ch17 - chloroplast and light dependent reaction
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What occurs during photosynthesis and what is the chemical reaction?
During photosynthesis light energy is absorbed and used to make glucose from carbon dioxide and water
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
is photosynthesis endothermic or exothermic
it is endothermic because it takes in energy
What occurs during aerobic cellular respiration and what is the chemical reaction?
During respiration glucose is broken down into carbon dioxide and water releasing energy which is temporarily stored in the form of ATP
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
is aerobic cellular respiration endothermic or exothermic
it is exothermic because it takes releases energy
What is the link between photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
Both of these processes occur in plants, the raw materials of one are the products of the other and vice versa
What are the 2 stages of photosynthesis and where do they occur?
Light dependent reaction which occurs in the thylakoid membrane
Light independent reaction which occurs in the stroma
what is another name for light dependent reaction
Z scheme
what is another name for light independent reaction
Calvin cycle
What is the site of photosynthesis?
Chloroplasts
What are the 2 functions of chloroplast ?
To absorb light energy
To convert light energy into chemical energy
What are the 7 structures in the chloroplast
Thylakoids
Grana
Intergranal lamella
Stroma
Starch grains
Ribosomes
Chloroplast DNA
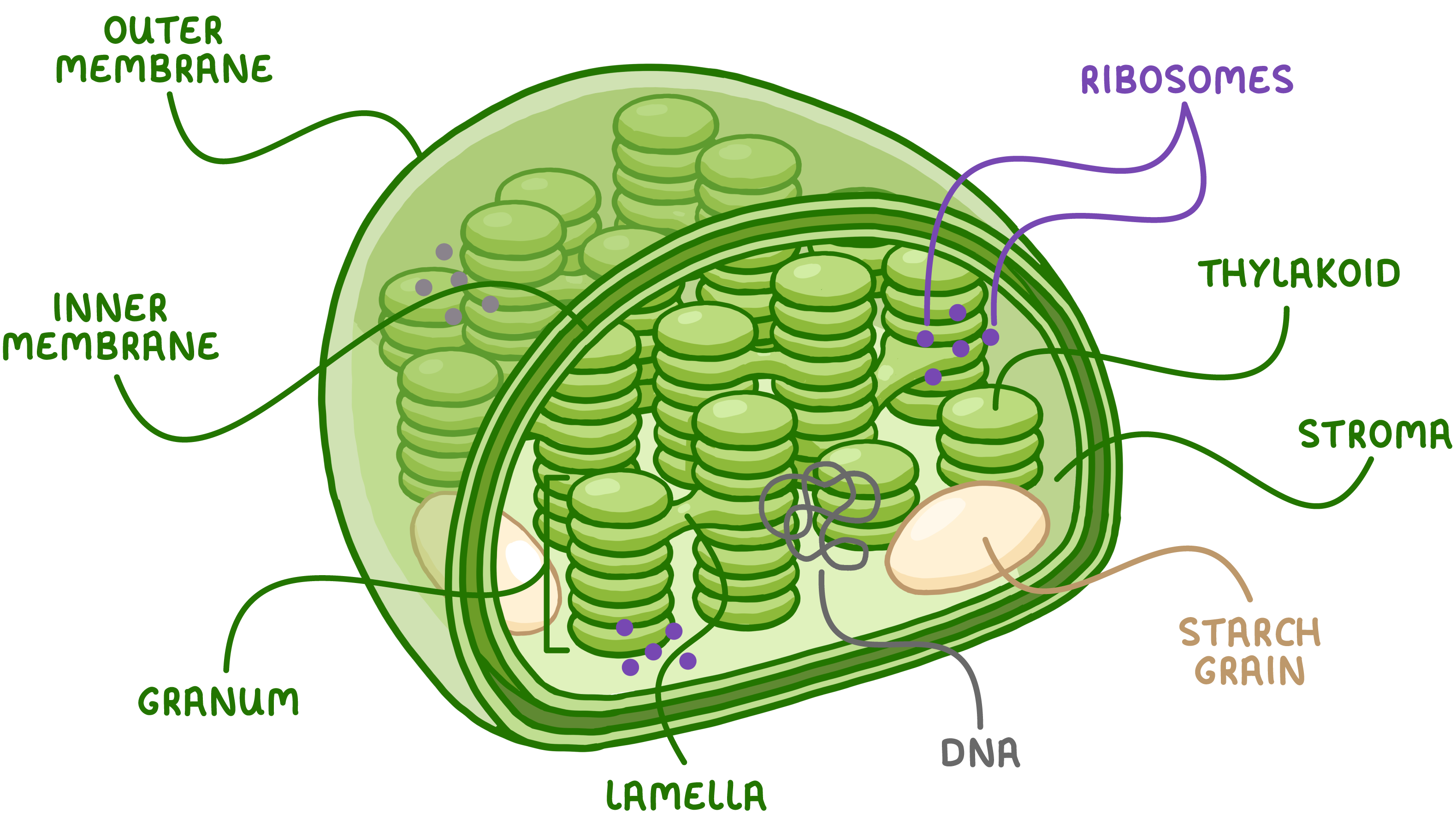
what is the function of these 7 structures
Thylakoids - flattened membranous sacs that contain photosystems with photosynthetic pigments
Grana - stacks of thylakoids
Intergranal lamella - extensions that connect grana together
Stroma - the fluid within the chloroplast
Starch grains - energy storage/ it stores glucose molecules
Ribosomes - for protein synthesis to create the enzymes coded by chloroplast DNA
Chloroplast DNA - contains its own DNA that has genes which code for enzymes involved in photosynthesis
What are photosystems and how many are there and their names?
> they are clusters within the thylakoid membrane that contain the photosynthetic pigments
> there are two:
Photosystem I
Photosystem II
What are photosynthetic pigments?
Pigments found within photosystems which absorb light
What are the 3 photosynthetic pigments and name their functions?
Chlorophyll a - main pigment, absorbs red & blue light and reflects green light (which is why most plants look green)
Chlorophyll b - accessory pigment
Xanthophylls and carotenoids - accessory pigment
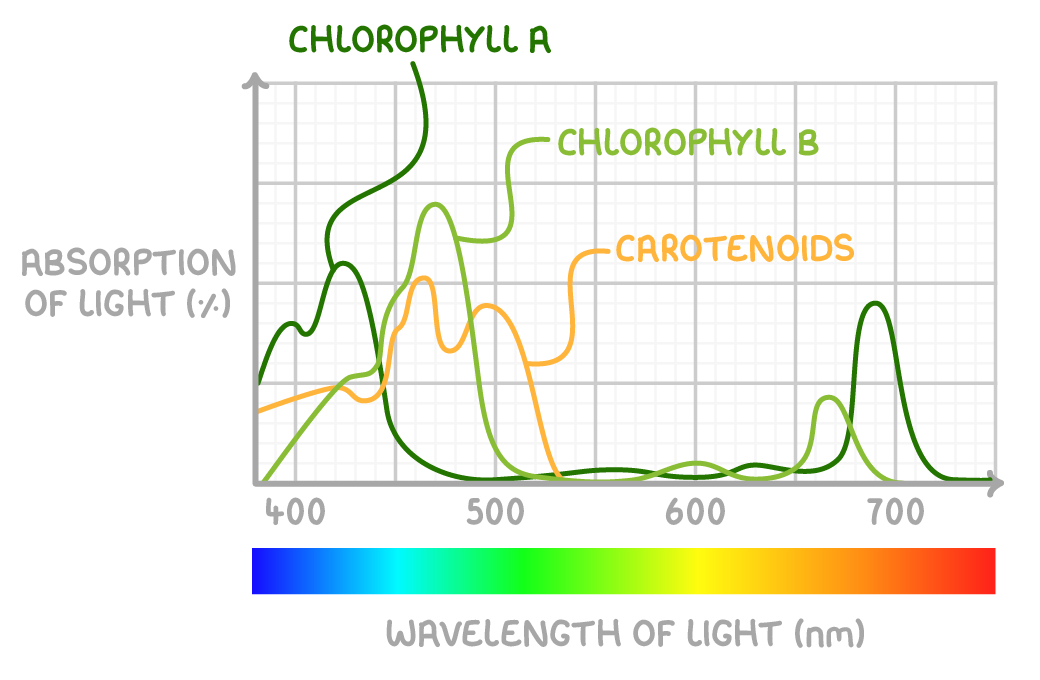
What is the function of accessory pigments?
they absorb other wavelengths of light to chlorophyll A which broadens the spectrum of light taken in
What do both photosystems have and what pigments do they contain
Light harvesting system = contains chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and xanthophylls + carotenoids
Reaction centre = contains two chlorophyll A molecules
How do the light harvesting system and reaction centres work together?
> light harvesting system absorbs the light energy which is transferred to the reaction centre
> reaction centre emits high-energy electrons
What is absorbed by photosystem I and II?
Light energy from the sun
What is the role of light energy absorbed by the photosystems?
Light energy excites electrons in Photosystem I and Photosystem II, boosting them to higher energy levels
light dependent reaction
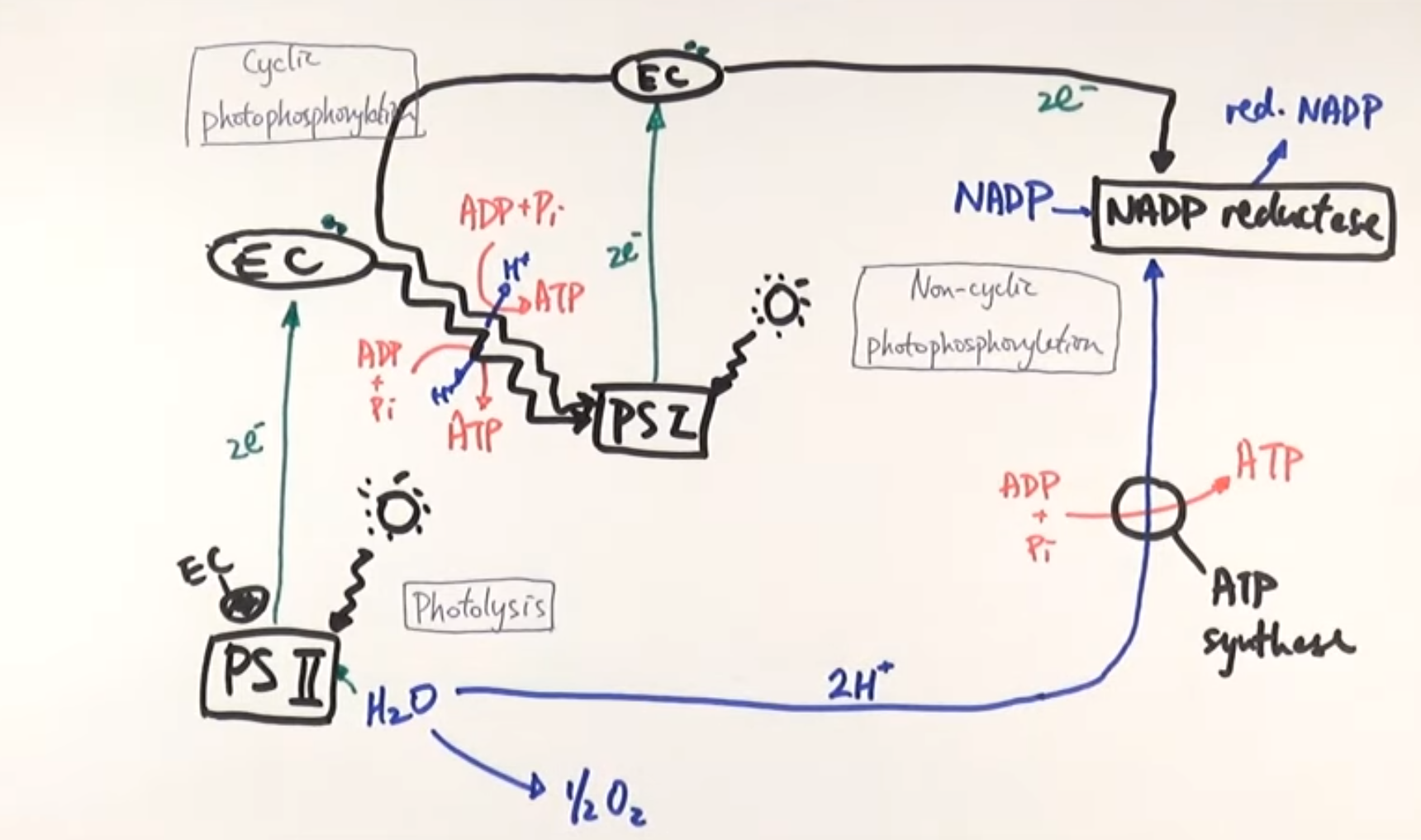
What molecule enters and is then broken down at Photosystem II?
Water molecules enter the thylakoid membrane into photosystem II and are broken down through photolysis
What is photolysis and what does it produce?
Photolysis is the splitting of water to produce 1/2Oxygen molecule and 2hydrogen molecules, protons and 2 electrons
What happens to the oxygen released during photolysis?
Oxygen is released as a byproduct
What happens to the protons released during photolysis?
Protons are used later during noncyclic phosphorylation
What happens to the electrons released during photolysis?
They enter Photosystem II and become excited by light energy
What are electron carriers?
Electron carriers take up excited electrons and transport them through the electron transport chain
What happens to electrons as they move through the electron transport chain?
As electrons move through the electron transport chain, they lose energy, which is used to pump protons and create ATP
Where do electrons arrive after passing through the electron transport chain from Photosystem II?
Photosystem I
What happens to electrons at Photosystem I?
Electrons at Photosystem I absorb more light energy and become re-excited
What are the two possible pathways for electrons after excitation at Photosystem I?
Electrons can either go into cyclic photophosphorylation OR go into noncyclic photophosphorylation
What is cyclic photophosphorylation?
Where electrons travel back down the ETC to photosystem 1 to make more ATP
What is noncyclic photophosphorylation?
Where electrons meet up with the previously released protons at the enzyme NADP reductase to reduce NADP into NADPH/ reduced NADP
Before the protons arrive at NADP reductase what other enzyme do they pass by?
ATP synthase
How does ATP synthase produce ATP?
ATP synthase uses the energy from protons moving across the thylakoid membrane to phosphorylate ADP, forming ATP
What is the purpose of the light-dependent stage?
use light energy to produce ATP and NADPH/reduced NADP
What are the products of the light-dependent stage that are then used in the light independent stage/ calvin cycle?
ATP and NADPH