Electrical Circuits and Saftey
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
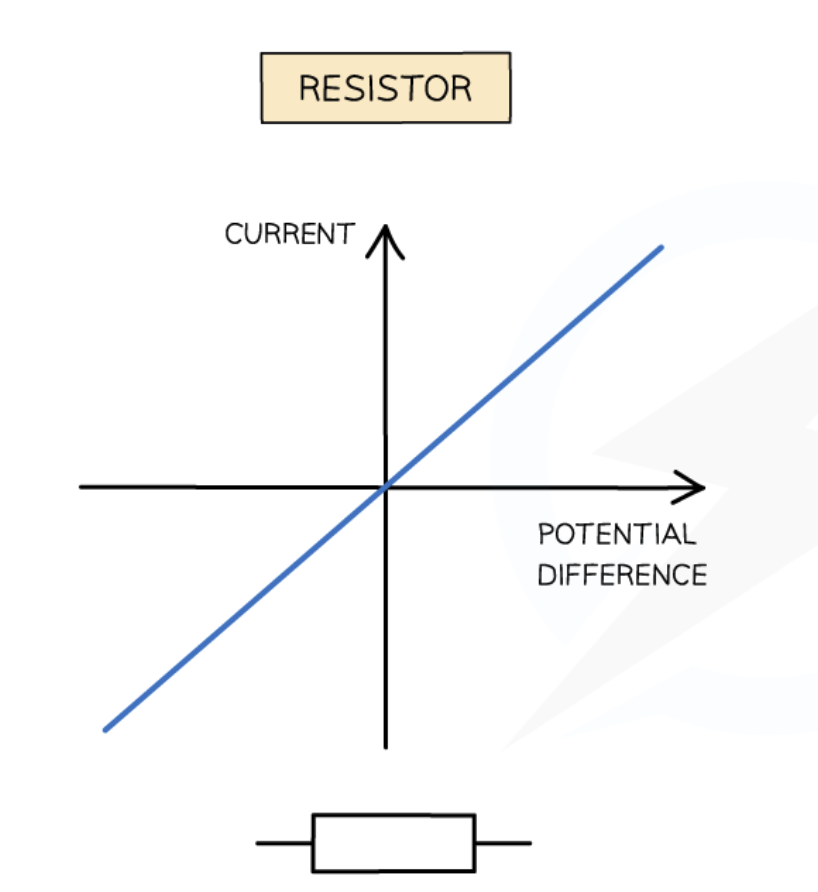
Current v Voltage for a standard resistor
Ohmic graph
Current v Voltage for a filament lamp
Non ohmic graph
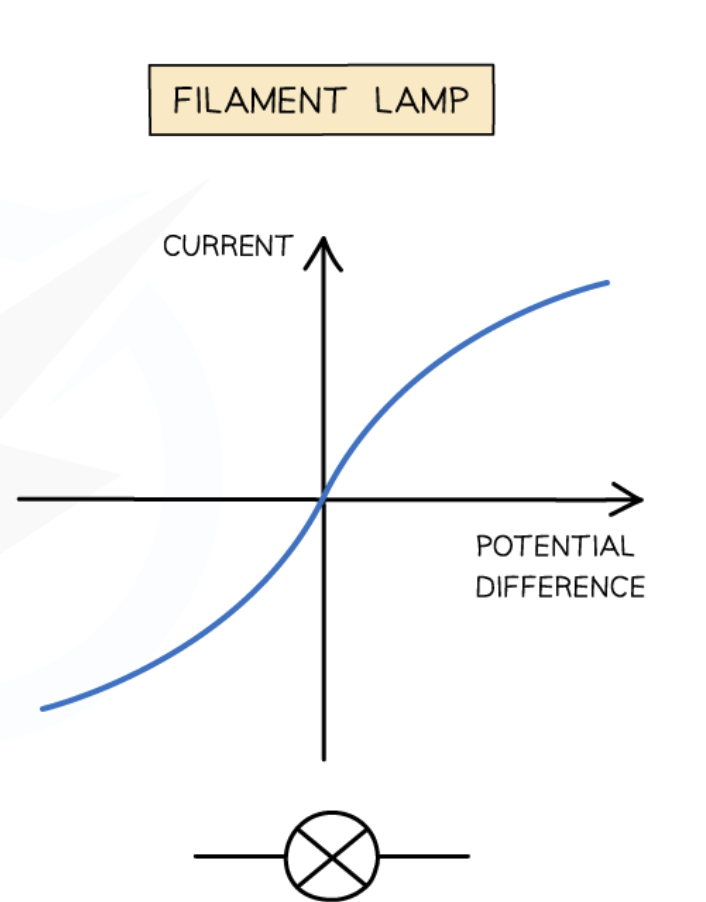
This is because as the current increases, the filament heats up, increasing resistance, meaning the current increases at a slower rate
Diode
A component that only allows current to flow in one direction. Can be used to convert alternating current to direct current by a process called rectification
Half-wave rectification
Use of a single diode to cut off all signals that go in the opposite direction of the diode
Full wave rectification
Use of multiple diodes to convert alternating current to direct current while maintaining all current flow
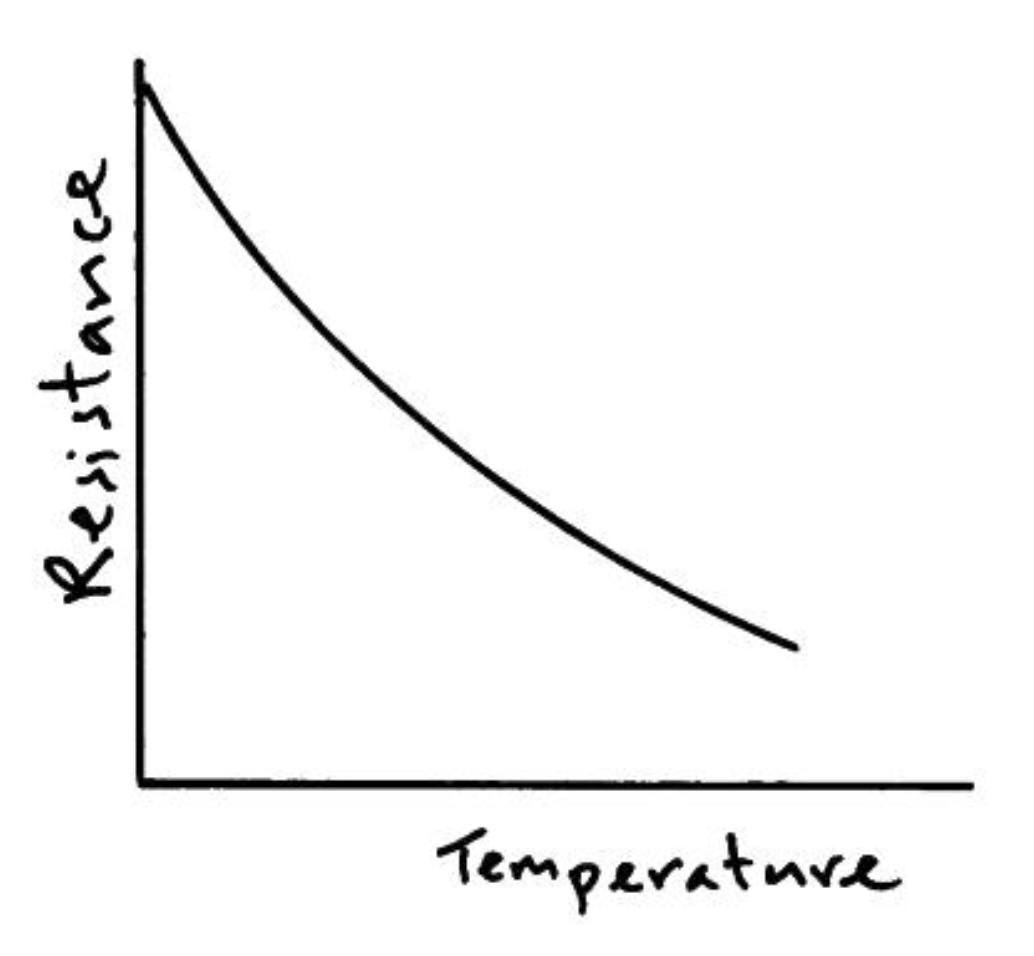
Thermistor
Resistance decreases as temperature increases
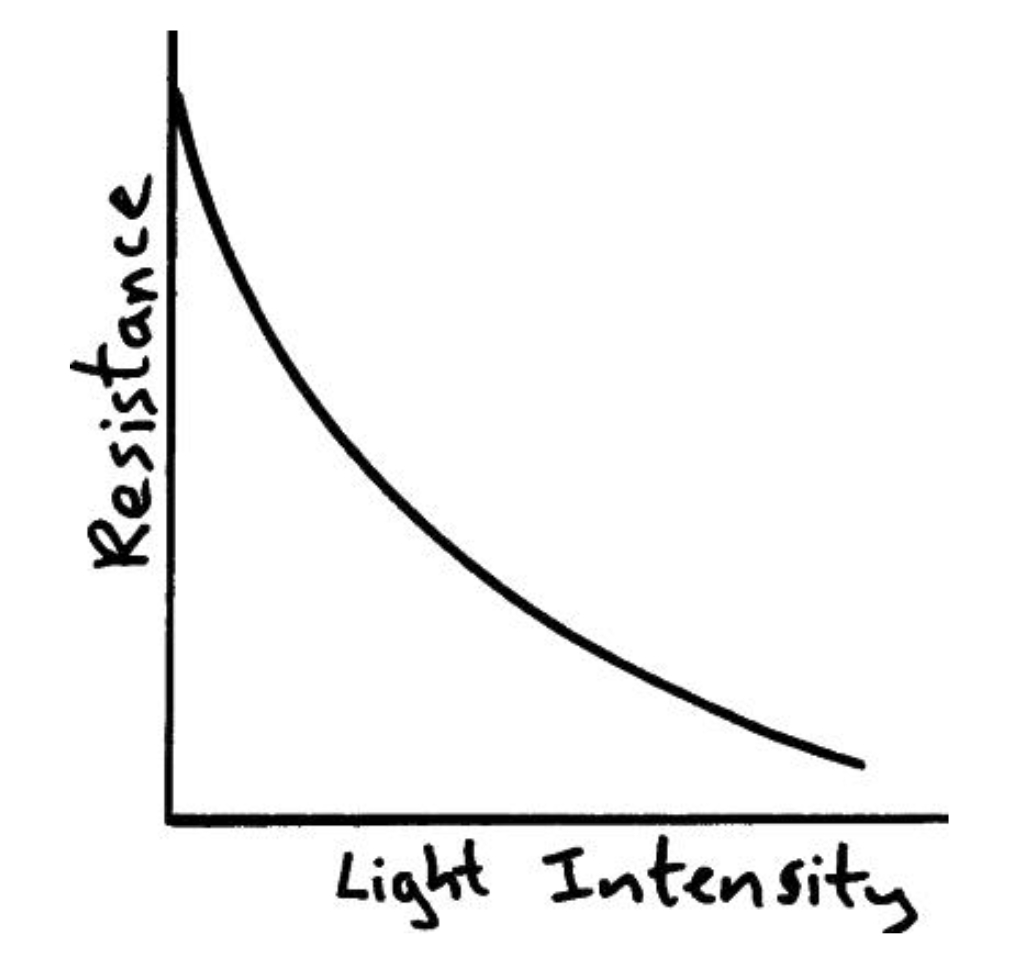
Light dependent resistor
Resistance decreases as it is exposed to more light
Potential dividers
Using resistors to split the voltage specific components receive. Can be calculated by:
Vout = Vin * R1 / R1 + R2
Relay
A special type of switch that is turned on and off by an electromagnet, used to allow a low-power input to control a high-current circuit, or to separate multiple circuits.
Fuses
Sacrifical devices that cause the wire to heat up and break above a certain current, breaking the circuit and protecting it from a power surge.
They come in power ratings of 3A, 5A and 13A
Circuit Breakers
Automatically operated switch that is designed to break the circuit to prevent damage from a power surge or short circuiting, works similar to relays using solenoids (electromagnets)
Why is a circuit breaker better than a fuse?
Fuse is one time use, needs to be replaced after it breaks
operate faster
cannot be replaced with the wrong sized wire
Plugs
Consist of an earth, live and neutral wire.
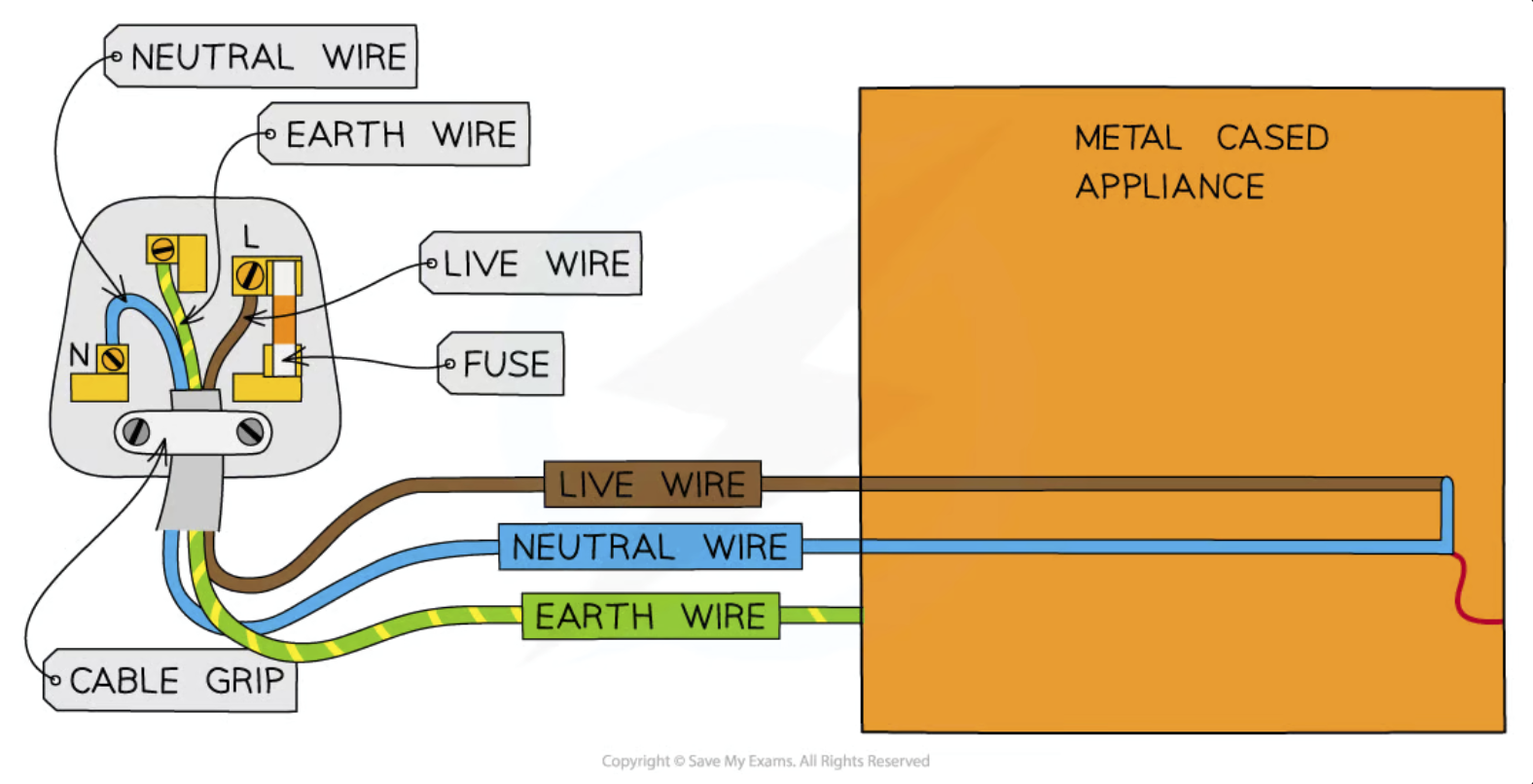
Live wire
Carries the electric charge, is brown in colour
Neutral wire
Forms the opposite end of the circuit to complete a full circuit with the plug and the device, blue in colour
Earth wire
Safety wire that earths the circuit to ensure the device does not become charged in case of a circuit fault, by running into a metal casing to carry away charge, yellow/green in colour
Double insulation
Some devices have insulation around each of the wires inside of an insulating case, to ensure that the device cannot become electrified.