Final Genetics Exam
1/229
Earn XP
Description and Tags
40 old on exam, 10 new about, Blue is first exam PRS questions, Green is second exam PRS questions, Purple will be new concept material
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
230 Terms
Recent discoveries in genetic engineering
allowed humans to genetically manipulate
plants (crops) for the first time
A. True
B. False
B
Gregor Mendel is generally recognized
as the father of genetics because he
A. Generated new varieties of pea
plants by random crosses of natural
varieties.
B. Discovered the principles of heredity
by crossing different varieties of pea
plants and analyzing their traits in
subsequent generations.
C. Discovered which genes were
responsible for the inheritance of
specific traits.
D. Both B and C are correct
E. All A, B and C are correct
B
How do you call a trait produced by a
set of alleles?
A. Allelic variation
B. Gene map
C. Genotype
D. Phenotype
D
A scientist crossed a stock melon plant that
produced tan seeds with a plant that
produced red seed. All 13 offspring produced
tan seeds. What can you conclude from these
data?
A. The tan seed phenotype is
dominant
B. The red seed phenotype is
dominant
C. Both parents were
heterozygous for the seed
color phenotype
D. This is a typical example of a
dihybrid cross
A
If tan seed color (S) is dominant over cream
(s), what is/are the possible genotype(s) that
tan seeds could have?
A. SS
B. Ss
C. ss
D. A and B
E. A, B and C
D
The probability that a plant is tall is ¾. The
probability that a plant has purple flowers is
¼. What is the probability that a plant is tall
AND has purple flowers?
A. ¾
B. 1
C. ½
D. 3/16
E. 9/16
D
What is the purpose of a test cross?
A. To determine if an individual is
homozygous recessive
B. To determine the genotype of
an individual
C. To determine the phenotype of
an individual
D. To determine the genotype
AND the phenotype of an
individual
B
9:3:3:1 is the expected phenotype
ratio for a __________ cross,
assuming complete dominance
A. Monohybrid
B. Dihybrid
C.Trihybrid
B
Which of the following is correctly
referred to as an F2 individual?
A. Any offspring of a cross where the
genotypes are Aa x Aa
B. Any offspring who has at least one
F1 parent
C. Any offspring for whom both
parents are F1 individuals
D. Any individual who is
heterozygous at the two loci under
consideration
C
In guinea pigs, white coat color (w) is recessive to
black (W). What is the probability that a heterozygous
black guinea pig and a homozygous white guinea pig
produce white offspring?
A. 0/4
B. ¼
C. 1/2
D. ¾
E. 4/4
C
Bacteria and Archaea are interchangeable
names to describe the same type of
organisms
A. True
B. False
B
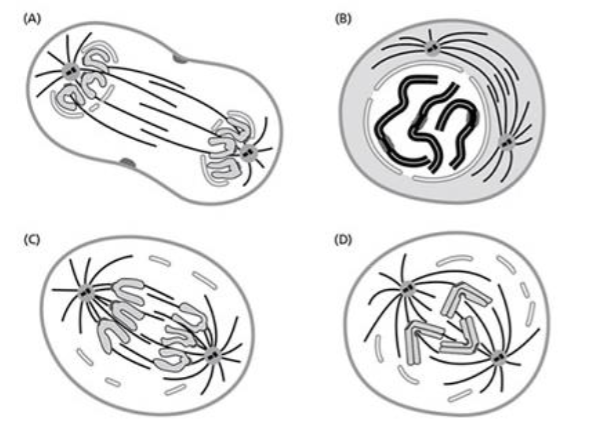
Which of these four cells is in anaphase of
mitosis? (You will probably have to check the
Zoom window to see the figure)
A. Cell A
B. Cell B
C. Cell C
D. Cell D
E. Cell E
C
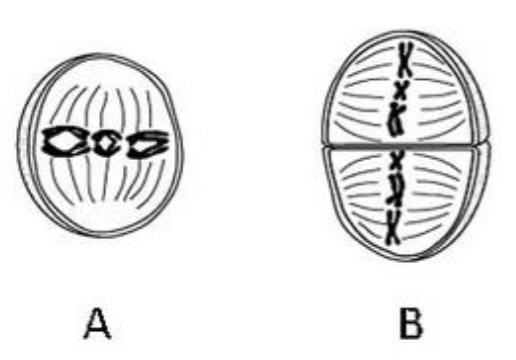
Based on the figure below, what stage of
cell division is depicted in Figure A?
A. Metaphase I
B. Anaphase I
C. Metaphase II
D. Interphase II
E. Telophase I
A
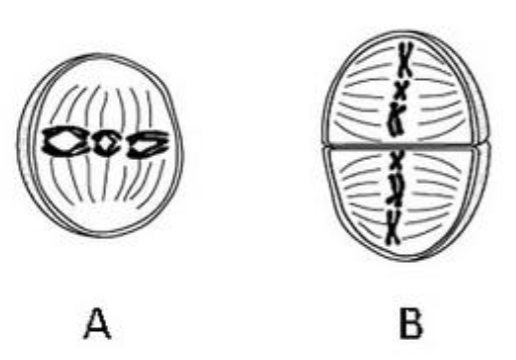
Based on the figure below, what is the diploid
chromosome number for this species? (Both
figures are the same cell at different stages of
cell division)
A. 2N = 12
B. 2N = 9
C. 2N = 8
D. 2N = 6
E. 2N = 4
D
Which statement is characteristic of the
bacteria and makes them different from
both the archaea and the eukaryotes?
A. Bacteria have no histones associated with
their chromosomes and the other two
groups do.
B. Bacteria do not have a nuclear envelope
and the other two groups do.
C. Bacteria have multiple chromosomes
whereas the other two groups have
single chromosomes.
D. Bacteria require mitosis for cell division
whereas the other two groups use
binary fission.
E. Bacteria have linear chromosomes
whereas the other two groups have
circular chromosomes.
A
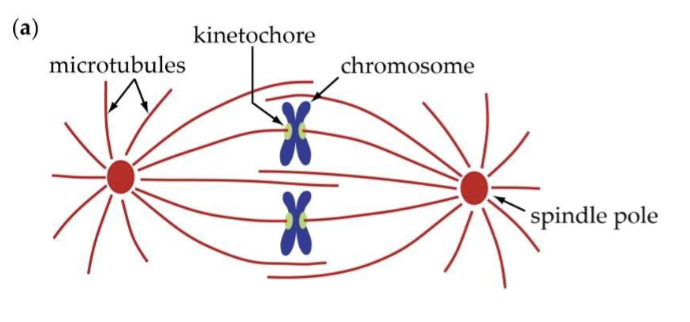
Which of the following statements best
describes the cell below?
A. This cell has 2 chromosomes
B. This cell has 2 sister
chromatids
C. This cell has 4 pairs of
chromosomes
D. This cell is in prophase
A
Which of the following is TRUE about
homologous chromosomes?
A. Usually are identical.
B. Are present only after S-phase.
C. Are always composed of two
sister chromatids
D. Are attached to a single
centromere in Metaphase I.
E. Usually have the same genes in
the same order as each other.
E
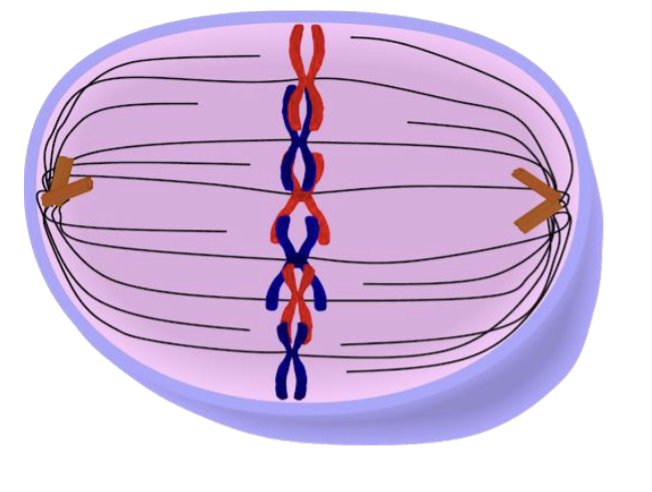
This cell in _________ contains
_____ chromosomes and _____
DNA molecules
A. Metaphase; 3; 6
B. Metaphase I; 3; 6
C. Metaphase; 6; 6
D. Metaphase I; 6; 6
E. Metaphase; 6; 12
E
Meiosis produces _____
A. Diploid somatic cells.
B. Haploid somatic cells.
C. diploid gametes.
D. Haploid gametes
D
In summary, Meiosis I
separates _____ while
Meiosis II separates _____
A. Homologous chromosomes;
Homologous chromosomes
B. Sister chromatids; Sister chromatids
C. Homologous chromosomes; Sister
chromatids
D. Sister chromatids; Homologous
chromosomes
C
The haploid amount of DNA in a human cell is
1.91 x 1012 Daltons. How much DNA (in
Daltons) do you expect to find after telophase
and cytokinesis of Meiosis I?
A. 3.82 x 1013 Daltons
B. 7.64 x 1012 Daltons
C. 3.82 x 1012 Daltons
D. 1.91 x 1024 Daltons
E. 3.82 x 1024 Daltons
F. 0.95 x 1012 Daltons
C
What are the overall consequences of
meiosis?
A. Four daughter cells are identical
to the parental cell
B. The chromosome number is
reduced
C. The daughter cells are
genetically different from each
other
D. Sister chromatids recombine
E. All of the above are correct
F. Only B and C are correct
F
Which of the following processes unique
to meiosis is NOT responsible for
introduction of genetic variation?
A. Crossing over
B. Random separation of
homologous chromosomes
C. Random separation of sister
chromatids
C
Which of the following options represents
a test cross?
A. TTSs x ttss
B. TTSS x TTSS
C. TtSs x TtSs
D. Ttss x Ttss
E. TTSs x ttSs
A
Which of the following options represents
a dihybrid cross?
A. TTSs x ttss
B. TTSS x TTSS
C. TtSs x TtSs
D. Ttss x Ttss
E. TTSs x ttSs
C
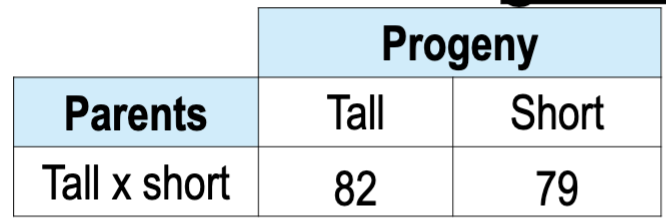
Tall plant height (T) is dominant over short (t). You
cross a tall and a short plant and obtain the following
tall and short progeny. What is the most probable
genotype of the parents?
A. TT x tt
B. TT x Tt
C. Tt x Tt
D. Tt x tt
E. tt x tt
D
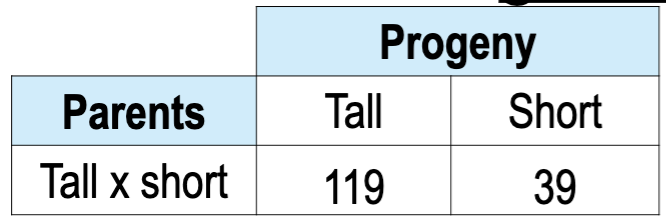
Tall plant height (T) is dominant over short (t). You
cross a tall and a short plant and obtain the following
tall and short progeny. What is the most probable
genotype of the parents?
A. TT x tt
B. TT x Tt
C. Tt x Tt
D. Tt x tt
E. tt x tt
C
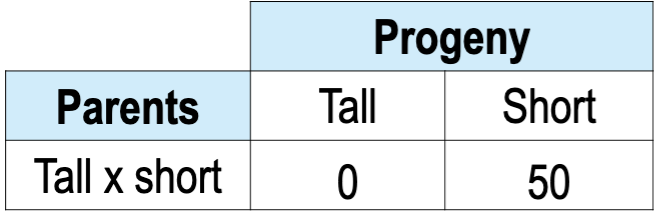
Tall plant height (T) is dominant over short (t). You
cross two plants obtain the following tall and short
progeny. What is the most probable genotype of the
parents?
A. TT x tt
B. TT x Tt
C. Tt x Tt
D. Tt x tt
E. tt x tt
E
Alkaptonuria results from an allele (a) that is
recessive to the allele for normal metabolism (A).
Sally is healthy and so is her mom. Her father has
alkaptonuria. What is Sally’s genotype?
A. AA
B. Aa
C. aa
D. Homozygous recessive
B
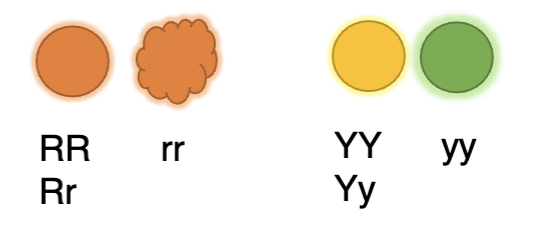
What is the probability of getting a round
and yellow seed from the RrYy x
RrYy cross?
A. 6/8
B. 9/16
C. 3/16
D. 1/16
E. 6/4
B
Which of the following genotypes could
represent a dull, orange and nonbitter
plant?
A. DDRRBB
B. DdRrBb
C. DDRrBb
D. DdRRBb
E. DdRrbb
• Dull: D
• Glossy: d
• Orange: R
• Cream: r
• Bitter: B
• Nonbitter: b
E
What is the probability of getting a dull,
orange and nonbitter seed from the F1
cross?
A. 27/64
B. 9/64
C. 6/64
D. 3/64
E. 1/64
• Dull: D
• Glossy: d
• Orange: R
• Cream: r
• Bitter: B
• Nonbitter: b
B
Sex is determined _____
A. Always by sex chromosomes.
B. Always by a small number of
genes on the Y chromosome.
C. Always by the number of X
chromosomes.
D. Always by the
presence/absence of a Y
chromosome
E. In many different ways in
different organisms.
E
Some animals and plants do not have sex
chromosomes but have genes that determine
sex. This type of sex determination system is
known as
A. Heterogametic sex determination
B. Homogametic sex determination
C. Chromosomal sex determination
D. Genic sex determination
E. Environmental sex determination
D
In mammals, how many X chromosomes are
active in a single somatic (non-germline) cell?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 1 for males, 2 for females
D. Different somatic cell types
will have different numbers of
active X chromosomes
A
The patchy distribution of color on
tortoiseshell cats results from
A. Cats having a single X chromosome
B. Multiple X chromosomes (XXY)
C. A Y-linked color determining gene
D. Random X-inactivation
E. Cats having environmental sex
determination
D
The modification of the amount of protein
produced by a sex chromosome is called __
A. Barr bodies
B. Dosage compensation
C. X-inactivation
D. X-linked expression
E. None of the above
B
You discover a new amphibian and name the sex
chromosomes A and B. If the female is
heterogametic and the male is homogametic, then
what would be the chromosome arrangement of
sex chromosomes in the adult?
A. Female AA and male BB
B. Female AB and male AB
C. Female AB and male BB
D. Female BB and male BB
E. Female XX and male XY
C
Which of the following scenarios best explains
the most likely origin and evolution of sex
chromosomes?
A. X and Y were never a pair, they pair up
only after all autosomes have paired
up, leaving no other
options
B. They were a pair of autosomes that
with time diverged and became the sex
chromosomes
C. We don’t really know, but scientists
believe sex chromosomes exist in the
last common ancestor for all eukaryotic
organisms
B
Males are haploid with respect to X. Any
allele on X is expressed in males
A. True
B. False
A
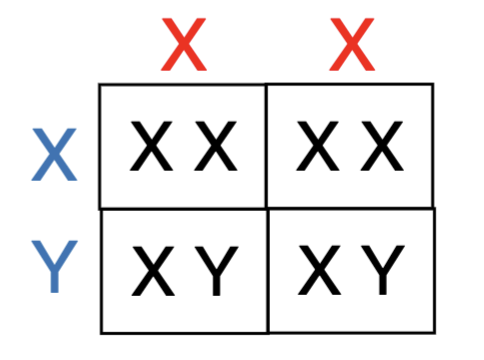
Crossing pure-breeding red eye females and
white males produced
A. All progeny with white eyes
B. All progeny with red eyes
C. Only the females with white eyes
D. Only the males with white eyes
E. Half of the females and half of the
males with white eyes
B

One form of red/green color blindness is inherited
as an X-linked recessive trait. Are there any of
the offspring from this cross colorblind?
Symbols:
• We will use + for the dominant,
normal allele
• c for the recessive, colorblind
allele
A. Yes, all of the offspring is affected
B. Only the females are colorblind
C. Only the males are colorblind
D. Only half of the females and half of the
males are colorblind
E. None of the offspring is colorblind
E
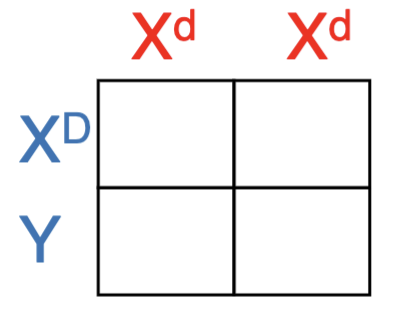
There is a form of metabolic vitamin D deficiency that is an X-linked dominant condition. What fraction of their daughters and sons will also have the disease?
A. All of the offspring will have the disease
B. Only the females will
C. Only the males will
D. Only half of the females and half of the
males will
E. None of the offspring will
B
Which of the following options correctly
represents the genotype of the fast-feathering
male and slow-feathering female birds?
• + is the slow, dominant allele
• s is the recessive, fast allele
A. Females are Z+ W and males Zs Zs
B. Females are Z+ Z+ and males Zs W
C. Females are Zs W and males Z+ Z+
D. Females are Zs Z and males Z+ W
E. Females are X+ X+ and males Xs Y
A
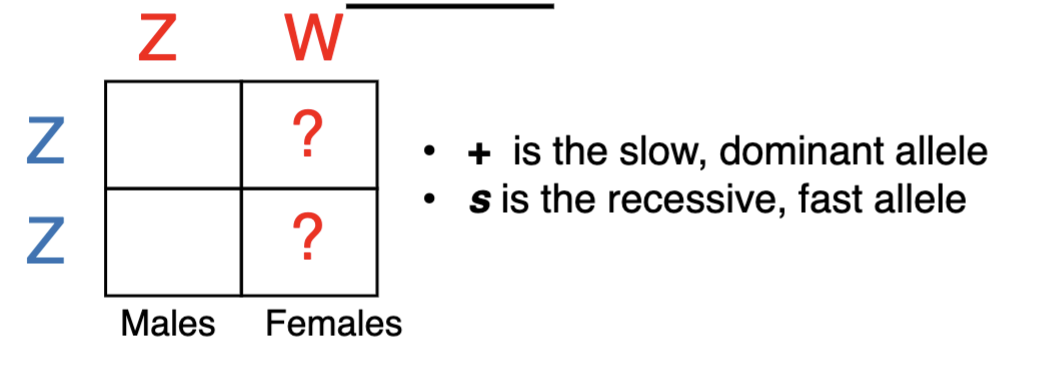
Fast-feathering is a Z-linked, recessive trait. The dominant
trait is slow-feathering. A fast-feathering male is crossed to
a slow-feathering female. What percentage of female
chicks will be FAST feathering?
A. None of them
B. 25% of them
C. 50% % of them
D. 75% of them
E. All of them
E
How many Barr bodies are present in a Poly-X
female (XXXX)? Hint: think about what Barr
bodies do and how many active X
chromosomes remain
A. None
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
E. 4
D
Which of the following is correct about X-
chromosome inactivation?
A. X-inactivation is a process that
systematically silences maternal or
paternal genes, based on the
chromosomal location of the trait
B. X-inactivation is a random process that
happens separately in individual cells
C. Dosage compensation is achieved in
animals by increasing the level of
expression on the male X-chromosome
D. Dosage compensation occurs in
individual cells that inherit the paternal
allele and X-inactivation in individual
cells that inherit the maternal allele
B
______________ is exhibited when the
heterozygote has a phenotype intermediate
between the phenotypes of the two
homozygotes
A. Complete dominance
B. Codominance
C. Incomplete dominance
D. Blended heterozygosis
C
In some cats, tail length is controlled by a single
gene. You have observed a large number of
families in these cats. In every single case where
one parent was long-tailed and the other was tail-
less, all of the offspring have short tails. This is
best explained ____
A. If the tail-length alleles show
incomplete dominance.
B. If long tails are dominant.
C. If tail length is X -linked.
D. If tail length is Y -linked.
E. As a particularly unlikely string
of observations.
A
Severity of symptoms of cystic fibrosis may
vary from one patient to the next. The
variation seen is representative of ___
A. Variable expressivity
B. Incomplete penetrance
C. Codominance
D. Dominant alleles
E. Recessive alleles
A
The term 'epistasis' refers to a situation
in which
A. A single gene has more than two
alleles.
B. Two genes share a single allele.
C. Two genes are found in different
chromosomes
D. Two independent genes both have
alleles with incomplete dominance.
E. The genotype at one locus affects the
phenotype observed at a different
locus
E
Allele C in chromosome 1 determines eye color in an
animal. Allele E chromosome 2 determines if the animal
has eyes, which is dominant over e (no eyes) . An animal
with the genotype CcEE has brown eyes and an animal
with the genotype CCee has no eyes. This is an example
of _____
A. Codominance
B. Incomplete dominance
C. Recessive epistasis
D. Dominant epistasis
E. Dosage compensation
C

When you look at the phenotype by looking at the
fruits themselves, you see that the fruits can be
purple, violet or white. At this level, the relationship
between the alleles is:
A. The purple allele is dominant
B. Incomplete dominance
C. The alleles are co-dominant
B

When you sequence the mRNA of the enzyme, you find
that violet plants have two different forms of the mRNA.
The two forms are identical except for a single nucleotide
difference, and they are both equally abundant in each
cell. At this level, the relationship between the alleles is:
A. The purple allele is dominant
B. Incomplete dominance
C. The alleles are co-dominant
C
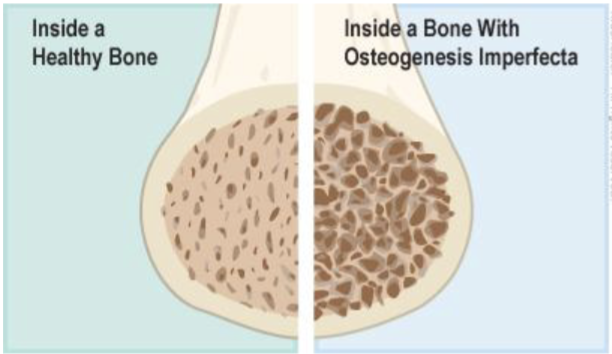
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a disease associated with a mutation in COL1A1, a gene than synthesizes collagen. Scientists studying _______ of this disease, found that 70% of mice that carry the mutated gene exhibited symptoms of OI
A. Penetrance
B. Expressivity
C. Epistatic interaction
D. Incomplete dominance
A
The difference between dominance and
epistasis is that _____
A. Dominance masks genes at
different loci
B. Epistasis mask genes at the
same loci
C. Epistasis masks genes at
different loci
D. All of the above
E. There is no difference
C

You cross a black Labrador (BB EE) with a yellow
Labrador (bb ee). What are the genotypes and
phenotypes of the expected progeny?
A. All of the progeny is Bb Ee, an
intermediate between black and
yellow = Brown
B. All progeny is Bb Ee (Black coat
and color deposited) = Black
C. Half of the progeny is Bb Ee (Black
coat and color deposited) = Black,
and half is bb ee (brown color and
color not deposited) = yellow
B

Which of the following genotypes will be associated
with a yellow Labrador?
A. BB ee
B. bb Ee
C. Bb EE
D. BB EE
A

What is the probability of obtaining a yellow
Labrador when crossing Bb Ee x Bb Ee?
A. 9/16
B. 3/16
C. 2/16 or 1/8
D. 4/16 or ¼
E. 5/16
D

The allele that masks the expression of the other
allele is known as the epistatic allele. In the
previous example, the epistatic allele is
A. E
B. e
C. B
D. b
B
• A woman (blood type A) gives birth to a baby (blood type O).
• What is the expected blood type for the father?
• Her husband (blood type AB)
The phenotype of the child born to
type A and type AB parents could
by explained by
A. Incomplete dominance
B. Recessive epistasis
C. Dominant epistasis
D. Codominance
E. Sex-linkage
F. Can’t be explained, he is
not the father
D
In animals, the mitochondrial DNA is
_____the nuclear genome and is inherited
_________.
A. Separate from; From both
parents
B. Part of; From both parents
C. Separate from; Only from
the mother
D. Part of; Only from the
mother
E. Separate from; Only from
the father
C
In some snails, all offspring of a mother
with the genotype LL or Ll will have
shells that coil to the left – regardless of
the offspring’s genotype. Which type of
inheritance is this?
A. Maternal effect
B. Cytoplasmic inheritance
C. Sex-linked
D. Sex-limited
E. Sex-influenced
A
Precocious puberty behaves as a dominant trait
in males, but has no effect (zero penetrance) on
females. What kind of trait is it?
A. X-linked dominant
B. Sex-determined
C. Sex-influenced
D. Sex-limited
D
In humans, a common form of colorblindness is
caused by mutations at a gene located on the X-
chromosome. Consequently, males are much more
likely to exhibit this form of colorblindness than are
females. Which type of inheritance is this?
A. Genetic maternal effect
B. Sex-linked
C. Sex-limited
D. Sex-influenced
B
When RNA or protein from the mother is loaded into
the oocyte and they affect the development of the
offspring independent of the offspring’s genotype, this
referred to as ______________.
A. Maternal inheritance
B. Maternal interference
C. Genetic maternal effect
D. Genomic imprinting
C
In some goats, the presence of horns is produced by an
autosomal gene that is dominant in males and recessive
in females. Which of the following represents a cross
between a horned female is crossed with a hornless
male?
A. H+ H+ male x H+ H+ female
B. H- H- male x H- H- female
C. H+ H- male x H+ H- female
D. H- H- male x H+ H+ female
E. H+ H+ male x H- H- female
D (unsure)
Genetic maternal effect is another
name for cytoplasmic inheritance
A. True
B. False
B
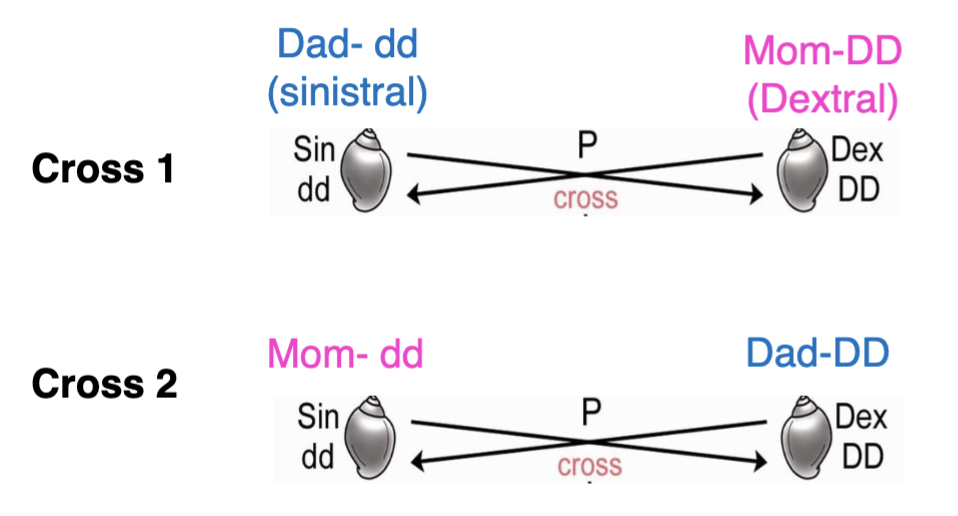
The two following crosses produce offspring with the
genotype Dd. Because D (dextral) is dominant over d
(sinistral), offspring from both crosses will be dextral
A. True
B. False
B

The color of leaves in these plants is determined by a
gene in chloroplastic DNA. What would be the
phenotype of the offspring in the following cross?
A. All plants would have green leaves
B. All plants would have white leaves
C. All plants would have variegated (white and
green splotches)
D. Half plants would have green leaves and
half would have white leaves
E. Some plants would have green leaves and
some white leaves, in a 3:1 ratio
A
Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) results
from a mutation in mitochondrial DNA. For this
disease, all of the following are expected EXCEPT
that ___
A. The disease is passed from mother to
all children.
B. A child who has the disease had a
mother who had LHON.
C. The severity of the disease varies
depending on how many copies of
mutated mitochondrial genes are
present.
D. None of the above; they are all true
C
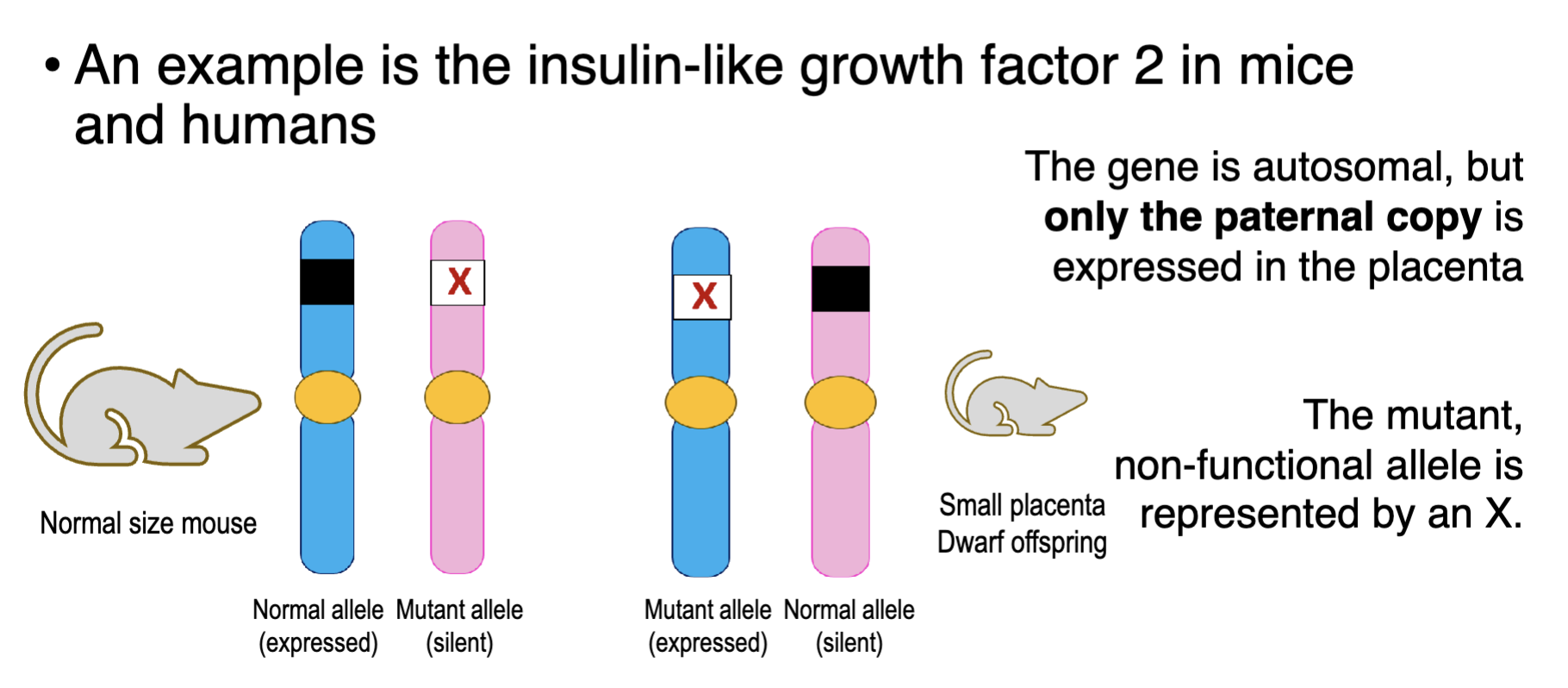
A female mouse carries a mutation in the IgF2
gene in chromosome 15. How is this going to
affect the phenotype of her offspring?
A. The offspring would die young
B. Only the male offspring would be
affected
C. Only the female offspring would be
affected
D. None of her offspring would be
affected
D
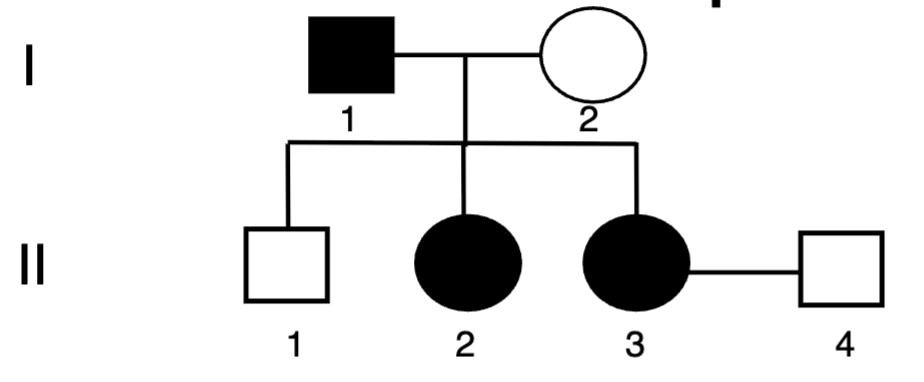
In the pedigree below, individual 1 in the
top row is an
A. Affected male
B. Unaffected male
C. Affected female
D. Unaffected female
A
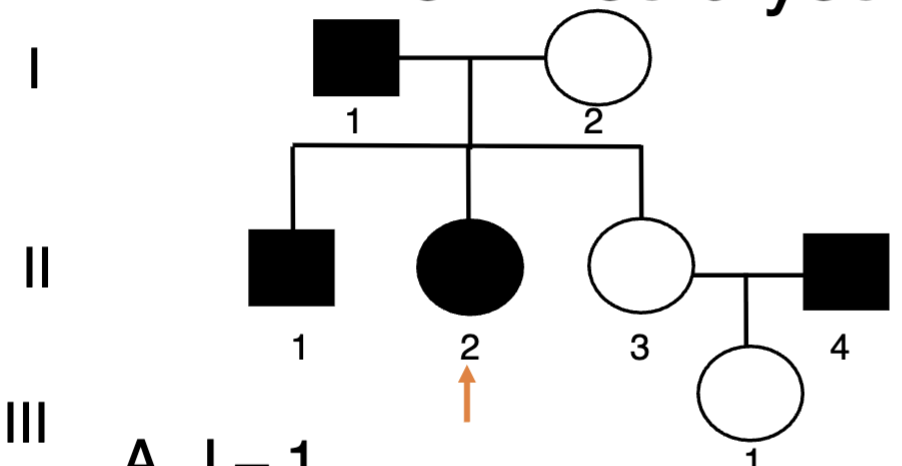
If you wanted to refer to the individual pointed
with an orange arrow in the pedigree below,
how would you describe them?
A. I – 1
B. I – 2
C. II- 2
D. II – 3
E. III - 1
C
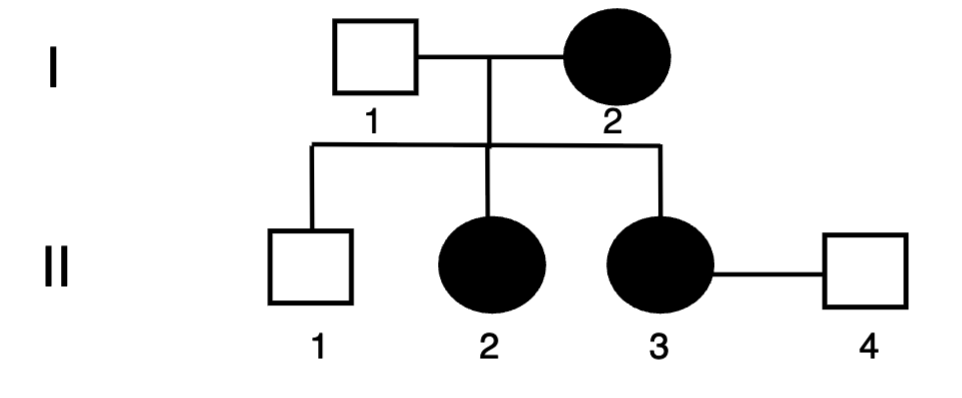
Which of the following statements best
describes the pedigree shown below?
A. The first generation have four children: two males
and two females
B. All the females in the second generation are carriers
C. All the females in the second generation are affected
D. Half of the females in the second generation are
affected
E. A and C
C
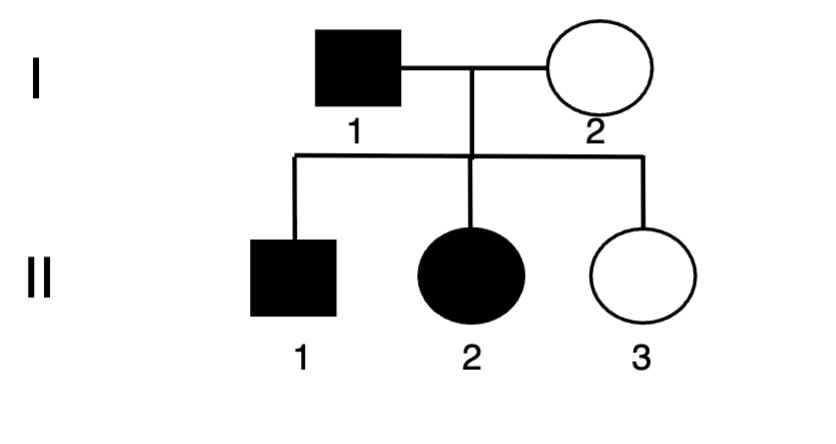
The pedigree below could represent a Y-
linked inherited trait
A. True
B. False
B
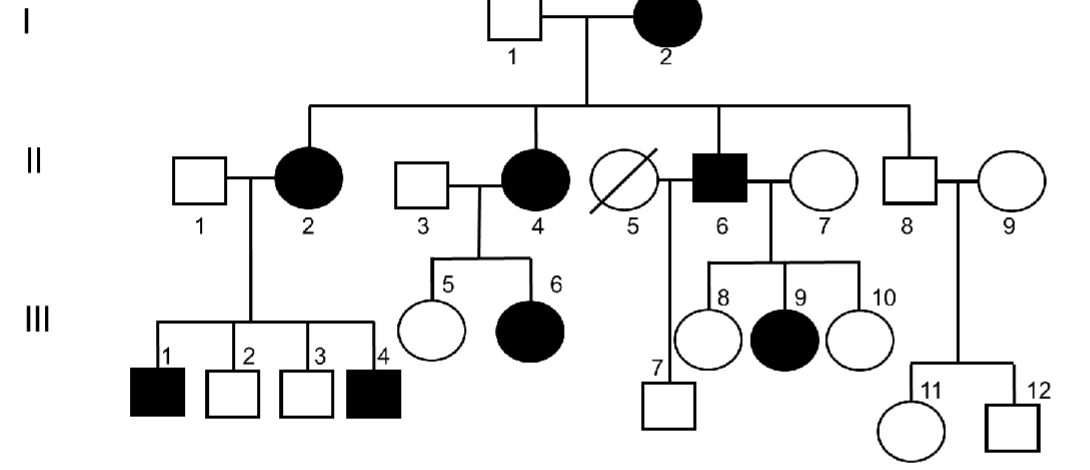
The pedigree below
represents the inheritance of a trait in a family. If the mutation
was recessive, what would individuals I-1, II-1 and II-3 have
in common?
A. They are heterozygous
B. They are homozygous dominant
C. They are homozygous recessive
D. They carry the mutated allele in the Y-
chromosome
A
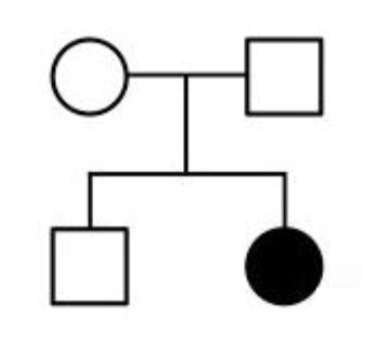
The following pedigree could represent
the mode of inheritance of an autosomal
dominant trait
A. True
B. False
B
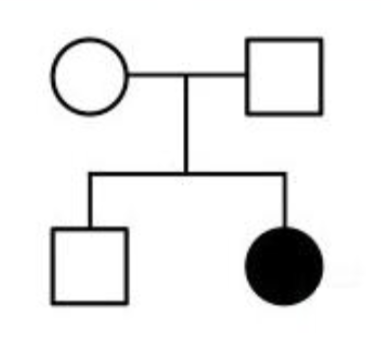
If the following pedigree represents the mode of inheritance of an autosomal recessive trait, what could be the genotype of the parents?
A. Both parents are homozygous recessive
B. Both parents are homozygous dominant
C. One of the parents is homozygous dominant
and the other one is homozygous recessive
D. At least one of the parents must be
heterozygous
E. Both parents must be heterozygous
E
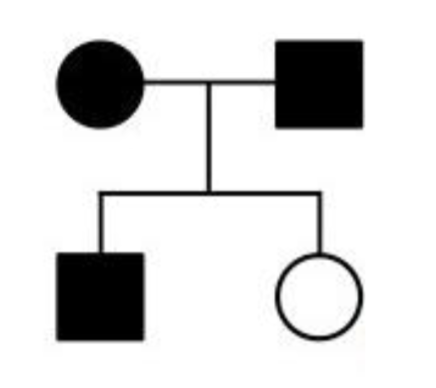
The following pedigree could also represent
the mode of inheritance of an autosomal
recessive trait
A. True
B. False
B
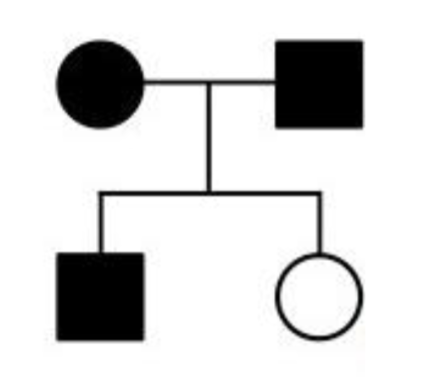
If the following pedigree represents the mode
of inheritance of an autosomal dominant trait,
what could you conclude about the genotype
of the parents?
A. Both parents are homozygous recessive
B. Both parents are homozygous dominant
C. One of the parents is homozygous dominant
and the other one is homozygous recessive
D. At least one of the parents must be
heterozygous
E. Both parents must be heterozygous
E
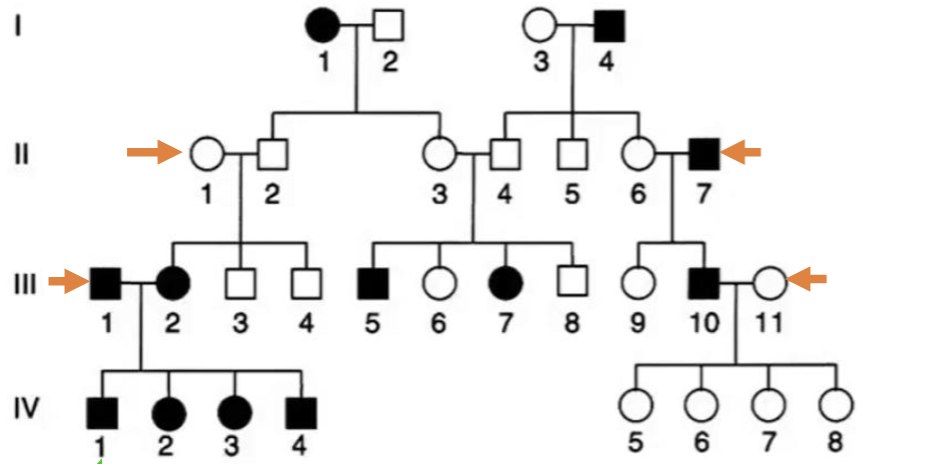
Which set of parents, by themselves,
shows that this trait must be recessive?
A. II – 1+2
B. II - 6+7
C. III - 1+2
D. III - 10+11
E. More than one set of parents could
support this
A
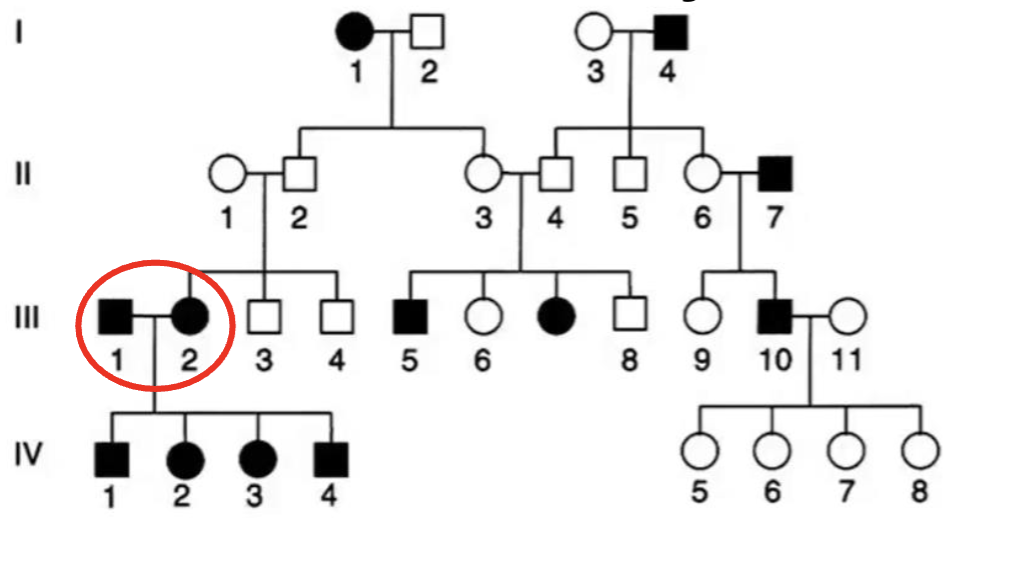
By focusing only on the cross between III
1+2,you can infer that:
A. This trait definitely dominant
B. This trait is definitely recessive
C. Cannot tell precisely from this
cross
C
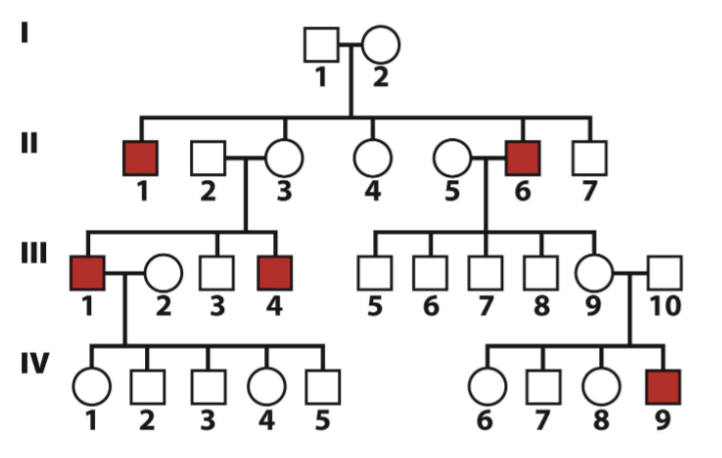
If the trait tracked in the following pedigree is inherited in
an X-linked recessive manner, what is the expected
genotype for II-3 and III-9?
A. Probably both homozygous
recessive
B. Probably both homozygous
dominant
C. Probably both heterozygous
C
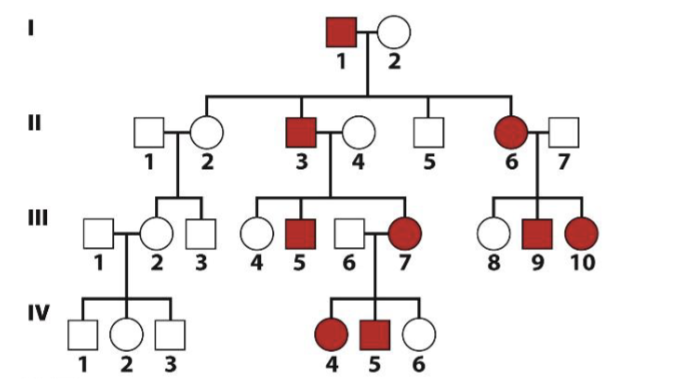
What is the most likely form of inheritance of this
disease?
A. Probably X-linked dominant
B. Probably X-linked recessive
C. Probably autosomal dominant
D. Probably autosomal recessive
D (im pretty sure)
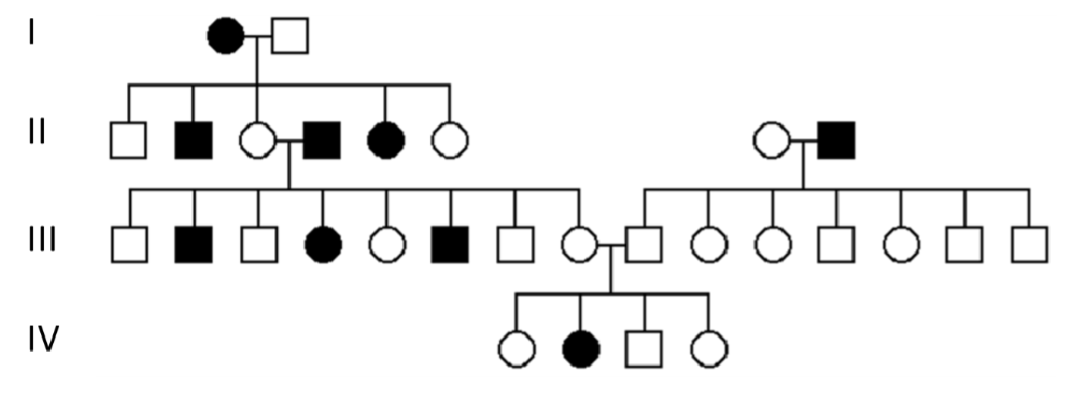
The following is a pedigree for in which some members are
“taste blind” (i.e., insensitive to bitterness or strong tastes).
What is the most likely mode of inheritance of this trait?
A. Definitely an autosomal dominant trait
B. Definitely an autosomal recessive trait
C. Definitely an X-linked dominant trait
D. Definitely an X-linked recessive trait
B
When performing a dihybrid cross, you
expect to see a 9:3:3:1 ratio. What is a good
explanation if you do not see a 9:3:3:1 ratio in
a dihybrid cross?
A. The two genes are found in different
chromosomes
B. The two genes are close to each
other and linked
C. One of the genes is dominant over
the other
D. The two genes assort independently
E. This proves that Mendel’s laws are
incorrect
B
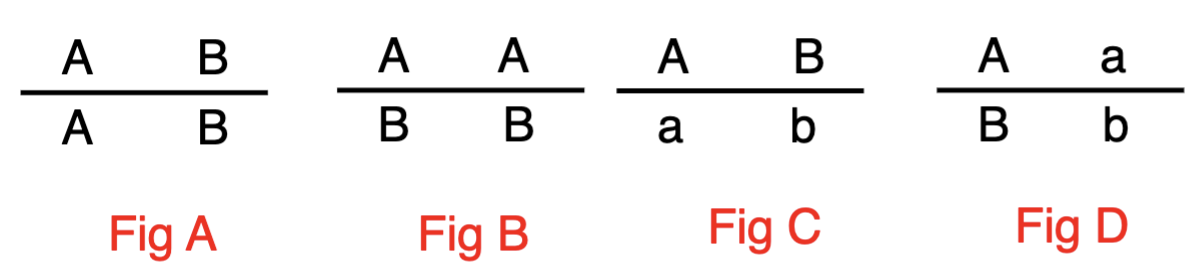
An individual is homozygous dominant for genes A and
B. If both genes are located in the same chromosome,
what would be the correct notation for the A and B loci?
A. Figure A
B. Figure B
C. Figure C
D. Figure D
A

An individual is heterozygous for genes A and B
and has the following genotype (look at picture). Which gametes are expected to be produced from that individual (assume genes A and B are unlinked)?
A. A, a, B and b
B. AA, AB, BB and bb
C. AA, Aa, aa, BB, Bb and bb
D. AB, Ab, ab and aB
D
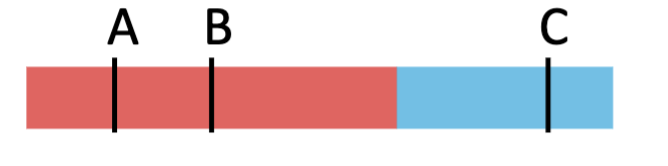
Two genes that lie far apart in the same
chromosome (A and C) are more likely to
undergo crossing over during meiosis, than two
genes that lie close together (A and B)
A. True
B. False
A
We testcross a tomato plant that is a dihybrid.
Tall (D) is dominant over dwarf (d), and smooth
(P) is dominant over hairy (p). What is the
cross?
A. DpDp x DpDp
B. DdPp x DdPp
C. ddpp x ddpp
D. DdPp x ddpp
D
Which of the following processes unique
to meiosis is NOT responsible for
introduction of genetic variation?
A. Crossing over
B. Random separation of
homologous chromosomes
C. Random separation of sister
chromatids
C

If genes N and Q are fully linked and no
crossing over occurs between them, what do
you expect to see from a dihybrid cross? (look at picture)
A. 1 and 2
B. 1 and 3
C. 1, 2 and 4
D. 1, 3 and 4
A
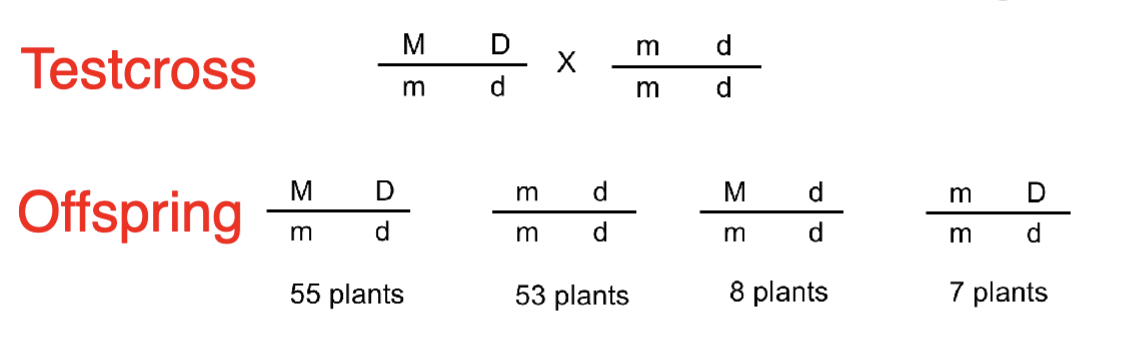
You testcross two tomato plants and obtain
the following results. What can you conclude
about these genes?
A. The genes are fully linked and no crossing over
occurred
B. The genes are somewhat linked but some
crossing over occurred
C. The genes are unlinked and assort independently
D. The genes are linked and assort independently
B
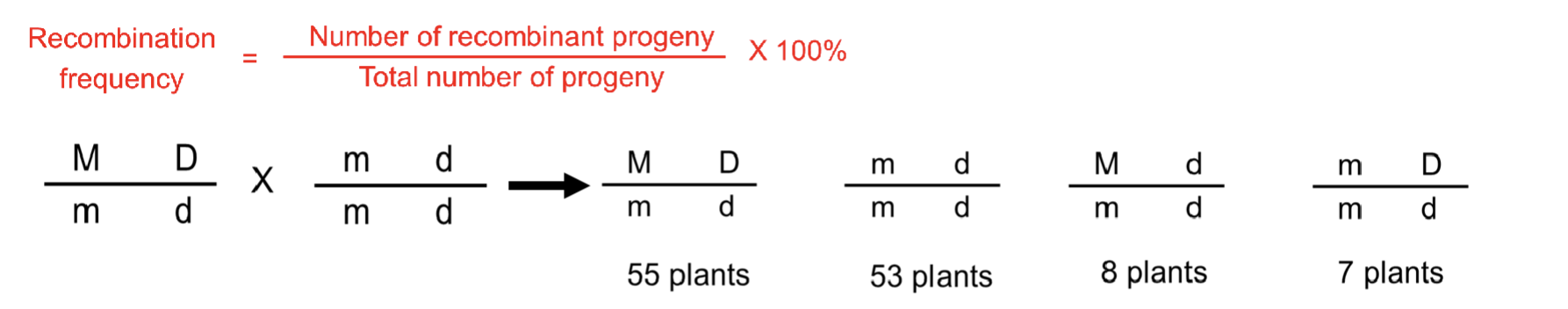
What is the recombination frequency of
the following cross?
A. 12%
B. 15%
C. 1.2%
D. 1%
E. 25%
A
In our practice problem, the recombination
frequency between genes M and D was
12.2%. Therefore, the distance from gene
M to D is approximately
A. 1200 base pairs (bp)
B. 120 centimorgans (cM)
C. 15 map units (m.u)
D. 12 map units (m.u)
E. 12 base pairs (bp)
D
You are mapping genes D, E and F. To do so,
you perform the required experiments and
determine that the recombination frequency
between D and E is 35% and the recombination
frequency between D and F is 19%. What can
you conclude about these genes?
A. D, E and F are in different
chromosomes.
B. D and E are closer to each
other than E and F
C. D and F are closer to each
other than D and E
C
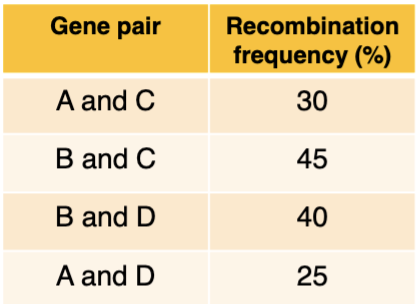
Based on the data about recombination
frequency, which genes are farthest apart?
A. A and C
B. B and C
C. B and D
D. A and D
E. A and B
B
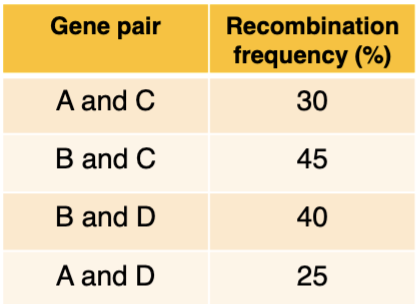
If the distance between B and C is 45 m.u and
between B and D is 40 m.u, what is the distance
between C and D?
A. 85 m.u
B. 20 m.u
C. 15 m.u
D. 10 m.u
E. 5 m.u
E
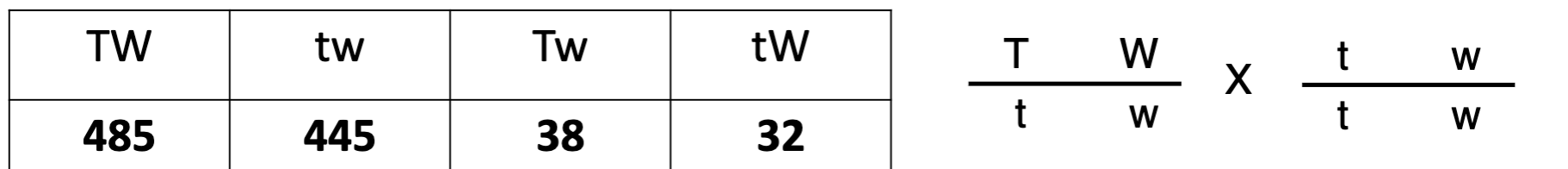
You cross a dihybrid individual TtWw with a homozygous ttww
and obtain the following numbers of each kind of offspring
phenotype combination. What is the recombination frequency
between these genes?
A. 0.07 or 7%
B. 0.96 or 96%
C. 0.039 or 3.9%
D. 0.45 or 45%
A