Anatomical Landmarks on Panoramic Images
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Articular Eminence
Rounded projection of the temporal bone located anterior to the glenoid fossa.
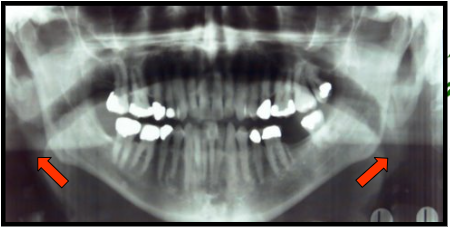
Glenoid Fossa
Concave depressed are of the temporal bone.
The mandibular condyle rests in this when the teeth are in maximum intercuspation or clenched together.
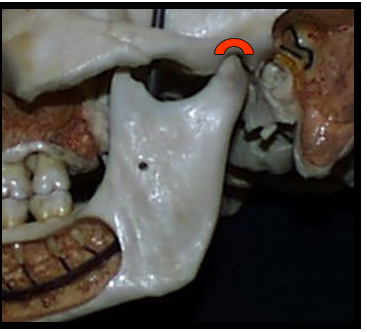
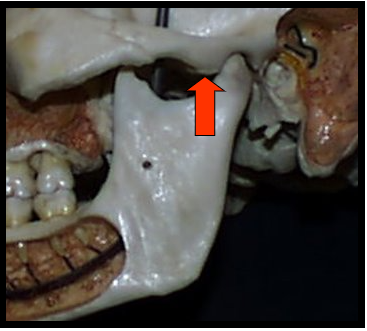
Articular Eminence and Glenoid Fossa
One appears as a concave radiopacity superior to the mandibular condyle.
One appear as a rounded radiopaque projection of the bone located anterior to the glenoid fossa.
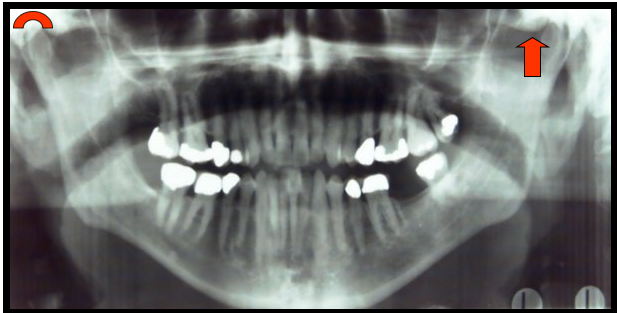
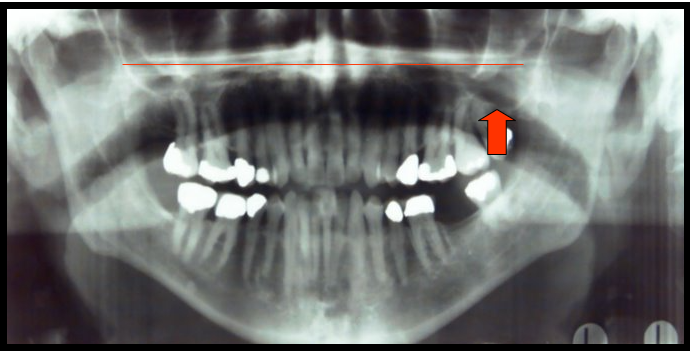
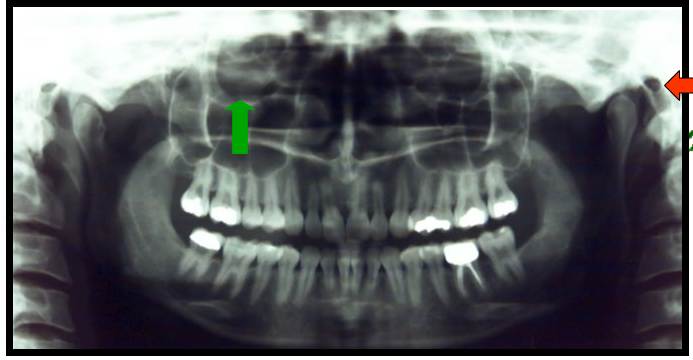
Maxillary Sinus
Paired cavities or compartments of bone that are located within the maxilla, superior to the maxillary posterior teeth.
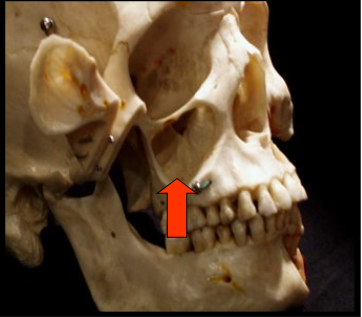
Hard Palate
The bony wall that separates the nasal cavity from the oral cavity.
Maxillary Sinus and Hard Palate
One appears as a horizontal radiopaque band superior to the apices of maxillary teeth.
One appears as paired radiolucent areas located superior to the apices of maxillary premolars and molars.
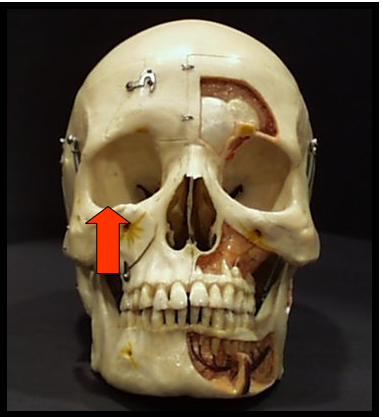
Orbit
The bony cavity that contains the eyeball.
External Auditory Meatus
Is a hole, or opening, in the temporal bone located superior and anterior to the mastoid process.
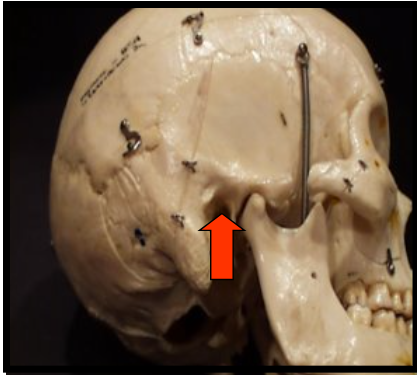
Orbit and External Auditory Meatus
One appears as a round radiolucent compartment with radiopaque borders located superior to the maxillary sinuses.
On most panoramic images only the inferior border of this is visible
One appears as a round or ovoid radiolucency anterior and superior to the mastoid process.
Nasal Fossa and Inferior Nasal Conchae
A pear-shaped compartment of bone located superior to the maxilla
Are wafer-thin, curved plates of bone that extend from the lateral walls of the nasal cavity.
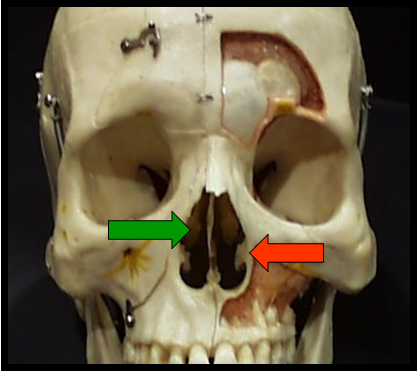
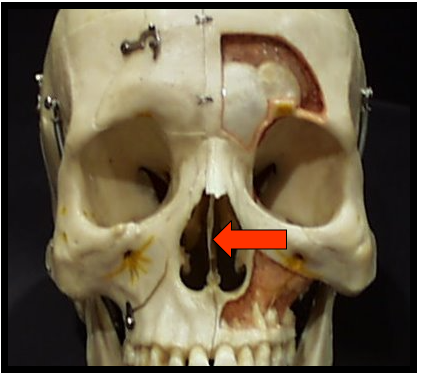
Nasal Septum
Vertical bony wall or partition that divides the nasal cavity into the right and left nasal fossa
Nasal Fossa, Inferior Nasal Conchae and Nasal Septum
Appears as a large radiolucent area superior to the maxillary incisors divided into two compartments or fossa
Appears as a vertical radiopaque partition that divides the nasal cavity
Appears as diffuse radiopaque masses or projections within the nasal cavity.
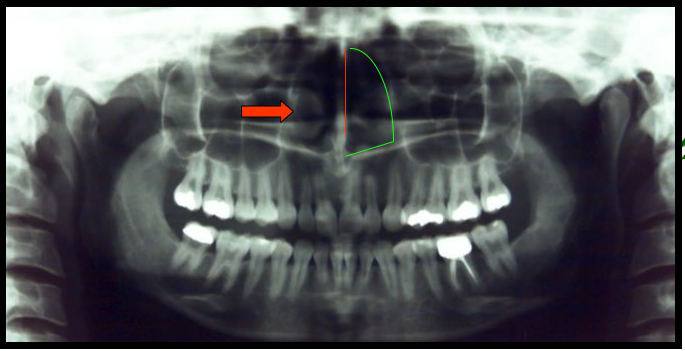
Anterior Nasal Spine
A sharp bony projection of the maxilla located at the anterior and inferior portion of the nasal cavity.
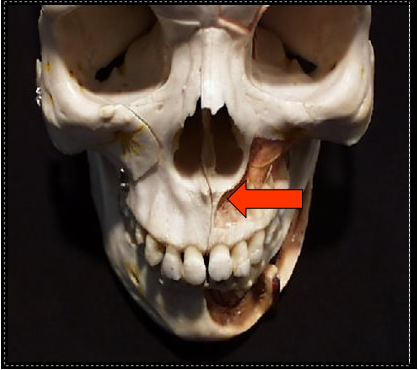
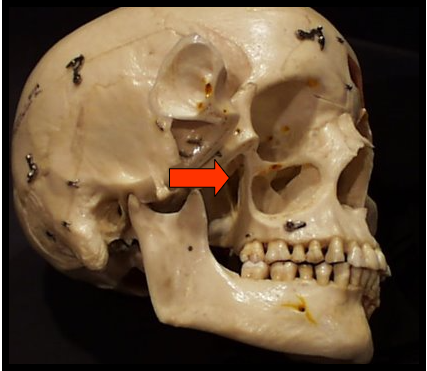
Pterygomaxillary Fissure
A narrow space that separates the lateral pterygoid plate and the maxilla
Anterior Nasal Spine and Pterygomaxillary Fissure
Appears as a V-shaped radiopaque area located at the intersection of the floor of the nasal fossa and the nasal septum.
Appears as a radiolucent area between the lateral pterygoid plate and the maxilla.
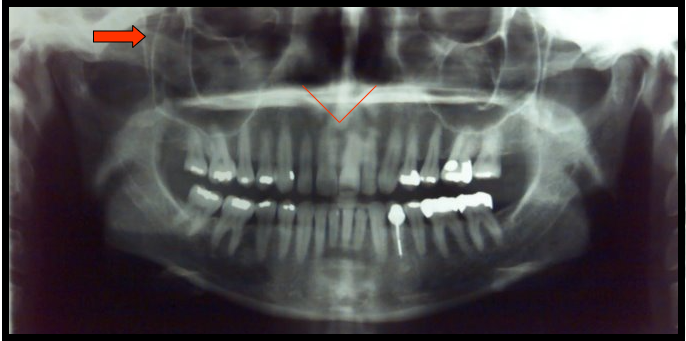
Mandibular Canal
A tubelike passageway through bone that travels within the body or length of the mandible.
Extends from the mandibular foramen to the mental foramen and houses the inferior alveolar nerve and blood vessels
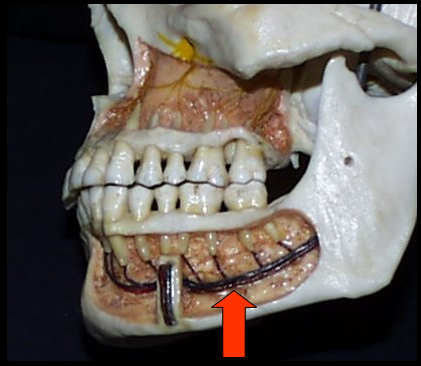
External Oblique Ridge
A linear prominence of bone located on the external surface of the mandible that extends downward and forward from the ramus to the molar region.
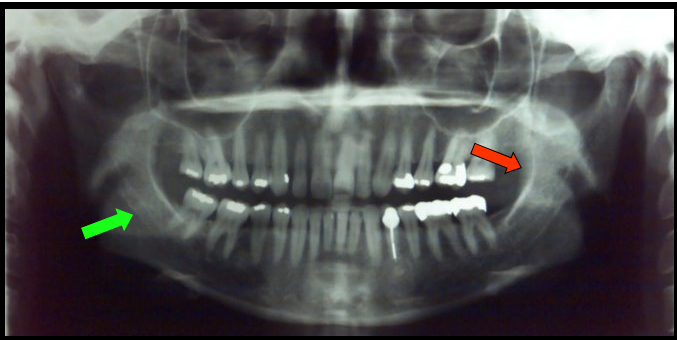
Mandibular Canal and External Oblique Ridge
Appears as a radiolucent band outlined by two thin radiopaque lines representing the cortical walls of the canal.
Appears as a dense radiopaque band that extends downward and forward from the ramus to the molar region.
Zygomatic Process
A bony projection of the maxilla that articulates with the zygoma or cheekbone.
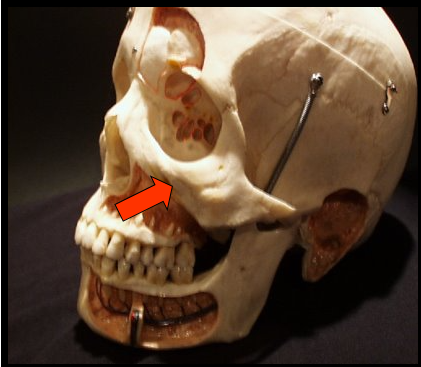
Zygomatic Arch
The cheekbone and it articulates with the zygomatic process of the maxilla.
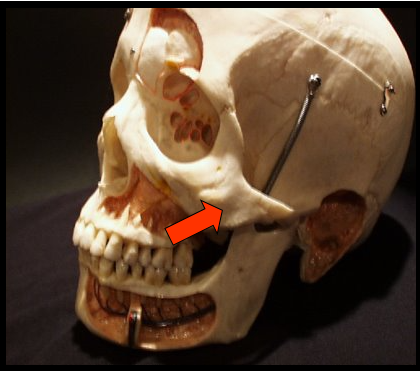
Zygomatic Process and Arch
Appears as a J or U-shaped radiopacity located superior to the maxillary first molar region.
Appear as a diffuse radiopaque band that extends posteriorly from the zygomatic process of the maxilla.
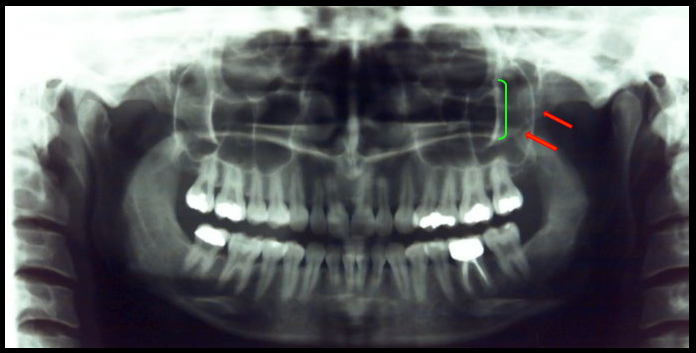
Inferior Border of Mandible
A thick, linear prominence of cortical bone that defines the lower border of the mandible.
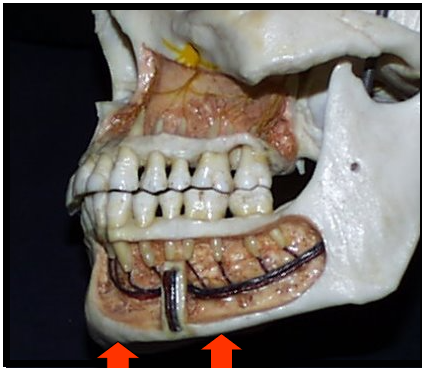
Submandibular Fossa
A scooped-out depressed are of bone located on the internal surface of the mandible, inferior to the mylohyoid ridge.
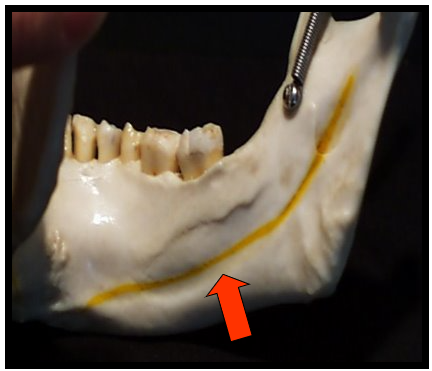
Inferior Border of the Mandible and Submandibular Fossa
appears as a dense radiopaque band that outlines the lower border of the mandible.
appears as a diffuse radiolucent area in the molar region.
These landmarks can be seen on intraoral images.
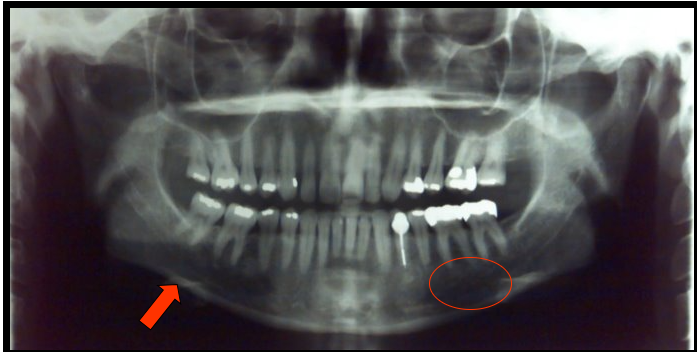
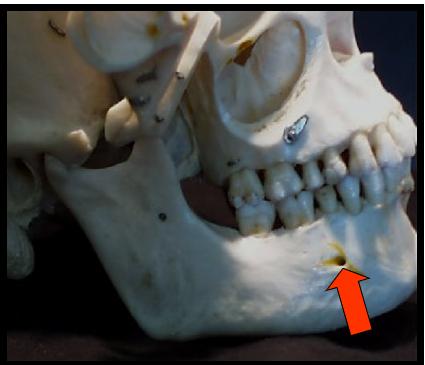
Mental Foramen
An opening or hole in bone located on the external surface of the mandible in the region of the mandibular premolars.
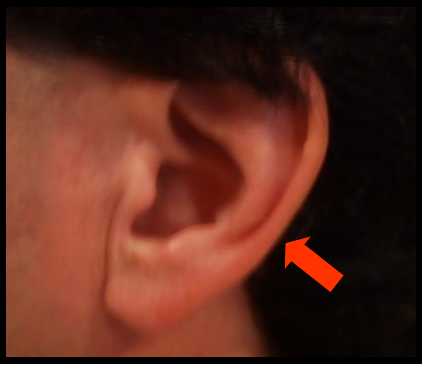
Soft Tissue of the Ear
outer portion of the ear is composed of cartilage with a thin covering of connective tissue and skin
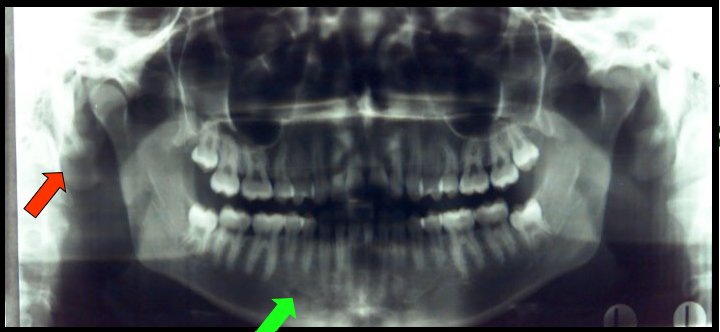
Mental Foramen and Soft Tissue of the Ear
appears as a small, ovoid or round radiolucency located in the apical region of the mandibular premolars.
This landmark can be seen in intraoral images.
appears as a radiopaque shadow posterior to the condyle.
This landmark is not visible on intraoral images.
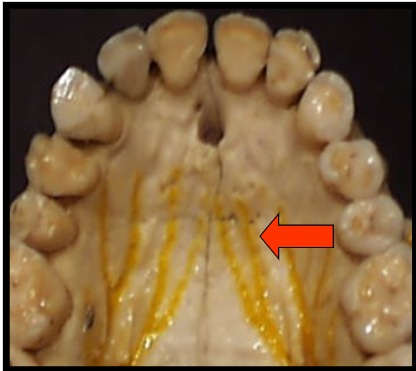
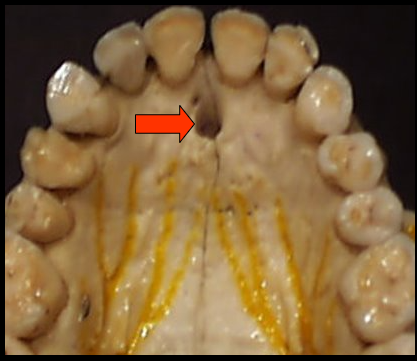
Incisive Foramen
an opening, or hole, in bone that is located at the midline of the anterior portion of the hard palate directly posterior to the maxillary central incisors.
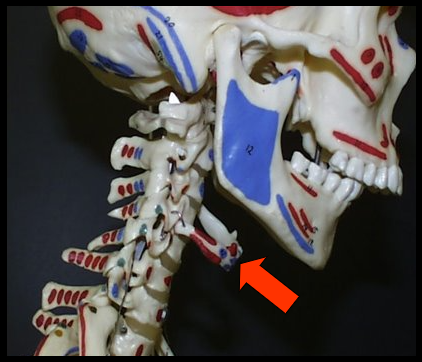
Hyoid Bone
A horseshoe-shaped bone that lies below the mandible, between the chin and thyroid cartilage.
Ligaments and muscles located inferior to the mandible support this
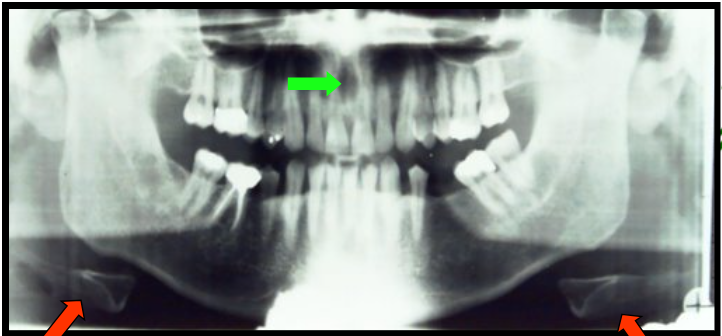
Incisive Foramen and Hyoid Bone
appears as a small, ovoid or round radiolucency located between the root of the maxillary central incisors.
appears as a “floating” curved radiopacity at or below the inferior border of the mandible.
is at the midline and as a result, appears as a double image and is seen on both the right and left sides of the panoramic image.
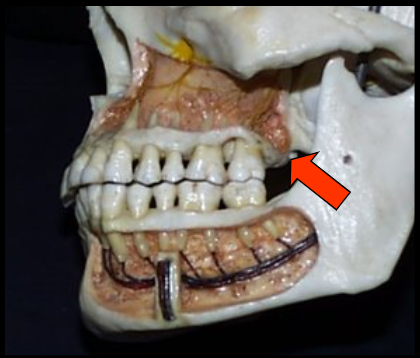
Maxillary Tuberosity
A rounded prominence of bone that extends posterior to the third molar region.
Infraorbital Foramen
A hole, or opening in bone inferior to the border of the orbit.
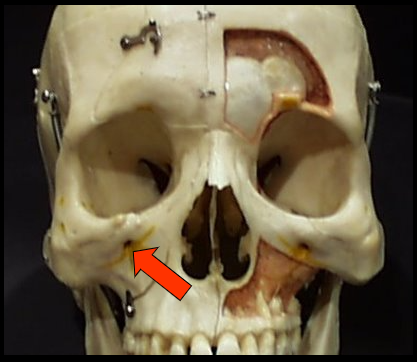
Maxillary Tuberosity and Infraorbital Foramen
appears as a radiopaque bulge distal to the third molar region.
This landmark is seen in intraoral images.
appears as a round or ovoid radiolucency inferior to the orbit.
It is not seen on intraoral images.
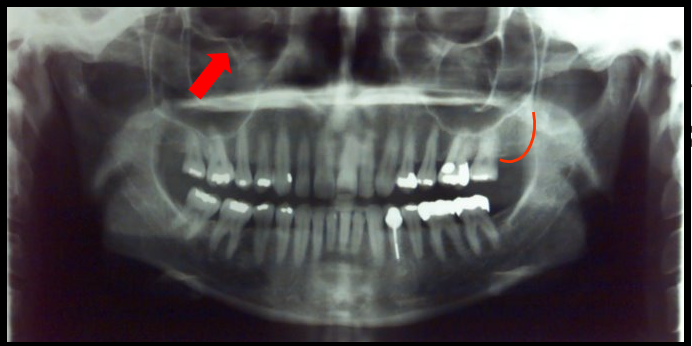
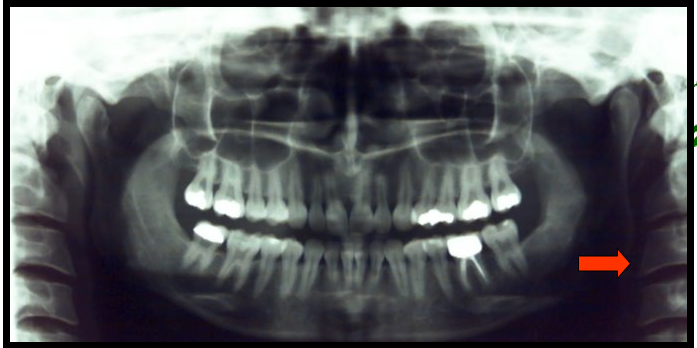
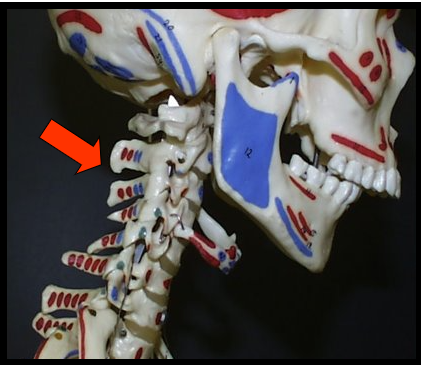
Vertibral Column
The vertebrae and intravertebral discs form this
It is flexible column that supports the head, neck and body and allows for movement.
It also protects the spinal cord which passes through the openings in the vertebrae.
appears as a long radiopaque column on the left and right edges of a panoramic image.
Air Spaces
The air spaces on a panoramic radiograph appear as wide radiolucent bands which form an arch shape spanning across or above the roots of the maxillary teeth then downward toward the angle of the mandible.
palatoglossal airspace
is the space between the palate and the tongue.
appears as a horizontal well-defined radiolucent band located superior to the apices of the maxillary teeth.
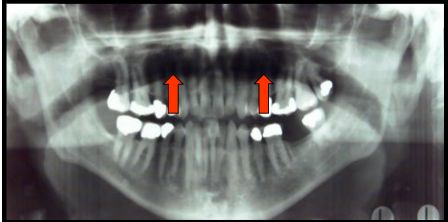
glossopharyngeal air space
is an outline of the pharnx.
appears as a vertical radiolucent band superimposed over the ramus of the mandible.