Exercise Physiology and Environmental Factors
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
How does altitude affect oxygen delivery to tissues?
It decreases PO₂, resulting in less oxygen availability.
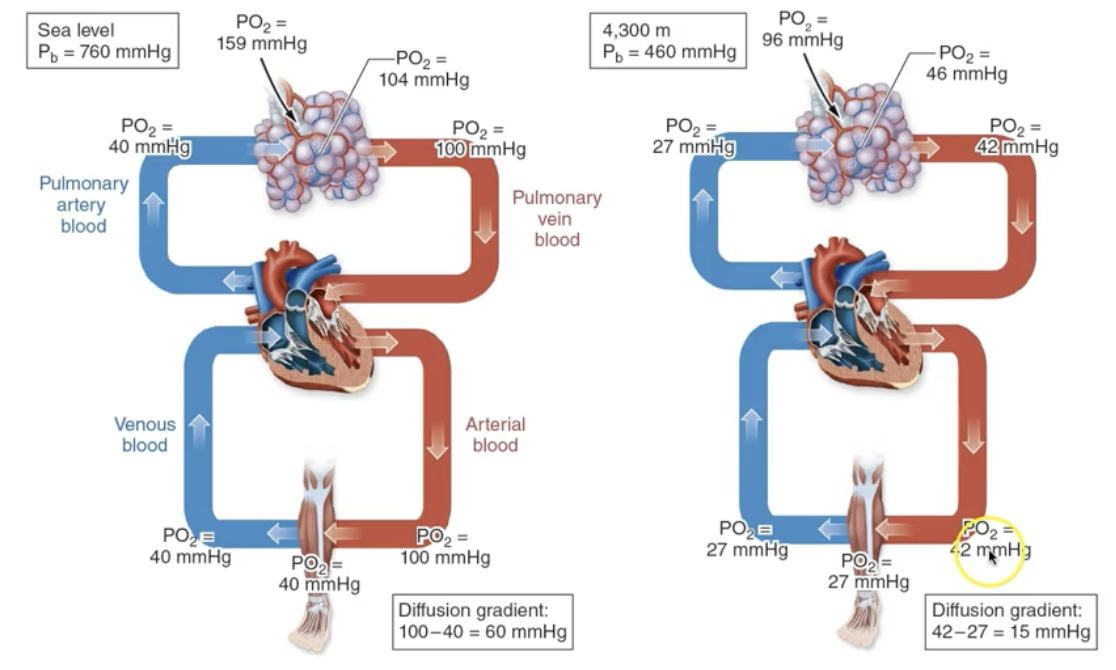
What happens to PPO2 at higher altitudes?
Less barometric pressure→Less PPO2
Do we want a larger DIFFERENCE in the arterial and venous O2 content? Why?
YES
It signifies a lot of O2 is being pulled out into the exercising muscle
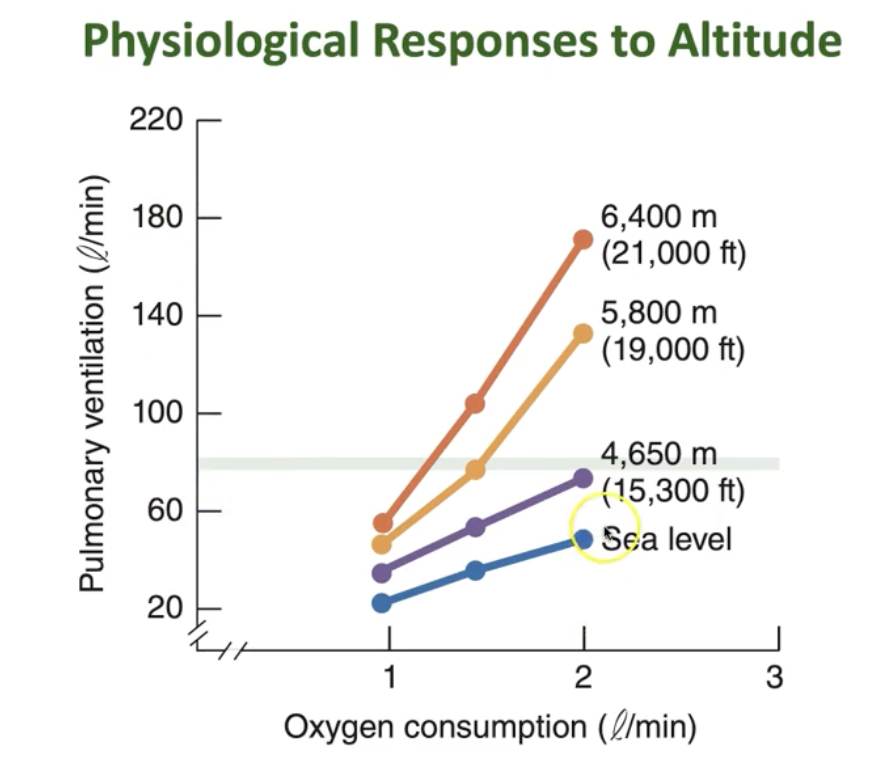
What physiological responses occur to altitude?
Increased pulmonary ventilation (More breathing)
Decreased oxygen consumption
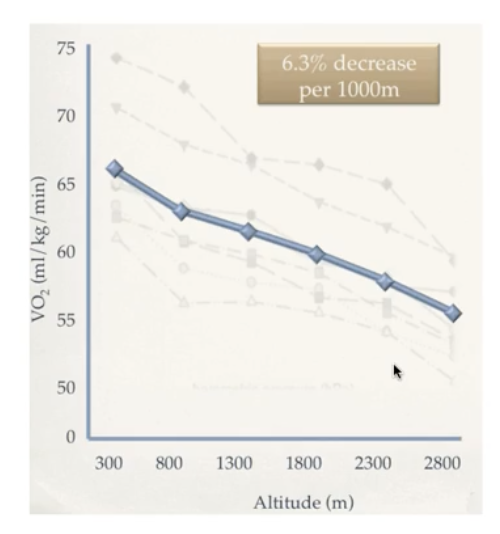
When we are more dehydrated, what happens to Hb concentration?
Decreases
What type of metabolism is preferred at higher altitudes?
CHO metabolism since we have LESS O2 available (So glycolysis would be favored)
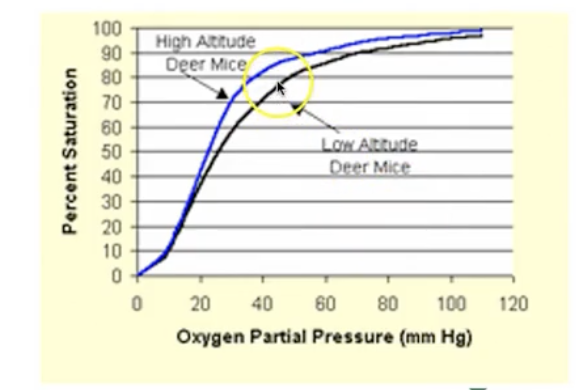
What does a leftward shift of the Oxyhemoglobin curve signify?
More binding of O2 to hemoglobin
What performance benefits are seen in short-term anaerobic activities at altitude?
Sprint/long jump performances can improve due to lower air density (Less resistance to high-speed movement)
What factors adversely affect long-term aerobic performance at altitude?
Decrease in VO2 max due to lower cardiac output
a-v O2 difference
What is acclimatization to high altitude?
Increased red blood cell production and improved oxygen transport
Can you see the effects of training at high altitudes w/o LIVING at high altitudes?
NO, you will fatigue before you can reap the benefits
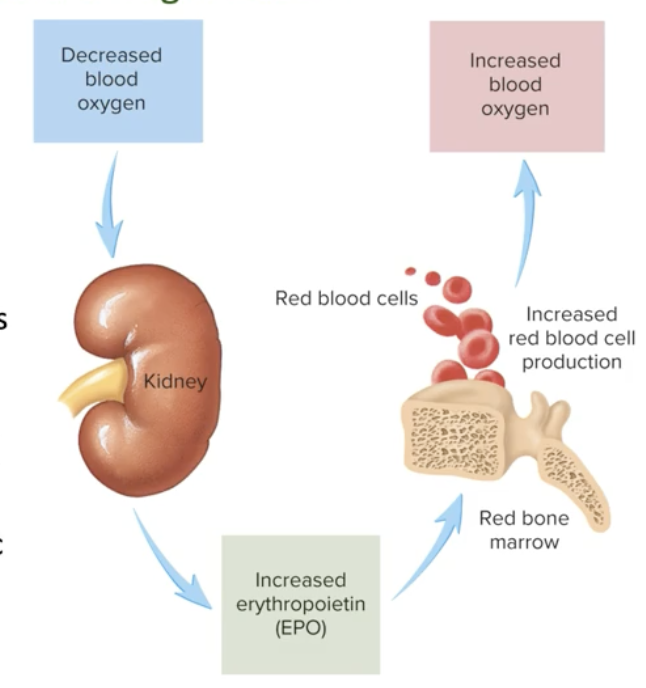
When we have a low PO2, what senses that and how does the body combat that?
Receptors sense low O2 in the cells→ HIF1 is released→ The kidneys receive that HIF1→ Kidneys release erythropoietin (EPO) → EPO goes to the bone marrow of certain bones→ in the bone marrow, EPO interacts with the stem cells of the bone marrow to produce more RBC→ RBC production Increases
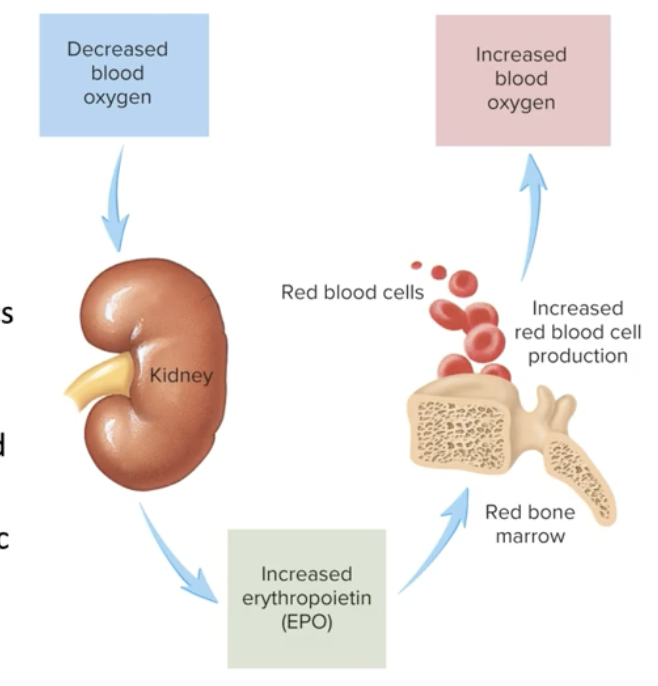
What is the role of erythropoietin (EPO) at high altitude?
Stimulates red blood cell production to improve oxygen transport.
What does Vascular Endothelial growth factor (VEGF) do?
Induces the production of blood vessels
What does Nitric Oxide synthase do?
Vasodilation
What are all the mechanisms that help the body increase O2 transport and RBC at high altitudes?
HIF1
Polycythemia
Vascular Endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
CREATES more blood vessels
Nitric Oxide Synthase (For Vasodilation)
Greater O2 saturation
Increase in plasma volume
Drop in Muscle mass
How does heat affect exercise performance?
It leads to cardiovascular dysfunction and reduced motor unit activation.
What are the main physiological responses to heat stress?
Increased heart rate
decreased stroke volume
What is the function of the preoptic-anterior hypothalamus (POAH)?
It regulates the body’s thermostat for temperature control.
What are the types of heat production mechanisms in the body?
Voluntary
Exercise
Involuntary
Shivering
Non-shivering thermogenesis
How does the hypothalamus help w/ heat production?
Hypothalamus→Pituitary→Thyroid→Thyroxine→Catecholamines
Catecholamines trigger your body to burn fuel for heat, especially via brown fat and metabolic activation.
What are the types of heat loss mechanisms during exercise?
Radiation (From the sun)
conduction (Contact of 2 surfaces)
convection (Heat transferred to air or water)
evaporation (Heat from skin converts H2O to water vapor)
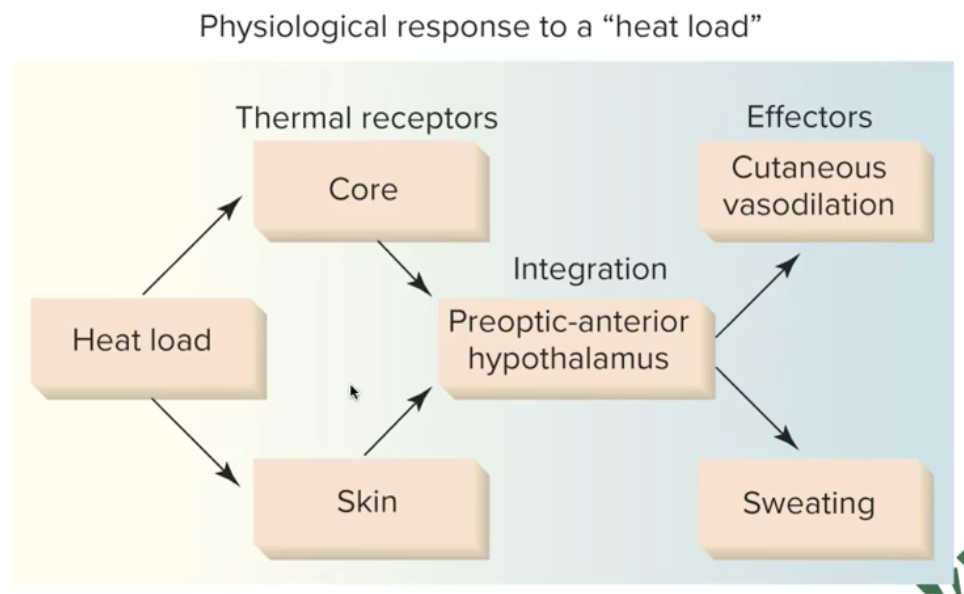
How does the Pre-optic Hypothalamus regulate the body when temp. is too high?
Vasodilating the vessels that are at the level at the skin (Allows for transfer of heat into air around us)
Sweating (evaporation)
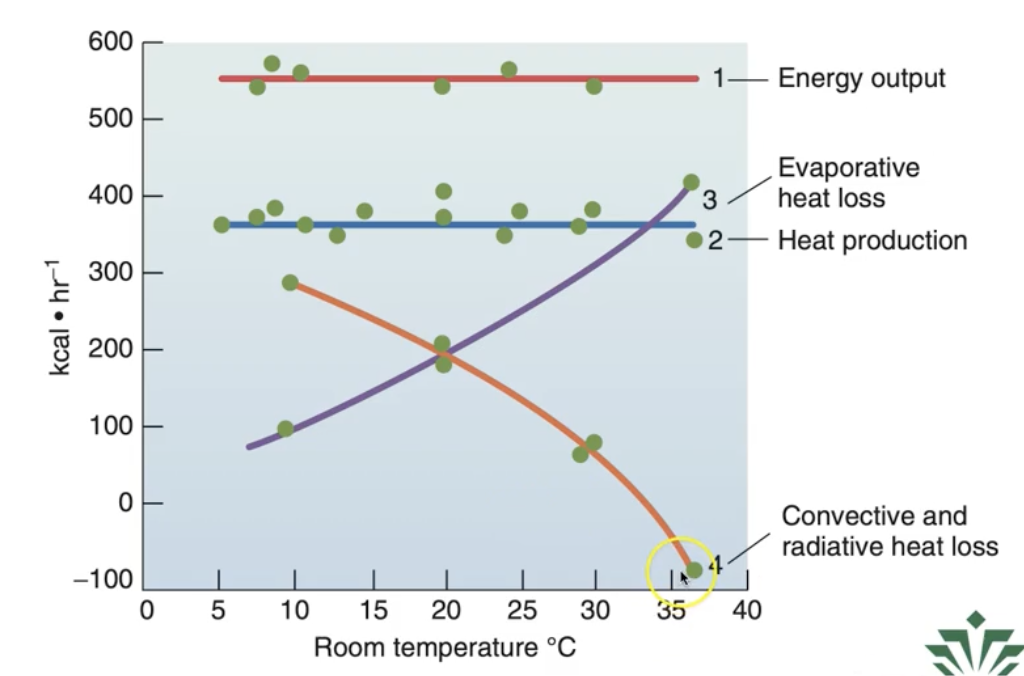
What is the greatest mech. used to maintain a steady heat production during exercise?
Evaporation
Chart shows how Temp. stays constant when looking at the effect that evap. has
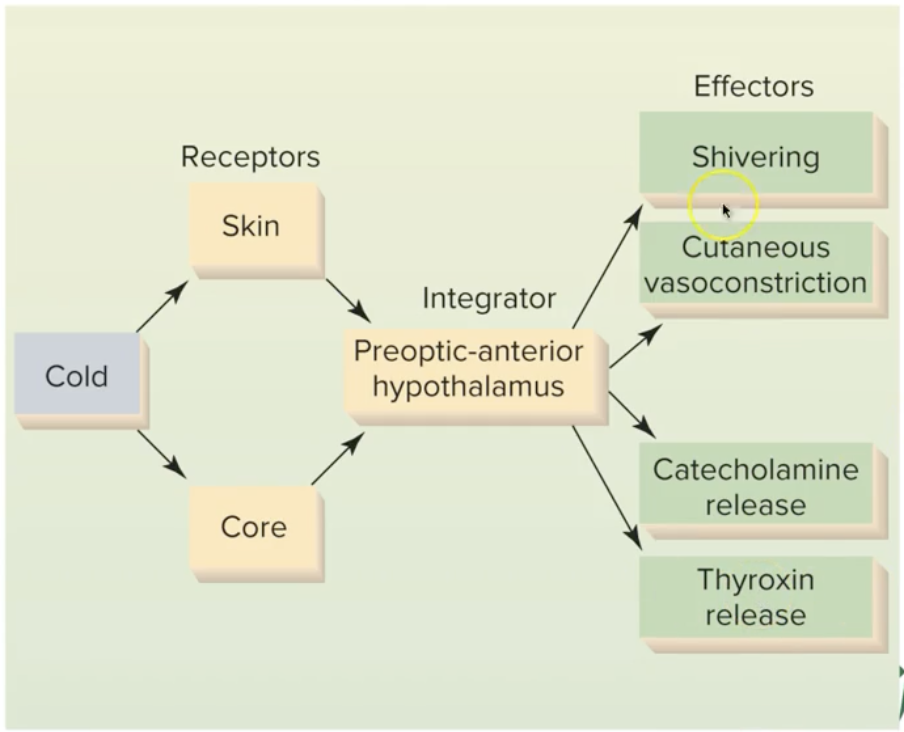
How does the Pre-optic Hypothalamus regulate the body when temp. is too low?
Shivering
Vasoconstriction
Catecholamine release
What happens when we exercise in a hot environment?
Impaired Exercise performance:
Drop in pH (Less muscle contraction)
reduces the “will” to exercise
reduction in MUR
Reduced stroke volume
Decreased cardiac output
Decreased muscle blood flow
Why doesn’t blood go to the exercising muscle during exercise in a hot environ?
The blood is going to the skin to cool off so that we don’t fry our brain
So that heat transfer can happen through the air (Convection)
Why does exercising in a hot environment reduce cardiac output?
Increased sweating→ leads to decreased blood volume→ decreases cardiac output
What is hyperthermia?
An elevated body temperature due to failed thermoregulation.
What are the 3 major factors that contribute to muscle fatigue?
Depletion of muscle glycogen
Accumulation of muscle lactate
Accumulation of free radicals
Impede cross bridge formation
These factors elevate type 3 and 4 afferent nerves (Chemoreceptors) to the CNS→ CNS tells the motor units, less activation and recruitment
What adaptations occur with heat acclimatization?
Increased plasma volume
Earlier onset of sweating
Higher sweat rate
Reduced Na+ chloride loss in sweat
Increased cellular heat shock proteins
How quickly can acclimatization be lost after inactivity?
Significant decline in 7 days, complete loss in 28 days.
What are some implications of heat illness during exercise?
Heat cramps, heat exhaustion, and heat stroke.
How can training influence the risk of heat-related illness?
Higher fitness levels relate to a lower risk of heat injury.
What is the impact of humidity on heat loss?
It decreases evaporation efficiency, increasing heat retention.
What are the symptoms of heat illness?
Cramps, lightheadedness, and decreased performance.
How does high altitude affect exercise responses?
What is the role of hormones during heat production and how do they connect w/ the preoptic Anterior hypothalamus?
Thyroxine and catecholamines boost heat production
The POAH signal pituitary which then stimulates the thyroid to release these hormones
Thyroxine boosts heat production by increasing metabolic rate, generating more body heat
How does heat impair performance?
Causing dehydration
Increasing CV strain
Reduced muscle blood flow
Accelerated fatigue
Describe adaptations for high altitude and heat?
High Altitude:
Increased RBC
Higher ventilation rate
Enhanced O2 utilization
Heat:
Increased sweat rate
earlier onset of sweating
expanded plasma volume