Chapter 27 - The Reproductive System
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
Function of reproductive system
Production of offspring
Four processes allow reproduction to happen
Gamete formation** → sperm and ova (egg)
Copulation** → sperm and egg must be brought together
Fertilization → combining genetic content of the sperm and the egg
Gestation and parturition → development and birth of the fetus
Zygote
a diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes
sometimes called a “single-celled embryo”
Embryo
Stage of development from soon after the fertilization of the ovum to week 8 of development
no longer single-celled
Fetus
stage of development from week 8 to birth
infant
after birth has occurred
Meiosis
nuclear division that occurs only in the gonads and results in the formation of gametes
similar in males and females
Importance:
Reduces the number of chromosomes in gametes by one half
Produces genetic variability
required for species survival, if all were exact same 1 disease could kill all
Before meiosis begins, chromosomes in diploid (2n) parent cell replicate
diploid = 2n = 46
haploid = n = 23
Sister chromatids
replicate chromosomes
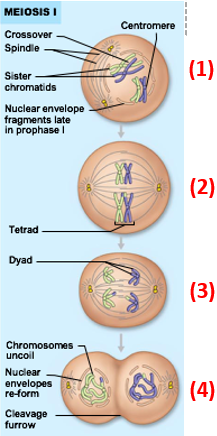
Meiosis I steps
Homologous chromosomes synapse to form tetrads
Crossing over occurs
exchange of genetic material
(1) in pic
Tetrads align randomly on spindle plate
(2) in pic
Homologous chromosomes separate & move to opposite poles
Sister chromatids do not separate here!
(3) in pic
Cleavage occurs
(4) in pic
Result of meiosis I = production of 2 daughter cells
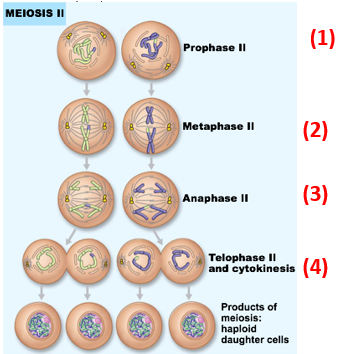
Meiosis II
Formation of new spindle
Chromosomes line up at equator
Sister chromatids separate & move to opposite poles
Cleavage occurs
Result of meiosis II = production of 4 haploid daughter cells
note: no chromosome replication, no crossover
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal (HPG) axis
The interaction of hormones released by the hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, and gonads
Important structures and their role in the HPG axis
Hypothalamus → releases gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
starts in brain
Anterior pituitary gland → releases follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) in response to GnRH presence
named after effect in female
Gonads → release sex hormones & produce gametes in response to LH and FSH
Male: testostrone
Female: Estrogen and Progestrogen
Male gonads
Testes
Enclosed & protected by scrotum
Composed of skin & superficial fascia
Importance of Scrotum
Scrotum allows testes to be ~3o lower than internal body temperature
sperm production needs lower temperature
high temperature slows down sperm production and makes them abnormal
Musculature allows testes to maintain optimal temperature
Dartos muscle: changes surface area of scrotal tissue
contracts → decreases area → decreases heat loss
Cremaster muscle: changes position of testes
elevates → keeps them warmer
depress → keeps them cooler
Testes Vasculature
Testicular arteries supply each testis
Testicular veins drain testes
temperature control too
blood absorbs heat from arteries
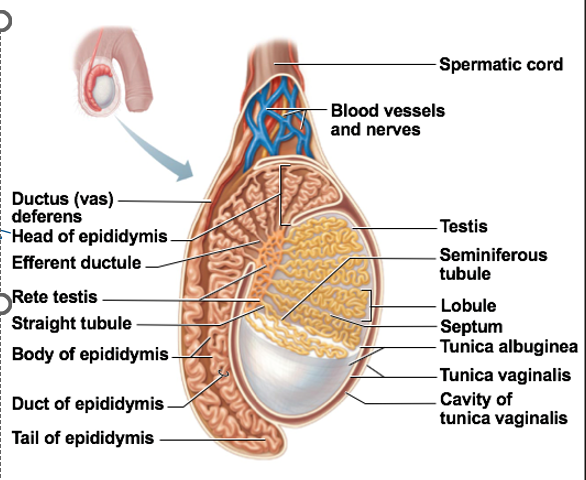
Nerve fibers, blood vessels, ductus deferens, & lymphatics form the spermatic cord
Innervation of testes
Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions serve each testis
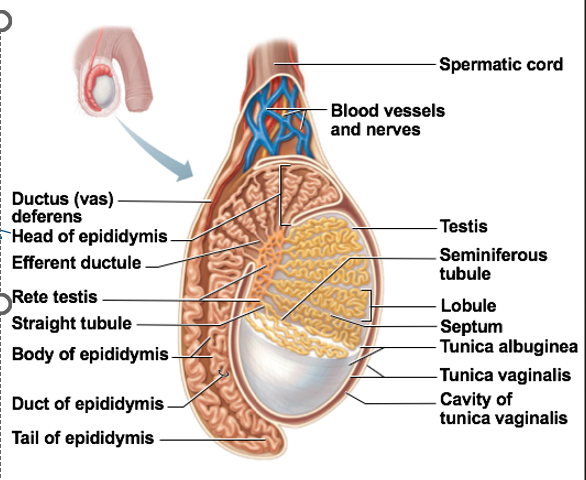
Seminiferous tubules
Function: location of sperm production
in the walls
Immature sperm move through rete testis to epididymis
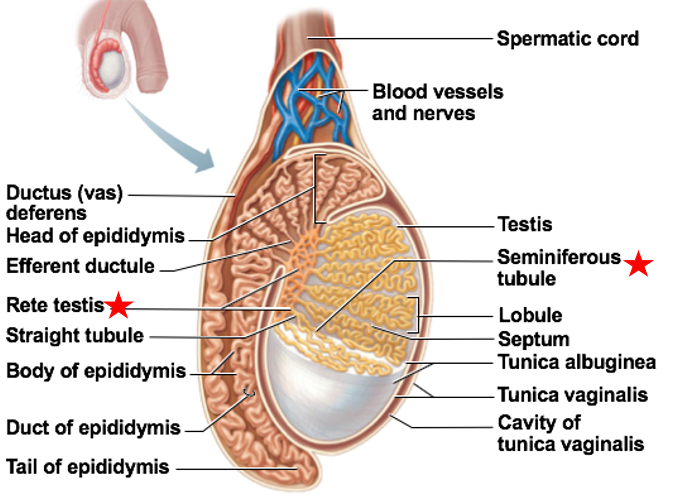
rete testis
small tubes off to the side of the seminiferous tubules
Immature sperm move through rete testis to epididymis
Testicular Cancer
Homeostatic Imbalance
Formation of malignant tumor in one or both testes
Can be seminoma or non-seminoma
seminoma: slightly more common 55%
non-seminoma: more aggressive and fast
usually just one testis
Symptoms: painless lump or swelling of testis, dull pain in lower pelvis and/or lower back
Treatment: chemotherapy & radiation, surgery
95% survival
surgery more common for non-seminoma
Testicular Cancer Causes
genetics & family history
chromosome 12
Klinefelter syndrome
XXY
persistent/chronic inflammation
all forms of cancer
bacterial/viral infection of testis
Accessory Ducts to Testes
Epididymis
Ductus deferens (vas deferens)
Urethra
Epididymis
Accessory Duct to Testes
stores immature sperm
As sperm travel through duct → develop ability to swim
composed of head, body, and tail
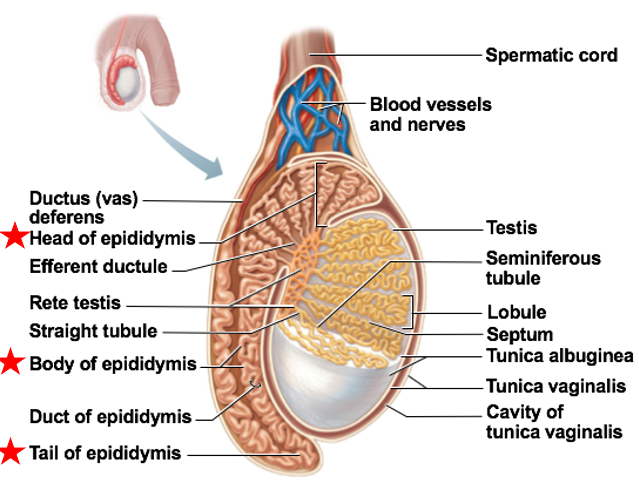
Ductus deferens (vas deferens)
Accessory Duct to Testes
transports sperm out of epididymis during ejaculation
Ends at ampulla
Ampulla ends at ejaculatory duct
Ejaculatory duct empties into urethra
The ductus deferens can be cut or cauterized → vasectomy
is reversible
no effect on testes
fairly effective but not immediately
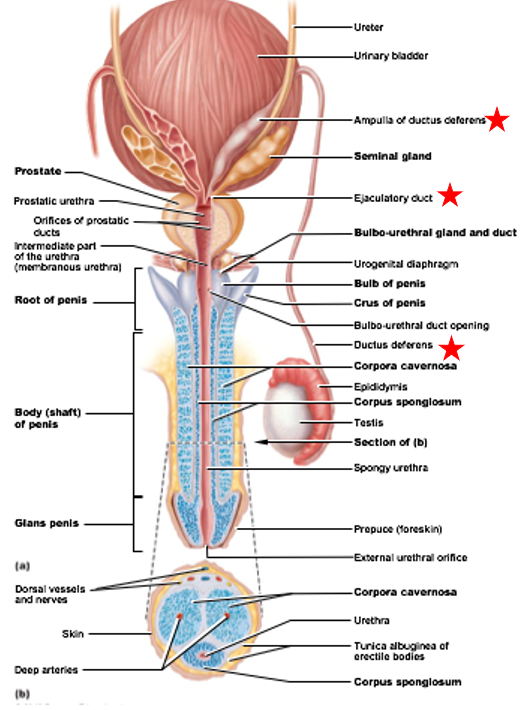
Urethra (male)
Accessory Duct to Testes
part of urinary and reproductive system
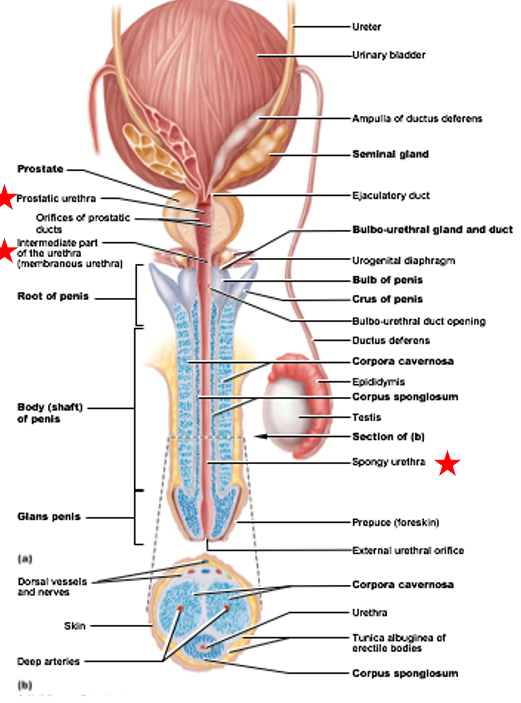
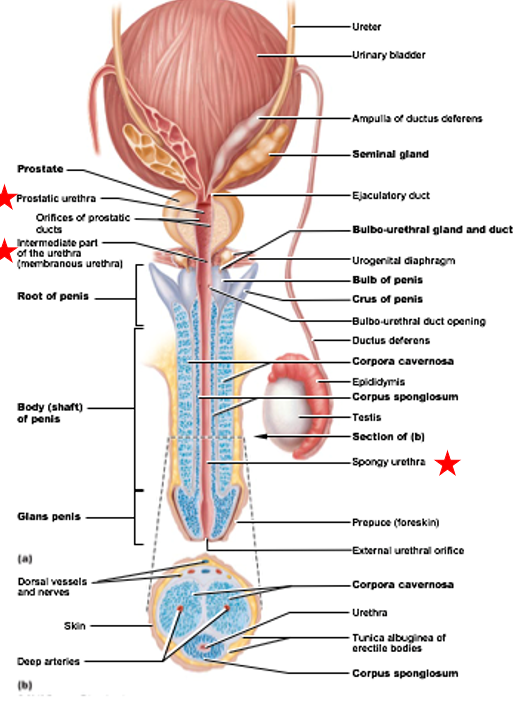
Divisions of male urethra
Prostatic urethra: portion surrounded by prostate gland
Intermediate part: connects (1) to (3)
pass through body wall structures
Spongy urethra: runs through penis & opens to exterior of body
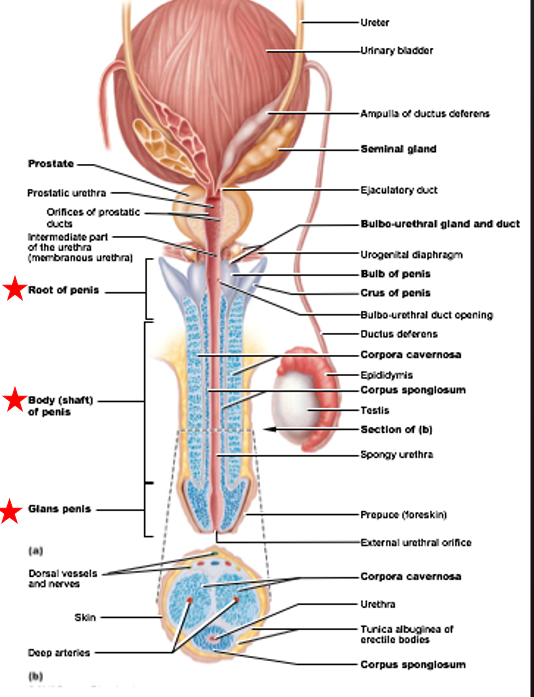
Penis
Function: deliver sperm to female reproductive tract during copulation
Ends in glans
Glans surrounded by prepuce
Male circumcision
a surgical procedure involving the removal of the prepuce
cultural
US: 80-85%
Everywhere else: <20%
health benefit: decrease likely hood of infection
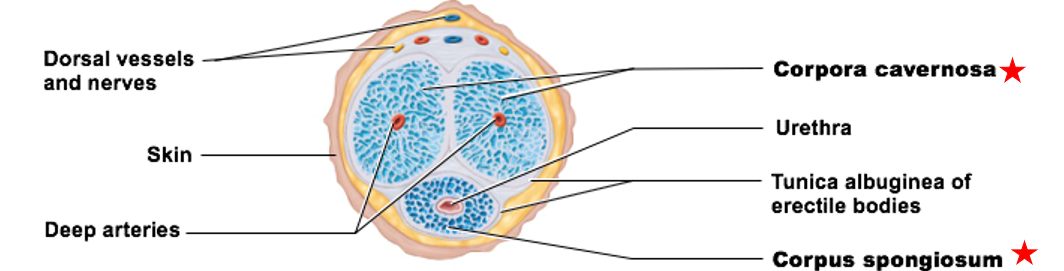
Internal Anatomy of the Penis
Erectile tissue
Erectile bodies:
corpus spongiosum
corpora cavernosa
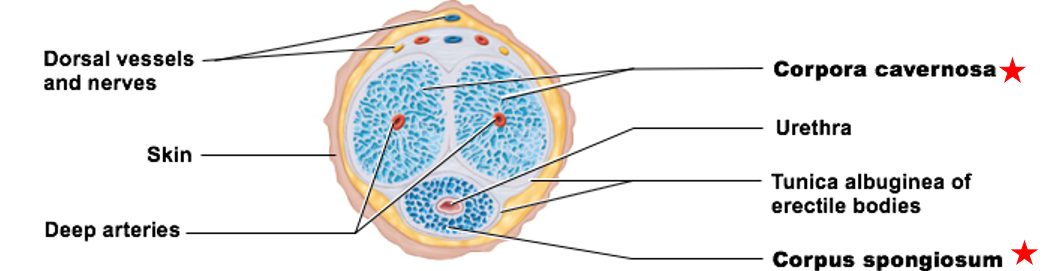
Erectile tissue
contains connective tissue, smooth muscle, & vascular space
Vascular spaces fill with blood
Two erectile bodies
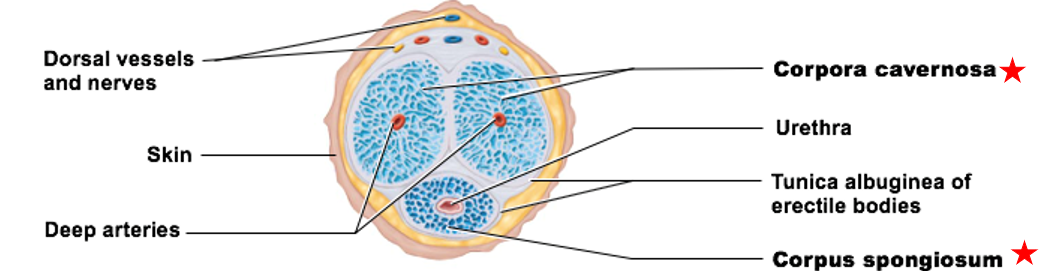
Corpus spongiosum
erectile body of the penis
immediately surrounds urethra
keeps it open
Distal portion forms glans
only 1
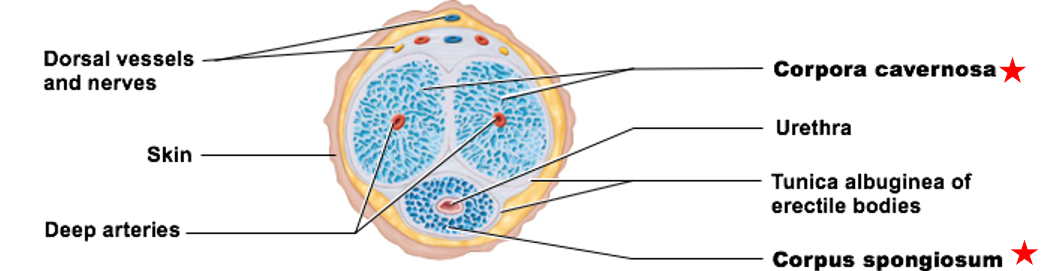
Corpora cavernosa
erectile body of the penis
paired structures that make up most of penile tissue
have 2
Accessory Glands of Male Reproductive System
seminal glands
prostate
bulbo-urethral gland
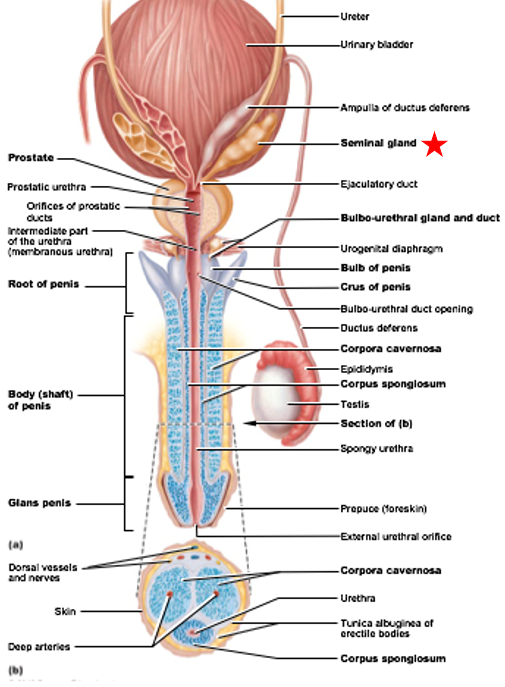
Seminal glands
Accessory Gland of Male Reproductive System
Empty into ejaculatory duct
seminal fluid - fluid part of semen
Secretions produced: fructose, prostaglandins, proteins
Prostate
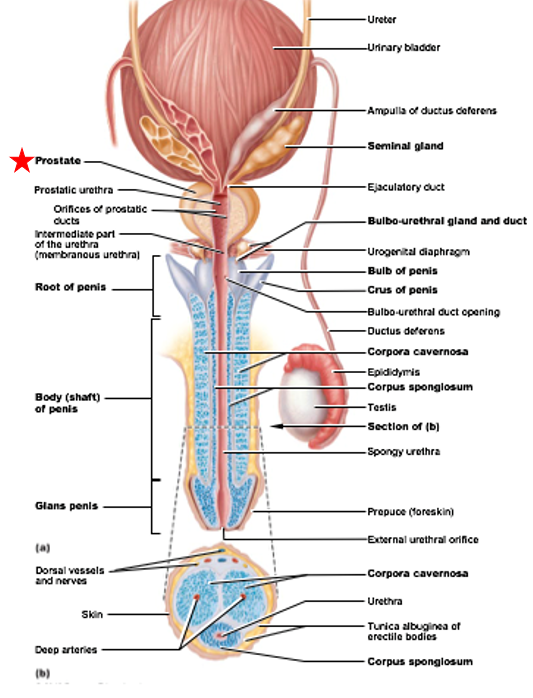
Accessory Gland of Male Reproductive System
Composed of 20-30 glands
Produce citrate, prostate-specific antigen (PSA), and substances that help activate sperm
PSA: makes semen more liquidy
Smooth muscle walls contract during ejaculation to release contents
Homeostatic Imbalances of the Prostate
Prostate cancer
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
Prostate cancer
Homeostatic Imbalance of the Prostate
1 in 6 men will develop prostate cancer
Usually develops later in life→age 50+
Ranges from slow-growing to highly aggressive
Men usually die with it, not because of it
Symptoms: difficulty urinating, blood in urine and/or semen, erectile dysfunction, etc.
Usually symptomless in early stages
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
Homeostatic Imbalance of the Prostate
Benign growth of prostate
Constricts prostatic urethra → makes urination difficult & painful
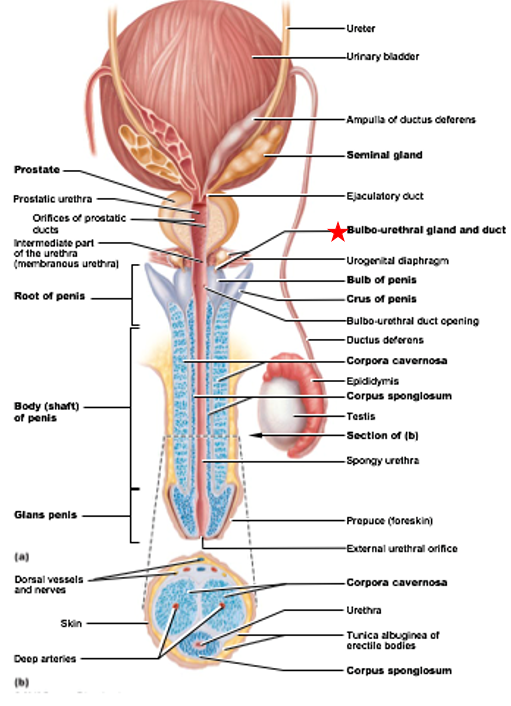
Bulbo-urethral glands
Accessory Gland of Male Reproductive System
Produces alkaline mucus
keeps sperm alive in the acidic vagina, as sperm are very sensitive to acidic conditions
Semen
combination of sperm with accessory gland secretions
Components of seminal secretion
prostaglandins
relaxin (and other enzymes)
fructose
antibiotic components
clotting factors
other
prostaglandins (function in seminal secretion)
decrease viscosity of mucus in female cervix, stimulate reverse peristalsis in uterus
make transport faster and more efficient
relaxin (and other enzymes) (function in seminal secretion)
promote & enhance sperm motility
swim faster and harder
Fructose (function in seminal secretion)
catabolized for sperm ATP synthesis
needed for sperm to move
Antibiotic components (function in seminal secretion)
destroy bacteria that could harm sperm
Clotting factors (function in seminal secretion)
coagulate sperm after ejaculation
so doesn’t leave female track
Other components (function in seminal secretion)
suppression of female immune system
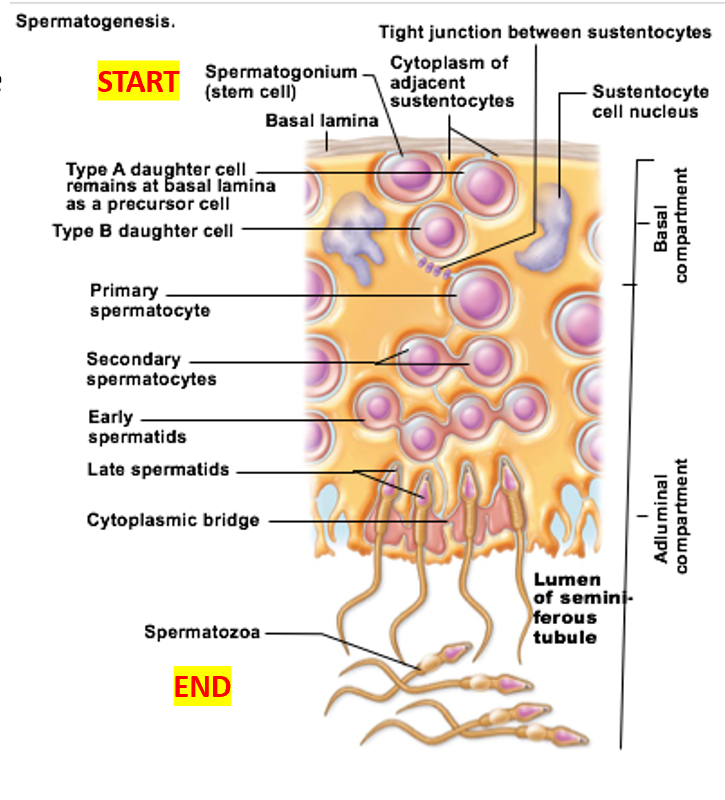
Spermatogenesis
production of male gametes
Important cell types of seminiferous tubules
Sustenocytes
spermatogenic cells
Myoid cells
interstitial endocrine cells
Sustenocytes
Important cell type of seminiferous tubules
surround, support, and nourish developing sperm
Adjacent sustenocytes joined by tight junctions → prevent sperm from “escaping”
Spermatogenic cells
Important cell type of seminiferous tubules
sperm-forming cells
Myoid cells
Important cell type of seminiferous tubules
contract to move immature sperm from tubules → epididymis
Interstitial endocrine cells
Important cell type of seminiferous tubules
secrete testosterone (with small amount of estrogen)
Spermatogonia divide by __
mitosis
Before puberty: spermatogonia become
all spermatogonia become more spermatogonia
After puberty: spermatogonia become
some become Type A daughter cells
others become Type B daughter cells
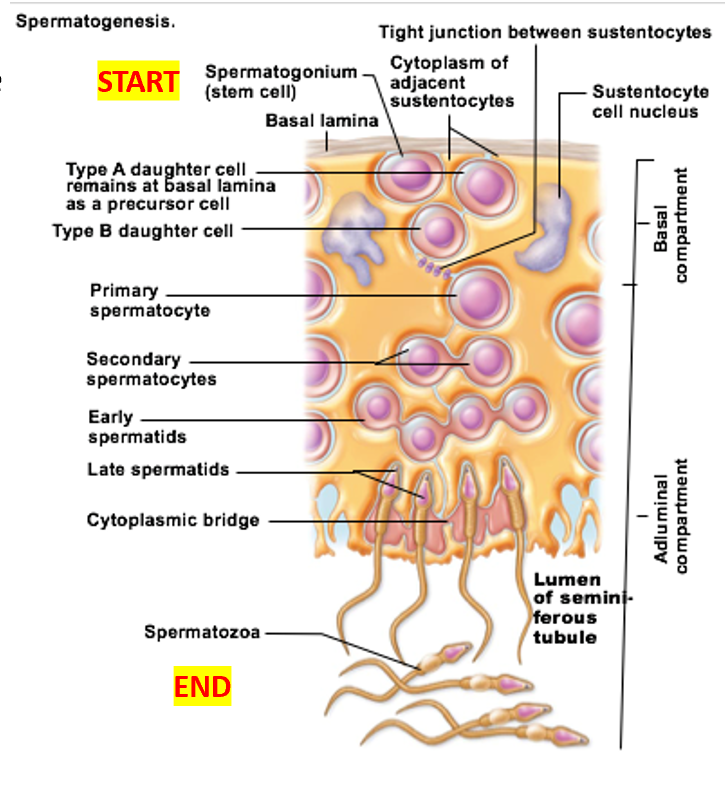
Spermatogonia: Type B cells become
primary spermatocytes
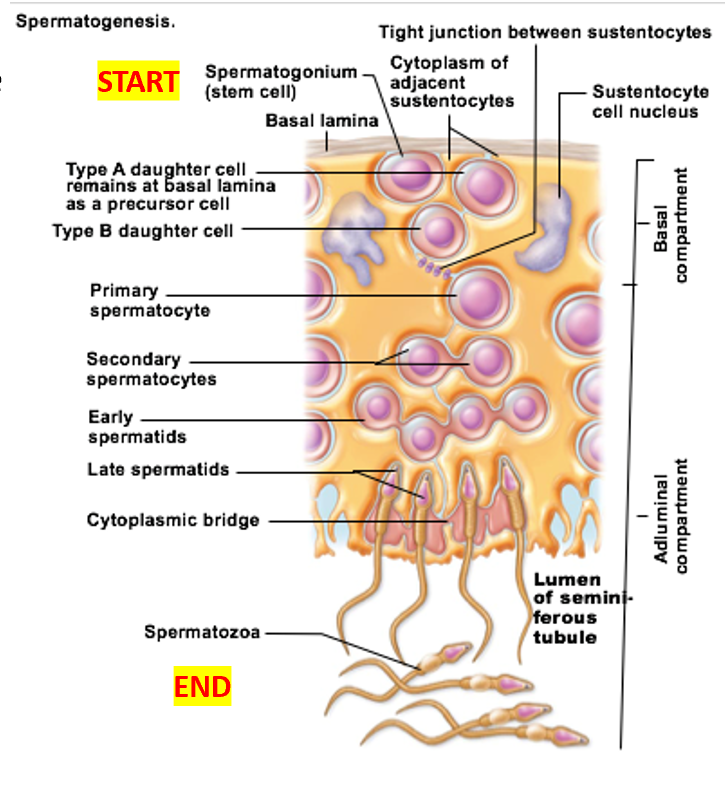
Spermatogonia: Type A cells become
maintain the germ cell population
Undergo self-renewal, remaining as stem cells
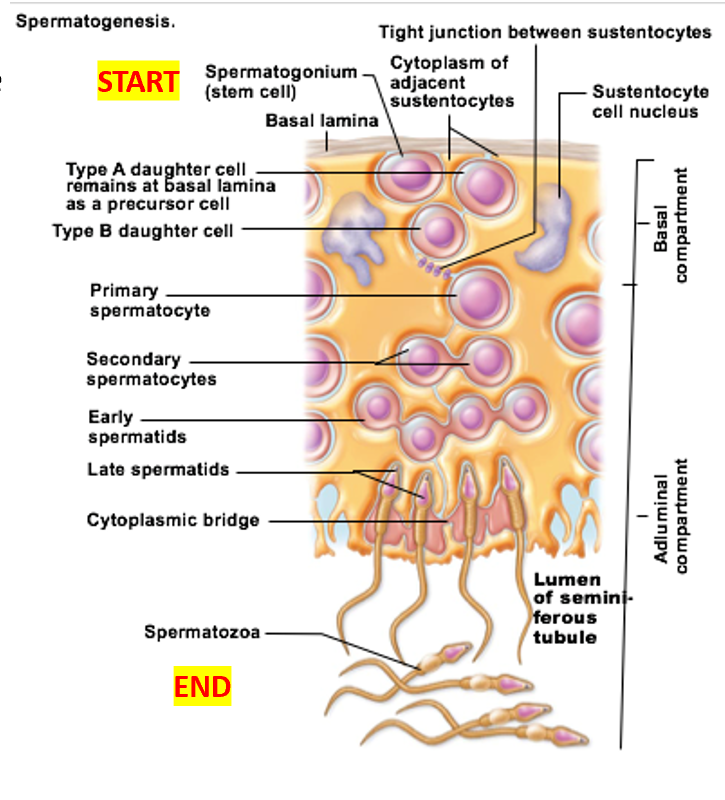
Primary spermatocytes undergo
meiosis I → Forms secondary spermatocytes
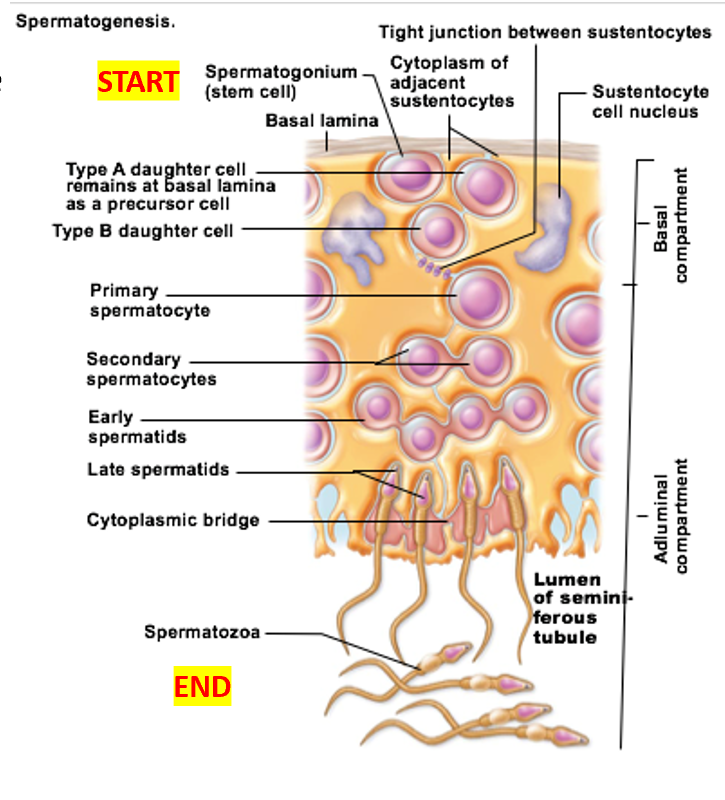
Secondary spermatocytes undergo
meiosis II → Form spermatids
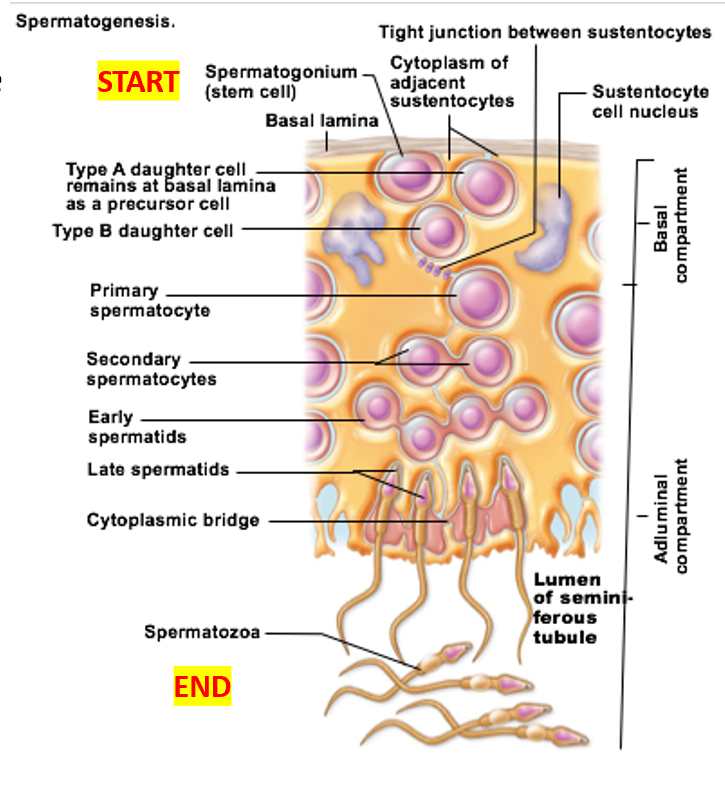
Spermatids undergo
spermiogenesis → functional (but still immature) sperm
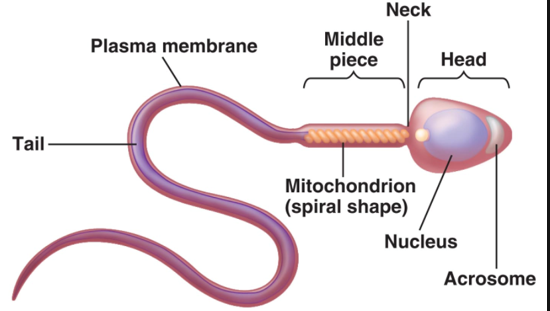
Sperm’s general areas
Head
acrosome
Midpiece
Tail
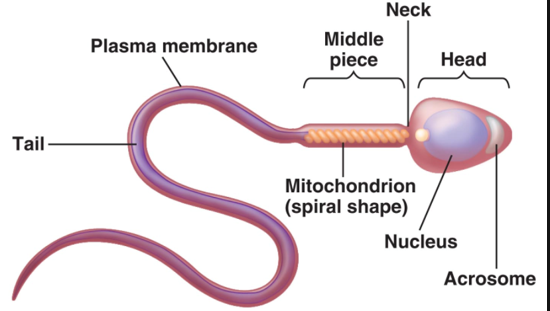
Sperm: Head
holds genetic material, has acrosome
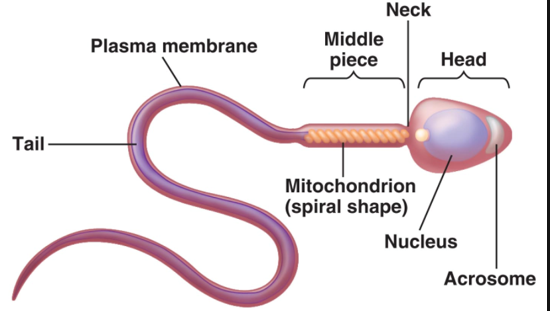
Acrosome
found in head of sperm
helmetlike structure that holds hydrolytic enzymes
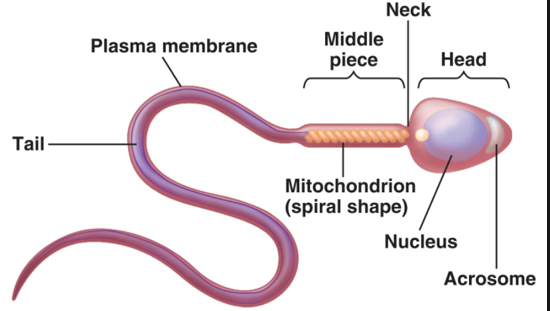
Sperm: Midpiece
metabolic area—contains mitochondria
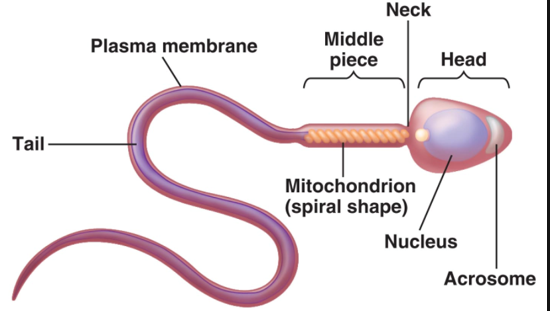
Sperm: Tail
locomotor region with flagellum
HPG Axis things specific to males
LH stimulates interstitial endocrine cells of testes to secrete testosterone
FSH stimulates sustenocytes to release androgen-binding protein (ABP)
in males: LH stimulates __ cells of testes to secrete __
LH stimulates interstitial endocrine cells of testes to secrete testosterone
in males: FSH stimulates __ to release __
FSH stimulates sustenocytes to release androgen-binding protein (ABP)
in males: ABP
ABP keeps local testosterone levels in testes high
in males: HPG axis primarily works _
The HPG axis primarily works after puberty
male Fetus has a surge of _ before birth
gonadotropins and testosterone
This surge drops quickly, does not appear again until around puberty
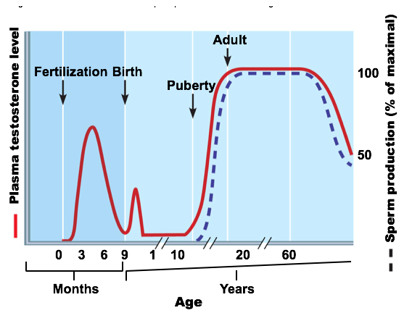
Effect of testosterone
Stimulates sperm production in testes
testosterone Secondary sex characteristics
Axillary, facial, pubic hair
Enhanced hair growth on chest and some body areas
Larynx enlargement & deepening of voice
Thick, oily skin
Increased skeletal muscle size & mass
Secondary sex characteristics
features induced in nonreproductive structures due to influence of sex hormone
Erection: When not aroused
When not aroused → arterioles supplying erectile tissue are constricted
Erection: When aroused
parasympathetic system stimulates release of nitric oxide (NO)
NO vasodilates blood vessels supplying erectile tissue
Filling of corpora cavernosa compresses drainage vessels → prevents blood from leaving
Corpus spongiosum also fills, but not as much
erection arousal caused by
touch, erotic sights, sounds, smells, emotional & higher mental activity** (thoughts)
Ejaculation
propulsion of semen from the duct system
Ejaculation caused by
initiation of spinal reflex
what occurs doing ejaculation
Accessory glands contract & release contents to prostatic urethra
Internal sphincter of bladder closes
Bulbospongiosus muscles of pelvis contract rapidly to propel semen out of the body
Female gonads
Ovaries
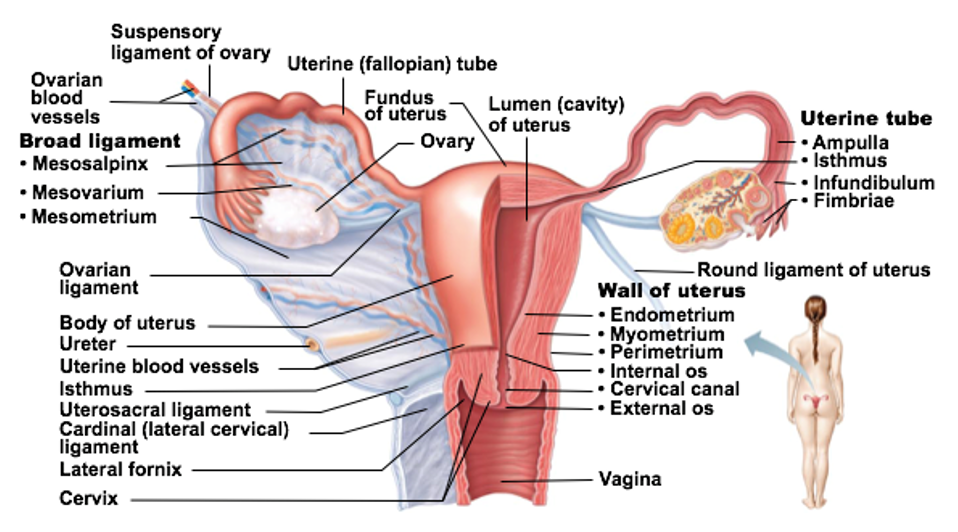
Ovaries supported by
Several ligaments
ovarian ligament
suspensory ligament
broad ligament
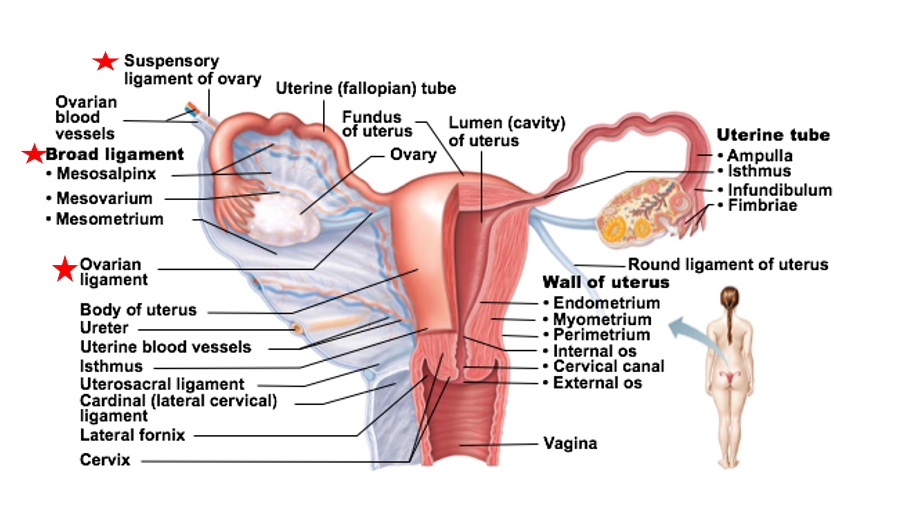
ovarian ligament
ligament that supports the ovaries
anchors ovary to uterus
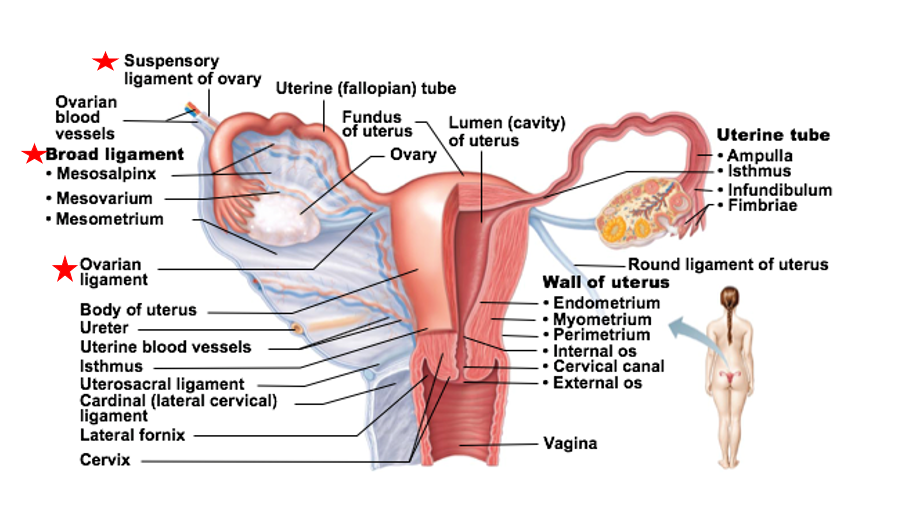
suspensory ligament
ligament that supports the ovaries
anchors ovary to pelvic wall
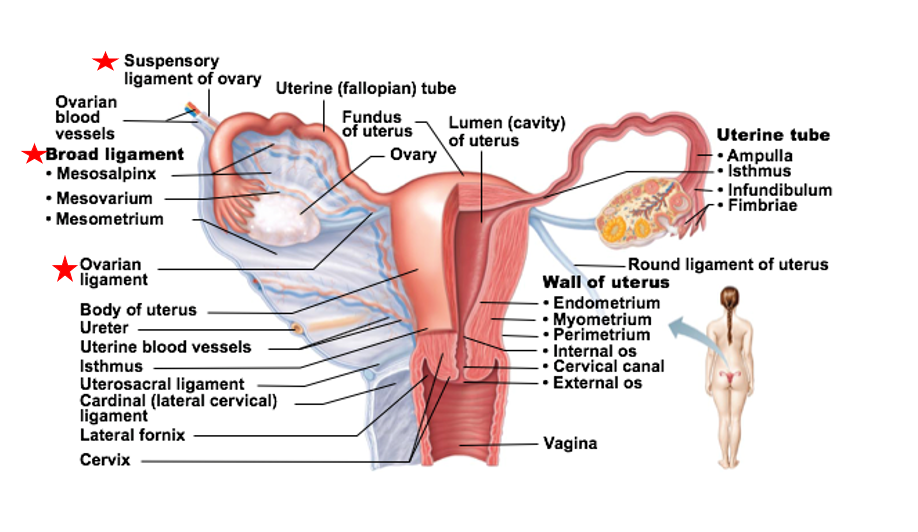
broad ligament
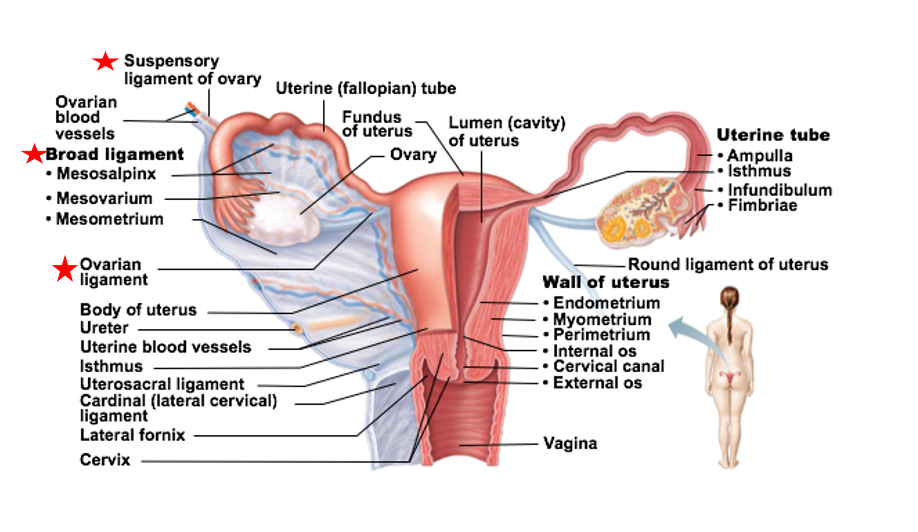
ligament that supports the ovaries
encloses the ovarian ligaments & supports uterine tubes, uterus, vagina
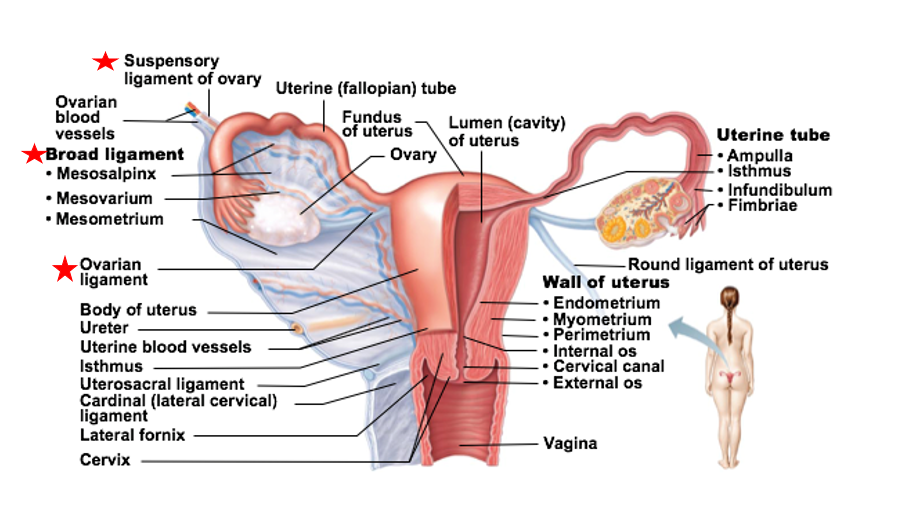
structure of ovaries
Each ovary has an outer cortex and inner medulla
Cortex is where forming gametes are found
Medulla contains blood vessels and nerves that serve ovaries
Homeostatic Imbalance of the Ovaries
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
Homeostatic Imbalance of the Ovaries
the ovaries & adrenal glands produce and release a higher-than-normal amount of testosterone
Ovaries usually covered with multiple fluid-filled cysts
Ovulation does not occur regularly (or at all) → leads to fertility issues
Many with PCOS have insulin resistance → leads to increased insulin production
effects pancreas
PCOS Caused by
unknown
probably involves
genetics
seen in relatives
lifestyle
smoking
stress
sleep
amount for exercise
diet
environmental factor
PCOS symptoms
irregular/light/missing menstrual periods, excess body hair, weight gain, oily skin, thinning hair, infertility, skin discoloration on neck/in armpits/under breasts
many secondary sex characteristic like males
PCOS treatment
There is no cure for PCOS
Treatment: change in diet & exercise, medications to stimulate ovulation, birth control (usually oral)
just symptom management
Accessory Ducts to Ovaries
Uterine Tubes (Fallopian tubes)
Uterus
Endometrium
Uterine Tubes
Fallopian tubes
Receive ovulated oocyte from ovary & is site of fertilization
Supported by mesosalpinx (of broad ligament)
Walls of tubes have smooth muscle cells, ciliated cells, and non-ciliated cells (supportive, ensure survival)
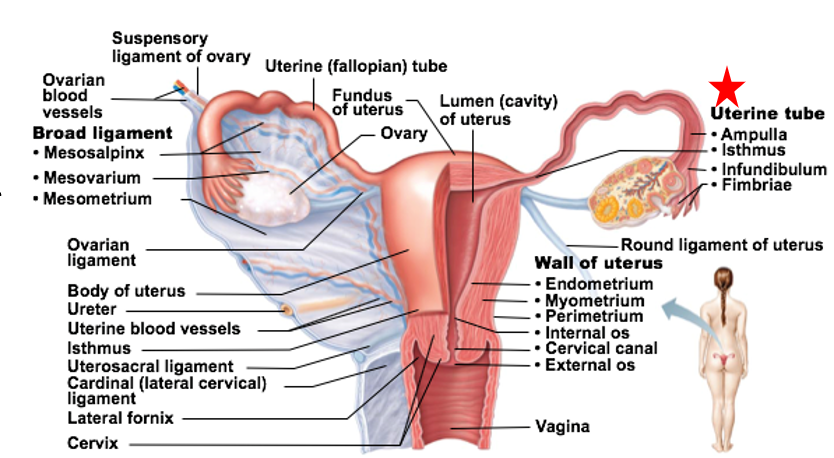
Regions of Uterine Tubes
Infundibulum: “end” of tube closest to the ovary
Fimbriae are fingerlike projections at end of each tube
Ampulla: middle portion
Site of fertilization (typically)
Isthmus: connects tube to uterus
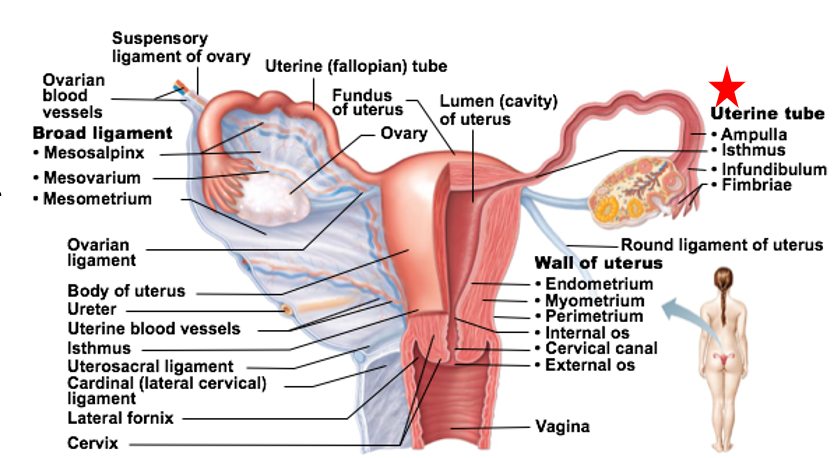
Uterus
Receives, retains, and nourishes a fertilized egg
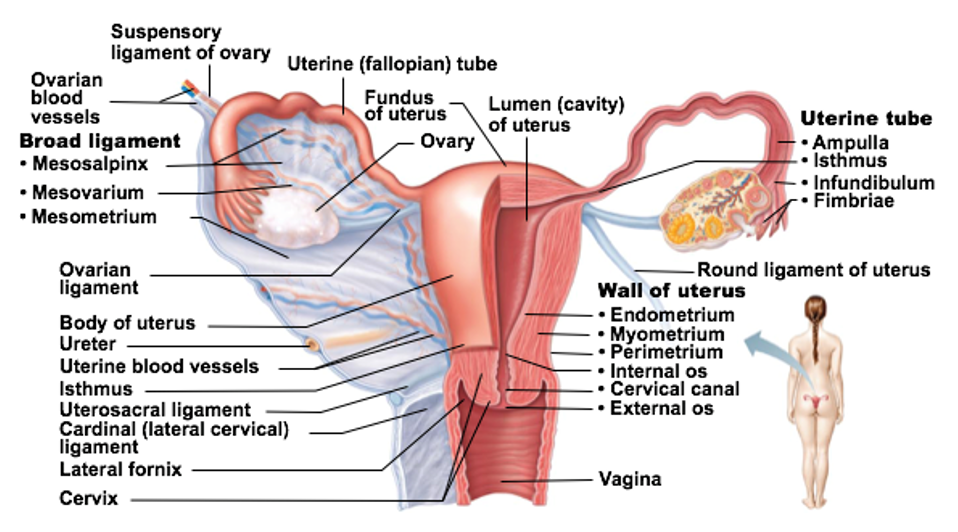
Uterus regions
Fundus: most superior dome-shaped region that meets with each uterine tube
Body: major portion
Cervix: neck of uterus leading into vagina
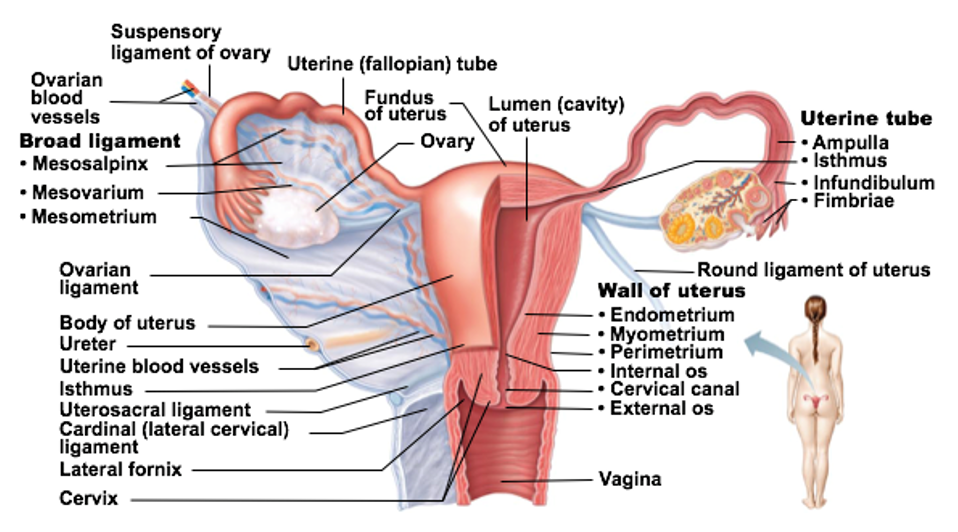
Glands in the cervix of the uterus _
Glands here secrete mucus to “block off” the uterus from the vagina
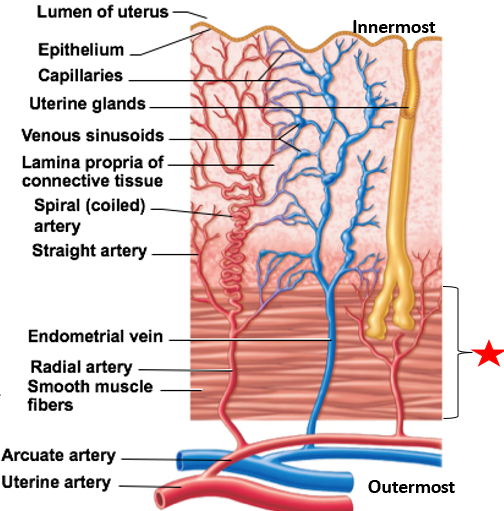
Uterine wall layers
Perimetrium
Myometrium
Endometrium
Stratum functionalis
Stratum basalis
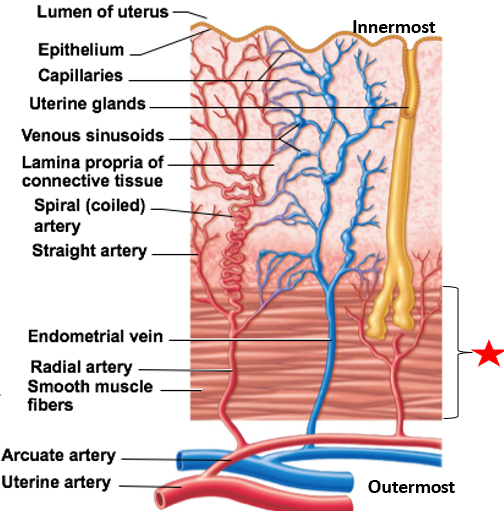
Perimetrium
outermost layer of uterine wall
visceral peritoneum
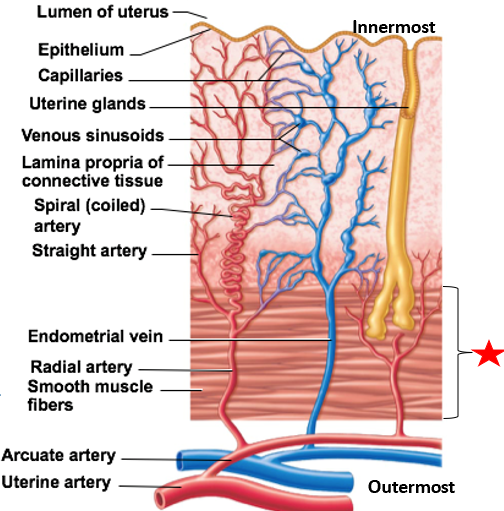
Myometrium
2nd layer of uterine wall
contains smooth muscle
Contracts during childbirth & without pregnancy (menstrual cramps)