Driving School: Unit 5, Lessons 1 and 2
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Risk factors
anything that can increase the possibility of a collision involved in driving
Identify
The first stop of the IPDE Process: you must know when to look, where to look, how to look, and what to look for
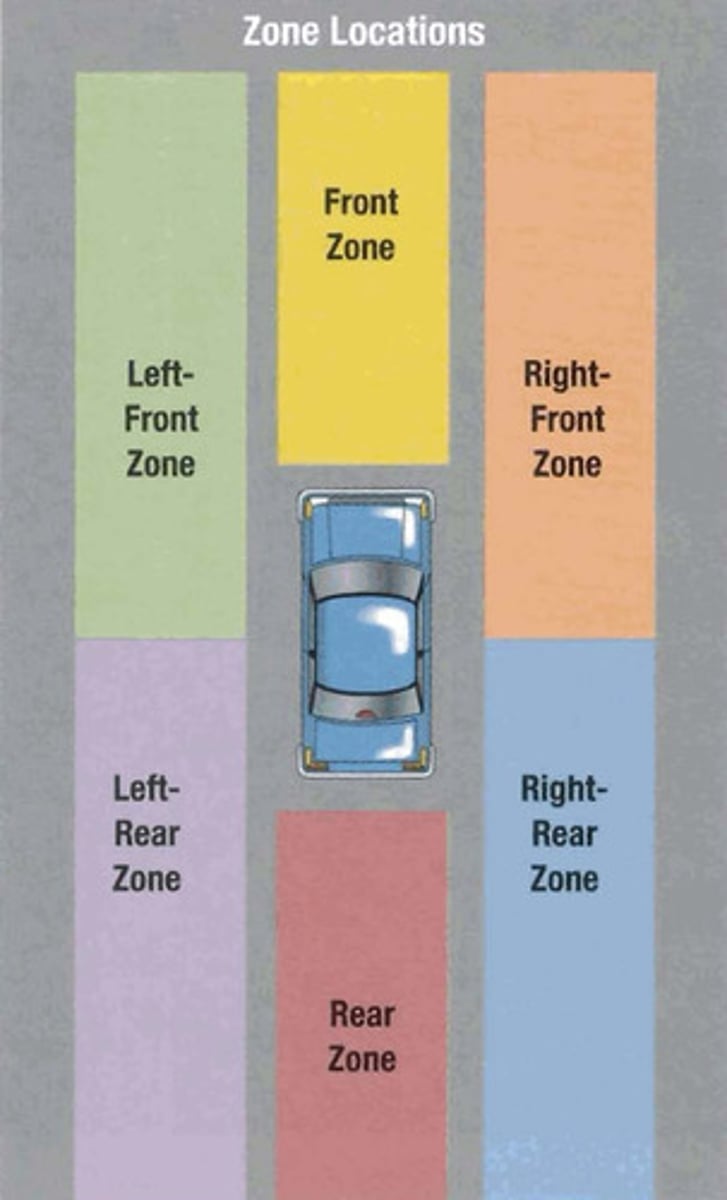
Zone
one of six areas of space around a vehicle that is the width of a lane and extends as far as the driver can see
Open zone
space where you can drive without a restriction to your line of sight or to your intended path of travel
Line of sight
the distance you can see ahead in the direction you are looking
Intended path of travel
the space your vehicle will occupy
Target area
the section of the roadway where the target is located in the center of your intended path and the area to its right and left
Closed zone
space not open to you because of a restriction in your line of sight or intended path of travel, such as a red traffic light
Target-area range
space from your vehicle to the target area
12-15-second range
space you will travel in during the next 12-15 seconds
4-6-second range
the space you will travel in during the next 4-6 seconds
Orderly visual search pattern
process of searching critical areas in a regular sequence/systematic manner
Aspects of vision
field of vision, depth perception, and scanning
Primary aspects of vision necessary for driving
central vision, peripheral vision, and depth perception
Field of vision
the area you can see around while looking straight ahead
Central vision
the area you can see clearly and sharply, a narrow cone of only up to 10 degrees
Peripheral vision
vision outside of the central vision, gets worse as distance from central vision increases
Depth percetion
the ability to judge the relative distance of objects correctly
Scanning
glancing continually and quickly with very brief fixations through your orderly visual search pattern
Why should one not stare?
blocks out side vision, causes lack of attention, and tends to create high-risk driving habits
Selective seeing
identifying and selecting only clues and events that restrict your line of sight or can change your intended path of travel
Ground viewing
making quick glances to the roadway in front of your vehicle, used to see where other vehicles are headed by checking the direction of their front wheels
Problem drivers
drivers who speed and/or pass without enough room or in a no-passing zone
Roadside hazards
bicyclists, pedestrians, parked vehicles, narrow roadways, etc.
What to do when you have identified a hazard
second step of the IPDE Process; once you identify a hazard, you predict how this hazard might affect your intended path of travel
Predict
taking the information you have identified and image what might happen
How to predict
Evaluate the situation and make a judgment about the possible consequences; scanning target areas can hep predict as well as knowledge and experience
What to predict - three major elements
actions of other roadway users, your control of your vehicle, and the consequences of your actions
Prediction actions of others - what to predict
Path, action, space, and point of conflict
What to predict about the control of your vehicle
traction, roadway, and weather conditions
Three things that hep with predicting
Knowledge, judgment, and experience