Option E-2 Tourism and sport at the local and national scale
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
primary tourist resources
pre-existing tourist attractions that often exist naturally e.g. the weather, wildlife, beaches, indigenous people or mountains
secondary tourist resources
facilities that have been purposefully built for tourists e.g. hotels, restaurants, golf courses and airports
physical attractions
attractions created by nature e.g. beaches, mountains, climate ones, caves, wildlife
cultural attractions
these are human made attractions e.g. cultural areas, historic buildings or monuments, amusement parks, festivals
heritage tourism
tourism based on historic legacy as its main focus e.g. natural landscape, historical buildings
adventure tourism
a form of tourism in natural areas that incorporates an element of risk, higher levels of physical exertion, and the need for specialised skills
tourism hotspots
places that experience high levels of tourist arrivals and
usually have a very large number of visits at the same time
sphere of influence
the area from which people are attracted from to use a service
leisure hierarchy
has a strong correlation with settlement hierarchy. Settlement hierarchy is usually measured by three variables:
- Population size
- Range and number of services
- Sphere of influence
larger settlements have higher order leisure facilities and services
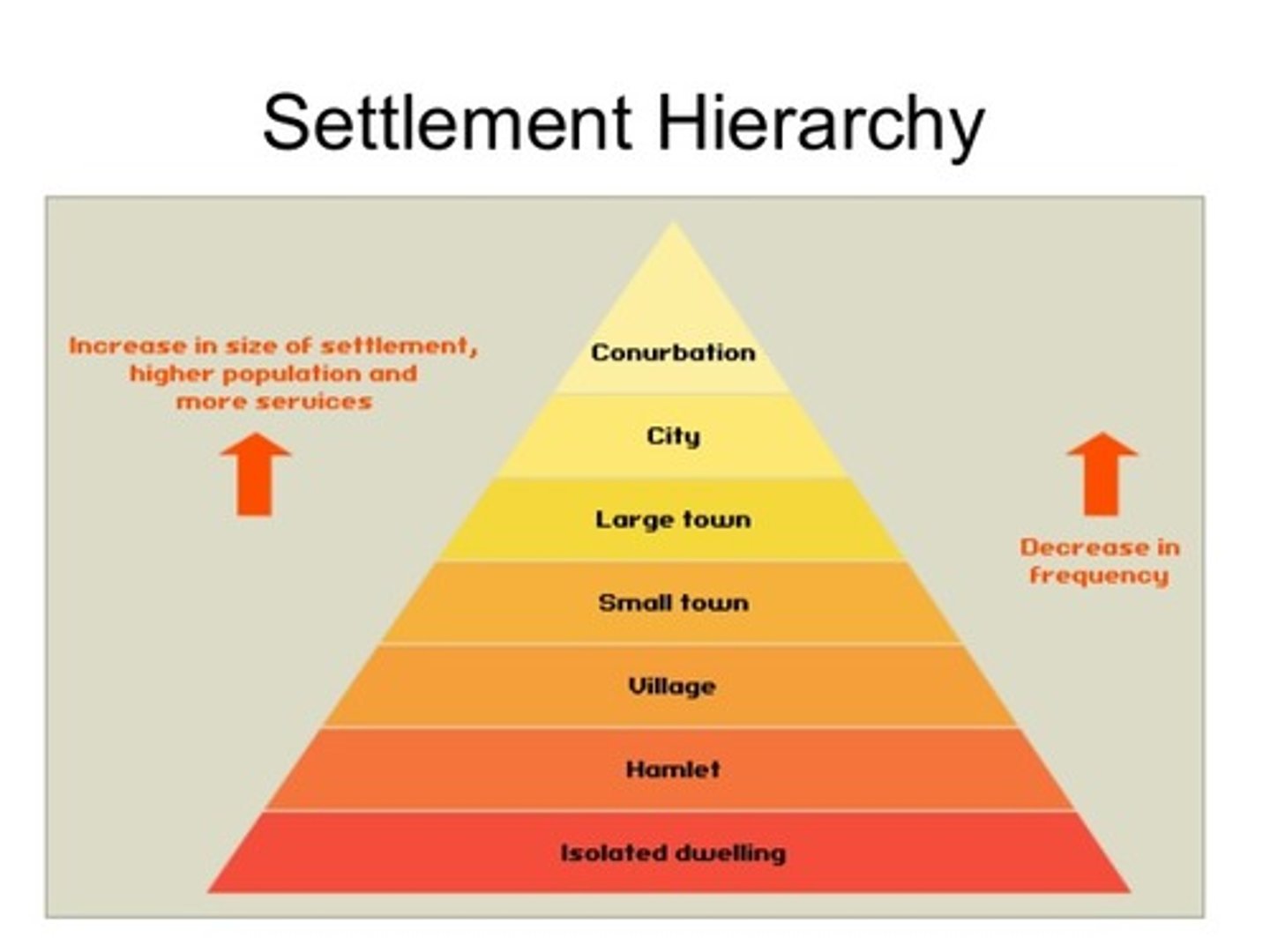
factors that influence the distribution of sports and tourist facilities
Accessibility: those that need high threshold populations tend to be located in the city centre e.g. shopping malls
Physical characteristics: some leisure facilities need certain physical characteristics e.g. a river for rowing, scenic wonders for a national park
History/tradition: some sports stadiums are located near the centre as they were built before land prices rose
Socio-economic characteristics: some facilities are located where they have demand from particular groups e.g. gyms for the upwardly mobile
Land cost: those that require more space tend to be in the suburbs and beyond e.g. golf courses
Government support: some facilities (recreation centres) are built with public $$$ to encourage a healthier, more cohesive community
sports league
an organization that coordinates a group of individual clubs that play each other over a period of time for competition championship
league system
when a number of teams are held together in a hierarchical fashion
CASE STUDY: Premier League
Premier League is an English professional league for men's association football clubs. At the top of the English football league system, it is the country's primary football competition.
Contended by 20 clubs, it operates on a system of promotion and regulation with the football league
Large clubs generally have a much larger sphere of influence than smaller clubs.
temporary sites
sites that are returned to another use after the leisure activity has taken place e.g. farmers fields used for music festivals
permanent sites for temporary events
sites that have leisure as their predominant use, but the leisure activity varies for short periods of time - e.g. city center parks
consequences of temporary sites of leisure
ECON PROS: can bring economic boost, people are employed (security, ticket sales, construction, cleaning - direct), nearby businesses may benefit (restaurants, transport - indirect)
ECON CONS: some may experience downfall of customers from crowdedness, prices may rise so locals struggle
SOCIAL PROS: cultural awareness, more work, increased aspiration
SOCIAL CONS: overcrowding, crime, breakdown of social structures
ENVIRONMENTAL: increased need for disposable cutlery, noise pollution, traffic congestion --> air pollution, waste, lacking recycling
POLITICAL PROS: community emphasized to wider audience, communal decision-making, civic pride
POLITICAL CONS: disagreement about location use can divide communities, benefits for one group may override negatives for another, small group makes big decisions, local gov may not be able to deal with problems from events
CASE STUDY: Thai Full Moon Party
The Thai Full Moon Party on Ko Phangan is a temporary large scale festival. It is an all-night beach party that takes place on the night of, before, or after every full moon, mostly attended by tourists and consists mainly of alcohol, drugs and loud music
factors that affect location of teams and supporters
- population size
- population characteristics, including affluence
- physical land characteristics (terrain)
- existing land use
- communication technology, including TV
- transport connections
Butler Model of Tourism
a model showing the evolution of tourist destinations which stipulates that a site exploited for tourism and leisure knows 6 phases in its evolution: exploration, involvement, development, consolidation, stagnation, decline or rejuvenation