Properties of acid and bases
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is an acid?
Substance that can donate a hydrogen ion e.g HCl
What is a base?
Substance that accepts a hydrogen ion, e.g NaOH (sodium hydroxide)
What is a monoprotic acid?
an acid that can lose 1 hydrogen ion, e.g HCl
What is a diprotic acid?
an acid that can lose 2 hydrogen ions e.g H2SO4
Strong acid and base: conductivity
Good electrical conductivity due to complete ionisation/dissociation of the acid or base
Weak acid and base: conductivity
Poor electrical conductivity due to little ionisation of the acid/base molecules
What is the difference between strength and concentration?
concentrated - lots of particles (either strong or weak)
dilute - not many particles (either strong or weak)
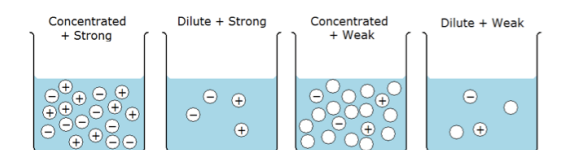
What is the dissociation of a strong acid and base?
complete ionisation dissociation into ions
What is the dissociation of a weak acid and base?
only partial dissociation into ions
What reaction occurs when a strong acid and base react with water?
complete dissociation into ions
HA + H2 → (H2O+) + A- or often shortened to HA → (H+) + A-
e.g HCl; BOH + H2O → (B+) + OH- + H2O
What reaction occurs when a weak acid and base reacts with water?
partial dissociation into ions
HA + H2O ←> H2O- + A- (equilibrium) e.g. CH2COOH ←> (H2O+) + CH3COO-
What’s an example of a strong acid?
HCl (hydrochloric acid) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
What’s an example of a weak acid?
Acetic acid (CH3COOH) and other carboxylic acids
Whats an example of a strong base?
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and potassium hydroxide (KOH)
What’s an example of a weak base?
Ammonia (NH3)