Week 7 (Chapter 27): Instrumentation of Dental Implants
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PPT- done
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Which of the following best describes the nature of a dental implant as defined in your notes?
A non-biologic (artificial) device inserted into the jawbone.
What are the primary clinical purposes of placing a dental implant?
To replace individual teeth and support fixed bridges or removable dentures.
Which of the following is considered the most critical clinical sign of implant failure?
Presence of implant mobility.
According to the success criteria, what is the maximum acceptable amount of vertical bone loss per year after the first year of function?
Less than 0.2 mm
On a radiograph, what should a successful implant look like in relation to the surrounding bone?
Absence of peri-implant radiolucency.
What is the biological definition of 'Osseointegration'?
Direct contact of living bone with surface of implant
body
Why is osseointegration considered the 'major requirement' for implant success?
It provides the necessary stability to support occlusal (biting) forces.
Which component of the dental implant is surgically placed into the bone and acts as the 'artificial root'?
Implant Body
What is the primary function of the 'Abutment' in an implant system?
To connect the implant body to the prosthetic crown.
Which specific feature of the implant body is designed to ensure seamless bone integration and provide mechanical stability?
Threads running down the entire body.
What is the primary function of the implant body in relation to the alveolar bone?
To provide stability and support for the entire prosthesis.
Which component acts as the 'connector' between the buried implant body and the visible prosthetic crown?
Abutment
What are most abutments made of to ensure biocompatibility with the surrounding gingival tissue?
Titanium or nonmetallic materials like Zirconia.
What is meant by the statement that titanium is not rejected by the body?
It is highly biocompatible, allowing bone cells to integrate without an immune response.
Besides biocompatibility, what are the other physical properties of titanium mentioned in your notes?
Strength and heat resistance.
Why is it contraindicated to use standard stainless steel scalers on a titanium implant abutment?
Stainless steel is harder than titanium and will scratch the implant surface.
How can the strength of titanium be improved for dental applications according to your notes?
By using an alloy mix of metals.
Why is it important to avoid leaving 'instrument residue' on the implant surface?
It can cause a foreign body reaction or localized inflammation.
Which of the following is the safest choice for removing soft biofilm from an implant abutment?
A plastic or resin-coated curette.
What is a primary aesthetic advantage of using Zirconia implants over Titanium implants?
Its ivory color prevents a dark or grayish shadow from showing through the gums.
Which physical property makes Zirconia suitable for long-term use in the jawbone?
High degree of fracture resistance and strength.
What is a major esthetic advantage of PEEK over titanium implants?
It mimics the natural color of teeth
Is PEEK a metal alloy or a synthetic polymer?
Synthetic polymer
Why is PEEK potentially less suitable for a patient with severe bruxism (teeth grinding)?
Because it has lower wear resistance and may wear down under heavy forces.
Which of the following is a significant 'drawback' of using PEEK for dental implants compared to titanium?
Lower resistance to wear and abrasion
PEEK is often described as having an 'Elastic Modulus' similar to what human structure?
Alveolar bone
Why is PEEK currently not used as widely as titanium in general dental practice?
Lack of a standard treatment protocol
Why might a clinician choose a PEEK abutment over a titanium one for a patient's front tooth?
Because PEEK prevents the gray shadow effect through thin gingival tissue.
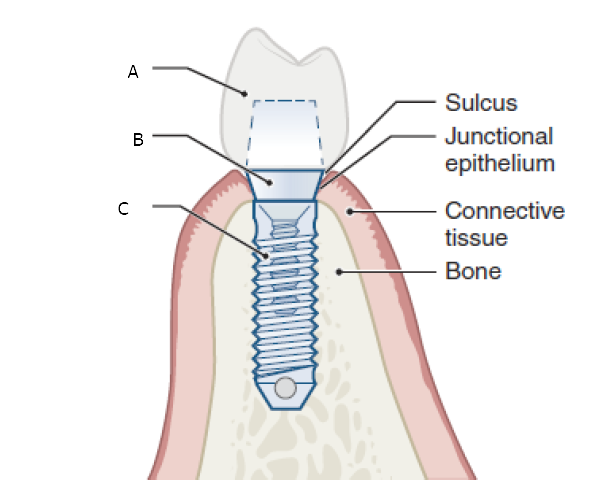
Label the picture correctly
A- Prosthetic crown B-Abutment post C- Implant fixture
Both periodontal disease and peri-implant disease share the same primary etiology, which is:
Oral biofilm (plaque)
Compared to periodontal inflammation around natural teeth, peri-implant disease is characterized by which of the following?
More pronounced tissue inflammation
How does the 'progression rate' of peri-implant disease compare to that of natural periodontal disease?
It progresses at a faster rate
Which statement is true regarding the 'probing depths' in peri-implant disease versus periodontal disease?
Probing depths tend to be deeper in peri-implant disease
Regarding the microorganisms found in peri-implant pockets, which of the following is correct?
Pockets can harbor more pathogenic microorganisms
Why is the inflammation in peri-implant disease described as 'more pronounced'?
Due to the structural differences and increased bacterial load
What is the primary goal of intercepting signs and symptoms during a maintenance visit?
To stop the disease before it progresses to advanced stages
A clinician uses a maintenance visit to 're-engage' a patient. What does this typically mean?
Encouraging the patient to improve their compliance with home care
Which of the following is an example of an 'interventional step' taken by a clinician during maintenance?
Professional biofilm removal using specialized plastic instruments
Why is 'patient compliance' particularly critical for implant success?
Because biofilm is the primary etiology for peri-implant disease
If a clinician misses the opportunity to 'intercept' early signs of peri-implant mucositis, what is the most likely outcome?
It may progress rapidly to peri-implantitis and bone loss
Parameters Assessed at Periodic Assessment Visits except?
Asthetic examination
Which parameter involves measuring the distance from the gingival margin to the base of the peri-implant sulcus?
Probing depths
Why is 'Occlusion' assessment a necessary part of an implant periodic visit?
To ensure no excessive force is damaging the implant or bone
According to current consensus, which of the following is true about probing an implant?
Gentle probing is safe and does not jeopardize the implant's longevity.
When is it generally safe to begin routine probing of a new implant?
3 to 6 months after abutment healing is complete
What is the most important factor in determining the change from 'health' to 'disease' during maintenance?
Comparing current probing depths to the initial baseline visit
If an implant had an initial probing depth of 3mm but now measures 6mm after one year, what does this indicate?
Significant change indicating potential peri-implant disease
Why is it particularly important to use 'gentle force' when probing an implant?
Because the biological seal is only weakly adherent and can be easily penetrated.
What is the benefit of dipping the probe tip in chlorhexidine before measuring?
It helps reduce the risk of introducing bacteria into the implant site.
Why is the biological seal around an implant considered more vulnerable than the attachment around a natural tooth?
It is only weakly adherent to the titanium surface
Which type of probe is specifically noted for being 'more flexible' and able to move around complex contours?
Plastic probe
What does applying a 'tight lateral force' during probing help to protect?
The titanium surface of the implant
When using a 'metal probe' on a titanium implant, what is the most important rule to follow?
Keep the touch light
If an implant shows 'Absence of bleeding upon probing,' what does this likely indicate to the clinician?
The peri-implant tissues are healthy and stable.
.
Why is 'Persistent bleeding' at successive appointments a major concern?
It indicates ongoing inflammation that may lead to bone loss.
What is 'Suppuration' primarily composed of in an infected implant site?
Necrotic tissue, dead neutrophils, and cellular debris.
What does the presence of suppuration around an implant site signify?
A positive indicator of active peri-implant disease.
Unlike natural teeth, which have a periodontal ligament that allows for slight 'physiological mobility,' how should a successful dental implant feel when tested?
It should have absolutely zero mobility.
If an implant body itself is mobile, what does this indicate about the 'Osseointegration'?
The osseointegration has been compromised or lost.
Why is it necessary to use a 'consistent radiographic technique' when monitoring an implant over several years?
To ensure that any bone level changes measured are real and not due to different camera angles.
True or False: Radiographic bone loss alone is a definitive indicator of current, active peri-implant disease.
False. It must be paired with clinical signs of inflammation like bleeding or pus.
What is the primary meaning of 'Interceptive' in the CIST protocol?
Stopping the disease at an early stage before it worsens.
In measuring Clinical Attachment Level (CAL) for an implant, what serves as the 'fixed reference point'?
The margin of the restoration
In the CIST protocol, what does the term 'Cumulative' imply regarding the treatment approach?
If one stage fails, it is maintained while adding the next stage of therapy.
According to the CIST stages, what is 'Stage 2' of the treatment regimen?
Antiseptic therapy
A patient has an implant with a 4mm pocket depth and no bone loss. According to the CIST protocol, what should the clinician do?
Perform both Stage 1 (Instrumentation) and Stage 2 (Antiseptic therapy).
What is the indicated therapy for an implant with a 2mm pocket depth and no signs of inflammation?
No therapy indicated, only maintenance.
Pocket depth 3mm or less with plaque and signs of inflammation?
Nonsurgical periodontal instruement
Pocket depth > 5mm with bleeding on probing but no bone loss?
First two stages of treatment
If an implant site has a pocket depth of 4mm but NO radiographic bone loss, which stages of CIST are applied?
Stages 1 and 2
What clinical finding triggers the transition from Stage 2 to Stage 3 in the CIST protocol?
Evidence of radiographic bone loss (2mm or less)
For a pocket depth >5mm with bleeding but NO bone loss, which cumulative regimen is indicated?
Mechanical instrumentation + Antiseptic therapy
A site has a 6mm pocket depth and 1.5mm of radiographic bone loss. Which therapy stage is newly added to the regimen?
Antibiotic therapy
When bone loss around an implant exceeds 2mm with a deep pocket (>5mm), what is the final stage of the CIST protocol?
Surgical therapy or referral to a specialist
Which of the following materials is commonly used to manufacture scalers and curettes specifically designed for debriding implant surfaces?
Plastic, Titanium, or Carbon fiber
Why does calculus not adhere to an implant surface as 'tenaciously' as it does to a natural tooth?
Because there is no microscopic interlocking with the smooth titanium surface.
How should the clinical scaling stroke be adjusted when removing calculus from an implant compared to a natural tooth?
Use much lighter lateral pressure.
What is the primary clinical consequence of scratching a titanium implant surface with a steel instrument?
It creates plaque-retentive surfaces that harbor bacteria.
According to the notes, what happens to 'dissolved titanium particles' that result from surface damage?
They can enter the circulatory system and spread to organ systems.
How does damage to the implant surface affect the surrounding alveolar bone?
It impairs 'osteoblastic attachment' to the bone.
instruments on an implant?
Short, controlled strokes with light lateral pressure.
What is a major biological risk of leaving plastic residue on an implant surface?
It can trigger a foreign body response and impair osteoblastic attachment.
What is a major advantage of the 'thinner blade' found on titanium instruments compared to plastic ones?
It allows for better access to deep pockets and interproximal areas.
Why is titanium more effective than plastic for removing residual cement around an implant?
Because it is more rigid and has greater strength.
Why is it a concern that titanium instruments can alter implant surface topography?
Because changing the surface texture can make the implant more prone to bacterial colonization.
What can happen on the implant surface after repeated use of titanium instruments?
Residual titanium particles from the instrument may be left behind on the implant.
What is the primary benefit of reinforcing a plastic instrument with carbon fiber?
It increases the instrument's strength and resilience compared to pure plastic.
What is the primary physical risk when applying 'excessive lateral force' to a carbon fiber instrument?
The tip can break off and become lodged in the peri-implant tissue.
What biological complication can arise from 'imbedded particles' of carbon fiber in the soft tissue?
An immunological reaction.
When using an ultrasonic scaler on an implant, what type of tip is mandatory to avoid surface damage?
Nonmetallic tips made of plastic or carbon fiber
Why are powered devices with nonmetallic tips considered 'more effective' than hand instruments of the same material?
Because they provide better lavage and biofilm disruption through vibration.
Which statement is true regarding the routine polishing of dental implants?
Implants do not require routine polishing; it should only be done when indicated.
What is the primary function of glycine powder in air polishing an implant?
To physically disrupt and dislodge the plaque biofilm.
Why is air polishing described as 'not a stand-alone' modality?
Because it cannot remove hard deposits like calculus or excess cement.
What is the generally appropriate maintenance interval for an implant patient during the first year after restoration?
Every 3 months
How should the maintenance frequency for dental implants be determined?
It is determined on an individual basis considering specific risk factors.
After the initial 12-month period, what is the generally considered interval for maintenance visits?
3 to 6 months
Why is it essential to identify 'risk factors' when establishing a maintenance schedule?
To estimate the prognosis and decide how frequently the patient needs monitoring.
Which of the following biological conditions would justify shortening the interval between maintenance visits?
Reduced bone support around the implant.
Why does Inflammation indicate a need for more frequent professional care?
Because it can lead to rapid bone loss (peri-implantitis) if not managed closely.