MOD4 Blood Borne Pathogens
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
risk of infection from needle poke without gloves on
HIV — 0.3%
HCV — 3.0%
HBV — up to 30.0% if non-immune
risk of infection from needle poke with gloves on
HIV — 0.15%
HCV — 1.5%
HBV — 15%
whats indicated by the presence of antigens
presence of the actual virus in the body in its infectious state
for most infections: ag = virus = bad news (infectious)
whats indicated by the presence of antibodies
recovery and subsequent immunity
for most infections: ab = immunity = good news
whats indicated by the presence of HIV antibodies
doesnt mean good news — although abs are developed, virus wont be destroyed bcs its hiding inside cells of the cellular immune system
the cells will be destroyed, immune system compromised, results in death
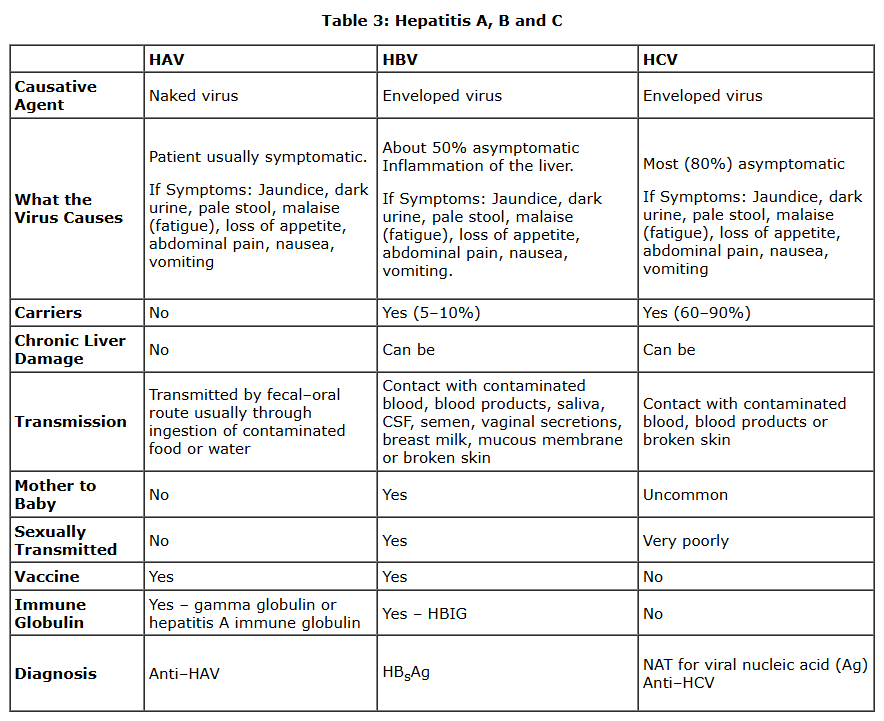
hepatitis
inflammation of the liver
commonly caused by viral infection of the liver
also caused by alcohol, bacteria, parasites, drugs, chemical toxins, other agents
jaundice
yellow pigmentation of the sclera (eye), skin, brain, etc
caused by liver problems — infected liver isnt able to process the breakdown of erythrocytic products, leads to build up of bilirubin levels in the blood
elevated bilirubin is deposited throughout the body
also gives urine dark amber colour and pale/light stool
hepatitis A virus HAV
small virus without an envelope
infected through ingestion of water/food contaminated w feces
associated with poor sanitation, personal hygiene and oral-anal sex
replicates in epithelial lining of oral cavity/intestine > enters circulatory system > invades and replicates in the liver > bile leaving liver carries more HAV into intestine
incubation period for hep A
15 to 50 days
symptoms of hep A
usually not evident until two weeks after virus invades liver
jaundice, pale stool, dark urine
diagnosis for HAV
test for antibodies against hep A virus (anti-HAV)
when are feces highly infective for HAV
two weeks before and about one week after the appearance of symptoms
hepatitis B virus HBV
small enveloped virus — unusually stable
can resist freezing, moderate heat, some chemical disinfectants
consists of a nucleic acid core surrounded by protein coat, surrounded by envelope w spikes
what antigenic areas are associated w HBV
hep B surface antigen HBsAg — part of outer envelope
core antigen HBcAg
E antigen HBeAg
core and E are part of the protein coat
how does HBV replicate in host
direct entry into blood stream is most efficient
can also enter through mucous membranes
transported by circulatory system to liver, where virus replicates
while HBV replicates, virus is carried in blood to other body fluids (blood, saliva, spinal fluid, tears, urine, semen, vaginal secretions, mothers milk)
asymptomatic infections for HBV
most ppl infected w HBV (60-70%) will have no disease symptoms and wont be aware of it unless tested for hep B antigens
symptomatic infections for HBV
majority will experience symptoms of 2w to 6m after exposure
average incubation period is 3m
symptoms: infl of liver, malaise, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, jaundice
fulminant infections
rapid, severe, sudden
seen in 1-3% of infected individuals
usually young people w good immune system
if majority of liver cells are infected, cell destruction from T cells will cause complete liver failure — will enter hepatic coma and may cause death, needs transplant
HBV carriers
5-10% of infected ppl will become carriers — even if asymp
reservoir of HBV — certain body fluids are infectious for 6-7 years
chronic viral infection of liver cells predisposes pts to primary hepatocellular carcinoma
transmission of HBV
through infected blood — minute amounts needed to infect
shared needles for drugs
sexual activities w blood exposure
tattoo/acupuncture/electrolysis w shared needles
shared razors, toothbrushes
needle sticks
blood spilled on broken skin
infective in blood spills for up to one week at room temp — blood-stained clothes/bandages
what antigen is tested for when diagnosing HBV
HBsAg — surface antigen, first appears in sample abt 2 months after exposure, level inc rapidly for abt a month, symptoms are evident
replication of virus diminishes, amt of antigen decreased
abt 5 months, lvl is undetectable
w/in few weeks, anti HBs antibodies will appear — recovery
anti HBs
hep B surface antibodies
produced by pt in response to surface antigen
indicates pt is recovering from HBV or has been immunized
anti HBc
hep B core antibodies
produced by pt in response to core antigen
diagnostic test for HBV during convalescent window
HBeAg
hep B e antigen
part of inner protein coat of the virus
indicates all body fluids are infectious
anti HBe
hep B e antibodies
produced by the pt in response to e antigen
indicates pt is clearing e antigen and becoming less infective
preventative measures for hep B
routine practices — PPE
hep B immunization — many healthcare orgs require vaccine against HBV
hep B immune globulin — HBIG available for short-term prevention when healthcare indiv exposed to infectious material, administered w/in 48hrs
hepatitis C virus
approx 20% of all cases of acute hepatitis
associated w intravenous drug abuse
found in blood
hepatitis D virus HDV
defective RNA virus that can only replicate in presence of HBV
associated w progressive liver damage and fulminant hepatitis
spread in blood, semen, vaginal secretions
whats the best protection against HDV
immunization aaginst HBV — HDV cant infect liver cells w/out presence of HBV
hepatitis E
spread fecal-oral route
esp serious for pregnant females
HIV
infection w virus — asymptomatic
enveloped RNA retrovirus w glycoprotein spikes
AIDS
clinical symptoms evident
components of HIV
core
center of virus
two strands of RNA
reverse transcriptase enzyme used to produce viral DNA from RN
protein coat
surrounds core
consists of proteins
lipid envelope
lipid bilayer, glycoprotein spikes protrude out — lollipop!
candy pt of lollipop is gp120
responsible for binding virus to host cell
hardiness of HIV
not very hardy — use routine sterilization, disinfection and cleaning methods to inactivate virus