Micro economics
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
“oppurtunity cost”
the benefit foregone of the next best alternative
how a ppf shows the concept of opportunity cost
The opportunity cost is shown by the slope of the PPF — as you move along the curve, producing more of one good means giving up some of the other. The amount of the other good that must be sacrificed is the opportunity cost.
List 4 factors of production (how we use our resources)
Capital - Machinery
Enterprise - entrepreneurs
Land- Resources
Labour - Workers and employees
Explain what a positive statement is
List an example
a positive statement is factual , can be tested , does not value judgement or personal opinion - may include data , stats , facts
eg-higher interest rates will reduce house prices
Explain what a Normative statement is and give an example
Value / judgement / personal opinion
“The government should provide basic healthcare to everyone”
what is an intermediate good?
a good used in the production of other goods
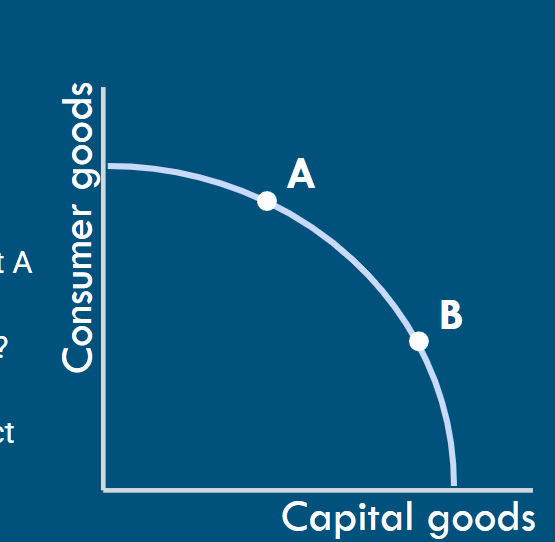
Explain what a Production Possibility Frontier shows
shows the combination of two goods that could be produced by an economy if all of its resources are employed fully and efficiently. It shows the productive potential of an economy
What would cause an outward shift in a PPF
-changes in total amount of avaliable production factors
-discovery of new natural resources eg rare minerals
-factors that lead to a bigger workforce eg immigration , increased retirement age , better childcare - more women are able to work
-advances in tech
What would cause an inward shift in a PPF
-natural disasters
-depletion of natural resources
-reduced size of workforces - emigration , increased school leaving age
a recession cause the closure of factories
What is a capital good
are those required to produce other goods - both capital and consumer goods - machinery , factory buildings
What is a consumer good
those that gift satisfaction to consumers - smartphones , , cars
what do the points A , B or C imply on the PPF
implies that all resources are fully and efficiently employed , therefore they indicate the maximum productive potential of an economy that resources are being used efficiently
What if an economy was operating inside its PPF at point x?
It would indicate that there are unemployed resources in the economy , some workers may be unemployed or some machinery may be unused it would also imply resources are not being allocated efficiently
How do workers , firms and regions specialise?
Setting certain tasks and skills to a specific worker (Perhaps the ones they are best suited to)
different firms specialise by producing different and specific goods and services
Advantages in the specialisation and the division of labour in organising production
-each worker specialises in tasks they’re best suited
-the worker only needs to be trained in one task
-less time wasted one worker on one task
as they are in the task they are best suited - increased productivity - more output
disadvantages in the specialisation and the division of labour in organising production
-monotony and boredom for workers
-loss of skills ; workers trained in a particular way have limited skills
-if a strike occurs the entire faculty would be at risk
buffer stock scheme
A scheme intended to stabilise the price of a commodity by purchasing excess supply in periods when supply is high, and selling commodity reserves when supply is low.
Explain the 4 functions of money
as a medium of exchange - enabling people to exchange their earnt money for goods and services
a store of value enabling people to save
a measure of value - enabling people to assess the value of different goods and services
a means of deffered payment - credit cards
What is a command economy
an economy in which production, investment, prices, and incomes are determined centrally by a government.
What is a free market economy
an economic system in which prices are determined by unrestricted competition between privately owned businesses.
Advantages of a free market
FLEXIBILITY - the system can respond quickly to a change in the wants of consumers
CUSTOMER SOVEREIGNTY - this implies whatever the customer buys determines what is produced
CHOICE - consumers have a wide variety of goods unlike a command economy
economical and political freedom
Disadvantages of a free market
INEQUALITY - those who own resources are likely to become richer than those without the resources
TRADE CYCLES - instability in the economy boom and slumps
monopolies - a firm may be a solo supplier of a good and may exploit consumers by raising prices
Advantages of a command economy
Greater quality - the state ensures everyone lives a minimum standard of living - no one is extremely rich
macroeconomic stability
full employment
No exploitations - privately owned monopolies cant exploit consumers
Disadvantages of a command economy
- less efficient as the government is not a profit maximising entity
- government may not know what's best due to asymmetric information
- choice restriction
- destroys incentives
how are resoucres allocated in a free market economy
In a free market economy, resources are allocated based on consumer demand and the decisions of producers. Prices act as signals, guiding where resources should be directed to meet the needs and wants of society.
the benefits of specialiastion and division of labour are mostly associated with who
Adam smith
PPF
Price elasticity of supply
Price elasticity of supply measures how much the quantity supplied of a product changes when its price changes."
income elasticity of demand
"Income elasticity of demand measures how much the quantity demanded of a product changes when consumer income changes."
Cross elasticity of demand
Cross elasticity of demand measures how much the quantity demanded of one product changes when the price of another product changes."
explain the role of incentives in the free market
Profit incentivises firms to be efficient and innovative.
Price changes incentivise consumers to buy more/less (law of demand).
Higher wages incentivise people to work or upskill.
why is supply inelastic in the short run
at least one factor of production is fixed
why do goods become more elastic overtime
because people find more alternatives
command economy failure
30 million deaths from a famine in China
what are economies of scale
when the average cost of producing a good or service falls as the quantity produced increases
advantages of division of labour and specialisation of trade
- if they trade these in these goods for goods that they do not produce, it can result in economic growth, more choice, lower prices
disadvantages of specialisation of trade
Overdependence on imported goods
- imports may exceed the value of exports
- if a country's goods are not competitive they can suffer
why is there income inequality in the free marker
there is freedom to own resources, those who own resources are more likely to earn more income than others
why may a deep recession lead to an inward shift of the ppf
deep recessions can lead to reduced investment in research and development, as well as decreased innovation. If technological progress slows down, the efficiency of production processes may decline, contributing to a contraction in the PPF.
labour hysteresis
labour hysterisis
when labour lose their skills/productivity after a deep recession
what YED should we expect inferior goods to have
We should expect inferior goods to have a negative YED value (
). This is because their demand falls as a consumer's income rises, as they switch to higher-quality alternatives
such as cheap, off-brand cereal, which is often replaced by more expensive, name-brand cereals when income increases
Cross elasticity of demand
Cross elasticity of demand (XED) measures how the quantity demanded of one good changes in response to a change in the price of another good
specialisation of labour
When a worker becomes an expert in a particular profession or in a part of a production process.
what if the XED is positive
substitute goods
What if the XED is negative
they are complimentary goods
why does a firm want to know XED
to know whether increasing the price of its product is going to lead to a huge fall in demand
They also know that complementary goods come in joint demand so they can sell both at a high price or if they sell one for too much the demand for their other good in joint-demand may fall
XED formula
% change in quantity demanded for good X / % change in price of good Y
advantages of division of labour and specialisation on trade
- if they trade these in these goods for goods that they do not produce, it can result in economic growth, more choice, lower prices
customer sovereignity
the power of consumers to decide what gets produced
If they are not public goods, why does the government provide healthcare?
it produces a positive externality
why may a deep recession lead to an inward shift on the ppf
deep recessions can lead to reduced investment in research and development, as well as decreased innovation. If technological progress slows down, the efficiency of production processes may decline, contributing to a contraction in the PPF.
labour hysteresis