Class 10: Urinary Elimination
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
what is the purpose of the kidney in the urinary tract?
to filter out the blood and create urine
what is the purpose of the bladder
it is a smooth muscle sac that temporarily stores urrine
what is the purpose of the urethra
it transports urine from the bladder to the exterior of the body
micturition
act of passing urine
how many mL of urine stimulates the sensory nerve endings (stretch receptors) to let someone know they need to pee
150ml to 250 ml
What are stretch receptors in bladder?
sensors in blood vessels that identify internal pressure
stretch receptors transmit impulses to where?
the 2nd-4th spinal sacral vertebrae
what sphincter relaxes voluntary and involuntary?
voluntary: external sphincter
involuntary: internal sphincter
when the internal sphincter relaxes, it stimulates what?
the urge to void!
if appropriate, the brain relaxes then ________ and the _______ muscle contracts which allows urination to occur.
internal sphincter
detrusor muscle
detrusor muscle
the smooth muscle layers of the bladder wall
allows the bladder to expand as it fills with urine and contract as it releases urine during voiding
most healthy people do not
void during sleeping sessions
the more urine that is produced
the more voiding that will occur
What is a diuretic?
A medicine/substance that increases urine formation
May increase urine formation and output
voluntary sphincter control begins at age
18-24 months
nocturia
excessive urination at night
increased fluid intake means
increase fluid output
normal output range is
1200 mL to 1500 mL
foods that can affect odor and color
beets and asparagus
foods that cause fluid retention are
high in sodium food
how does exercise help to urinate?
it increases metabolism and optimal urine production and elimination
what can result in poor urinary control and stasis
immobility
decreased bladder and sphincter tone
what makes the bladder muscles weaker
indwelling catheter
muscle trauma
why do ladies have a voiding difficulties
pregnancy- baby puts pressure on bladder
old ladies- decrease in estrogen (menopause)
if the kidneys can't make urine then
toxins stay in the body
if the kidney functions are poor then the
heart functions will be poor
neurogenic bladder
a urinary problem caused by interference with the normal nerve pathways associated with urination
Impaired neurologic function interfering with urination
BPH
benign prostatic hypertrophy
when the prostate wraps around urethra in men causing retention
retention
inability to empty the bladder
incontience
inability to control urination
calculus
a urinary stone
Anticoagulants
treats blood clots
may cause possible hematuria (affects urinary elimination)
hematuria
blood in the urine
Phenazopyridine
Urinary Tract Analgesic
can cause orange urine
Antidepressants, antipsychotics, antihistamines, and opioids can
increase urinary retention and overflow incontinence
sedatives may
used slows brain activity
may worsen urge incontinence (urinary elimination factor)
NSAIDS may
decrease blood flow to kidneys leading to renal failure (factor influencing urinary elimination)
rifampin
cause urine to be orange
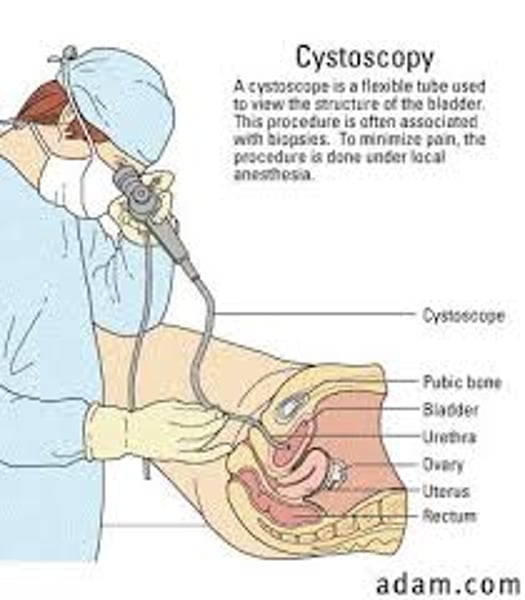
cystoscopy
visual examination of the urinary bladder, urinary bladder wall and urethra
Small kidney stones can be removed
sample tissues taken for biopsy
Retro pyelography can be done simultaneously
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
the amount of filtrate formed per minute by the two kidneys combined
anuria
absence of urine
glycosuria
glucose in the urine
oliguria
Decreased urine output.
Scant Urine Output
Oliguria output is USUALLY ___ mL
less then 400 ml/day or 30ml/hour for an adult
KNOW THESE NUMBERS (park said)
Polyuria (diuresis)
excessive urination
may be associated with diabetes mellitus/insipidus, and chronic nephritis
proteinuria
presence of protein in urine
pyuria
pus in the urine
aka white blood cells urine
aka cloudy urine
polydipsia
excessive thirst
leads to compulsive intake of excessive amounts of fluid
urinary frequency
voiding at frequent intervals
urinary urgency
sudden, compelling urge to urinate
dysuria
painful or difficult urination
urinary hesitancy
difficulty in starting a urinary stream
common in bph
describe urine
color, odor, volume
why is the bladder scanner important?
it is the best way to measure urine in the bladder and is a good way to see urine in bladder and to know what is really going on
urinating on yourself can cause
skin breakdown due to the acidity
urethral meatus
external opening of the urethra
Assessing Urine output for continent patients
use a bedpan, urinal, or specimen hat in bed or bathroom
Assessing Urine output for Incontinent patients
note number of incontinent episodes and have weight absorbent pads
indwelling catheter
remains inside the body for a prolonged time based on need
Assess every time before bag is emptied. Measure urine before flushing down the toilet
Types of urine samples
clean catch or midstream
sterile by catheterization
what does a urinalysis describe
description of urine
blood, ph, cloudiness, WBC, etc
urine culture and sensitivity
diagnostic lab procedure that identifies bacterial infection of urinary system and determines best antibiotic to treat it
Ultrasonic bladder scan
used to estimate and evaluate the volume of urine in the bladder.
Evaluate bladder emptying and post void bladder volume
what is the BUN and creatinine test for the bladder?
a blood test used to look at kidney functions. if the levels are high then the kidneys are not functioning right
Creatinine levels are usually
men: 0.6-1.2 mg
women:0.5-1.1 mg
BUN levels
7-20mg
IV pyelography
a radiographic study of the kidneys and ureters
Uses contrast dye for radiologic examinations
Visualize structural and functional abnormalities
retrograde pyelogram (RP)
x-ray image of the renal pelvis and ureters after injection of contrast through a urinary catheter into the ureters from the bladder.
Visualize fistulas, tumors, or ruptures
renal arteriography
radiographic study to assess the arterial blood supply to the kidneys
Assess renal blood flow
fistula
an abnormal passage, usually between two internal organs or leading from an organ to the surface of the body
intake and output (I&O)
term for measurements of all the fluids that enter and leave the body
REVIEW HOW TO DO IT
when do you clean a catheter
3 times a day
once a shift
after every bowel movement
what if the balance is positive or negative for I&O?
positive- more intake
negative- more output
the balance for I&O is
intake minus output
retention causes
weight gain
every 1000 ml you retain, you will gain
1 kg
urinarystasis
a stop in urinary flow
what is a good exercise to strengthen pelvic floor
kegel exercises
multiple times a day for at least three months
contract for 10 seconds, relax for 10 seconds, repeat
risk factors for catheters that are unnecessary
loss of muscle tone
uti
infection
when should you review catheter needs
daily
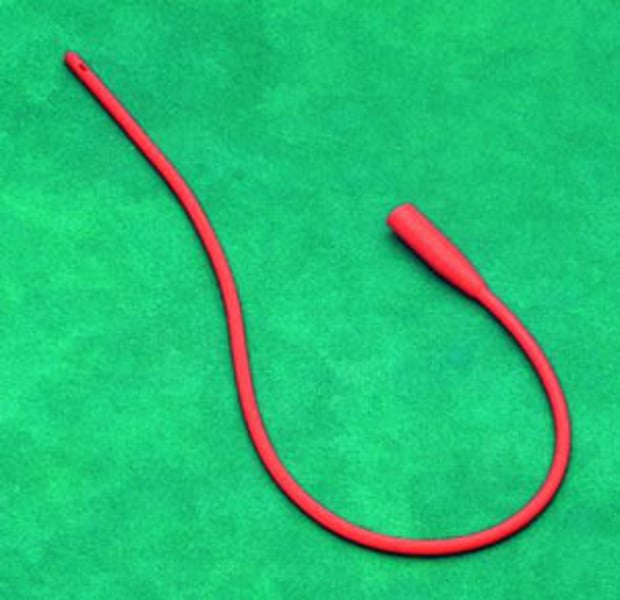
what is a straight catheter
A catheter that is inserted and removed after urine has been drained out or specimen collected

What is an indwelling/foley catheter?
retained for longer periods in the bladder by means of a small balloon that anchors it against the bladder neck
remains in place until pt is able to void completely and voluntarily or for as long as accurate measurements are needed
either two lumen or three lumen (one for drainage, one to inflate ballon and the third for irrigation)
they can be used on short-term or long-term basis
suprapubic catheter
catheter inserted into the bladder through a small abdominal incision above the pubic area
Long term continuous drainage that is surgically inserted
double lumen catheter
Designed for indwelling catheters, provides one lumen for drainage and second to inflate the balloon
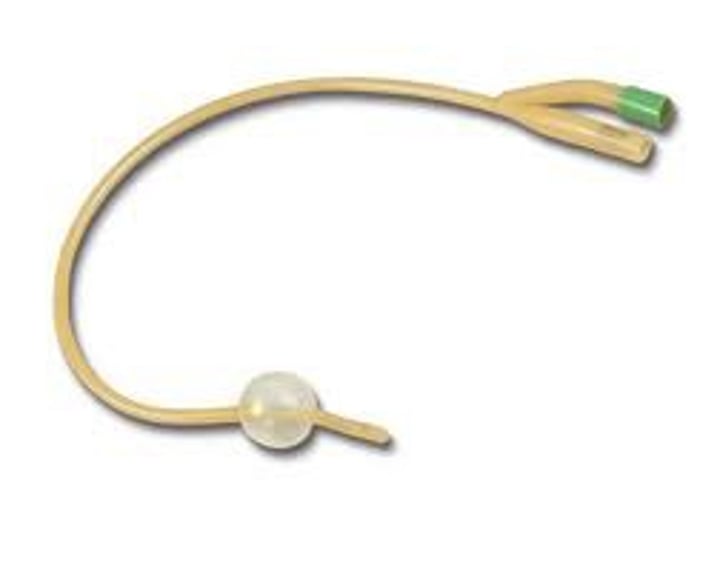
triple lumen catheter
used for bladder irrigation (1), urinary drainage (2), and inflation of the balloon (3)
where should the catheter bag be placed?
below the bladder
back flow of urine
urinary reflux
Bladder irrigation
Removes mucus, blood clots, and other tissue from the bladders
Introduces medication into the bladder
Open intermittent bladder irrigation
Insert syringe into lumen of catheter and instill solution into catheter. With syringe still connected, aspirate back to remove clots/debris. Disconnect syringe and discard returned solution and repeatedly irrigate with solution until returned solution comes back clear (e.g. without mucous, debris or clots)
Closed continuous bladder irrigation
Continuous bladder irrigation (CBI) is a medical procedure that flushes your bladder with a sterile liquid. It also removes urine (pee) from your body at the same time. Healthcare providers often use it to prevent or remove blood clots after surgery on the urinary system.
triple lumens are only really used for
surgical procedures
the urge to pee is from
pressure on the bladder
a client has an indwelling catheter and complains that he feels like he needs to urinate? what should you do?
see if the catheter is patent
what does it mean if a catheter is patent
it means the catheter is open with no kinks or anything closing it