OCR Gateway Chemistry (separate, higher)
1/72
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Melting Point
The temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid.
Boiling Point
The temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas.
A change of state is…
the transformation of a substance from one physical state to another, such as solid to liquid or liquid to gas.
New substances are made in…
A chemical reactions and involve chemical changes. Not often reversible (except in reversible reactions)
Dalton’s Model 1803
Atoms cannot be broken down
Atoms are different for each element
Smallest particle
Thomson’s Model 1897
Discovered electrons as negative particles
Atoms contain positive charge with electrons embedded
Plum pudding model
Gold Foil Experiment
Alpha particles fired at gold foil, proved that the atom is made up of a positive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negative electrons
Rutherford’s Model 1911
Planetary Model
Central positive nucleus containing most of the mass
Electrons orbit the nucleus
Bohr’s Model
Electrons occupy energy levels (shells)
Sub-atomic particles
Name | Relative Mass | Charge |
Electrons | 1/2000 (ish) | -1 |
Protons | 1 | +1 |
Neutrons | 1 | 0 |
Isotopes
Same number of protons, different number of neutrons resulting in different atomic masses.
Ions
Different number of electrons than the element, can have different chemical properties. Charged Particles
Element
Contains atoms with the same atomic number
Compound
Contains two or more elements bonded together
Mixture
Contains two or more different substances, not bonded, can contains elements and/or compounds
Formulation
A mixture designed to be useful, contains specific amounts of each substance
Purity
A pure substance consists of only one compound or element, has a set boiling point
Simple distillation
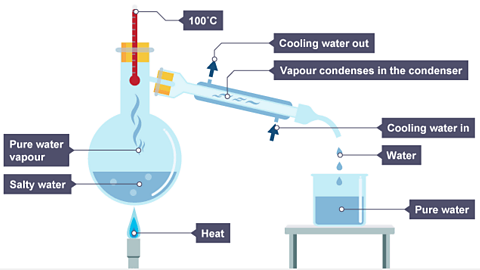
Used to separate a compound from a solution based on different boiling points.
Fractional distillation
Used to separate liquids from a mixture of liquids, as they all have different boiling points.
Crystallisation
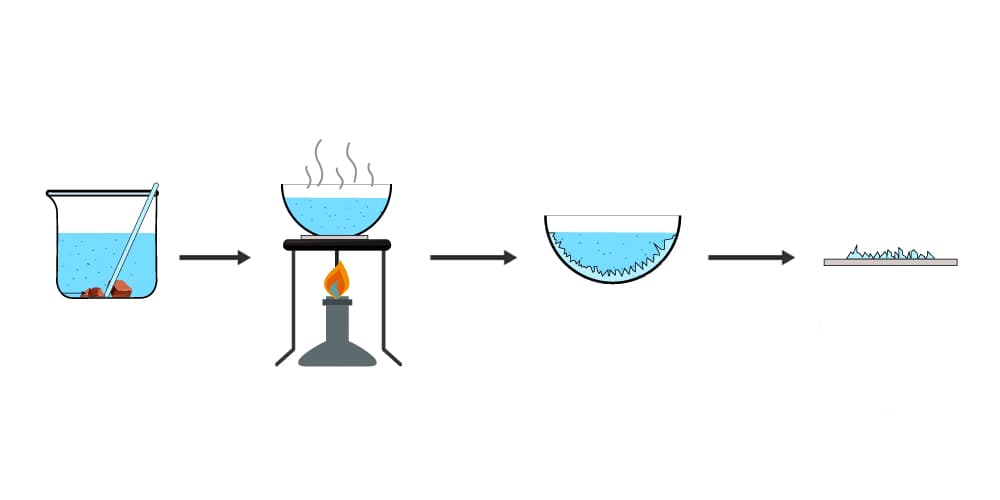
Used to produce solid crystals from a solution by evaporating the liquid leaving solid crystals behind
Filtration
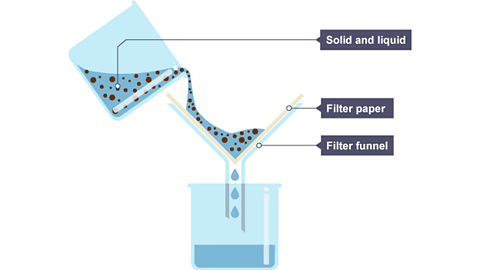
Used to separate a mixture of an insoluble solid from a liquid
Paper chromatography
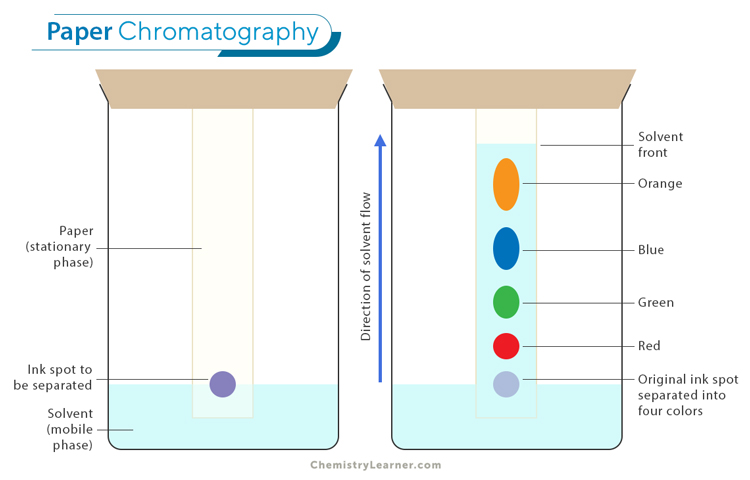
Thin layer chromatography
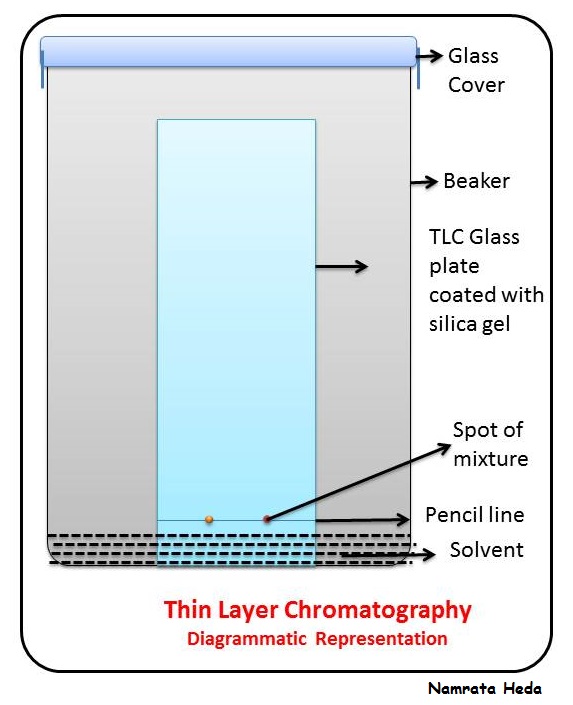
Rf value
Difference travelled by substance divided by the distance travelled by solvent.
Mendeleev’s periodic table 1869
Arranged elements in order of increasing mass, & arranged elements with similar properties below each other, leaving gaps for undiscovered elements
Modern periodic table
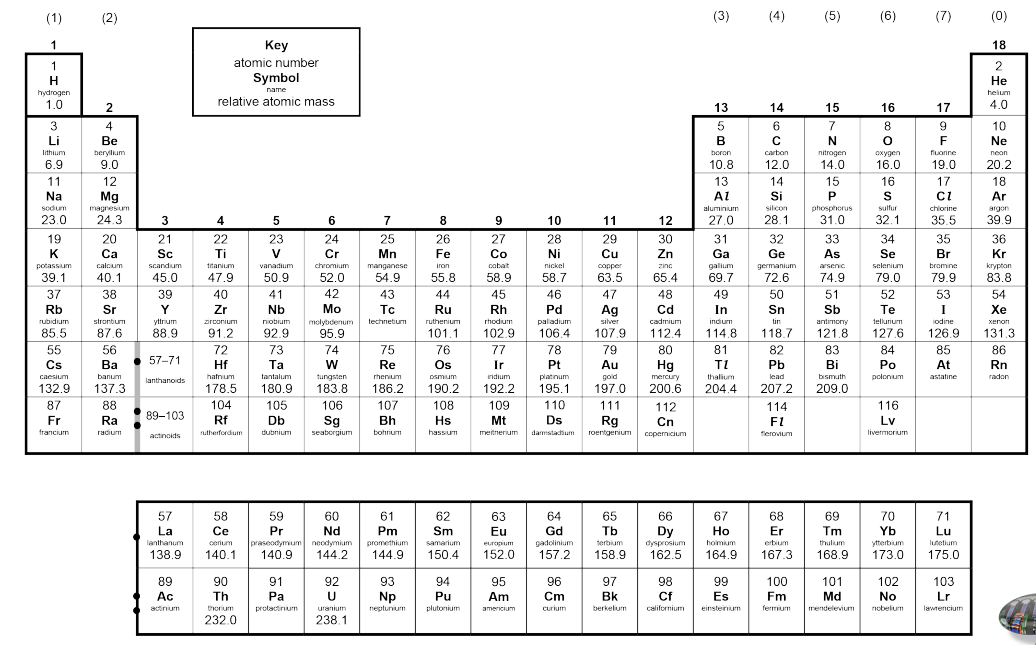
Horizontal rows are periods in order of increasing atomic number. Vertical columns are groups, arranged by similar properties. Metals on the left hand, non-metals on the right, transition metals in the middle
Physical properties of metals
Shiny
High BP
Good Conductors of electricity & heat
High Density
Malleable
Physical properties of non-metals
Dull
Low BP
Poor Conductors (insulators)
Low Density
Brittle
Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonds are formed when a metal atom transfers one or more of its electrons to a non-metal atom, to have a full outer shell, resulting in the formation of positively and negatively charged ions that are held together by electrostatic forces. Ions in an ionic compound are arranged in an ionic lattice.
Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are formed when two non-metal atoms share one or more pairs of electrons, achieving full outer electron shells.
Simple molecular
Elements or compounds, held together by covalent bonds. These substances often have low melting and boiling points and may exist as gases or liquids at room temperature. Only contains a few covalent bonds
Giant covalent
Contains many atoms and covalent bonds
Usually consists of carbon
e.g Diamond,graphite and fullerenes
Usually very high mp and bp
Metallic bonding
Electrons leave outer shells, forming positive metal ions & a sea of de-localised electrons. Regular arrangement forming a metallic lattice.
Avagadro’s Constant
6.022 × 1023 atoms per mole.
The mole is
A unit of measurement for the amount of a substance. E.G. 12g of Carbon is 1 mole of carbon
Mass of an atom =
Ar of substance / Avagadro’s constant
Molar mass
The mass of one mole of that substance
Is equal to the Ar or Mr of the substance
Mass (g) =
Molar mass (g/mol) * amount (mol)
Limiting reactants
The substance used up in a reaction
Exothermic
Gives out energy (hot)
e.g. combustion
Endothermic
Takes in energy, temperature decreases
e.g. electrolysis
When bonds break
energy is taken in, energy is released when these bonds reform. If endothermic more energy is taken in then given out. If exothermic more energy released than taken in.
Reaction profile, endo or exo?
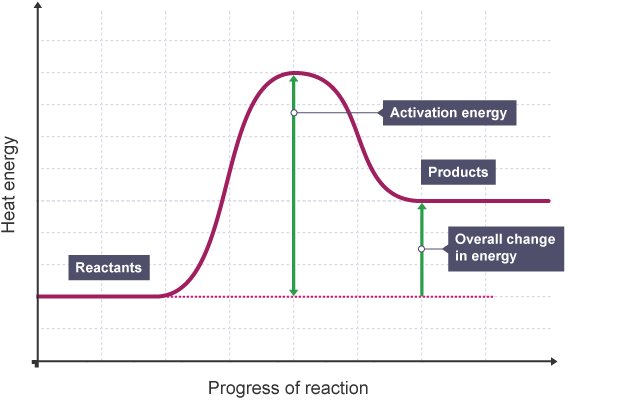
Endothermic
Product line higher than reactant line - meaning more energy taken in then given out
Reaction profile, endo or exo?
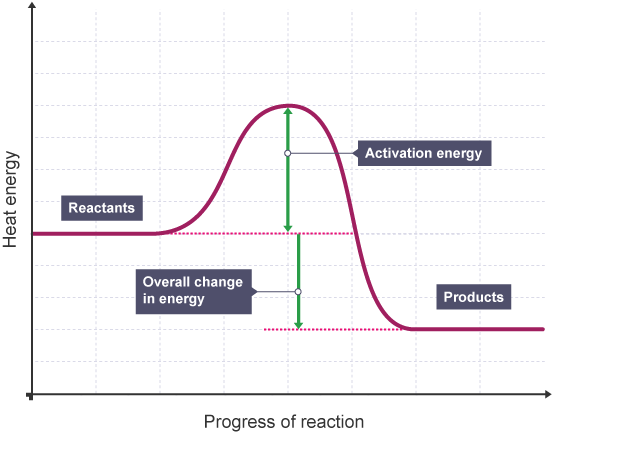
Exothermic
Product line lower than reactant line - meaning more energy is released than taken in.
Bond energies
used to calculate energy changes in reactions.
Energy change = energy in - energy out
Oxidation (reactions)
Gain of oxygen
Reduction (reactions)
Loss of oxygen
Oxidation (electrons)
Loss of electrons
Reduction (electrons)
Gain of electrons
OILRIG
oxidation is loss, reduction is gain
Acids
Sources of H+ ions
Acidic solutions
Alkalis
Sources of OH- ions (hydroxide)
Alkaline solutions
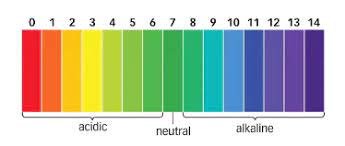
pH scale
Less than 7 = acidic (Often red - orange with universal indicator
Equal to 7 = neutral (Green)
More than 7 = alkaline (Turquoise - blue)
A pH meter can also be used to measure the pH of a solution
A base
A substance that reacts with acid to from exclusively an acid and water
An alkali is a soluble base
Neutralisation
A chemical reaction where an acid reacts with a base forming a salt and water
Usually an acid+metal hydroxide = salt + water
Acid + metal
Salt + hydrogen
Acid + carbonate
salt + water + carbon dioxide
Nitric acid
Nitrate salt
Phosphiric acid
Phosphate
Hydrochloric acid
Chloride
Strong acids
Completely dissociate in a solution
Weak acids
Partially dissociates in a solution
Electrolytes
Ionic compounds, either molten or dissolved in water
Cations
Positively charged ions
Anions
Negatively charged ions
Cathode
Negatively charged electrode, attracts the cations
Anode
Positively charged electrode, attracts the anions
At the cathode…
Cations gain electrons
At the anode…
Anions lose electrons
At the cathode (solutions)
Metals are produced if it is less reactive than hydrogen
Hydrogen will be produced if it is more reaction than the metal
At the anode (solutions)
Oxygen is produced unless halide (group 7) ions are present & will form their respective halogens
Electroplating
Uses electrolysis to put a thin layer of metal onto a metal object
This can be to prevent corrosion or for appearance
Purifying copper
Uses electroplating
The cathode is pure copper
The anode is impure copper
The solution is copper (III) sulfate
This allows for the transfer of copper ions from the anode to the cathode, resulting in purified copper.