module 1: terminology and the body plan
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
structural and functional organizations
chemical level
cell level
tissue level
organ level
organ system level
organism level
chemical level
interaction of atoms
cell level
structural and functional unit of living organisms
tissue level
group of similar cells and the material surrounding them
organ level
two or more types of tissues functioning together
organ systems
group of organs that function together
organism level
any living system
directional terminology
yay
anatomical position
body erect, face forward, feet together, palms face forward

supine
lying face upward
palms are up
prone
lying face downward
palms are down
directional terms
superior (cephalic) vs inferior (caudal) means toward or away from the head
superior (cephalic)
closer to the head
eg. My nose is superior to my mouth
inferior
closer to bottom of the torso
Medial
closer to the midline is called medial
Lateral
further away from the midline is called lateral
eg. My eyes are lateral to my nose
proximal
Proximal if it’s closer to the attachment point
Distal
Distal if it’s further away from the attachment point
proximal vs distal
used to describe linear structures
superficial vs deep
relative to the surface of the body
superficial
the surface area
deep
closer to the midline deeper in the body
Anterior (ventral)
anything closer to the front of the body
toward the front
Posterior (dorsal)
closer to the back of the body is posterior
toward the back
Body planes
Sagittal
Frontal/coronal
transverse/cross
oblique
sagittal
vertically through the body - separates right and left
frontal or coronal plane
divides the body into anterior and posterior sections
transverse/cross
divides body into anterior and posterior sections
oblique
other than a right angle
planes through the organs
longitudinal
cut along the length of the organ
cross/transverse
cut at right angle to length of the organ
Right threw the organ/up and down
oblique
cut at any angle but a right angle
BODY CAVITIES
dorsal body cavity houses:
cranial cavity
vertebral canal
central nervous system
ventral body cavity houses:
diaphragm: divides into the thoracic and abdominpelvic cavities
thoracic cavity: contains lungs and heart
mediastinum: contains all structures of the thoracic cavity except the lungs
abdominal cavity: stomach, liver, intestines, spleen, pancreas, kidneys
Pelvic cavity: contains urinary bladder, part of large intestine and reproductive organs
serous membranes
thin layer of epithelial tissue
cover the organs of trunk cavities and lines the cavity
balloon analogy: fist inside a waterballoon
one continuous layer of ballon that’s folded in on itself for 2 layers and in between the layers there is fluid
visceral serous membrane : the inner wall closest to the organ
parietal serous membrane: outer layer comes in contact with the wall cavity
cavity between the two membranes filled with lubricanting serous fluid that is produced by the membranes
pericardium
serous membrane around the heart
visceral pericardium
parietal cavity
pericardial cavity: filled with pericardial fluid
pleura
serous membrane around the lungs
parietal pleura
visceral pleura
pleural cavity contains the pleural fluid
peritoneum
serous membrane around the abdominal cavity
mesenteries: folds upon itself and goes from organ to organ
BODY PARTS AND REGIONS
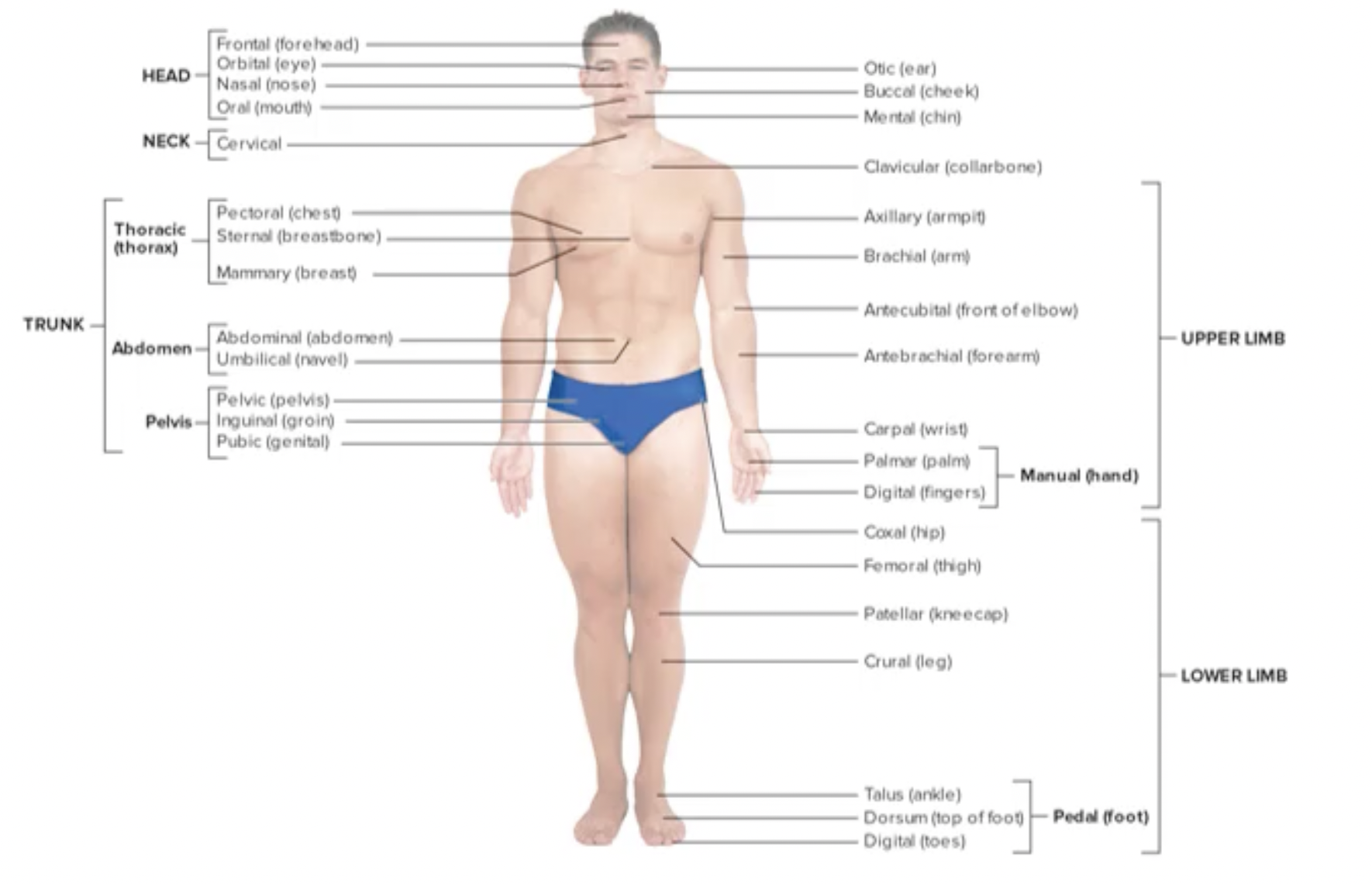
head region
frontal (forehead)
orbital (eye)
otic (ear)
nasal (nose)
buccal (cheek)
oral (mouth)
mental (chin)
neck region
cervical
clavicular (collarbone)
upper limb
axillary (armpit)
brachial (arm)
anticubital (front of elbow)
antebrachial (forearm)
carpal (wrist)
manual (hand)
palmer (palm)
digitals (fingers)
trunk
thoracic (thorax)
pectoral (chest)
sternal (breastbone)
mammary (breast)
abdomen
abdominal (abdomen)
umbilical (navel)
pelvis
pelvic (pelvis)
inguinal (groin)
pubic (genital)
lower limb
coxal (hip)
femoral (thigh)
patellar (kneecap)
crural (leg)
pedal (foot)
talus (ankle)
dorsum (top of the foot)
disgitals (toes)