Web Development 2.1 - 2.16
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
HTML (HyperText Markup Language)
defines over 130 elements.
HyperText
is a textual language for creating webpages.
Markup
are instructions to a browser about the rest of the document.
Language
A valid HTML document must follow the HTML language rules.
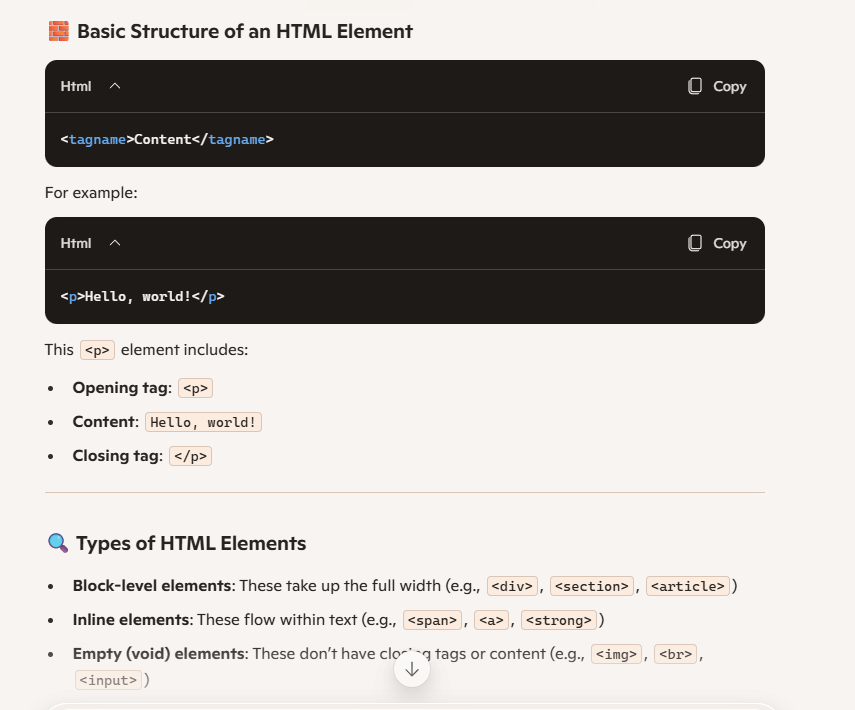
Element
is a single HTML structure.
Elements are represented with HTML tags.
Opening tag:
<p>Content:
Hello, world!Closing tag:
</p>
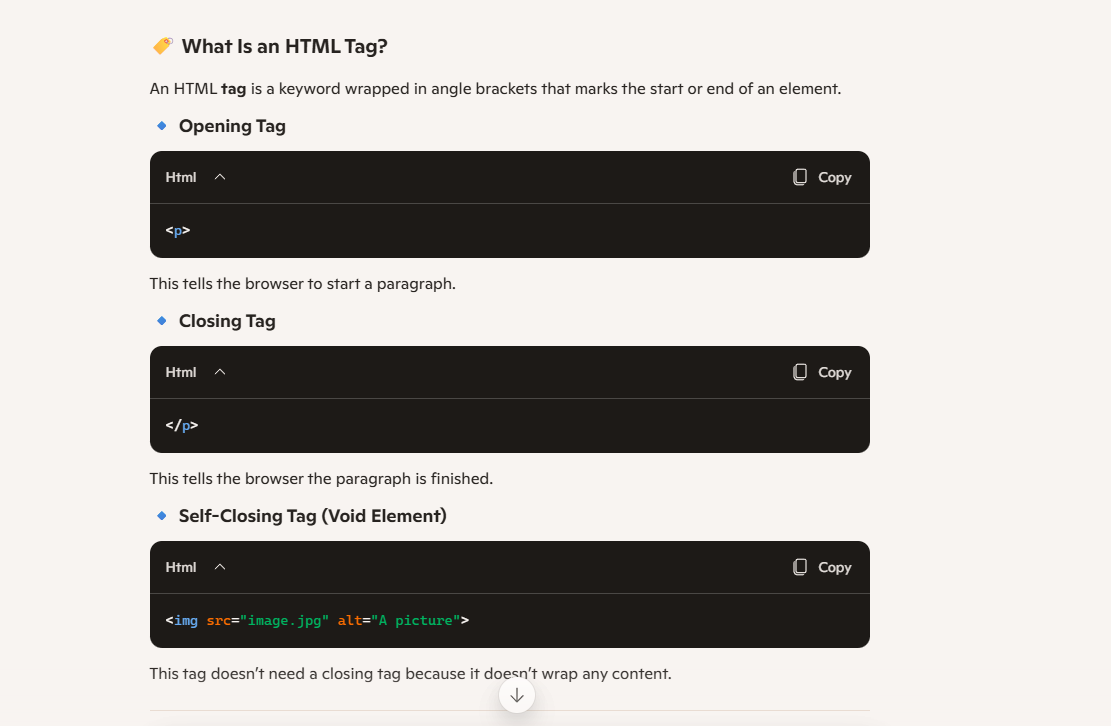
Tag
is a markup instruction identified by <, the tag name, and >.
An opening tag indicates the element's starting point in the document.
A closing tag has a forward slash (
/) before the tag name and indicates the element's ending point in the document.
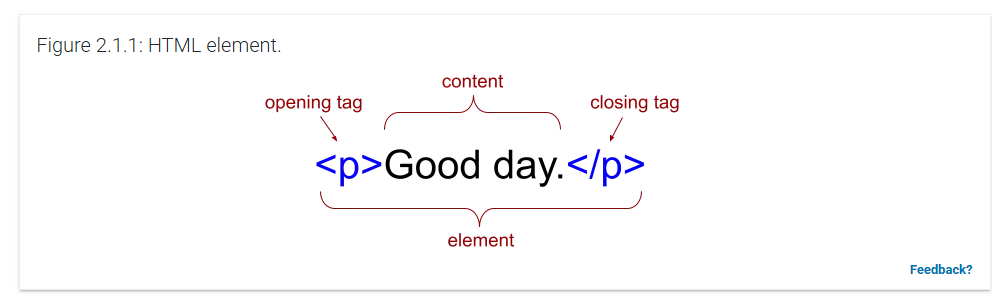
Content
The opening and closing tags surround the element's content, which can be text or other elements.
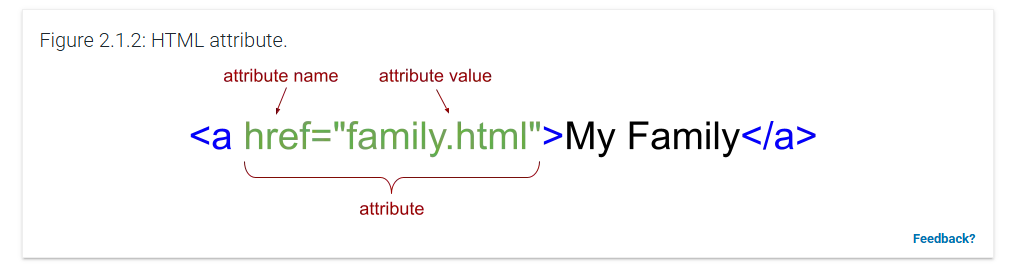
element ATTRIBUTE
provides additional information about the element and is included only in the opening tag.
An attribute has a name and a value, specified using the form: name="value".
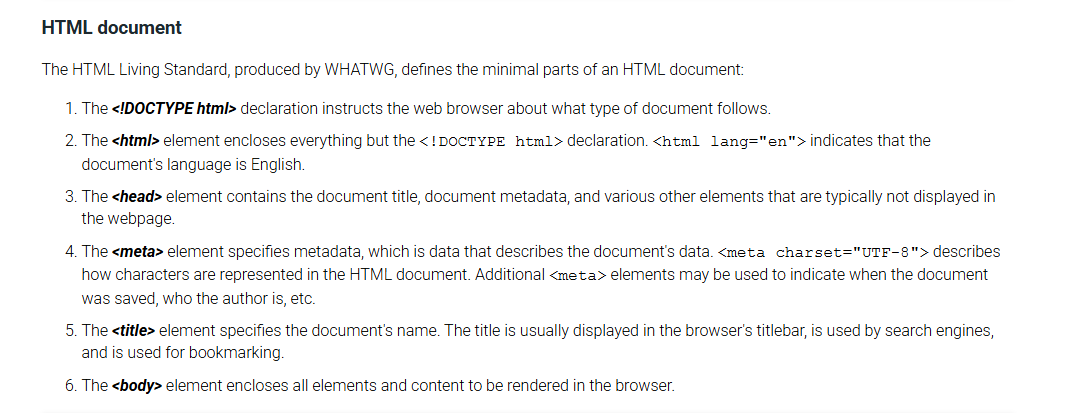
HTML Document
Living Standard, produced by WHATWG, defines the minimal parts of an HTML document.
Deprecated feature
is part of a language that is officially discouraged because newer or better features exist, or because the deprecated feature is no longer considered safe.
Ex: The <center> element is an officially deprecated element that should no longer be used.
HTML validator
checks that an HTML document conforms to the standard. Good practice is to use tools like the W3C Markup Validator to check document conformance.
2.3 Basic HTML elements
<p> element creates a paragraph in an HTML document.
A paragraph is enclosed in HTML by the <p> opening and </p> closing tags.
Browsers visually separate paragraphs from other text with spacing above and below.
Paragraph
is enclosed in HTML by the <p> opening and </p> closing tags. Browsers visually separate paragraphs from other text with spacing above and below.
whitespace
an unprinted character such as the spaces between words and lines of text.
Whitespace characters include spaces, tabs, and newlines.
<br> element creates a line break
creates a line break in a paragraph, such that the content after the line break appears on a new line.
is a void element, so only the opening tag is needed.
Section
is a collection of related content created with a <section> element.
used to group related content together within a document. It helps organize your page into meaningful blocks
Heading
provides a title for each section. Headings are bold by default and are visually separated from the other text by extra spacing.
Text Heading elements exist for six levels of sections: <h1>, <h2>, <h3>, <h4>, <h5>, and <h6>.

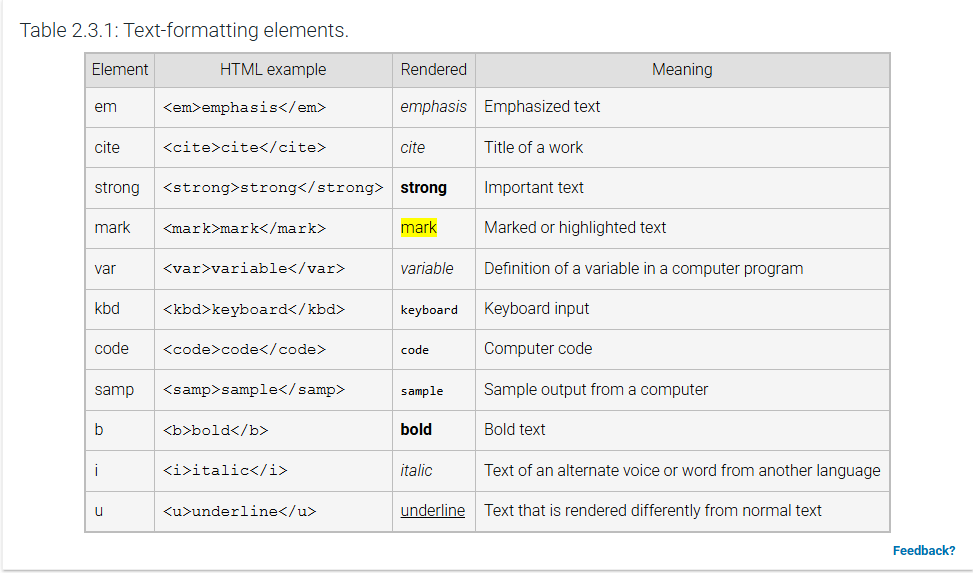
Text formatting
elements cause the enclosed text to render in a different font in the browser:
<em> element indicates emphasized
<strong> element indicates text that has strong importance
<cite> element denotes a title
<mark> element denotes important content that should be highlighted
<b> element indicates text that needs attention, text in bold.
<i> element indicates text in an alternative voice, italics
<u> element denotes text that should appear differently
Ex: Misspelled is often misspelled as mispelled.
Comment
is a portion of the document that is not displayed by the browser.
A comment begins with the <!-- character sequence and ends with the --> character sequence.
Everything between <!-- and --> is ignored by the browser.
<!-- This is an HTML comment -->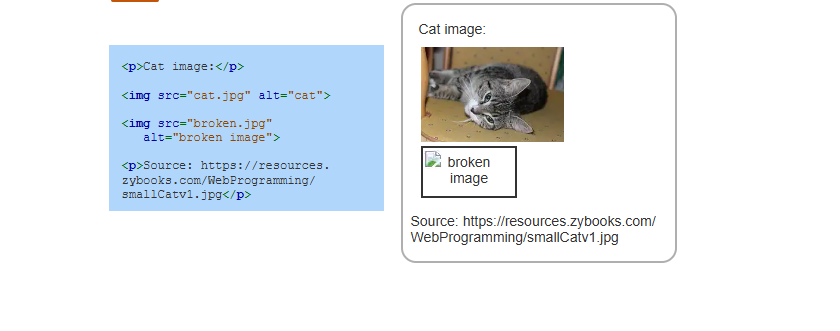
<img> element
is a void element that displays an image in a webpage.
The <img> element has two required attributes:
The src attribute specifies the URL of the image file to display.
The alt attribute provides a text description to use as an alternative to displaying the image.
Ex: <img src="https://example.com/family.jpg" alt="Smith family reunion"> displays the image family.jpg, but the text "Smith family reunion" displays if the image cannot be displayed.
width attribute and height attribute
are optional <img> attributes that tell the browser how many pixels the image should occupy.
Ex: <img src="logo.png" alt="Logo" width="200" height="100"> makes the logo.png image display in a rectangle that is 200 × 100 pixels.
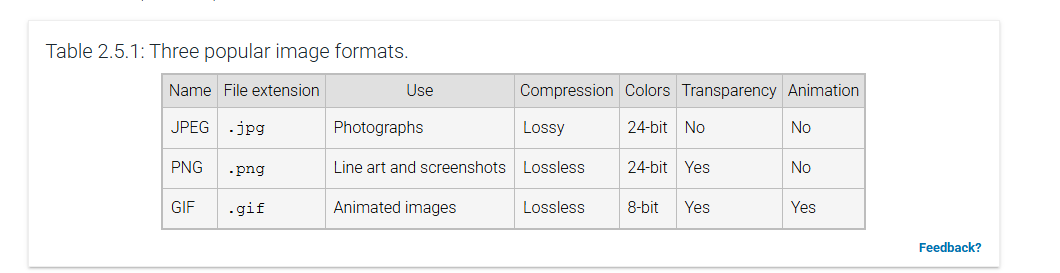
Image formats
support three popular image formats:
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format)
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
image format is commonly used for digital photographs.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
image format is commonly used for line art, screenshots, or images requiring transparency.
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format)
image format is commonly used for simple animated images.
lossy compression
meaning that some of the original picture information is lost when compressed.
A photograph is best saved as a JPEG image because humans cannot easily perceive the quality loss in a photograph.
True color
which is approximately 16 million different colors.
Favicon
is a small icon that identifies a website and typically displays in a browser tab. A representation of a website.
anchor element <a>
defines a hyperlink in a webpage.
href attribute
specifies the hyperlink's URL. Ex:
<a href="https://wikipedia.org/">Wikipedia</a> displays the hyperlink Wikipedia and causes the browser to request the URL https://wikipedia.org/ when the hyperlink is clicked.
Commom URL schemes
file
ftp
http
https
mailto
Fragment
URL can point to a section of a document by adding hashtag.
ID attribute
<div id="about">This is the About section</div>is like a label on a part of the page.
The href="#label" is like a button that takes you to that label.
graphical hyperlink
image link uses an image inside a hyperlink instead of text.
Target attribute
indicates how the browser should display the link when clicked.
Section 5
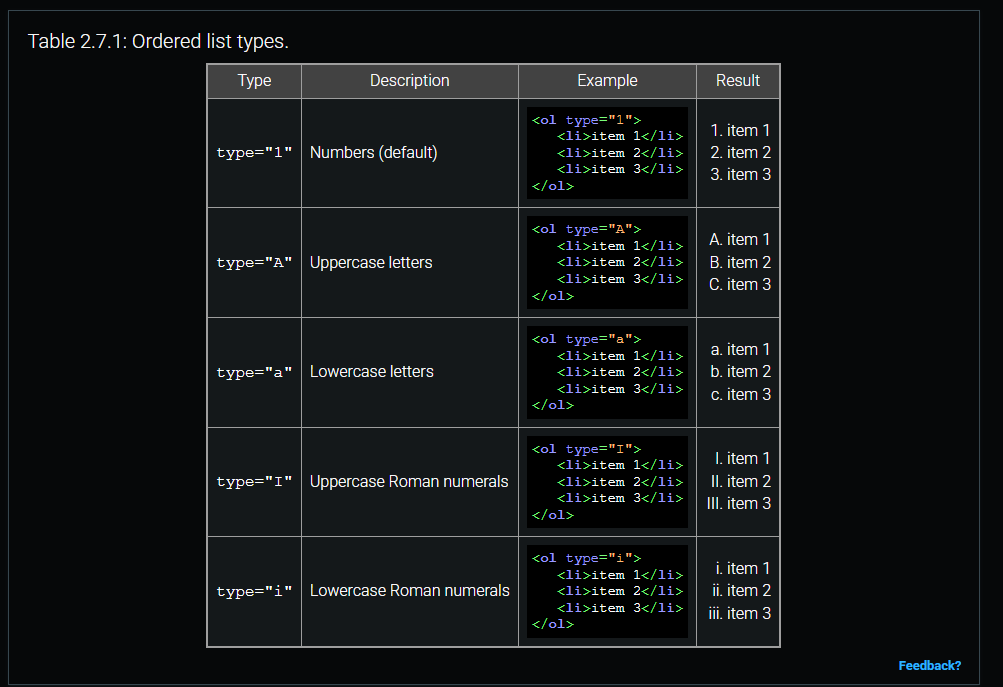
Unordered list / List item / Ordered list
is a collection of items, usually indented and shown using bullets.
created with the <ul> element.
is created with the <li> element.
is a sequenced collection of items, usually indented and shown using numbers or letters,
created with the <ol> element.
Section 2.8 Tables
Table / Cell
is an HTML structure created with the <table> element that organizes data into rows and columns.
A Cell is a location in the table at a specific row and column.
<tr> element creates a table row, which contains all the row's cells.
<th> element creates a table cell containing table header information about the data.
<td> element creates a table cell containing table data.
Table caption defines a short descriptive text for a table and is created with the <caption> element.
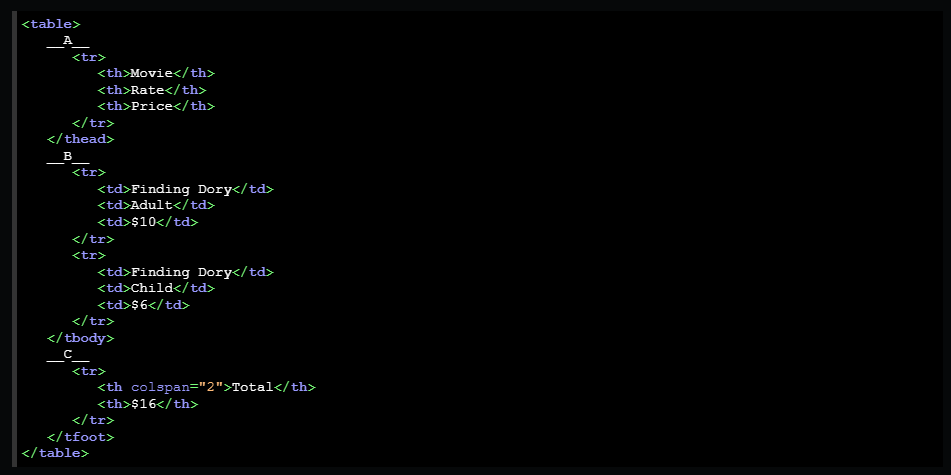
Header, body, and footer
The <thead> element specifies the table header.
The <tbody> element specifies the table body.
The <tfoot> element specifies the table footer.
The <thead>, <tbody>, and <tfoot> elements do not affect the layout of the table.
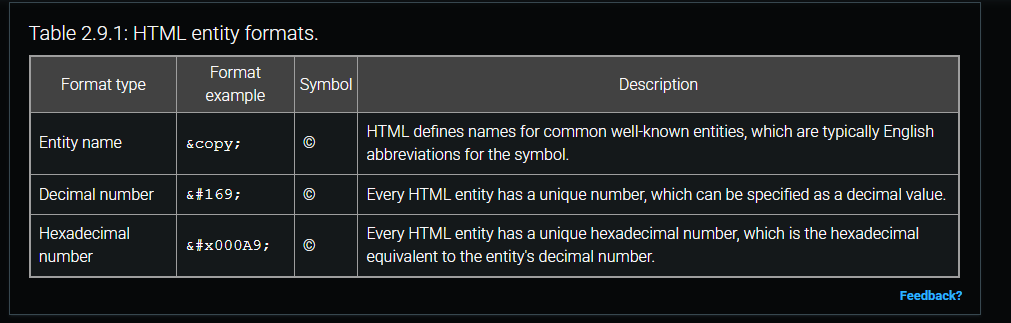
Entity
is a mechanism for writing special characters or symbols in HTML, such as mathematical symbols, characters in most languages, and many other symbols.
Section 2.10 Example: Band webpage
Wireframe
is a blueprint, showing where the future content will be arranged.