LEC 4: Pesticides
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
hi 2/14/25 2:26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What is the purpose of pesticide? What are they used for in agriculture?
The purpose of pesticides: To kill or harm some form of life
Pesticides are used to control various pests and disease carriers, such as mosquitoes, ticks, rats and mice 👈
Pesticides are used in agriculture to control weeds, insect infestation and diseases
There are many different types of pesticides; each is meant to be effective against specific pests
List 8 types of pesticides used in agriculture
Herbicides
Insecticides
Fungicides
Rodenticides
Larvicides
Molluscicides
Bactericides
Algacides
What are the benefits of pesticides?👈
Produces more crops on lesser land
Prevents human/livestock diseases
Controls plant-based diseases
Keeps deforestation + soil erosion in check
Helps gain food sufficiency
Do pesticides go away?
Pesticides don’t just go away
They persist in the environment where they remain and/or are transported over long distances + make their way into biological systems👈
What is bioaccumulation and biomagnification? 👈
Bioaccumulation
Buildup of higher concentrations of toxins in organisms that cannot be excreted or broken down (non-biodegradable)
Biomagnification
Buildup of toxins in organisms higher up
in the food chain (they ultimately have the most toxisn bc they eat the smaller ones)
What are some biological effects of pesticides? What does it depend on?👈
Have diverse biological/physiological effects on the exposed organism
Neurological issues (eg, Parkinson’s disease), genetic defects, impacts on the endocrine system, and developmental disorders
Specific types of cancer in some cases (eg, glyphosate exposure has been linked to non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma)
Recall: Depends on the dose (how much), duration (timeframe of exposure) and frequency (how many exposure events)!
What are 3 ways of grouping pesticides? (classification based on..)
Classification based on the mode of entry/action
Classification based on pesticide function and the pest organism they kill (targeted)
Classification based on the chemical composition of the pesticide --- the most common and useful method --- because this method gives the clue about the efficacy, physical, and chemical properties of pesticides👈
There are 4 classification Based on the chemical composition of the pesticides: explain these 2 Organochlorbines + Organophosphates - what do they target + what animals
Organochlorines
The main effects of organochlorine pesticides are on the nervous system by interfering with different ion channels, namely GABA receptors
Are persistent and frequently can bioaccumulate in fat tissues of aquatic organisms such as fish and crustaceans
Organophosphates
A group of synthetic chemicals that poison insects and mammals by damaging an enzyme in the body called acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase: An enzyme that is critical for controlling nerve signals in the body
The damage to this enzyme kills pests and may cause unwanted side effects in exposed humans
These pesticides are non-persistent
However, organophosphates are more toxic to humans and other mammals than, for example, carbamates
There are 4 classification Based on the chemical composition of the pesticides: explain these 2: Carbamates + Pyrethrin + pyrethroids - what do they n where are they used
Carbamates
Also work by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase
benefits to society, as
they protect and increase agricultural production,
protect human and animal health from insect-vector-mediated diseases
Overexposure of humans and animals to these pesticides often results in poisonings
Pyrethrin and pyrethroids
Alter the activity of the sodium ion channels of nerves
Commonly used to control insects in various settings, including households, gardens, and agriculture
Pesticides vary in the number of species they control - describe broad-spectrum pesticides + narrow-spectrum pesticides
Broad-spectrum Pesticides
Non-selective
Developed to kill a large range of pests (including beneficial ones)
Typically work by attacking the muscular or nervous system
eg, most organochlorines, organophosphates, pyrethroids
Narrow-spectrum Pesticides
Selective 👈
Targets only the intended organism(s)
Designed to interact with a characteristic of the pest that is specific to that organism, such as a pheromone, hormone or physical feature (eg, molting/shedding)
eg, diacylhydrazines
Organochlorines + organophosphates are broad-spectrum - how many pests are they developed to kill?
Broad-Spectrum:
developed to kill a large range of pests (including beneficial ones) aka non-selective pesticides
eg, organochlorines, organophosphates 👈
Most are lipophilic compounds = readily enter the tissues of organisms!
Exposure to roundup (glyphosate) has been linked to the development of certain cancers in humans (eg, non-Hodgkin lymphoma)!
Are pyrethrin + pyrethroids broad spectrum agents?
Pyrethrin and pyrethroids (synthetic derivatives of pyrethrin)
Both are broad spectrum agents👈
Target a wide range of pests in both agricultural and non-agricultural settings
Are carbamates narrow-spectrum or broad?
Narrow-Spectrum:
aka selective pesticides, target only the intended organisms
eg, Diacylhydrazines
Explain the 2 sources of natural pesticides: organic + inorganic
Organic Pesticides
eg, pyrethrum, nicotine, neem oil, and all botanical pesticides are products of living organisms
Often, they are chemicals that plants and microbes use to protect themselves from parasites, predators, and pathogens
Organic pesticides are often lower in toxicity than older synthetic pesticides but this is not always the case. Organic does not necessarily equal low toxicity and environmentally safer.
Inorganic Pesticides
eg, borates, silicates, and sulfur are minerals that are mined from the earth and ground into a fine powder
Some work as poisons and some work by physically interfering with the pest. Older "inorganics" included such highly toxic compounds as arsenic, copper, lead and tin salts
Current inorganic pesticides are relatively low in toxicity and have a low environmental impact
Explain the 3rd source of natural pesticides: Biorational pesticides. Included is a diagram that shows the similarities + differences in organic + inorganic compounds
Biorational Pesticides
Have minimal impact on species for which they are not intended (called non-target species). Biorational pesticides include certain plant oils, insecticidal soaps, microbials (such as Bacillus thurengienesis and entomopathogenic nematodes), botanicals (made from plants) and insect growth regulators. The biorational pesticides should therefore be your first choice whenever a pesticide is needed
Refer to synthetic, organic, or inorganic pesticides that are both low toxicity and have a very low impact on the environment
What are natural pesticides? List 3 advantages + disadvantages.
Plants produce many natural pesticides that they use for their own defense against insects and disease organisms 👈
Advantages:
Eco-friendly
Safer for user
Very effective when used carefully
Disadvantages:
Short-term activity
May be more expensive than older conventional pesticides
Less narrow-spectrum quality (especially when compared to newer synthetic pesticides)
Chrysanthemum (shown above) contains a natural neurotoxin (pyrethrins) that attacks the nervous system of all insects without causing harm to birds and mammals
What are signal words for relative toxicity of pesticides? Caution, warning, danger
Describes the acute (short-term) toxicity of a pesticide
The (toxicologically) appropriate signal word MUST appear on every pesticide label
CAUTION: LD50 of greater than 500 mg/kg
Lowest degree of relative toxicity
WARNING: LD50 of greater than 50 to 500 mg/kg
Reflects an intermediate degree of relative toxicity
DANGER: LD50 of 50 mg/kg
Reflects highest degree of relative toxicity
Signal words - toxicity of pesticides - Caution, warning, danger, danger-poison
Signal words for relative toxicity of pesticides blue graph
How does pesticide resistance develop?
Pesticide resistance can develop over time when pesticides with the same mode of action (same way of affecting pests) are repeatedly applied in the same area
Resistance occurs when a pesticide exhibits reduced effectiveness or no longer controls the pest population at the formerly effective rate 👈
How do insects develop resistance to insecticides (3)?
Insects develop resistance to insecticides through a variety of mechanisms, including:
Mutations in genes that target insecticides
Increased detoxification
Behavioral changes👈
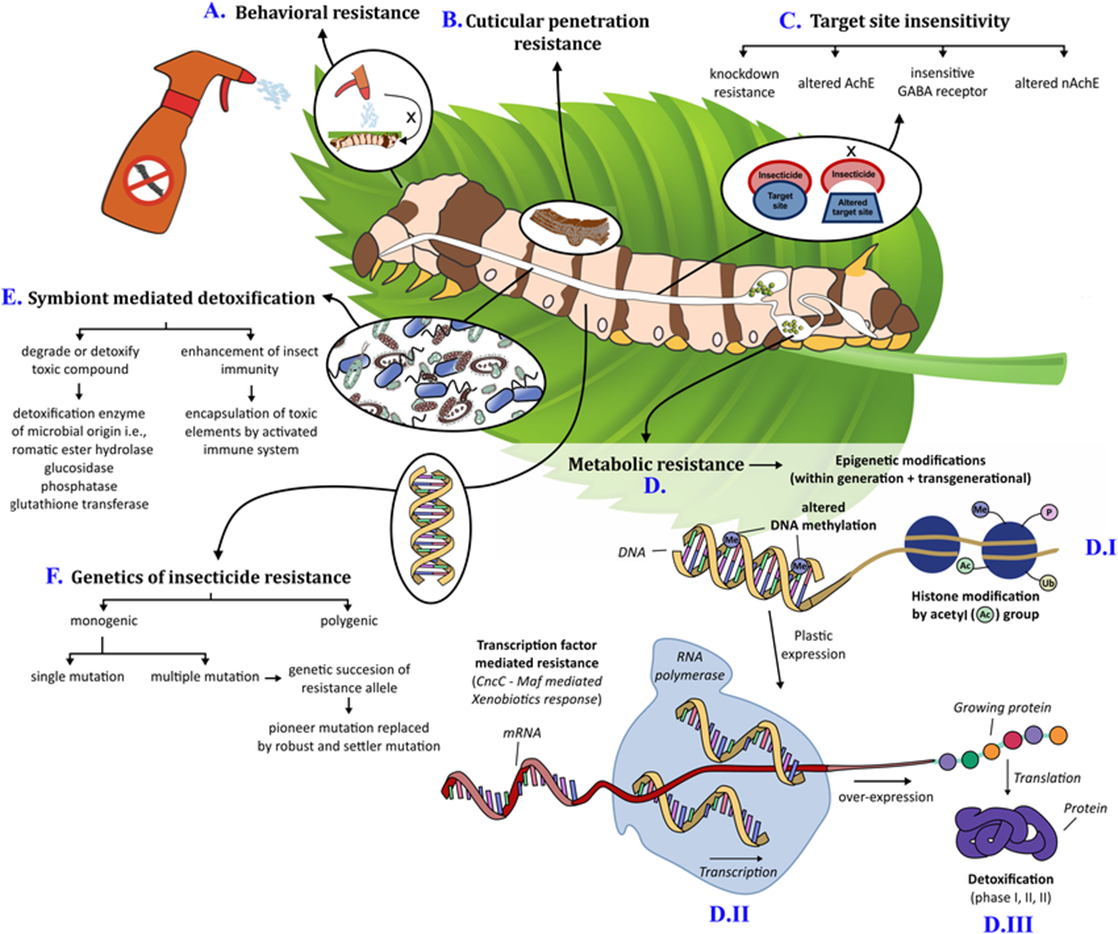
What is Genetical Modified Organisms (GMO) -what does it create
A genetically modified organism, or GMO is a plant, animal, bacteria, virus or other organism whose genetic makeup has been modified in a laboratory using genetic engineering or transgenic technology
This creates unique combinations of plant, animal, bacterial, and virus genes that do not occur in nature or through traditional crossbreeding methods
List some benefits + risks of GMOs