Microbial Growth and Environmental Factors
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Binary Fission
Primary bacterial reproduction method involving cell division.
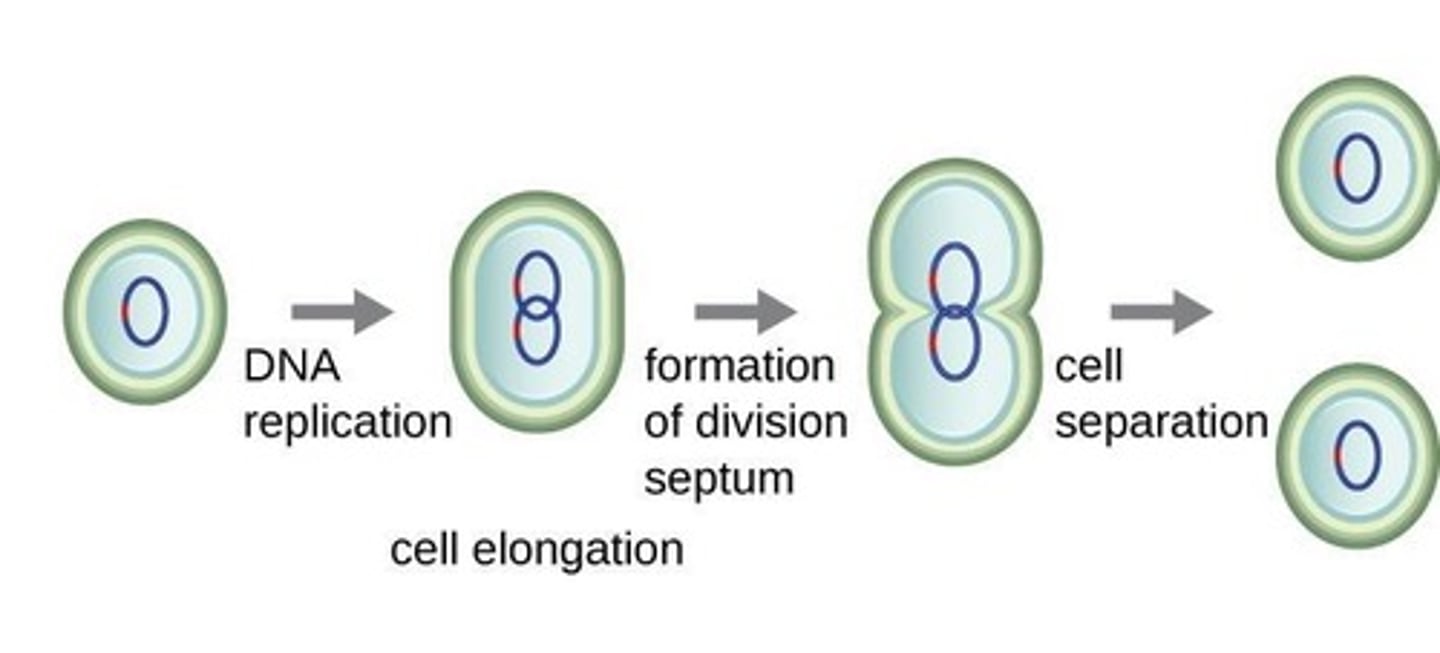
Cytokinesis
Division of cytoplasm during cell division.
FtsZ Protein
Protein that directs cytokinesis in bacteria.
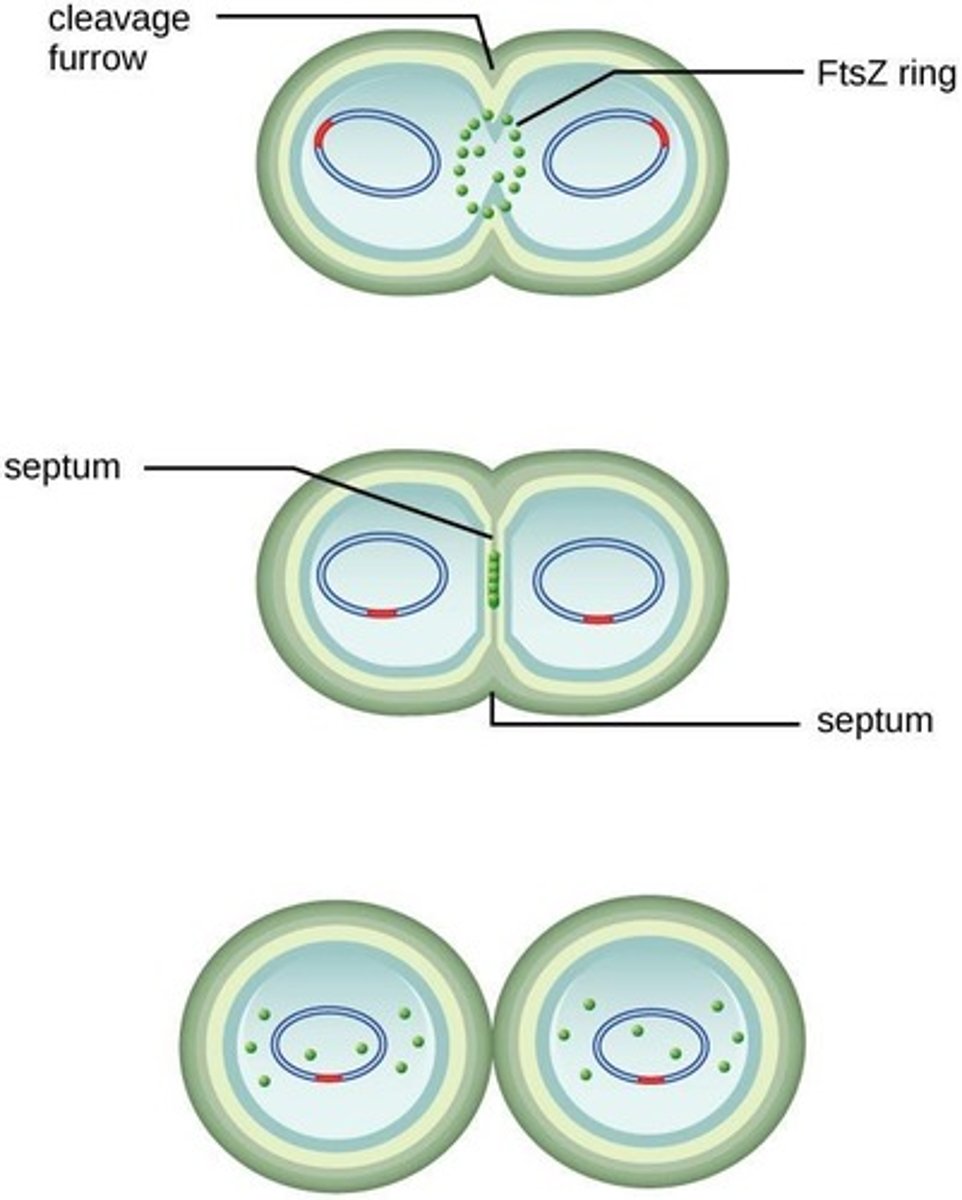
Z Ring Assembly
Formation of divisome for cell division.
Generation Time
Time required for bacterial population to double.
E. coli Generation Time
Approximately 20 minutes for population doubling.
S. aureus Generation Time
Approximately 30 minutes for population doubling.
B. subtilis Generation Time
Approximately 120 minutes for population doubling.
M. tuberculosis Generation Time
Approximately 15-20 hours for population doubling.
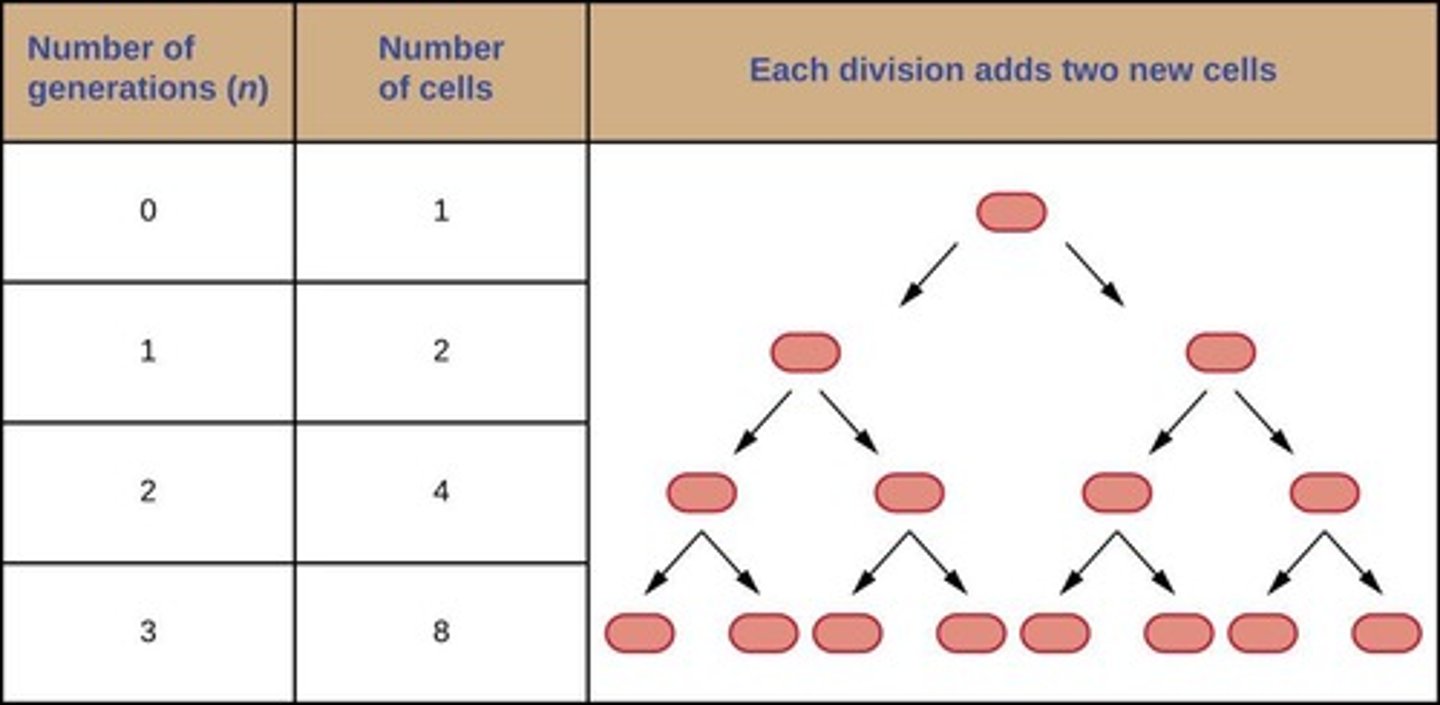
Population Size Calculation
Predicts cell number using Nn = N0 * 2^n.
Lag Phase
Initial phase with no population change after inoculation.
Log Phase
Exponential growth phase with active cell division.
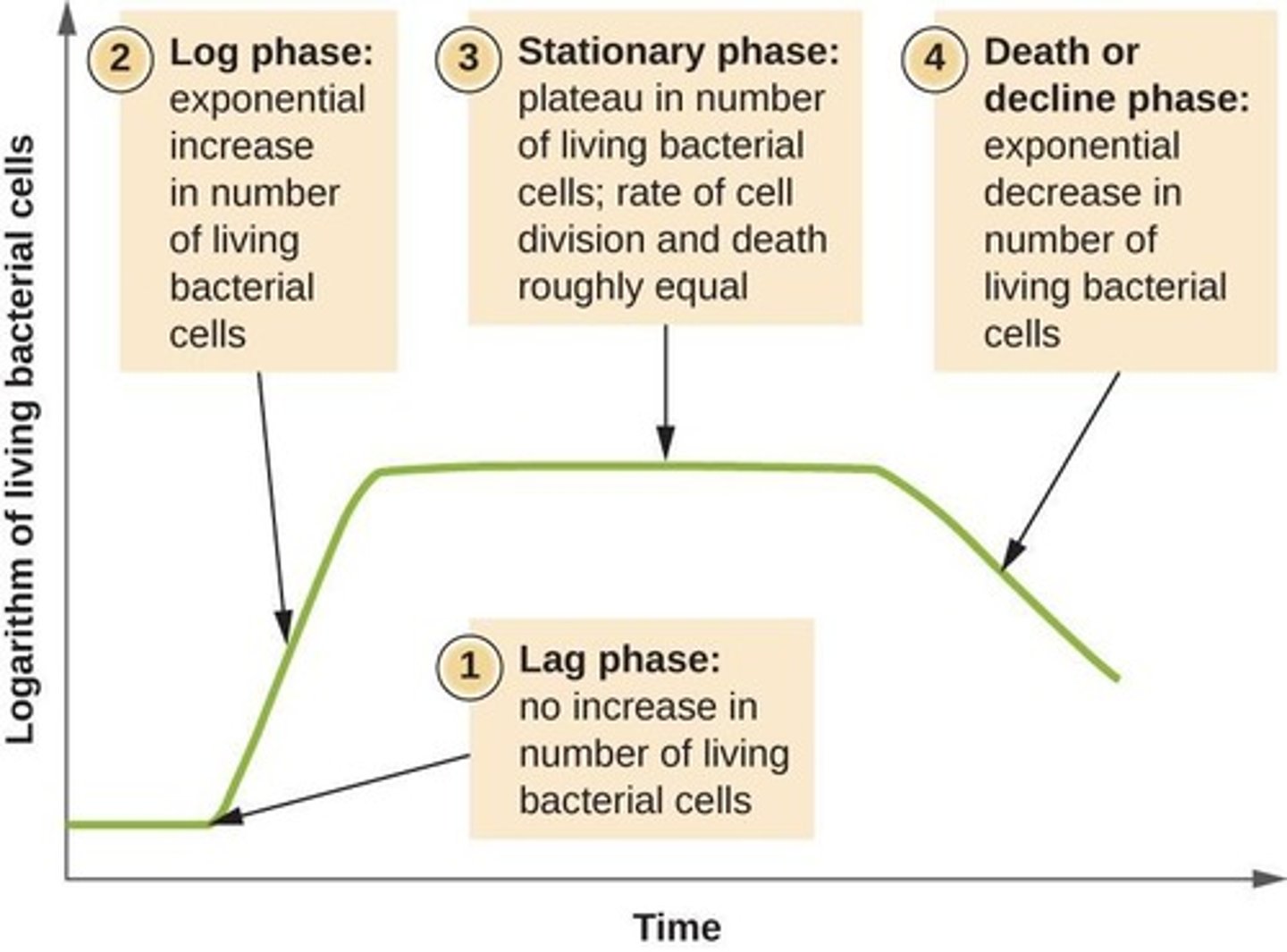
Stationary Phase
Phase where cell replication equals cell death.
Death Phase
Phase with more cell death than replication.
Closed Culture
Culture system with limited resources and nutrients.
Open System Cultures
Culture system with infinite resources and nutrient replenishment.
Chemostat
Device maintaining continuous culture with constant nutrient supply.
Culture Density
Number of cells per unit volume in a culture.
Exponential Growth
Growth pattern where population increases rapidly.
Sporulation
Process of endospore formation under stress conditions.
Persisters
Surviving cells with slow metabolism during adverse conditions.
Virulence Factors
Molecules that enhance pathogenicity of microorganisms.
Microscopic cell count
Cells counted manually under a microscope.
Fluorescent staining
Staining method to distinguish live and dead cells.
Coulter count
Measures cell density via electrical resistance.
Viable cell count
Counts only living cells on solid media.
Optical Density
Measures turbidity using a spectrophotometer.
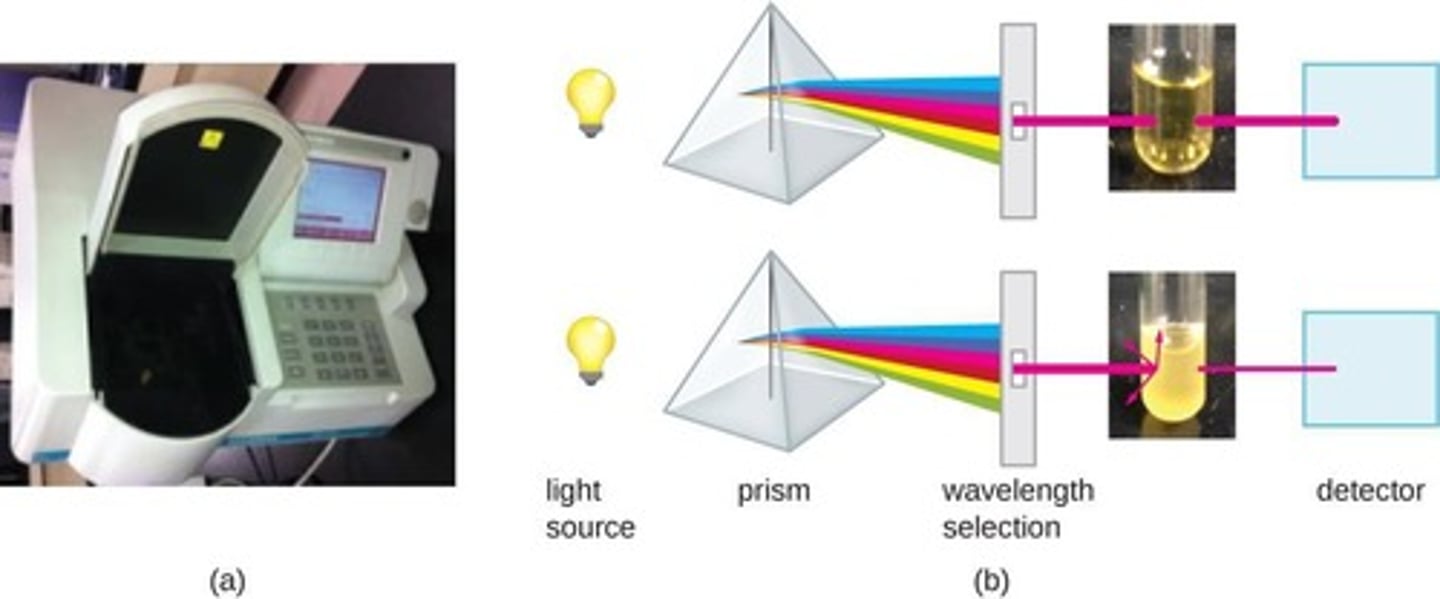
Direct microscopic cell count
Cells counted in calibrated slide chamber.
Petroff-Hausser chamber
Calibrated slide for direct cell counting.
Colony Forming Units (CFU)
Count of viable cells per volume.
Serial dilution
Dilution method to achieve countable CFU range.
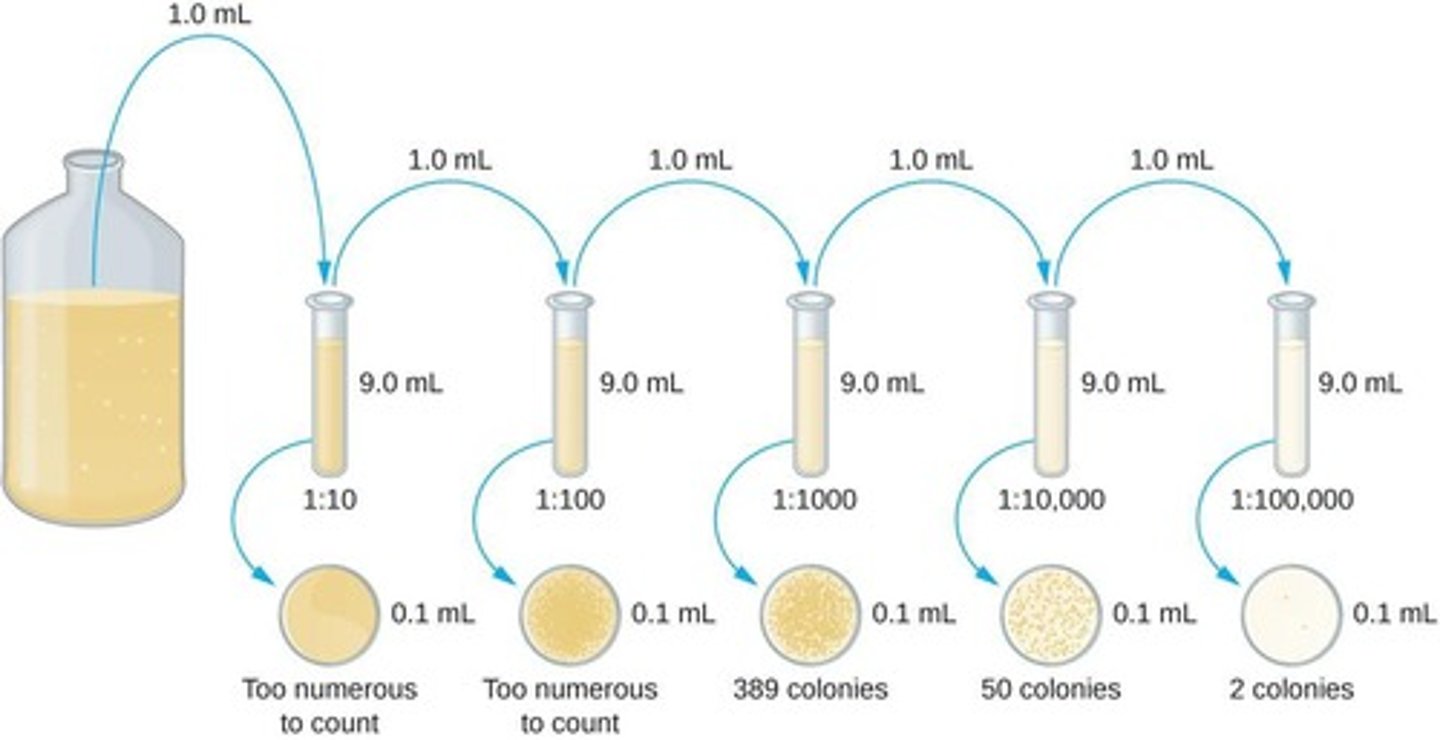
TFTC
Too Few To Count; <30 CFU/ml.
TNTC
Too Numerous To Count; >300 CFU/ml.
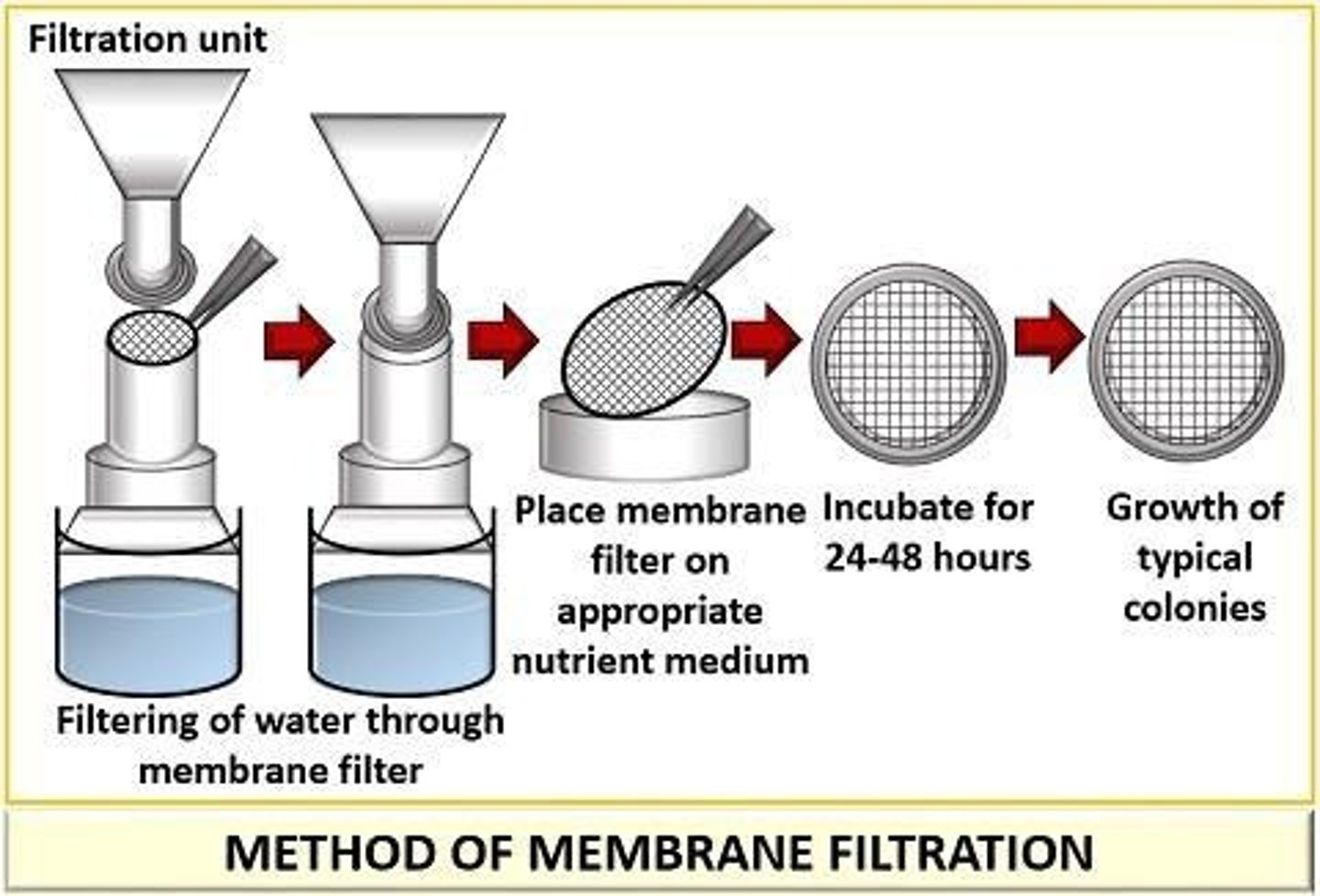
Membrane filtration technique
Filters known volume for microbial counting.
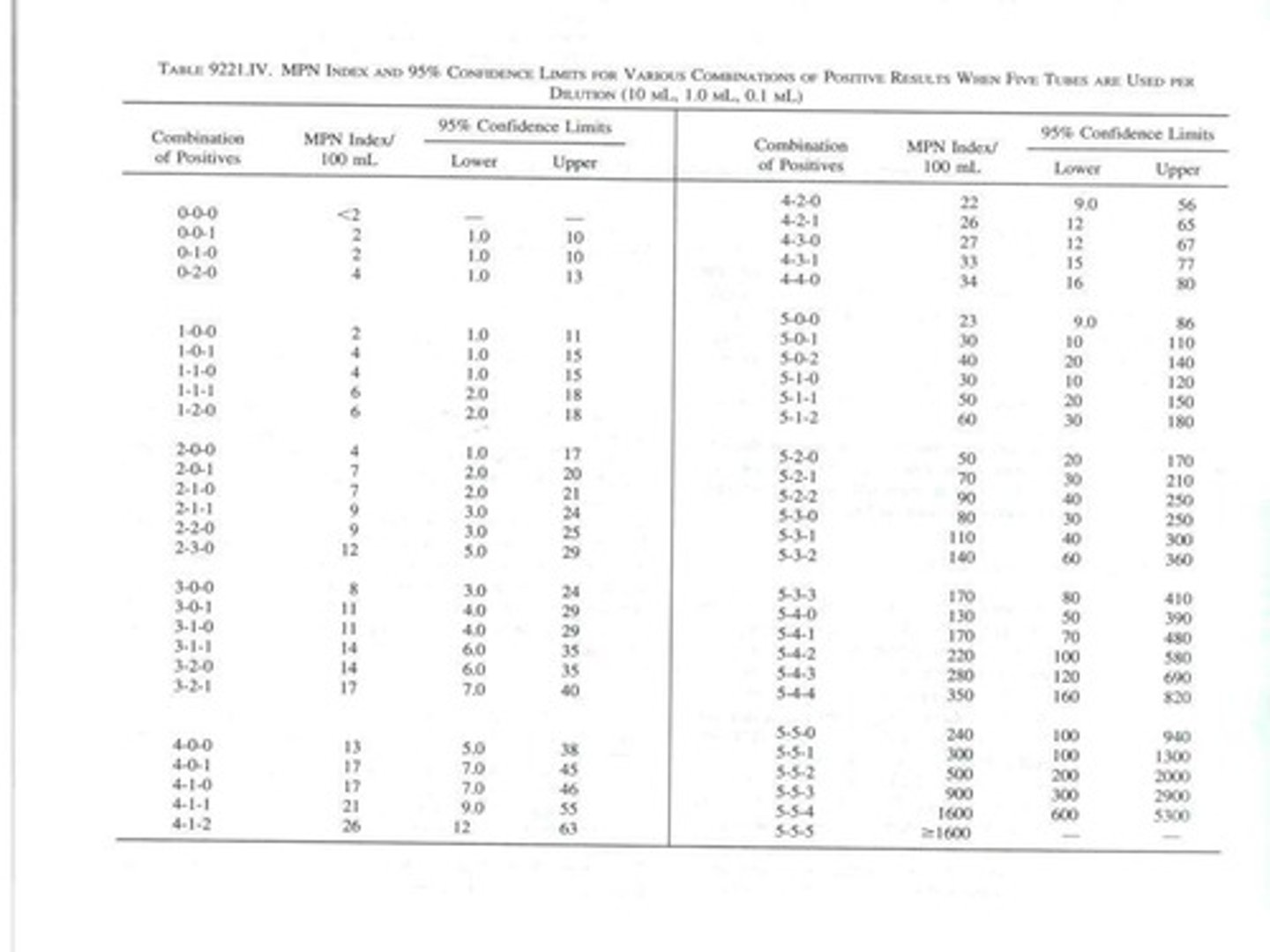
Most Probable Number (MPN)
Statistical method for low cell counts.
Log dilution
Dilution method using logarithmic scale.
Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS)
Matrix secreted by biofilm organisms.
Quorum sensing
Cell communication based on population density.
Budding
Asymmetric division method in some microbes.
Fragmentation
Asexual reproduction via breaking into parts.
Biofilm
Microbial community in protective matrix.
Secondary colonizers
Microbes that join established biofilms.
Autoinducer
Molecule triggering cellular responses in quorum sensing.
Biofilm
Community of microorganisms adhering to surfaces.
Quorum Sensing
Cell communication regulating biofilm formation.
Autoinducer
Molecules triggering cellular responses in quorum sensing.
N-acylated Homoserine Lactones
Signaling molecules in Gram-negative bacteria.
Short Peptides
Signaling molecules in Gram-positive bacteria.
Normal Biota
Beneficial microorganisms residing in the body.
Antibiotic Resistance
Biofilms protect microbes from antibiotic effects.
EPS
Extracellular polymeric substances aiding biofilm structure.
Oxygen Level
Concentration of O2 affecting microbial growth.
Optimal Oxygen Concentration
Ideal O2 level for microbial growth.
Minimum Permissive Oxygen Concentration
Lowest O2 level allowing microbial growth.
Maximum Permissive Oxygen Concentration
Highest O2 level allowing microbial growth.
Obligate Aerobes
Require oxygen for survival and growth.
Facultative Anaerobes
Can grow with or without oxygen.
Aerotolerant Anaerobes
Tolerate oxygen but do not use it.
Microaerophiles
Require low oxygen levels for growth.
Fluid Thioglycolate Medium (FTM)
Medium used to determine oxygen tolerance.
Optimal Growth pH
Most favorable pH for microbial growth.
Acidophiles
Microbes thriving in acidic environments.
Mesophiles
Microbes growing best at moderate temperatures.
Halophiles
Microbes requiring high salt concentrations.
Barophiles
Microbes thriving under high atmospheric pressure.
Photoautotrophs
Organisms using light for energy and carbon.
Selective Media
Promotes growth of specific organisms while inhibiting others.