Semester 1 Review (AP Human)
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
203 Terms
absolute location
The exact position of an object or place, measured within the spatial coordinates of a grid system.
cartography
science or art of making maps
circular pattern
Objects that circle another object, another name for it is Centralized Pattern; For example, in an Islamic city, houses and public buildings may circle around the mosque, or house of worship.
cultural landscapes
The products of complex interactions between humans and their environments.
distortion
a change in the shape, size, or position of a place when it is shown on a map
equator
an imaginary line drawn around the earth equally distant from both poles, dividing the earth into northern and southern hemispheres and constituting the parallel of latitude 0°.
formal regions
Also called uniform regions, an area that has striking similarities in terms of one or a few physical or cultural features.
functional (nodal) regions
areas organized around cores, or nodes
GIS
Geographic Information System; a computer system that captures, stores, analyzes, and displays data.
globalization
Actions or processes that involve the entire world and result in making something worldwide in scope.
Greenwich Mean Time
The time in that time zone ecompassing the Prime Meridian, or 0 degrees longitude
GPS
Global Positioning System; uses a system of satellites, tracking stations, and receivers to determine precise absolute locations on earth.
grid pattern
Also called a rectilinear pattern, reflects a rectangular system of land survey adopted in much of the country under the Ordinance of 1785. Streets form grids and are sometimes labeled "1st", "2nd", "3rd" streets and so on.
human geography
a branch of geography that focuses on the study of patterns and processes that shape human interaction with the built environment, with particular reference to the causes and consequences of the spatial distribution of human activity on the Earth's surface
latitude
The numbering system used to indicate the location of parallels drawn on a globe and measuring distance north and south of the equator.
linear pattern
when the pattern in along straight lines, like rivers, streets, or railroad tracks.
location
The position of anything on Earth's surface.
longitude
The numbering system used to indicate the location of meridians drawn on a globe and measuring distance east and west of the prime meridian (0°).
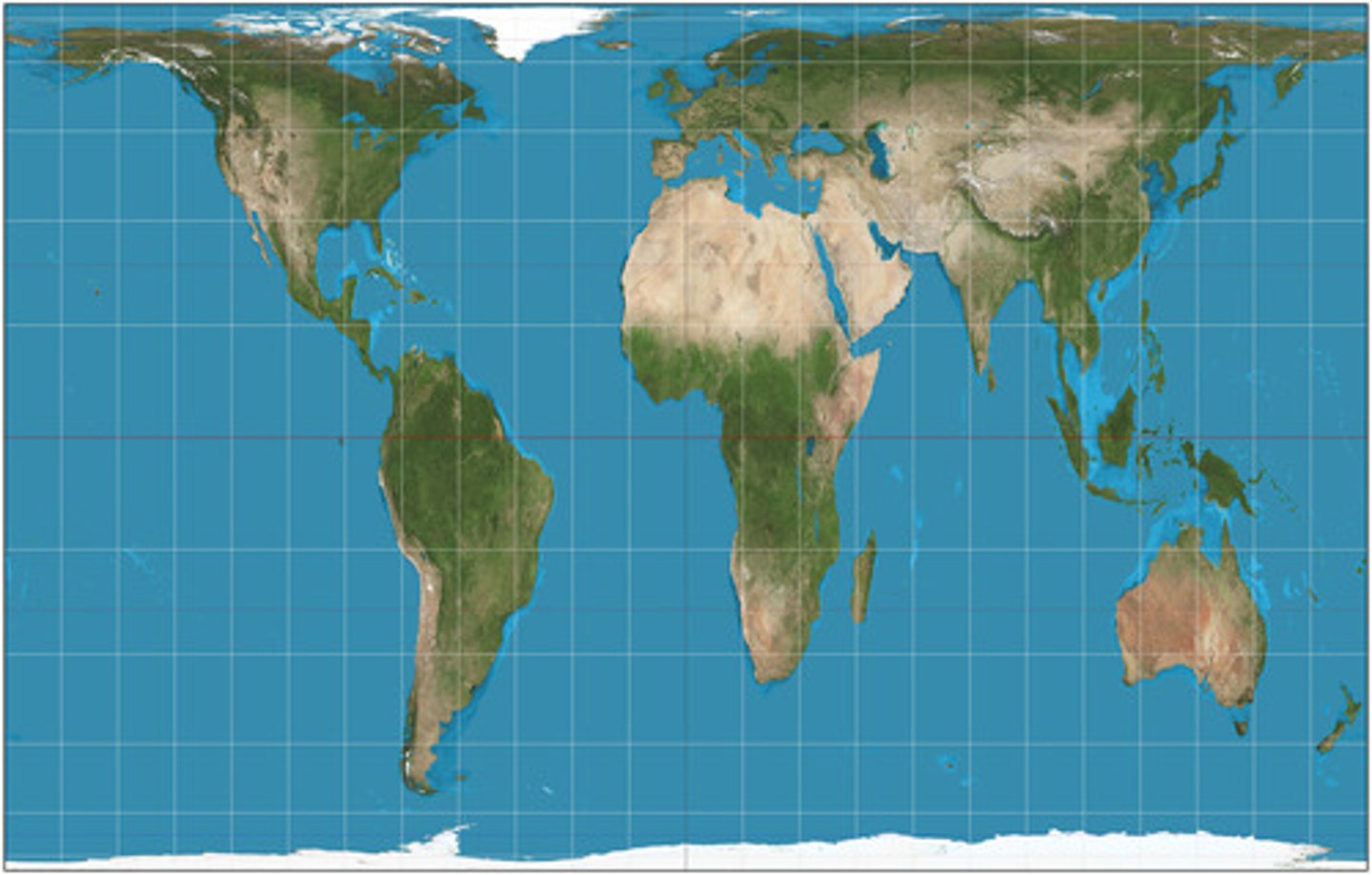
Mercator projection
a map projection of the earth onto a cylinder
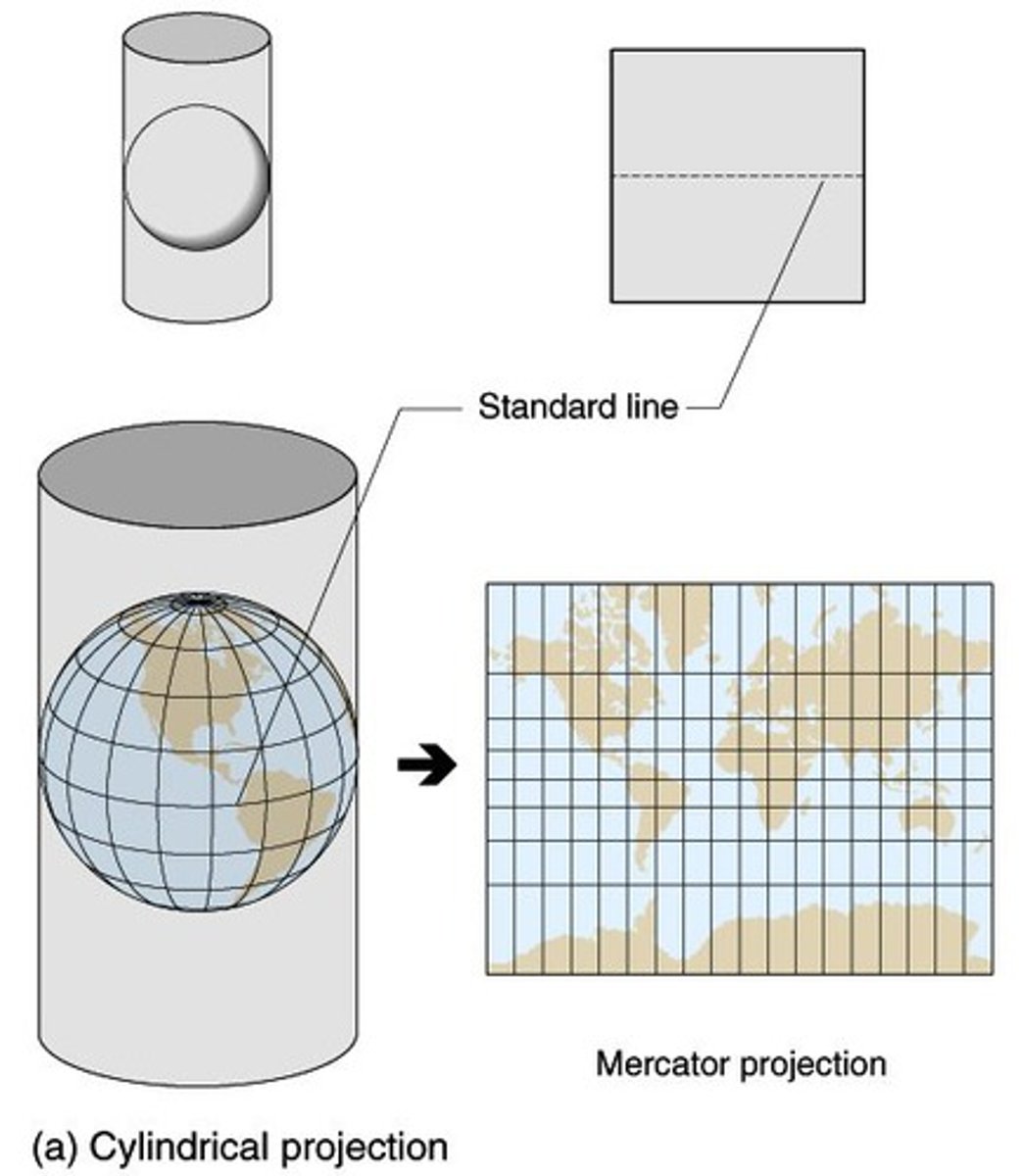
meridian
an arc drawn between North and South poles that measures longitude
parallel
A circle drawn around the globe parallel to the equator and at right angles to the meridians.
pattern
the arrangement of objects on earth's surface in relation to other objects
perceptual (vernacular) regions
places that people believe to exist as a part of their cultural identity
periphery
the outer boundary of a region; Countries that usually have low levels of economic productivity, low per capita incomes, and generally low standards of living. The world economic periphery includes Africa (except for South Africa), parts of South America, and Asia.
Peters Projection
An equal-area projection purposely centered on Africa in an attempt to treat all regions of Earth equally.
place
A specific point on Earth distinguished by a particular character.
physical geography
one of the two major divisions of systematic geography; the spatial analysis of the structure, processes, and location of the Earth's natural phenomena such as climate, soil, plants, animals, and topography.
physical site characteristic
A location that includes climate, topography, soil, water sources, vegetation, and elevation.
prime meridian
The meridian, designated at 0° longitude, which passes through the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, England.
random pattern
a pattern that exists if no regular distribution can be seen
regionalization
the organization of earth's surface into distinct areas that are viewed as different from other areas
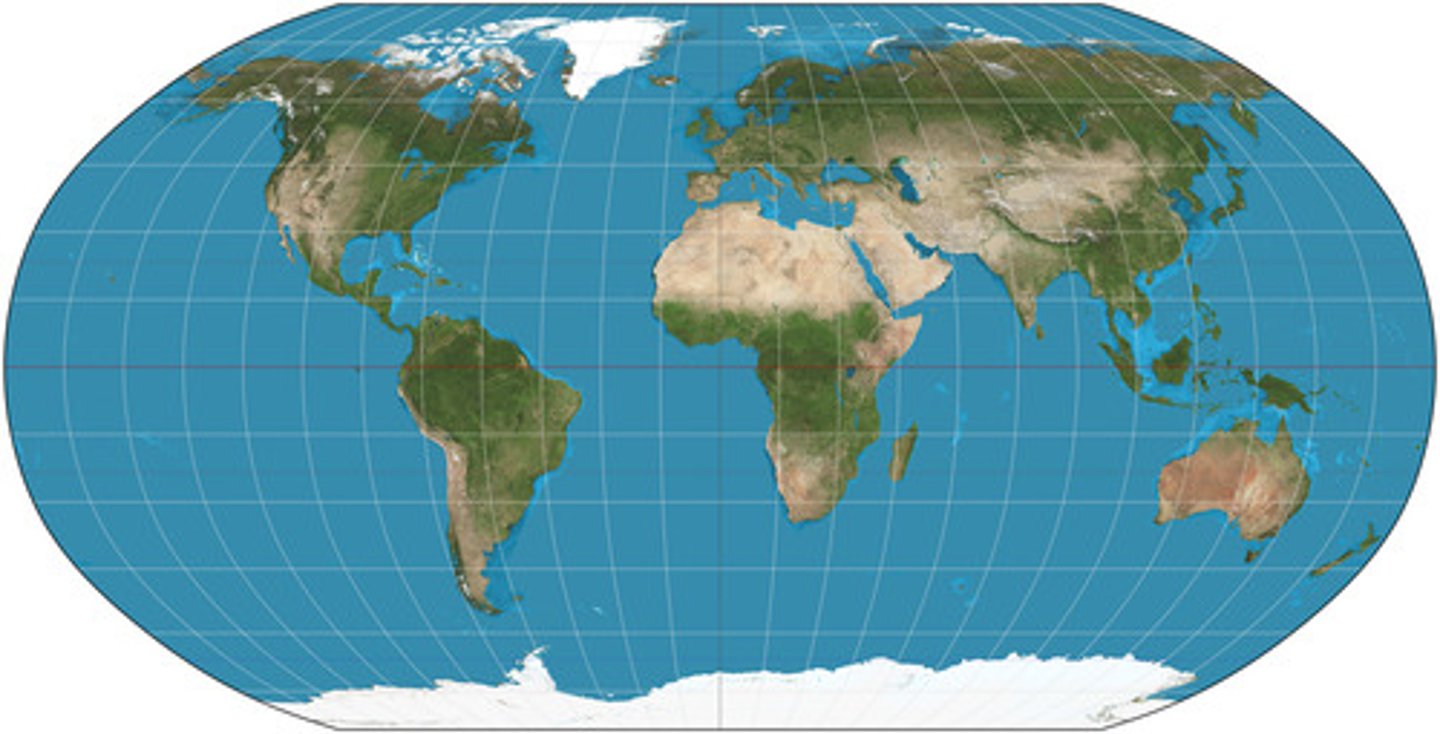
Robinson projection
Projection that attempts to balance several possible projection errors. It does not maintain completely accurate area, shape, distance, or direction, but it minimizes errors in each.
scale
The ratio between the size of an area on a map and the actual size of that same area on the earth's surface.
site
the physical and human-transformed characteristics of a place
situation
characteristic that refers to relative location
space
the physical gap or distance between two objects
space time compression
the reduction in the time it takes to diffuse something to a distant place, as a result of improved communications and transportation systems
spatial organization
organization according to location, position, or direction
spatial perspective
observing variations in geographic phenomena across space
time zone
24, 15 degree sections that each represent a different hour of the day
topography
A description of surface features of land.
toponym
Place names given to certain features on the land such as settlements, terrain features, and streams.
U.S. Census Bureau
a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System responsible for producing data about the American people and economy.
activity space
The space within which daily activity occurs.
agricultural revolution
The time when human beings first domesticated plants and animals and no longer relied entirely on hunting and gathering
AIDS
Immune system disease caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) which over a period of years weakens the capacity of the immune system to fight off infection so that weight loss and weakness set in and other afflictions such as cancer or pneumonia may hasten an infected person's demise
arable land
land suitable for growing crops
arithmetic growth
population growth where population increases by the same amount over each time interval
arithmetic population density
The population of a country or region expressed as an average per unit area. The figure is derived by dividing the population of the areal unit by the number of square kilometers or miles that make up the unit
awareness space
Locations or places about which an individual has knowledge even without visiting all of them, includes activity space and additional areas newly encountered or about which one acquires information.
carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
chain migration
migration of people to a specific location because relatives or members of the same nationality previously migrated there
circulation
Short-term, repetitive, or cyclical movements that recur on a regular basis.
critical distance
the distance beyond which cost, effort, and means strongly influence our willingness to travel
crude birth rate
The number of live births per year per 1,000 people.
crude death rate
The number of deaths per year per 1,000 people.
demographic equation
The formula that calculates population change. The formula finds the increase (or decrease) in a population. The formula is found by doing births minus deaths plus (or minus) net migration. This is important because it helps to determine which stage in the demographic transition model a country is in.
demography
Scientific study of human populations.
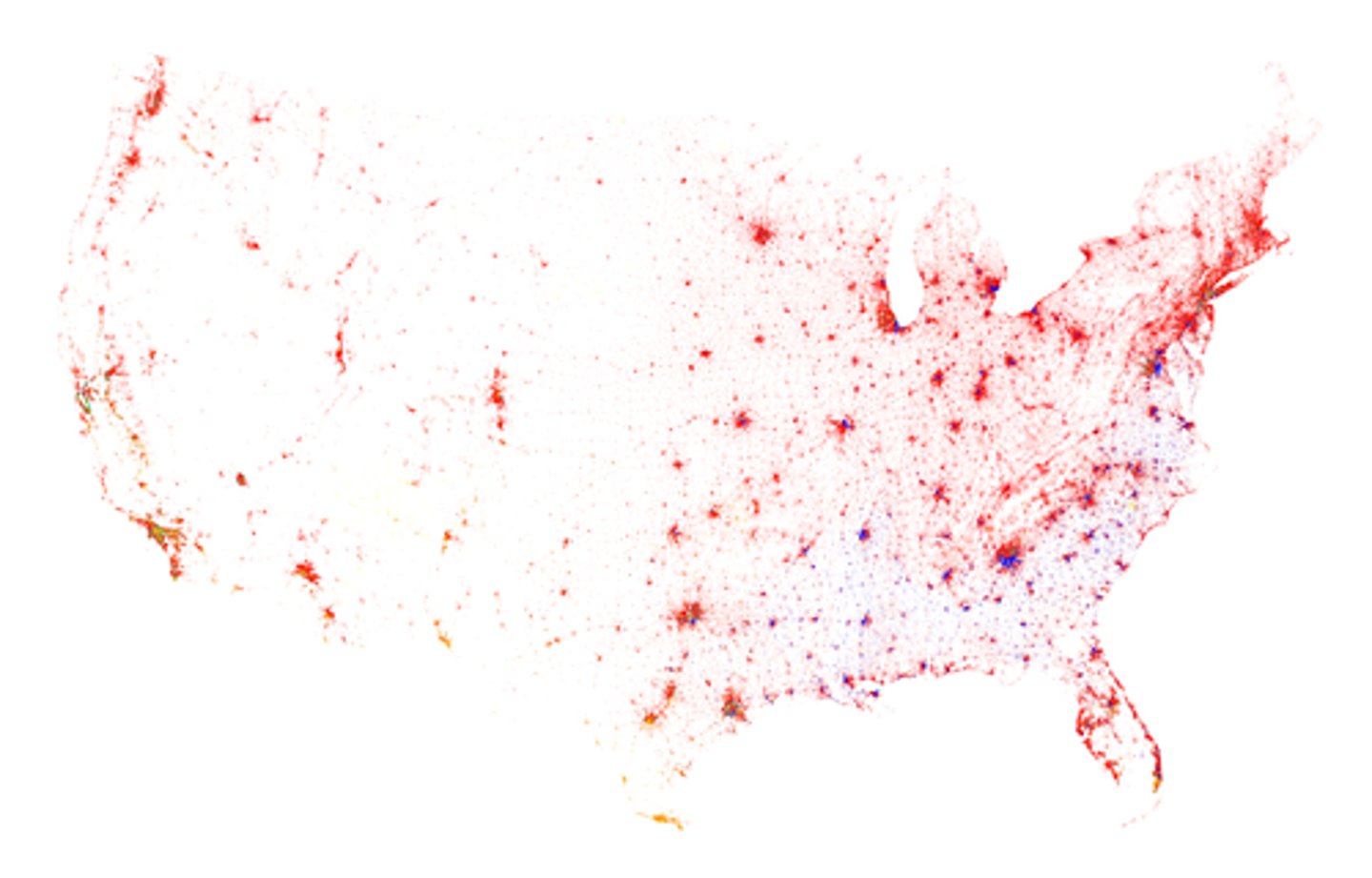
population density
A measurement of the number of persons per unit land area.
dislocation
people forced from their home due to ethnic strife, war, or natural disasters
distance decay
the effects of distance on interaction, generally the greater the distance the less interaction
dot maps
Maps where one dot represents a certain number of a phenomenon, such as a population
doubling rate
The length of time needed to double the population
emigration
Migration from a location (Exit migration)
endemic
Native or confined to a particular region or people
epidemiologic transition
The shift from high death rates to low death rates in a population as a result of modern medical and sanitary developments. Also called the "mortality revolution"
ethnicity
Identity with a group of people that share distinct physical and mental traits as a product of common heredity and cultural traditions.
exponential growth
Growth whose rate becomes ever more rapid in proportion to the growing total number or size. Also called population growth at a "geometric rate"
female infantcide
The preference to have a son is so extreme that it reduces the survival rate of baby girls
forced migration
Human migration flows in which the movers have no choice but to relocate.
gravity model
A mathematical formula that describes the level of interaction between two places, based on the size of their populations and their distance from each other.

immigration
Movement of individuals into a population (In migration)
Industrial Revolution
A series of improvements in industrial technology that transformed the process of manufacturing goods.
infant mortality rate
The percentage of children who die before their first birthday within a particular area or country.
in-migration
the total number of immigrants who arrive in a country in a given time period
internal migration
Permanent Movement within a particular country.
inter-regional migration
Permanent movement from one region of a country to another
intervening obstacles
Any forces or factors that may limit human migration.
intervening opportunity
the presence of a nearer opportunity that greatly diminishes the attractiveness of sites farther away.
intra-regional migration
Permanent movement within one region of a country.
life expectancy
A figure indicating how long, on average, a person may be expected to live
linear growth
Expansion that increases by the same amount during each time interval.
Thomas Malthus
Eighteenth-century English intellectual who warned that population growth threatened future generations because, in his view, population growth would always outstrip increases in agricultural production.
migration
Form of relocation diffusion involving permanent move to a new location.
migration selectivity
Only people exhibiting certain characteristics in a population choosing to migrate
natural increase
Population growth measured as the excess of live births over deaths. Natural increase of a does not reflect either emigrant or immigrant movements.
neo-Malthusians
group who built on Malthus' theory and suggested that people wouldn't just starve for lack of food, but would have wars about food and other scarce resources
net-migration rate
Difference between immigrants and emmigrants per 1,000 people
one child policy
A policy implemented by the Chinese government as a method of controlling the population.
out-migration
the total number of immigrants who leave a country in a given time period
overpopulation
The number of people in an area exceeds the capacity of the environment to support life at a decent standard of living.
pandemic
Disease that occurs over a wide geographic area and affects a very high proportion of the population.
physiological population density
The number of people per unit of area of arable land, which is land suitable for agriculture
population concentrations
Areas of the world with large population density.
population explosion
The rapid growth of the world's human population during the past century, attended by ever-shorter doubling times and accelerating rates of increase
population geography
a division of human geography concerned with spatial variations in distribution, composition, growth, and movements of population.
population pyramid
A model used in population geography to show the age and sex distribution of a particular population.
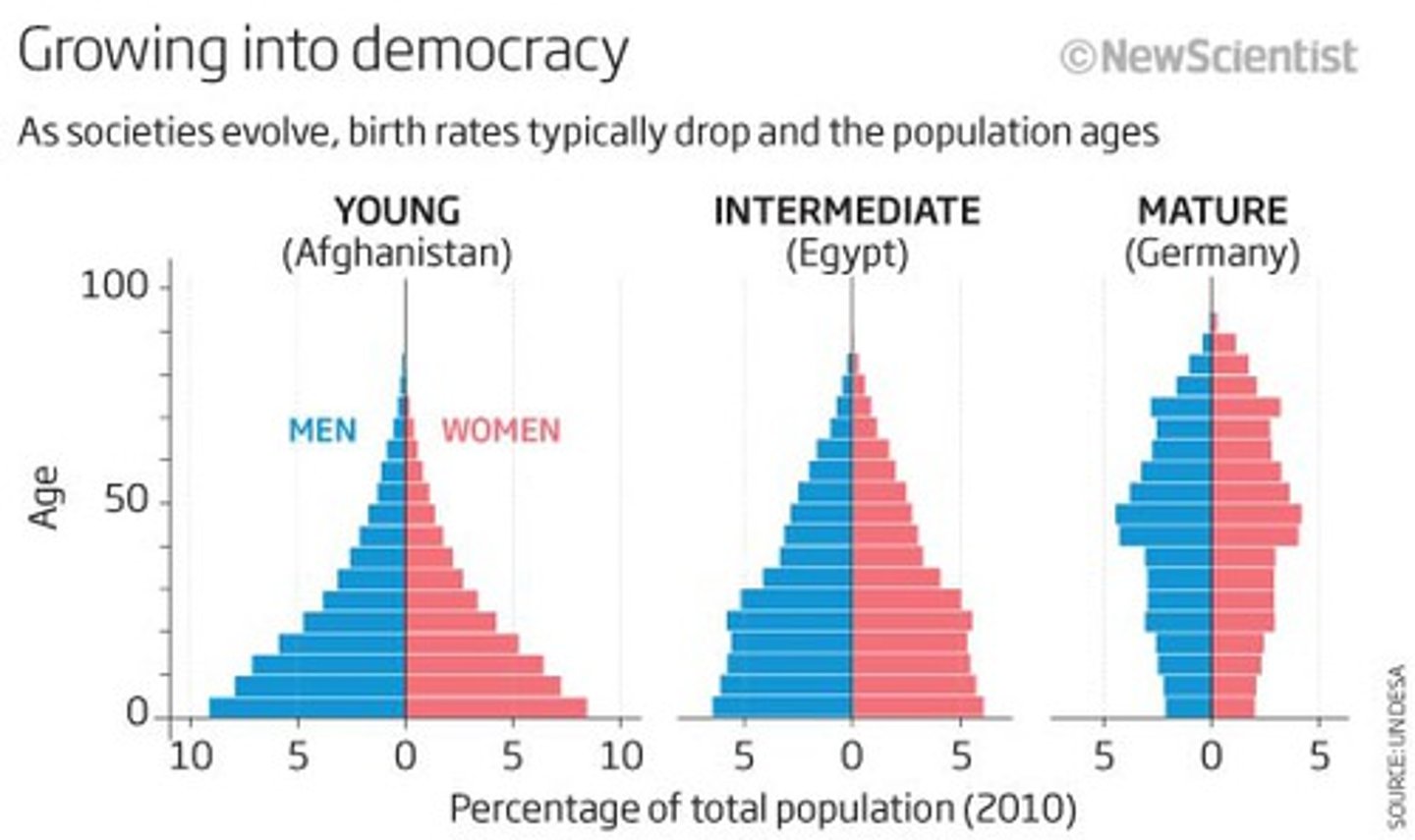
pull factors
Factors that induce people to move to a new location. Also called "centripetal factors"
push factors
Incentives for potential migrants to leave a place, such as a harsh climate, economic recession, or political turmoil. Also called "centrifugal factors"
race
A group of human beings distinguished by physical traits, blood types, genetic code patterns or genetically inherited characteristics.