15- Animal Behavior
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
______ is the study of animal behaviors, which can be inherited or learned
ethology
______ behaviors are inherited behaviors, which have been shaped over time by _____
innate; natural selection
an animal's ______ refers to their ability to reproduce viable and fertile offspring
fitness
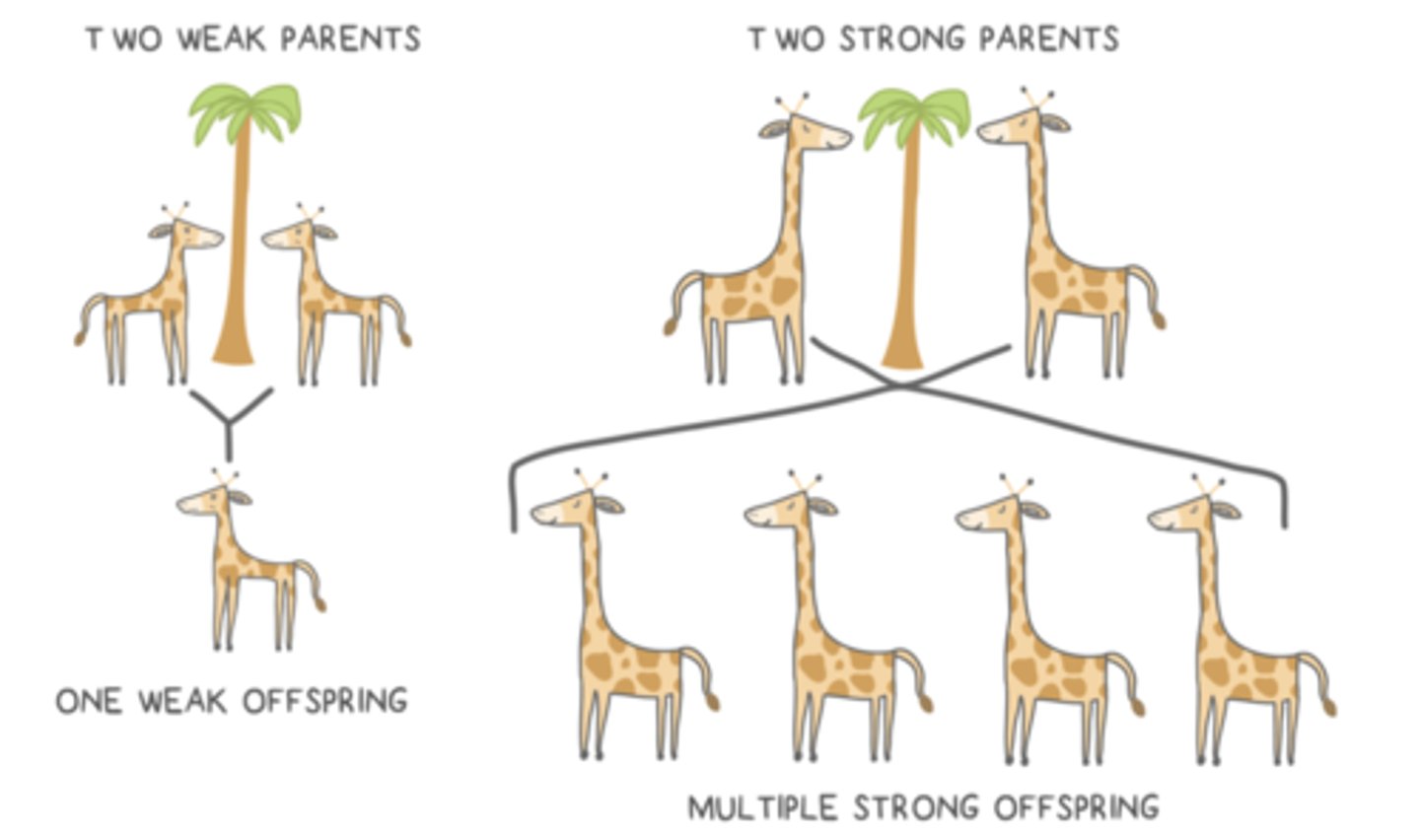
innate/inherited behaviors should increase an animal's _____
fitness
______ is the study of how innate behaviors increase fitness
behavioral ecology
the types of innate behaviors are: ______, ______, ______, and ______
instincts; reflexes; fixed action patterns (FAP); imprinting
______ are innate behaviors that occur without any thought and don't need to be taught
instincts
give example(s) of common instincts:
a baby suckling on a presented nipple
a ______ is an involuntary, rapid response to a stimulus
reflex
(innate behavior)
most reflex arcs in humans involve a ______ circuit
neural
the two types of reflex arcs are: ______ and _____
simple; complex
______ reflexes are the most rapid reflexes because ______ nerves synapse directly into the spinal cord
simple; peripheral
an example of a simple reflex is the ______ reflex (knee-jerk reflex)
patellar
When the patellar tendon below the knee is tapped, the leg reflexively kicks outward
the peripheral nerves are called ______ neurons and ______ neurons
afferent sensory ; efferent motor
______ sensory neurons travel from the stimulus to the CNS
afferent
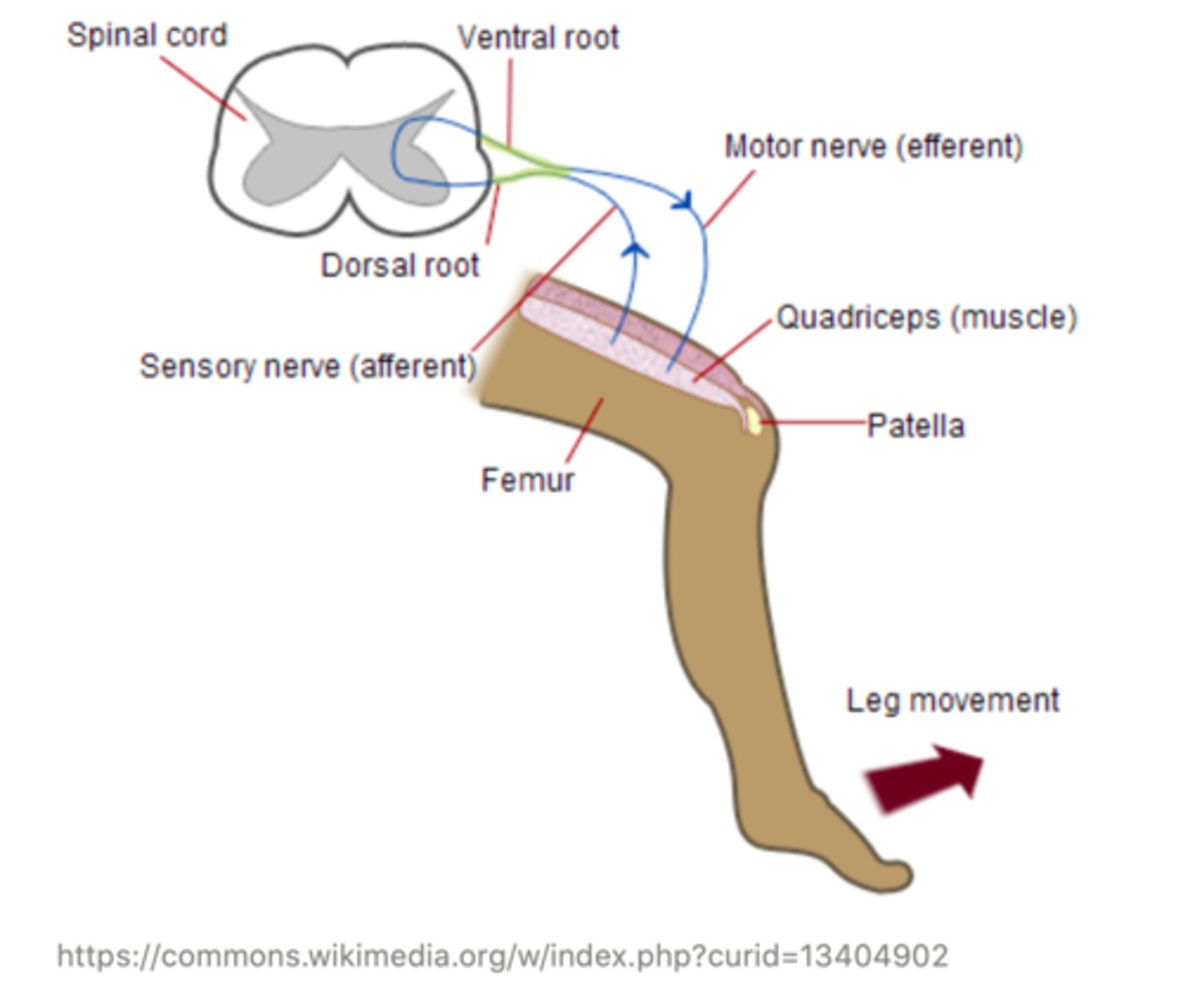
______ motor neurons travel from the CNS to a muscle in order to coordinate a muscle contraction (response to the stimulus)
efferent
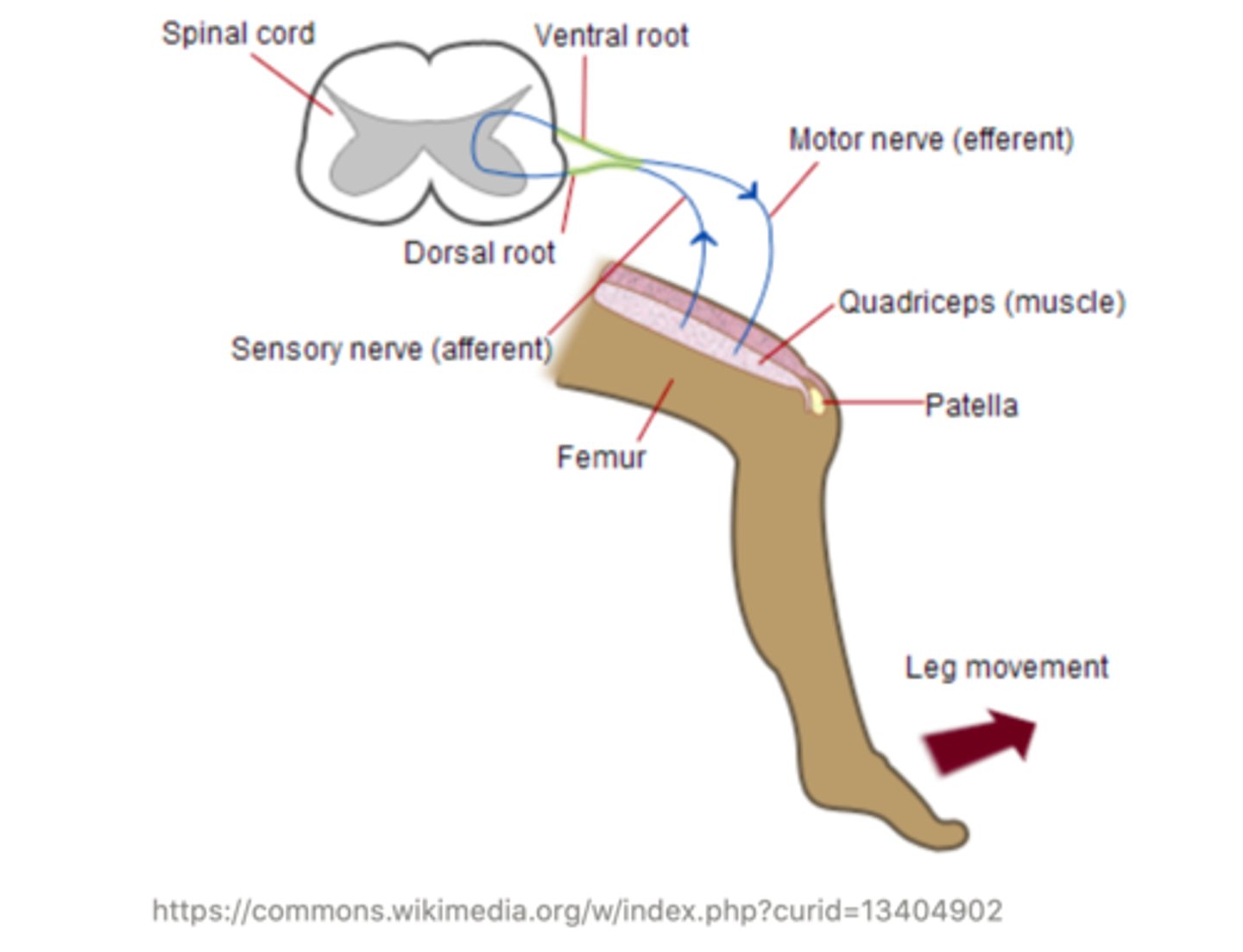
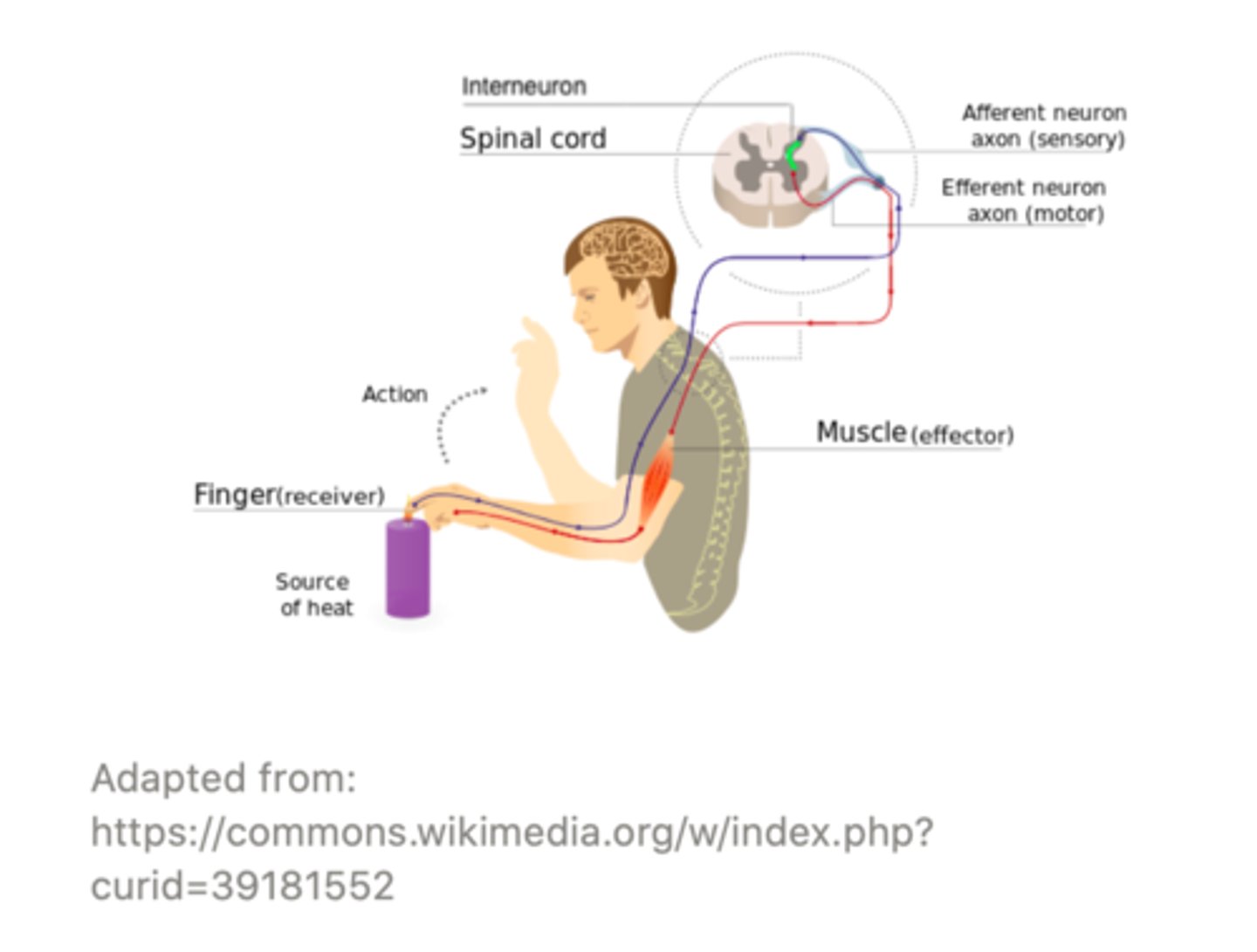
Complex reflexes are ______ than simple reflexes because the peripheral nerves are separated by an intermediary, called an ______.
slower; interneuron
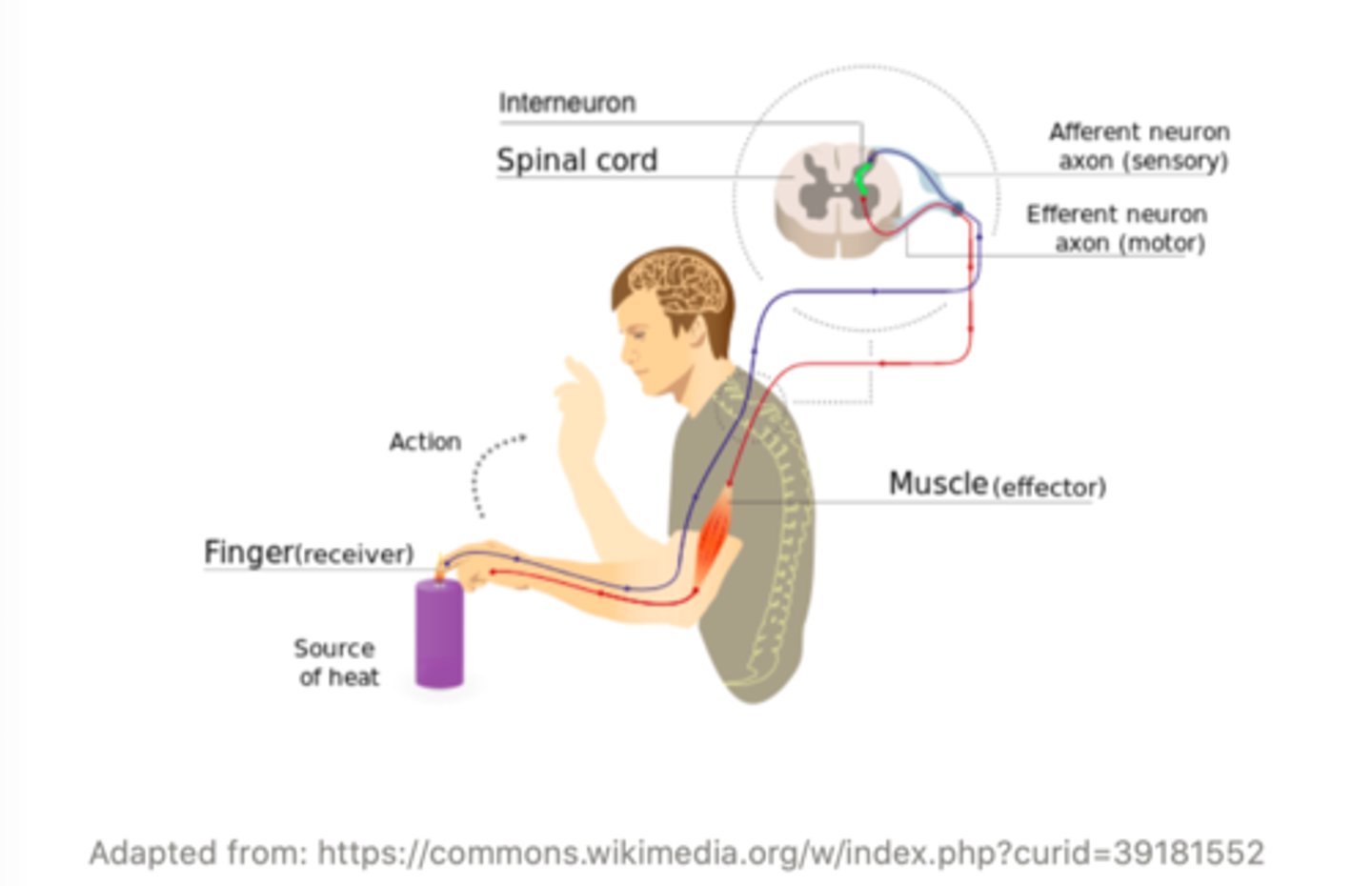
_____ allow the appropriate response to be selected by the spinal cord or brain for a given stimulus
interneurons
(hence complex reflex)
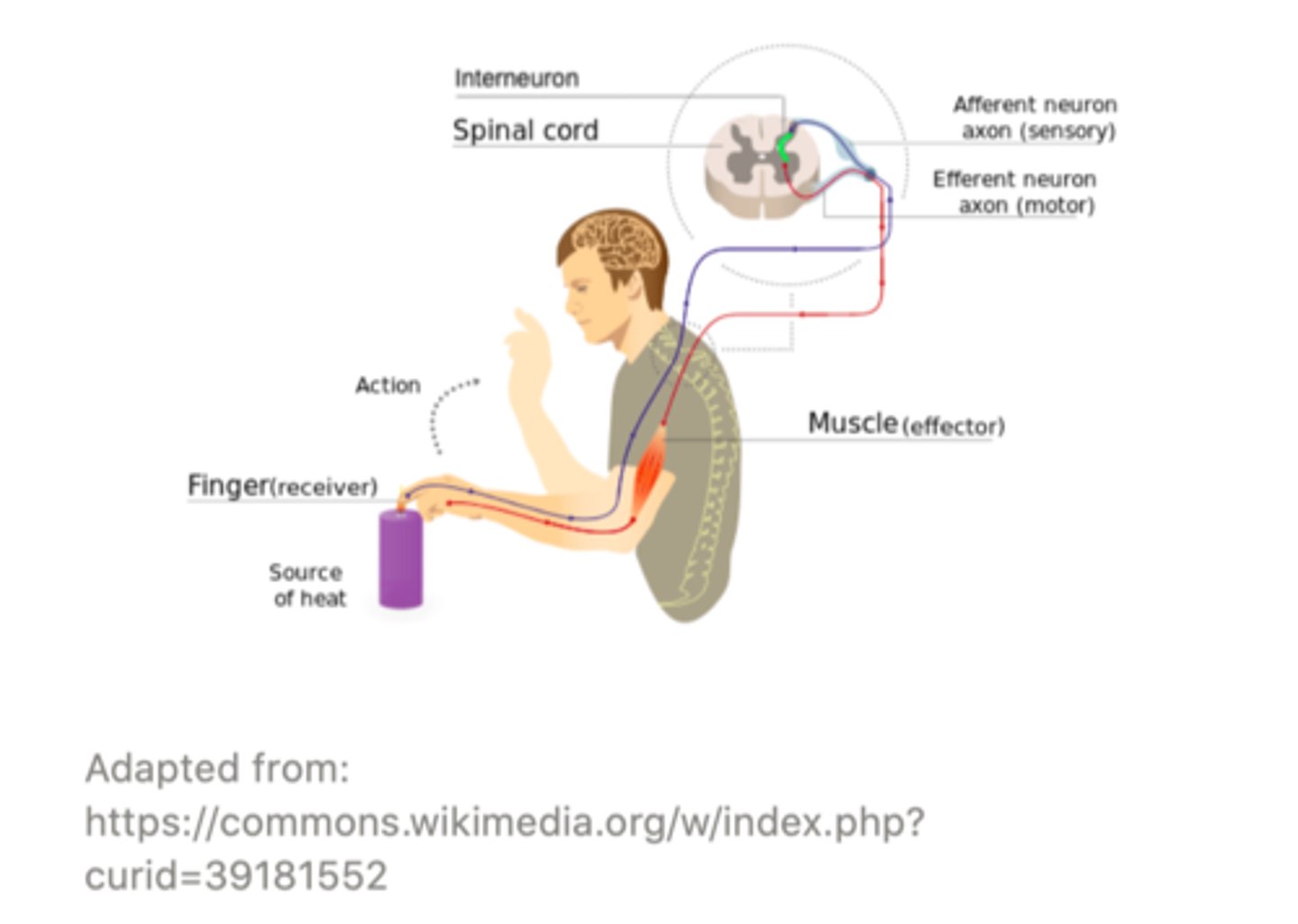
an example of a complex reflex is the ______ reflex
withdrawal
(hand on hot stove)
a ______ is an innate behavior that is initiated by a specific stimulus and once initiated the behavior will almost always continue to completion (even when the stimulus is removed during the behavior)
fixed action pattern
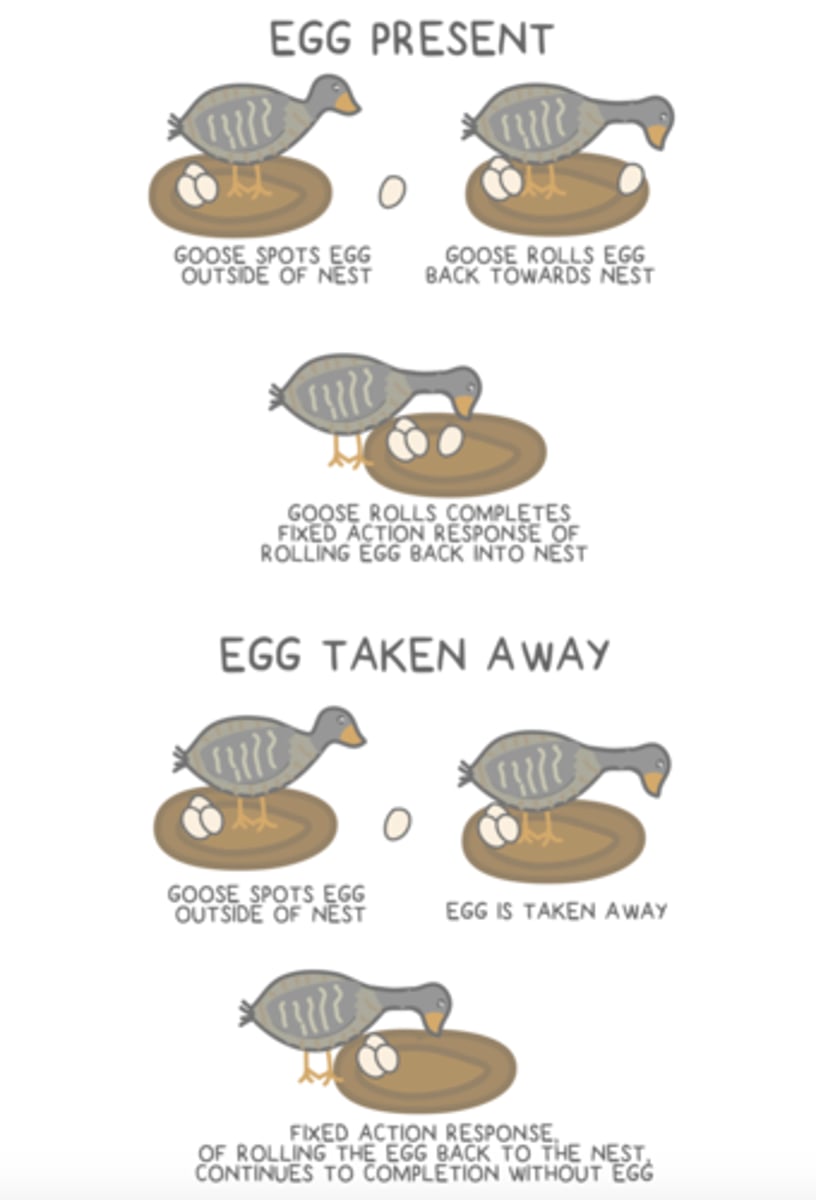
the stimulus that initiates a fixed action pattern may also be called a _____ or ______ stimuli
releaser; sign
fixed action patterns tend to ______ fitness because they generate predictable responses to a stimulus, and because they are ______
increase; inherited/innate (they don't need to be learned by every subsequent generation)
______ is an innate way animals learn certain behaviors, and once this behavior is acquired, it can never be forgotten
imprinting
imprinting can only occur during a very limited time of an animal's life, known as the ______
critical period
______ behaviors ______ an animal's fitness because they allow animals to adapt to unexpected events, creating behaviors that will be more advantageous the next time that event occurs
learned; increase
the common forms of learning behaviors include: ______, ______, and ______
classical conditioning; operant conditioning; associative learning
______ involves learning to pair a neutral stimulus to an unconditioned stimulus
classical conditioning
______ stimuli do not elicit a physiological response
neutral
______ stimuli do elicit a physiological response that is called an unconditioned response
unconditioned (innate response)
in response to a conditioned stimuli there will be a ______
conditioned response
_____ occurs when a conditioned organism responds to stimuli that is not identical to the original conditioned stimulus
stimulus generalization
according to the stimulus generalization gradient, as a stimulus differs from the original conditioned stimulus more and more, what happens to the conditioned response?
as a stimulus differs from the original conditioned stimulus more and more,
the conditioned response will get smaller and smaller in magnitude
_____ involves the ability of an animal to differentiate between a conditioned stimuli, and other similar (but different) non-conditioned stimuli
stimulus discrimination
______ is when an animal learns to associate one of its behaviors with either a reward or a punishment
operant conditioning
In operant conditioning, if the action is ______, the animal is more likely to perform that action. If the action is ______, the animal is less likely to perform that action
rewarded; punished
the 4 types of operant conditioning include: ______, ______, ______, and _____
positive punishment; negative punishment;
positive reinforcement; negative reinforcement
adding something bad to decrease a behavior is known as ______
positive punishment
(pushing a dog's nose when he jumps)
adding something good to increase a behavior is known as _____
positive reinforcement
(giving a dog a treat when he jumps)
taking away something good to decrease a behavior is known as ______
negative punishment
(no longer paying attention to the dog when he jumps)
taking away something bad to increase a behavior is known as ______
negative reinforcement
(not pushing a dog's nose when he doesn't jump)
a ______ is an enclosed apparatus that contains some sort of lever for an animal to press, and upon pressing the lever, the animal will receive some sort of reinforcement to encourage the behavior or punishment to discourage the behavior
skinner box
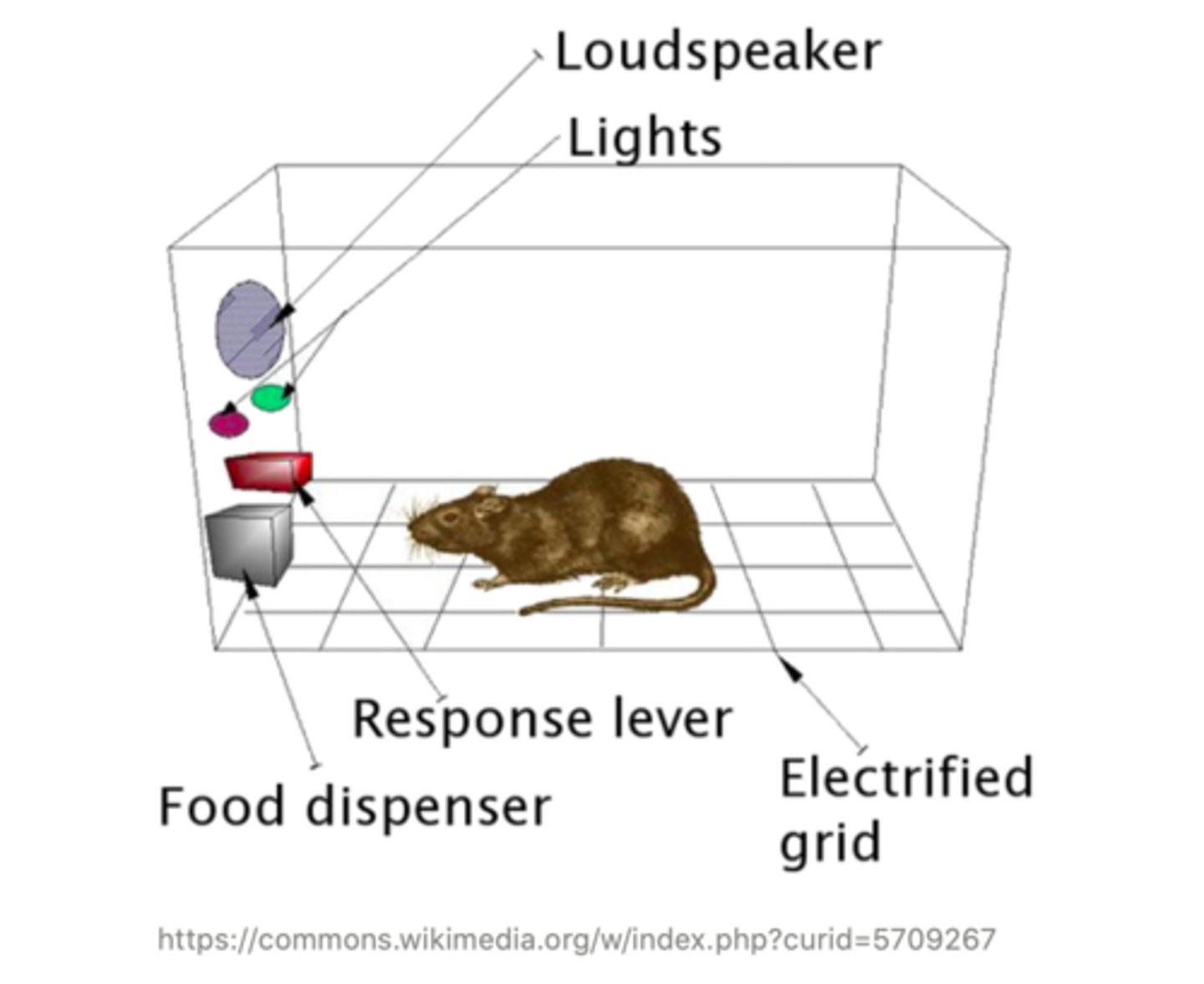
______ occurs whenever an animal learns that two things are connected
associative learning
associative learning is beneficial to an animal's fitness because ______
it allows them to be more efficient in responding to a stimulus
classical and operant conditioning are types of ______ learning
associative
______ is a type of associative learning that occurs when an animal associates landmarks with a specific location
spatial learning
spatial learning is beneficial to the animal because it ______
allows animals the ability to return to a location they know is safe and they can sense if they're in an area where there might be perceived danger
______ is the phenomenon where a learned behavior is forgotten if it stops eliciting the expected response
extinction
_____ is a process where extinct behaviors are remembered through re-association
recovery
______ learning occurs when you are not associating a stimulus with a behavior
non-associative
______ occurs when an animal increases a behavioral response, whenever the stimulus that elicits the response occurs more often/frequently
sensitization
______ occurs when an animal learns to decrease a behavioral response in the face of a repetitive, meaningless stimulus
habituation
Habituation increases an animal's fitness because ______
it allows them to ignore what is irrelevant and focus more of their attention on what actually matters
______ occurs whenever an animal learns a behavior by watching another animal perform that same behavior
observational learning
observational learning is beneficial because it allows the animal to learn a new behavior without receiving ______, and it increases the animal's fitness because ______
reinforcement; it decreases the amount of time required to learn the behavior (efficiency)
______ occurs when an animal is placed in a scenario it has never faced before, yet they are able to do something that results in something good happening
insight
insight is beneficial because it allows the animal to learn behaviors without receiving ______, and it increases the animal's fitness because ______
reinforcement; it allows them to efficiently respond to unexpected events
animals typically have 3 types of movement: ______, ______, and ______
kinesis; taxis; migration
______ occurs when animals change their speed in random directions
kinesis
animals that move by kinesis will ______ if it is in a favorable environment and ______ if it is in an unfavorable environment
slow down; speed up
how does kinesis increase an animal's fitness?
it allows them to spend more time in a favorable environment (because they slow down here)
______ is movement that has a specific direction, either towards or away from a stimulus
taxis
taxis is a ______ change in ______ or speed
non-random; direction
______ taxis is directed toward a stimulus
positive
______ taxis is directed away from a stimulus
negative
______ is a type of taxis that has a directional response to the stimulus of light
phototaxis (can be positive/negative)
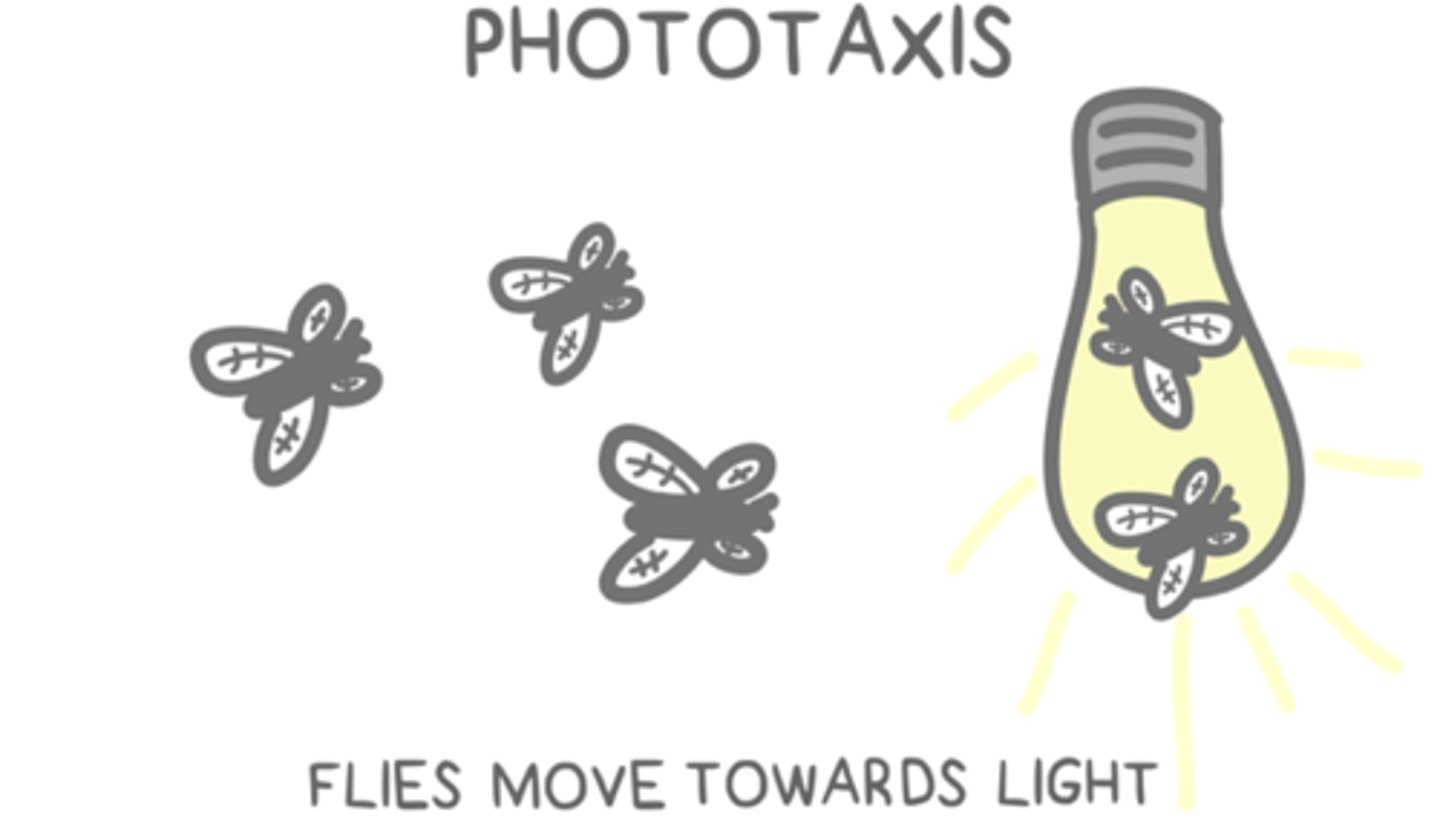
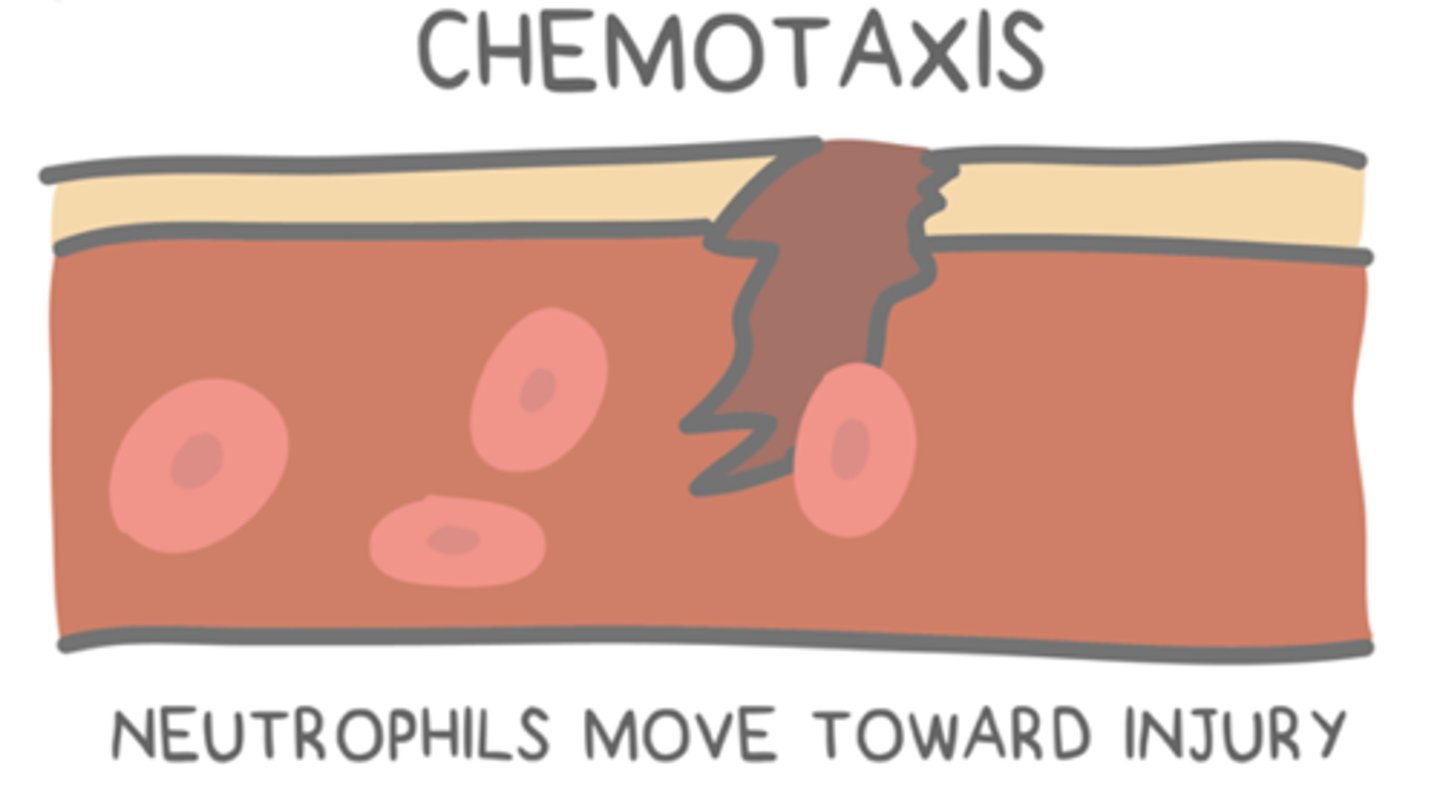
_____ is a type of taxis that has a directional response to a chemical signal
chemotaxis (can be positive/negative)
______ is defined as the relatively long-distance movement of animals from one area to another due to instinct
migration
migration is often ______, and is associated with moving from one area to another based on the availability of certain resources and environmental temperatures
seasonal
several types of communication include: ______, ______, ______, and ______
visual; auditory; tactile; chemical
visual communication can occur surrounding ______ behavior, ______ behavior, and ______
aggressive; submissive; courtship/mating rituals
______ communication communicates sounds
auditory
auditory communication is useful at ______, over ______, and through ______
night; long distances; water
______ communication is communication through touch
tactile
chemical communication occurs through hormone-like chemicals called ______
pheromones
______ pheromones (chemical communication) are used to attract mates or inform animals about beneficial environments
inviting
______ pheromones (chemicial communication) can be used as a signal to stay away
alarm
______ pheromones trigger immediate and reversible behaviors
releaser
______ pheromones trigger long-term (physiological) behaviors
primer
what do honeybees use as a means of auditory, tactile, and chemical communication?
the waggle dance (they walk in a figure-8 pattern while vibrating their wings and 'wagging' their abdomen)
*it is not a form of visual communication because a beehive is too dark
______ behaviors allow animals to interact for the purposes of companionship, finding food, protection, and mating
social
______ is a social behavior where animals group together (into a pack or herd) to better achieve some goal
cooperation
(ex. coordinated hunting)
______ behaviors occur when animals compete for food, territory, or mates
agonistic
agonistic behaviors may be broken down into ______, ______, and ______
threats; aggression; submission
aggressive behaviors between animals are often _____ to avoid both animals sustaining significant injuries
ritualized
the phenomenon in which a threat, followed by submission, can avoid aggression and the harm associated with it is called ______
appeasement behavior
a _____ is the 'pecking order' of animals within a group and is a socially accepted order
dominance hierarchy
top ranking animals, called ______ animals, are typically the most physically capable and receive the best access to resources
alpha
______ refers to the behaviors a group of animals use to protect their territory
territoriality
______ are another type of feeding behavior that allow animals to quickly locate foods that are abundant and safe to eat
search images

search images are achieved by ______ what the food that is safe to eat looks like
abbreviating
______ behaviors refer to the sacrifices an animal might make for its relatives
altruistic
altruism increases the altruist's (individual doing the sacrificing) _____ fitness
inclusive
inclusive fitness is the ______
sum of an animal's direct and indirect fitness
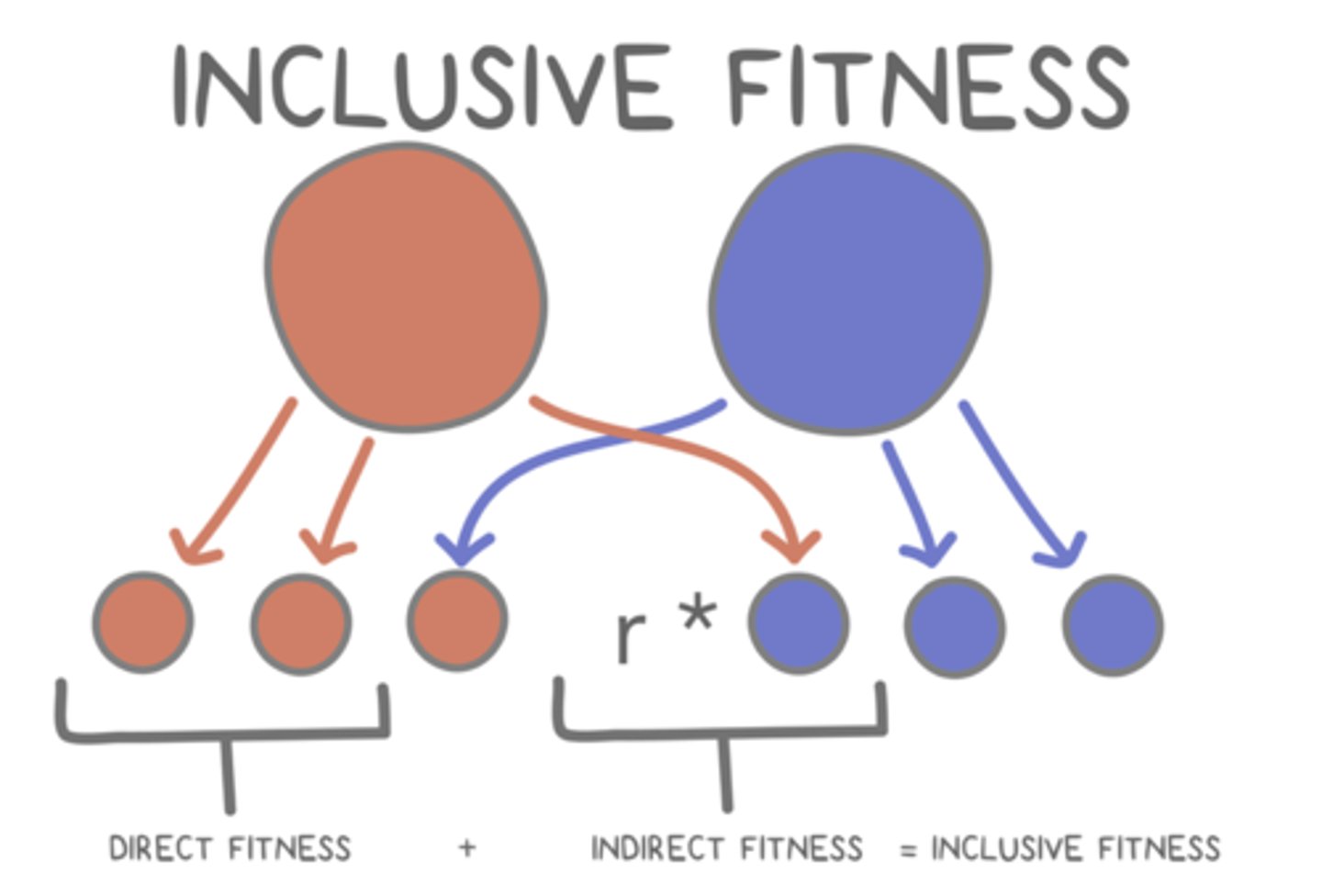
______ refers to the number of genes an animal can pass onto the next generation of its own
direct fitness
______ refers to the number of genes passed onto the next generation by an animal's relatives
indirect fitness
Hamilton's rule of altruism says that indirect fitness needs to _____ direct fitness for altruism to occur
exceed
r x B > C
where,
r x B = altruists' indirect fitness
C = direct fitness ("the cost")
______ refers to the way an individual animal's inclusive fitness is increased by indirect fitness
kin selection
kin selection is a form of natural selection, where ______ are the most fit
altruists
(because they maximize their indirect fitness)
_____ altruism refers to the sacrifices an animal might make for an unrelated animal of the same species in anticipation for a later reward
reciprocal
animals organize themselves into any one of several advantageous groups like ______, ______, ______, and ______
herds, flocks, schools, packs