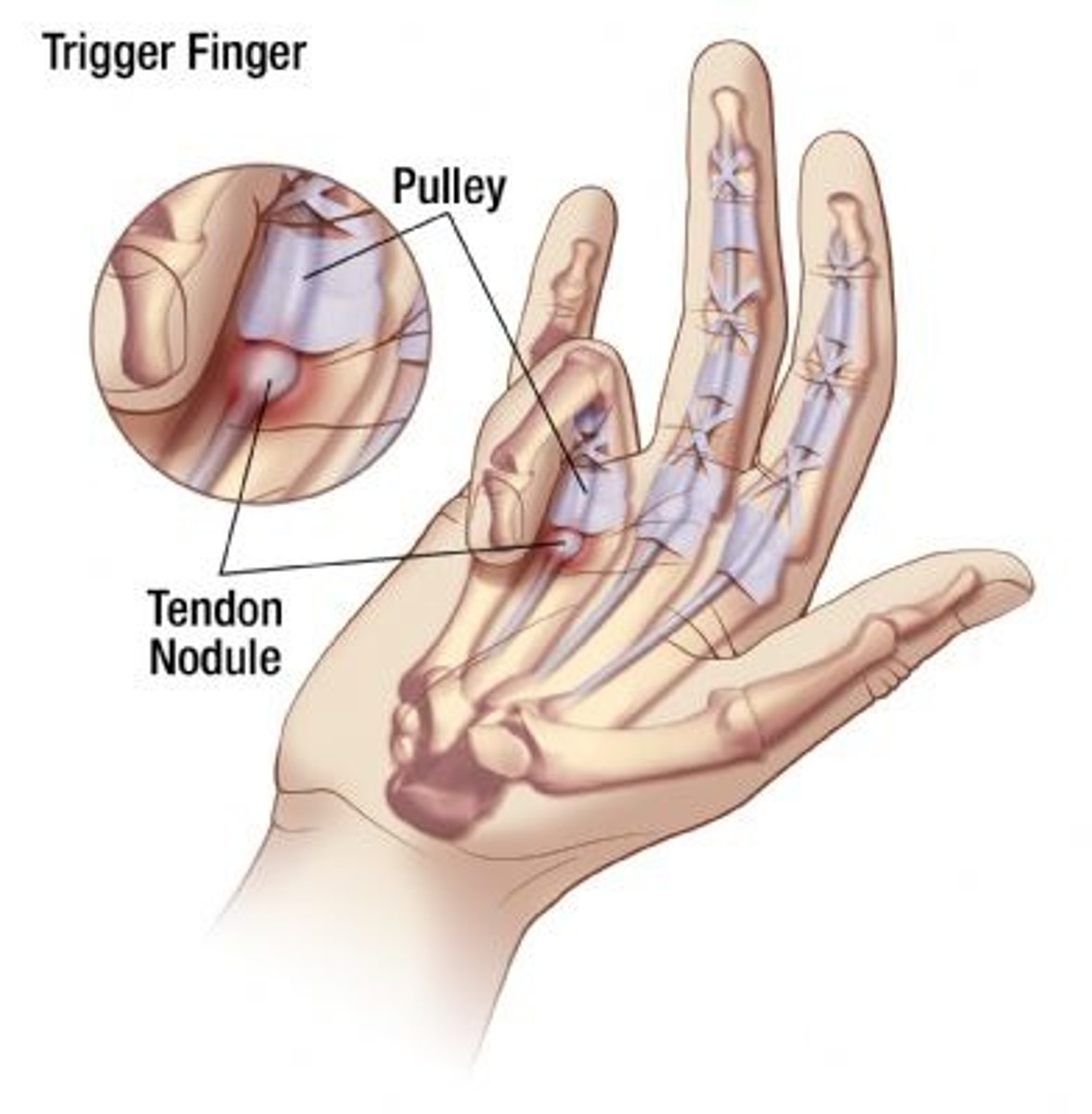
trigger finger
- common on middle/ring finger
- inflammation created thick flexor tendon and nodule in tendon sheath
- finger locked in flexion once nodule is to large to pass