Motor Pathways II: Corticobulbar Pathway and other Relevant Information from the Brainstem
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
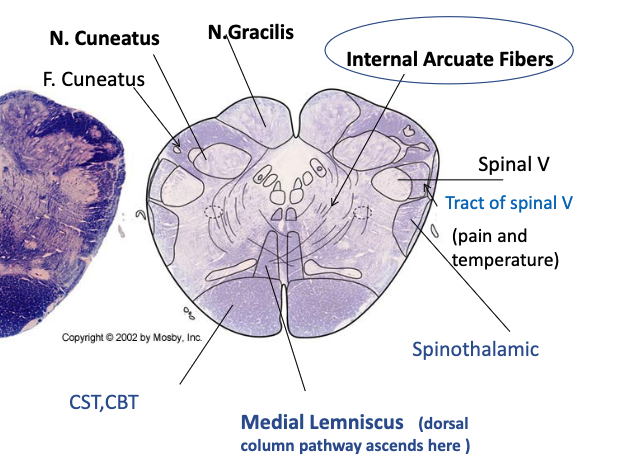
where is the decussation of the dorsal column pathway?
caudal medulla via internal arcuate fibers to form the medial lemniscus
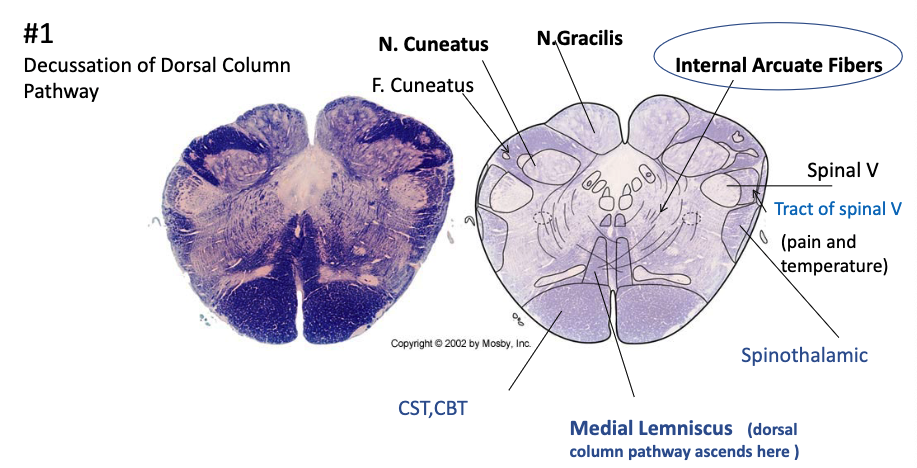
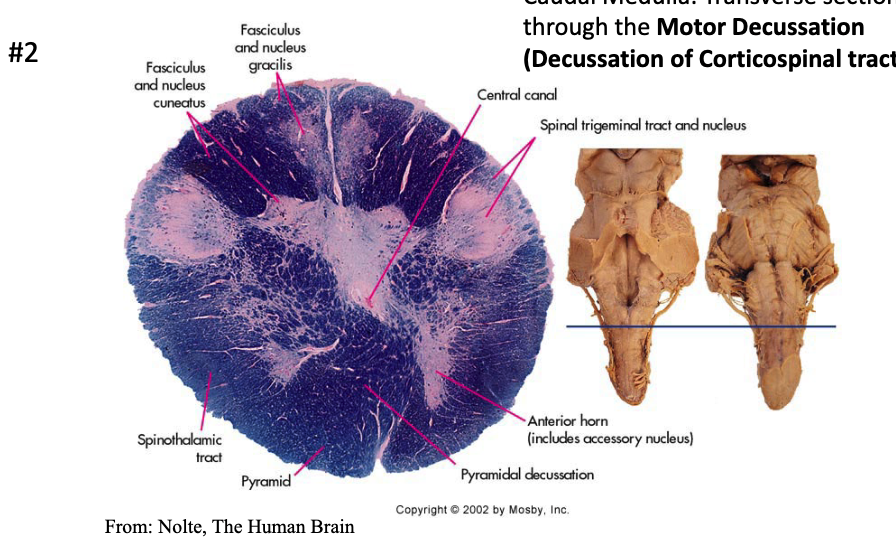
where is the decussation of the corticospinal tract?
at the caudal medulla, specifically at the pyramidal decussation
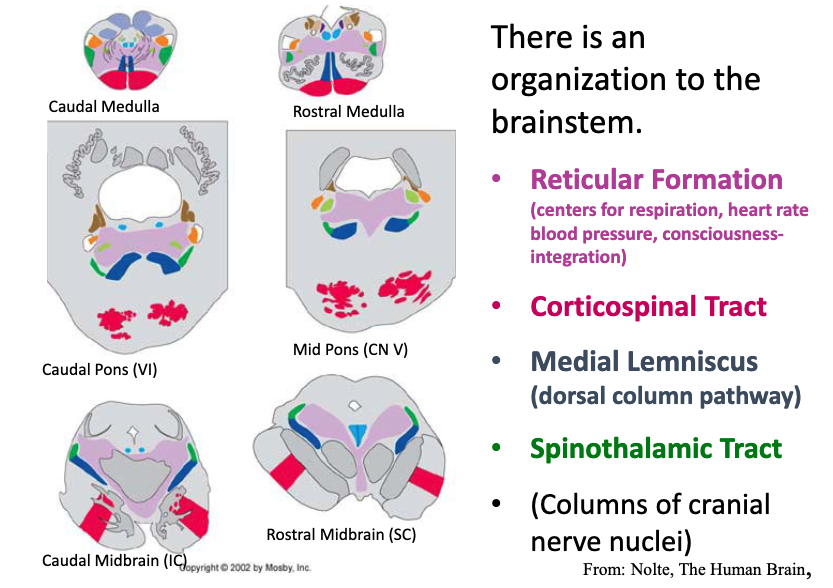
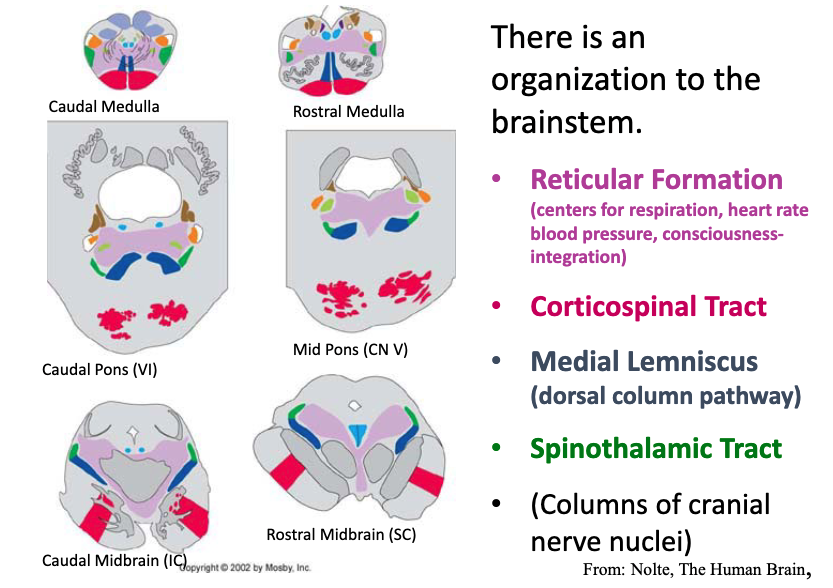
the reticular formation is important for…?
centers for respiration, heart rate blood pressure, consciousness-integration
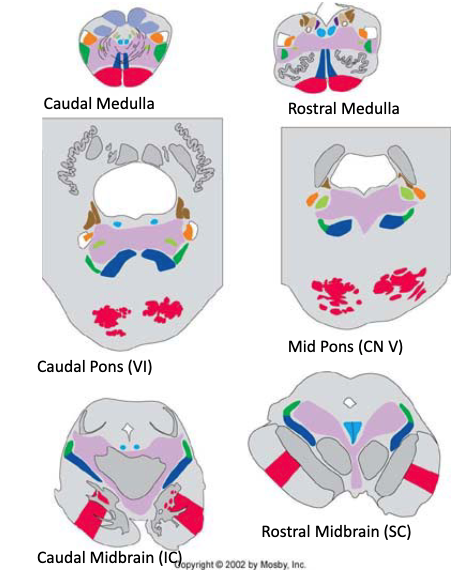
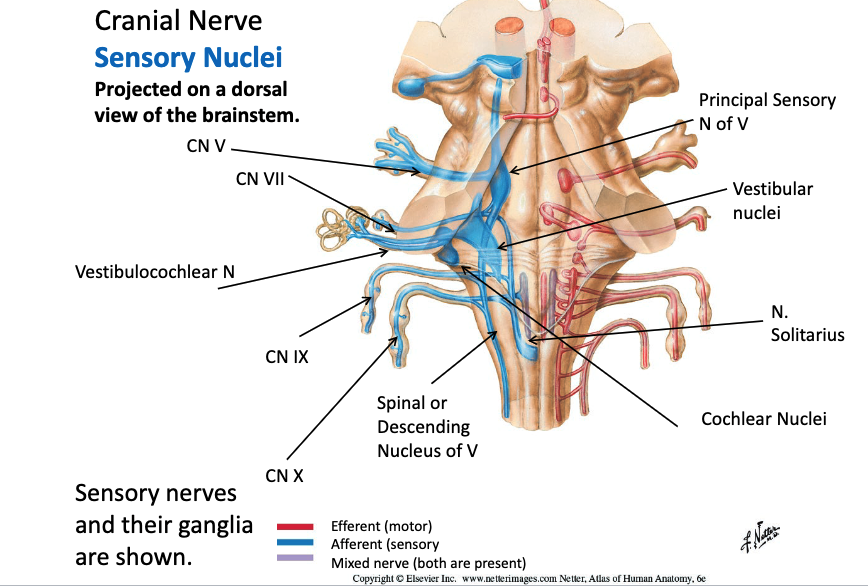
which nucleus of V conveys pain and temperature and crude touch?`
spinal nucleus of V (analagous to spinothalamic tract)
which nucleus of V conveys fine touch and dental pressure?
principal (chief) nucleus of V (analagous to dorsal column pathway)
which nucleus of V conveys proprioceptive input from muscles of mastication?
mesencephalic nucleus of V (jaw jerk reflex)
which nucleus of V innervates mucles of mastication?
motor nucleus of V
CN Motor Nuclei are Collections of _____________! They send their axons out to _____
lower motor neurons (like we find in ventral horn of spinal cord)
muscle
Motor cranial nerve nuclei receive cortical input via the…? what is the exception?
corticobulbar pathway
EXCEPT CN nuclei that innervate muscles for eye movement receive input from cortex via a different pathway (gaze centers to enable eye to move together)
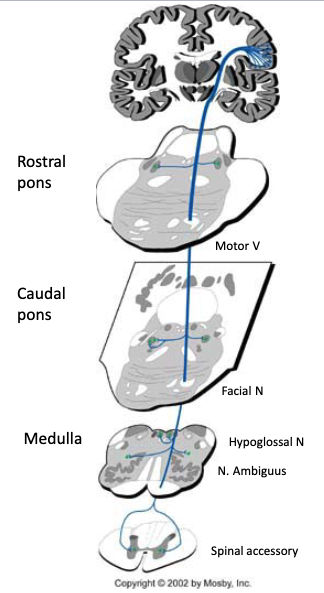
The corticobulbar tract supplies ______innervation to the cranial nerve nuclei supplying the head and face
upper motor
The corticobulbar tract provides input to the nuclei innervating…?
muscles of the face,
muscles of mastication,
muscles of the tongue
muscles of the pharynx and larynx and
sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
the corticobulbar pathway provides cortical input to
the motor cranial nerve nuclei
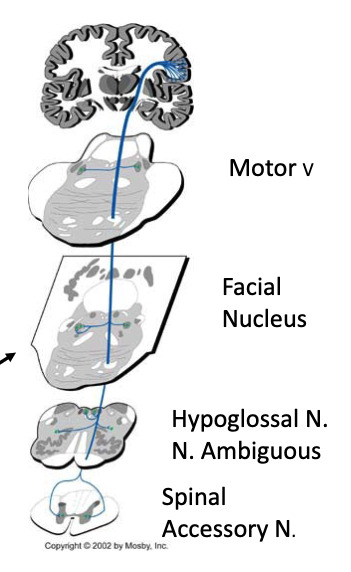
corticobulbar pathway provides ________ input to motor cranial nerve nuclei with one exception:
bilateral
EXCEPT neurons for lower face receive only contralateral input
corticospinal pathway provides ________ input to LMN
contralateral
Motor cranial nerve nuclei (Except III, IV, VI) receive cortical input via the ________ pathway
corticobulbar
what is the most noticeable affect of a corticobulbar lesion?
Paralysis of the contralateral Lower Face
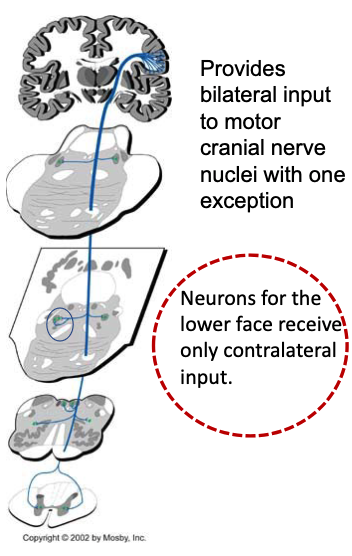
Neurons that control the upper/lower face receive bilateral Corticobulbar innervation.
Neurons that control the upper/lower face receive only contralateral innervation
upper
lower
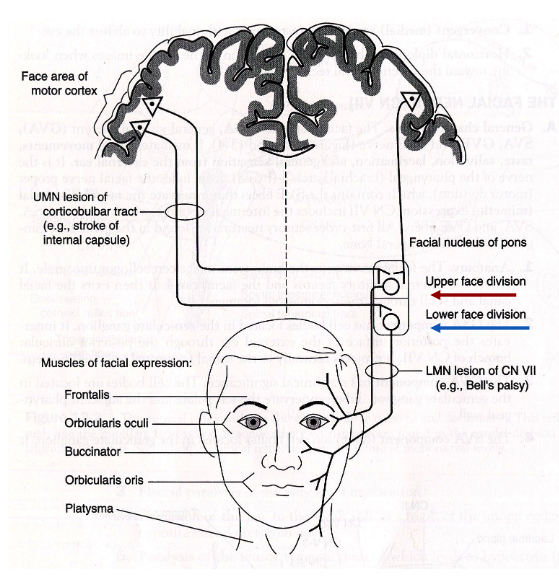
how does an UMN lesion affect the face?
In an UMN lesion (A), the upper face is spared because both hemispheres contribute to movement of the upper face
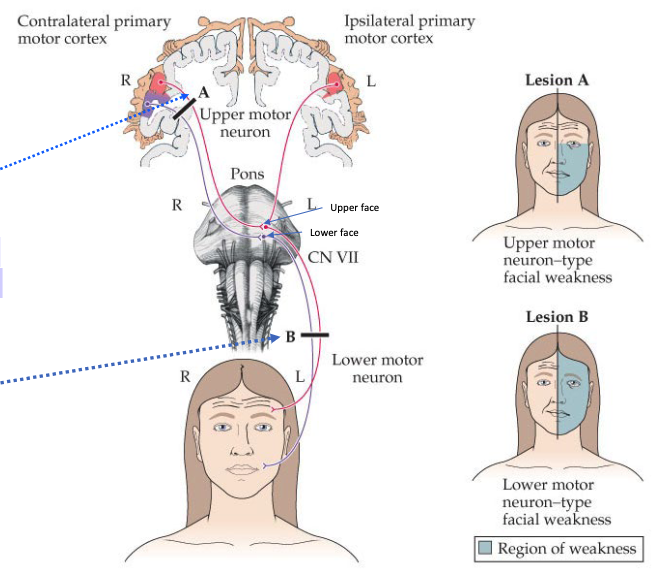
how does an LMN lesion affect the face?
In a LMN lesion (B), the entire face is affected on the side of the lesion. More profound as it interrupts the final pathway for facial control
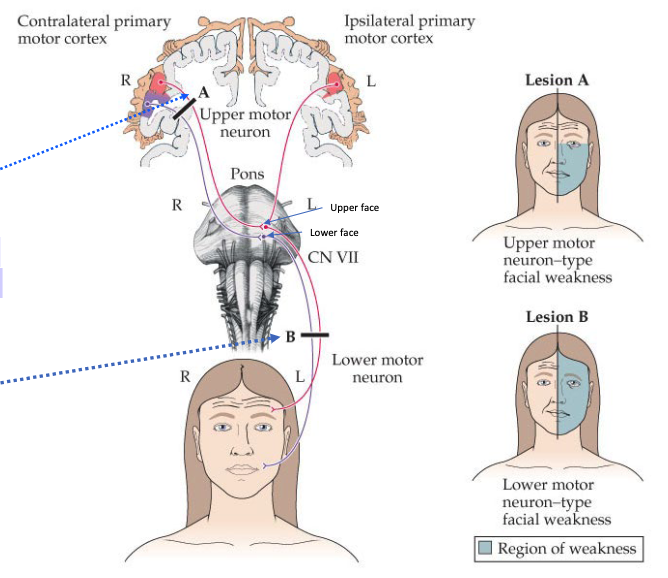
Because of the bilateral innervation of the corticobulbar tract, unilateral lesions of the tract will not result in
paralysis. Some level of weaknesses may be noted
With the exception of the neurons that control the lower face, what kind of damage of the corticobulbar tracts would be required to reveal paresis or paralysis?
bilateral
what is amyotropic lateral sclerosis (ALS)?
• Progressive neurodegenerative disease
• Both upper and lower motor neurons degenerate (corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts)
• Results in muscle weakness and atrophy
ALS is limited to which system?
somatic motor system
what are UMN symptoms of ALS?
Spasticity and hyperreflexia, difficulty speaking, inappropriate motor expression of emotions
what are LMN symptoms of ALS?
weakness of limbs, atrophy, fasciculation, difficulty chewing, swallowing, moving face and tongue
t/f: there is also loss of sensory function and bowel/bladder function in ALS patients.
false
when do patients with ALS die?
Patients die when innervation of the major respiratory muscles fails
which region of the brain is the destination of the spinothalamic and dorsal column pathways?
primary sensory cortex
which region of the brain is the origin of corticospinal and corticobulbar pathways?
primary motor cortex
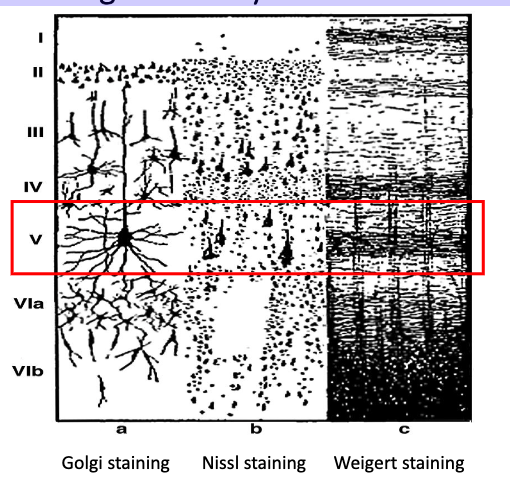
Corticospinal Tract Neurons and Corticobulbar Neurons originate in layer # of the motor strip
V (these are very large motor neurons)
cranial nerve nuclei are analagous to
ventral horn cells in spinal cord (both are lower motor neuron sites of origin)
what are the 2 components of the voluntary motor system?
upper and lower motor neurons
where do Upper motor neurons originate? what are the 2 types of UMNs?
in the motor strip
corticospinal neurons innervate spinal segments
corticobulbar neurons innervate CN nuclei
where do lower motor neurons originate?
In the ventral horn of the spinal cord
In cranial nerve motor nuclei
Innervation of cranial nerve motor nuclei by the corticobulbar pathway is _______ (with the exception of the neurons that control the muscles of the lower face, which is contralateral only)
bilateral
Unilateral lesions of the corticobulbar pathway produces ________.
only weakness and not paralysis
Only bilateral lesions cause paralysis (with the exception of neurons that control the lower face)
t/f: The corticobulbar pathway also controls the cranial nerve nuclei involved in eye movement (III, IV, VI).
false
They receive cortical input via a different pathway
Cortical input for the cranial nerve nuclei involved in eye movement originates in what area of the brain?
area rostral to the motor strip
Cortical input for eye movement is orchestrated through a gaze center to enable the eyes to move together.