Biology Section 4 | Quizlet
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is respiration?
it is the process of transferring energy from glucose, this process happens in every living cell
What is the energy from respiration used for?
its used to make ATP
What is the function of ATP?
it stores the energy from the glucose, when a cell needs energy it gets broken down
What are two things the energy from glucose is transferd to?
- ATP
- heat
What are the two types of respiration?
aerobic and anaerobic
When does aerobic respiration happen?
when the cell has oxygen available
Which is more efficient, aerobic or anaerobic respiration?
aerobic respiration
What is the formula for aerobic respiration?
C6H12O6 + O2 -> CO2 + H2O +(energy)
glucose + oxygen -> carbon dioxide + water +(energy)
opposite of photosynthesis
When does anaerobic respiration happen?
when the cell does not have oxygen
Describe an example of when anaerobic respiration happens.
when you exercise your body cant supply enough oxygen to your muscles. hence your muscle respire anaerobically
Is anaerobic respiration efficient or not?
it is not efficient
What happens to the glucose during anaerobic respiration?
it is partially broken down
What is the word equation for anaerobic respiration?
glucose -> lactic acid +(energy)
Can plants and fungi respire without oxygen?
yes
What is the word equation for aerobic respiration in plants and fungi?
oxygen + glucose -> carbon dioxide + water
Whats the word equation for anerobic respiration in plants and fungi?
glucose -> ethanol + carbon dioxide + (energy)
Whats a use of anerobic respiration?
it is useful with yeast for baking
Describe the experiment to show that respiration makes carbon dioxide using plants?
- soak some beans in water so that they can germinate
-biol some beans to kill them, so they cant respire
- add each type of bean in sealed test tube with carbon dioxide indicator
- it goes from orange to yellow in the presence of carbon dioxide
- leave the beans for a set amount of time, the germinating beans should have the indicator yellow
What is the carbon dioxide indicator used in the respiration experiments?
hydrogen carbonate indictor
When your running why do you become hot?
respiration produces a bit of heat along with the ATP
Describe the experiment to test how respiration produces heat?
- prepare a set of germinating beans and dead beans
- place each type of beans in a flask with a thermometer and seal the top with cotton
- use cotton to seal so that oxygen can still come in for aerobic respiration whilst still trapping most of the CO2
- record the temperature daily for a week
- the flask with germinating beans will have increased temperature and the dead beans will have no change
What type of reaction is respiration, and why?
exothermic as it releases energy (through heat)
What happens to the products of respiration and photosynthesis in plants?
the carbon dioxide or oxygen is released through the stomata
What is the top part of your body called?
the thorax
What is the muscle that separates the top half of your body to the bottom part?
the diaphragm
What are the lungs surrounded by, give 2?
- pleural membranes
- ribcage
What is the function of the ribcage?
to protect the lungs
What runs between the ribs?
intercoastal muscle
Describe how the tubes the air passes through split?
trachea - bronchi (two bronchus) - bronchioles - alveoli
Where does gas exchange happen in the thorax?
in the alveoli
Describe what happens to the thorax when you breathe in?
- intercoastal muscle and diaphragm contract
- diaphragm flattens
- ribcage and sternum go up and out
- thorax volume increases
- the pressure is decreased hence drawing in air
Describe what happens to the thorax when you breath out?
- intercostal muscles and diaphragm relax
- diaphragm moves up
- ribcage and sternum retract and down
- thorax volume decreases
- pressure is increased hence pushing air out
Why do you need more oxygen when exercising?
because your cells respire more
What happens when your breathing rate increases?
your cells receive more oxygen and more carbon dioxide is produced
Describe the experiment to see the effect of exercise on your breathing rate?
- sit still for a set amount of time and then measure the amount of breaths
- then exersise for a set amount of time and then measure your amount of breaths
- repeat and calculate the average
- there will be an increase in breathing rate as your cells respire more and hence need more oxygen
Describe the experiment to test the release of carbon dioxide when you breathe?
- breath through the mouthpiece
- the first tube will remain clear as oxygen only has a bit of carbon dioxide
- when you breath out the carbon dioxide made when respiring will bubble through the limewater
- the limewater will turn cloudy proving that your breath has carbon dioxide
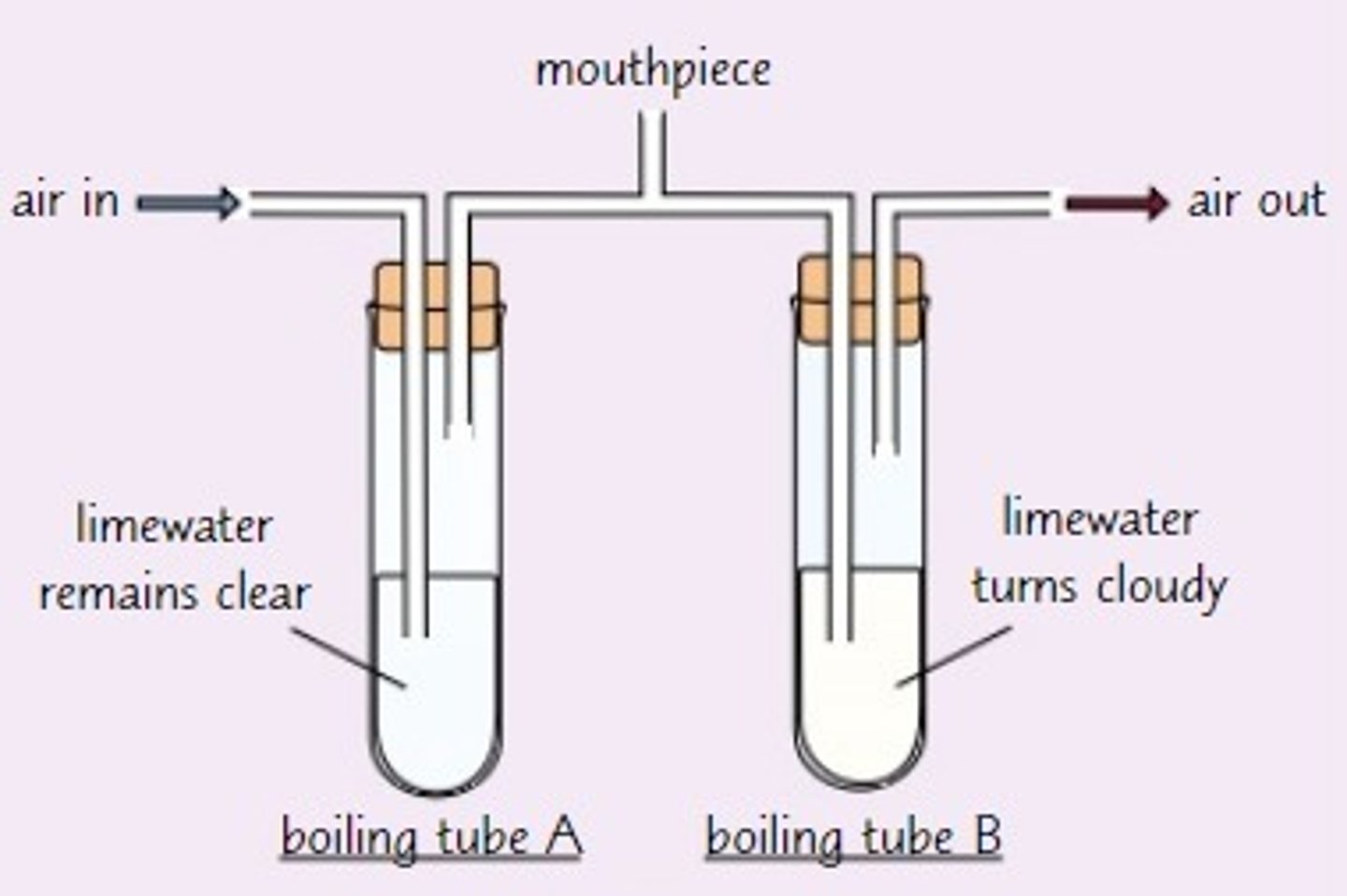
Whats the indicator for carbon dioxide?
limewater, goes from clear to cloudy in the presence of carbon dioxide
How to we know the carbon dioxide made when breathing in the limewater experiment was from respiration and not just inhaled from the air?
if the carbon dioxide was inhaled from the air the first tube would also be cloudy, but it was not
Does gas exchange happen in just plants?
it takes place in plants an humans
Where does gas exchange happen in humans?
in the alveoli
What are alveoli?
tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs
What type of blood passes by the alveoli?
de oxygenated blood which has a lot of carbon dioxide
What are the alveoli surrounded by?
blood capillaries
Describe the gas exchange between the alveoli and the blood?
- the blood passing has CO2 as it had just passed through the body giving oxygen to cells
- the CO2 diffuses into the capillaries from a high concentration to low
- the oxygen from the capillaries diffuses into the blood cells
- the CO2 is then breathed out as it travels from the alveoli to the lungs
Describe the process of gas exchange between cells?
- when the blood reaches the body's cells through the capillary
- oxygen is released from the red blood cells and diffuses into the cells, from high concentration to low concentration
- CO2 diffuses out of the cells and into the blood, from high concentration to low.
- this blood is then carried back to the lungs where it will obtain oxygen
Give 5 ways the alveoli are adapted for gas exchange?
- large surface area (lots of places for diffusion to occur)
- has a moist lining for gases to dissolve into
- one-cell thick walls
- a large blood supply to maintain the concentration gradient
- permeable walls
How does smoking tobacco affect gas exchange?
- it reduces the surface area of the alveoli hence decreasing the rate of gas exchange
What is the disease called which is caused by damaging the alveoli?
emphysema
What is the function of cilia and mucus?
they catch dust and bacteria before they reach your lungs
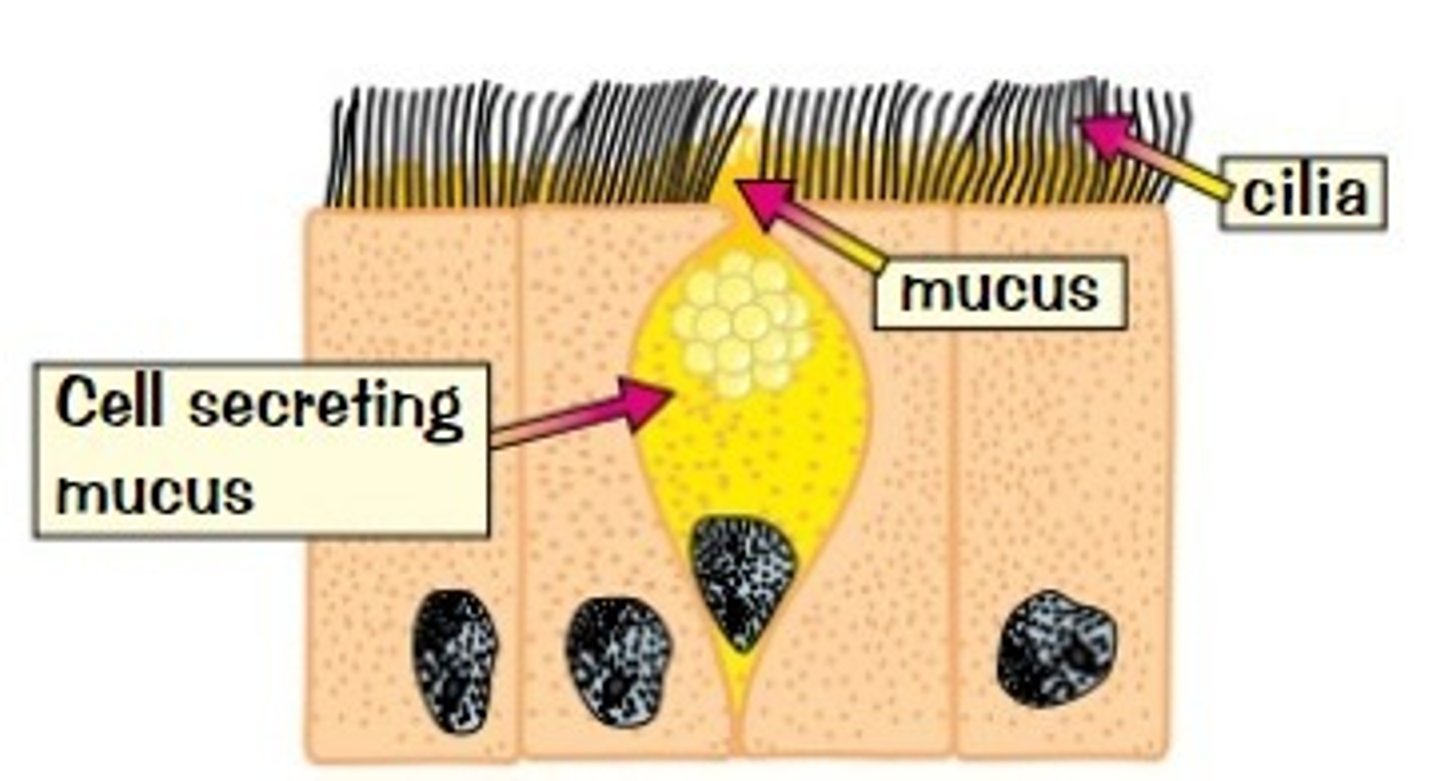
How does smoking increase your chance of chest infections?
the tar of the smoke damages the cilia, hence the dust and bacteria are able to get to the lungs and infect it.
Apart from cilia what else does the tar irritate, and what can it lead to.
- it irritates the bronchi and bronchioles, which causes mucus to be made
- too much mucus so the cilia can work
- this leads to things like smoker cough
What is an element on cigarette smoke?
carbon monoxide
How does carbon monoxide affect the body?
- it affects the amount of oxygen the blood can carry
Why does the blood not being able to carry enough oxygen affect the body?
- the heart rate increases trying to supply blood faster
- this increases the blood pressure which damages the artery walls
- this makes the formation of blood clots more likely
- this leads to coronary heart disease
what are the chemicals in smoke called and what do they do?
carcinogens, they lead to cancer